BISC306 Exam 3
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Which hormone directly stimulates sodium reabsorption in the kidneys?
- angiotensin I
- erythropoietin
- aldosterone
- renin
aldosterone
The volume of air flowing into the alveoli during inhalation/inspiration is increased when there is an increase in (select all that apply)
a. airway resistance
b. airway resistance and the pressure gradient from the atmosphere to the alveoli
c. the pressure gradient from the atmosphere to the alveoli
d. the rate of action potential firing in the motor neurons to the inhalatory/inspiratory muscles
c. the pressure gradient from the atmosphere to the alveoli
d. the rate of action potential firing in the motor neurons to the inhalatory/inspiratory muscles
What does a right shift on the hemoglobin saturation curve mean?
A. It means hemoglobin is being generous and giving up oxygen to the blood
B. It means that hemoglobin is being stingy and hanging on to oxygen, not releasing it to the blood
C. Hemoglobin does not bind oxygen
A. It means hemoglobin is being generous and giving up oxygen to the blood
A patient has a kidney condition that results in the loss of albumin in the urine that exceeds the body's albumin production. The resulting hypoalbuminemia will lead to edema of the extremities. Which of the following is likely to be noted?
A. Increased lymph flow
B. Decreased interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
C. Increased in plasma oncotic pressure
D. Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
A. Increased lymph flow
The word "countercurrent" within "countercurrent multiplier" refers to the opposite direction of flow of _______
(couldn’t find any multiple choice options)
tubular fluid within the ascending & descending limb of the nephron loop
Generally, a very _______ percent of Na+ in the tubular fluid is reabsorbed, and the reabsorption takes place _________.
high, along the entire tubule
Place the regions of the nephron in the correct order for the process of urine formation.
a: Capsular space of glomerulus
b: Nephron loop
c: Collecting duct
d: Distal convoluted tubule
e: Proximal convoluted tubule
a, e, b, d, c
If there is an accumulation of acidic products in the plasma, one would expect
a.an increase in respiration rate.
b.a decrease in respiration rate.
c. no influence on respiration rate
d. an increase in residual volume.
a. an increase in respiration rate.
Most carbon dioxide is transported in the blood
a. in the form of bicarbonate ions
b.bound to hemoglobin.
c.dissolved in the plasma.
d. by the leukocytes
e. in the form of carbonic acid
a. in the form of bicarbonate ions
In which of the following sequences does PO2
progressively decrease?
a. body tissue, arterial blood, alveolar air
b. body tissue, alveolar air, arterial
blood
c. blood in aorta, atmospheric air, body tissues
d. atmospheric air, blood in aorta, body tissues
e. body tissue, aorta, alveolar air
d. atmospheric air, blood in aorta, body tissues
During exercise, the oxygen
-hemoglobin dissociation curve
a.shifts to the right.
b.shifts to the left.
c.doesn't shift.
a.shifts to the right.
Mr. Jones has a blood pH of 7.00 and a temperature of 100.5
F. His oxygen-hemoglobin
dissociation curve would
a.shift to the right, causing more O2 to be released to his cells.
b.shift to the left, allowing less O2 to be released to his cells.
c. show no change, allowing the O2 concentration to remain stable.
a.shift to the right, causing more O2 to be released to his cells.
When carbon dioxide levels in the blood increase, the:
a. condition is called hypocapnia.
b. pH of the blood increases.
c. blood becomes more acidic.
d.number of hydrogen ions in the blood decreases.
e.blood becomes more alkaline.
c. blood becomes more acidic.
A patient has severe pneumonia, which has thickened the respiratory membrane. Despite oxygen therapy, he still has rapid respiration and feels as if he is not getting enough air. This is
because:
a. the oxygen increases the stimulation of the carotid and aortic bodies.
b. the oxygen stimulates the respiratory center to increase the respiratory rate.
c. his blood pH increased and stimulated an increase in his respiratory rate.
d. even though he is receiving enough oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions accumulate in his blood and cause the respiratory rate to continue to increase.
d.even though he is receiving enough oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions accumulate in his blood and cause the respiratory rate to continue to increase.
As the result of an asthmatic attack:
a. ventilation exceeds the ability of blood to pick up oxygen.
b. ventilation is inadequate to oxygenate blood.
c. pulmonary blood flow is reduced while ventilation remains normal.
d. the surface area available for gas exchange increases.
e. bronchioles dilate.
b. ventilation is inadequate to oxygenate blood.
If the total pressure of a mixture of
gases was 760 mm Hg and its composition is 20% oxygen,
0.04% carbon dioxide, 75% nitrogen, and 5% water vapor, then the partial pressure of oxygen would be
a.740 mm Hg.
b.20 mm Hg.
c.148 mm Hg.
d.152 mm Hg.
e.200 mm Hg.
d. 152 mm Hg.
Solving: .2×760=152
During inspiration, contraction of the diaphragm causes the volume of Mr. Jones' thoracic cavity to increase and the pleural pressure to decrease. The pressure in his alveoli (Palv) will:
a. decrease below atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move out of his lungs.
b. become greater than atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move into his lungs.
c.decrease below atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move into his lungs.
d. become greater than atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move out of his lungs.
c.decrease below atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move into his lungs.
Air moves from High pressure—>Low pressure
Which of the following is part of the upper respiratory tract?
a.lungs
b.pharynx
c.bronchi
d.bronchioles
b. pharynx
all else is part of lower resp. tract
Which of the following is NOT true about oxygen/hemoglobin dissociation in the region directly surrounding exercising muscles?
A. Lactic acid release increases pH shifting the curve to the right
B. Increased heat produced during vigorous activity promotes oxygen dissociation, shifting the curve to the right
C. All of the above answers are correct
D. CO2 increases causing pH to decrease leading to increased oxygen dissociation
A. Lactic acid release increases pH shifting the curve to the right
The erythrocyte (red blood cell) count increases after a while when an individual goes from a low to a high altitude because the ________.
A. Temperature is lower at higher altitudes
B. Concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes
C. Concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is higher at higher altitudes
D. Basal metabolic rate is higher at high altitudes
B. Concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes
You may have noticed that after a large meal you have had some difficulty breathing. Which explanation is most accurate with regard to this situation?
A. Oxygen to the lungs is restricted due to fullness in the stomach.
B. The large quantity of food retards pulmonary blood flow.
C. A full stomach impedes contraction of the diaphragm, limiting inhalation.
D. The food presses on the bronchi making air flow difficult.
E. It's just difficult to fill the lungs since blood-filled oxygen is flowing primarily to the stomach.
C. A full stomach impedes contraction of the diaphragm, limiting inhalation.
Following an automobile accident, a broken rib penetrates into the pleural cavity without piercing through the skin. This leads to a lung collapse. Why does this occur?
A. A decrease in thoracic volume leads to an equality of intrapleural and alveolar pressures
B. Intrapleural pressure is now equal to atmospheric pressure
C. Intrapleural pressure is now equal to the pressure inside of the lung
D. Pleural fluid is now leaking into the thoracic cavity
C. Intrapleural pressure is now equal to the pressure inside of the lung
The reason air flows out of the body during expiration is that during that time:
A. intrapulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
B. atmospheric pressure is greater than intrapulmonary pressure.
C. Intrapleural pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
D. Intrapleural pressure is greater than intrapulmonary pressure
A. intrapulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
Which of the following INCORRECTLY describes mechanisms of CO2 transport?
A. As bicarbonate ions in plasma
B. Just over 20% of CO2 is carried in the form of carbaminohemoglobin
C. 7-10% of CO2 is dissolved directly into the plasma
D. Attached to the heme part of hemoglobin
D. Attached to the heme part of hemoglobin
Which of the following provide the greatest surface area for gas exchange?
A. Alveolar ducts
B. Respiratory bronchioles
C. Alveolar sacs
D. Alveoli
D. Alveoli
The symptoms of hyperventilation may be averted by breathing into a paper bag because it ________.
A. Reduces brain perfusion by constricting cerebral blood vessels
B. Helps retain oxygen in the blood
C. Lowers blood pH levels
D. Helps retain carbon dioxide in the blood
D) Helps retain carbon dioxide in the blood
The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air in the alveoli and blood in the lungs is called:
A. Systemic respiration
B. Cellular respiration
C. Ventilation
D. External respiration
E. Internal respiration
D) External respiration
The amount of air that can be inspired above the tidal volume is called ________.
A. Expiratory capacity
B. Vital capacity
C. Reserve air
D. Inspiratory reserve volume
D. Inspiratory reserve volume
T/F The total dead space in the lungs includes anatomic dead space and any portion of the alveoli that has little or no blood supply.
True, dead space equals anatomical and physiological dead space
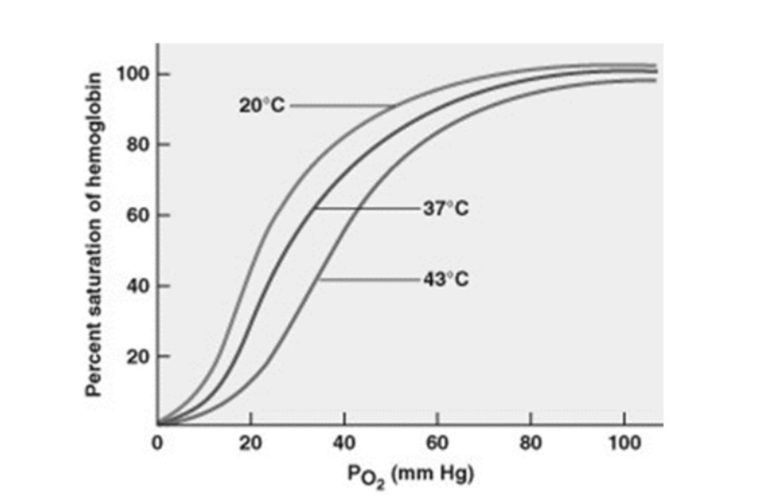
Based on this graph which of the following are true?
A)Greatest delivery of O2 from the blood to the surrounding tissues occurs at 37C, normal body temperature.
B) Fevers are dangerous because less O2 is being released/delivered to body cells.
C) Colder blood temperatures release more O2 from hemoglobin.
D) Hemoglobin has a lower affinity for O2 under higher body temperature conditions.
D) Hemoglobin has a lower affinity for O2 under higher body temperature conditions.
Organize the items listed into the proper sequence of events for gas exchange.
a: O2 is transported to cells by circulatory system.
b: O2 is drawn into the lungs during inhalation.
c: Cells use 02 and generate CO2.
d: CO2 is exhaled.
e: The circulatory system transports CO2 to the lungs.
b, a, c, e, d
Oxygenated hemoglobin releases oxygen more readily when the pH is more basic.
A. True
B. False
B) False
Suppose a person has a total lung capacity (TLC) of 6.00 L, inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) of 3.30 L, and a tidal volume (TV) of 0.60 L. Calculate this person's functional residual capacity (FRC).
TLC-(IRV+TV)
6-(3.3+.6)=
2.1 L
Your patient arrives with a GSW to the thorax. The wound is a clear entry, but no exit. He has severe difficulty breathing. What is causing this?
A) His intrapleural pressure is lower than his lung pressure
B) His intrapleural pressure is higher than his lung pressure
C) He is just bleeding out, walk it off
D) The diaphragm is contracting, expelling air from the thorax
B) His intrapleural pressure is higher than his lung pressure
If a student inhales as deeply as possible and then blows the air out until he cannot exhale any more, the amount of air that he expelled is his:
A) tidal volume.
B) minimal volume.
C) inspiratory reserve volume.
D) vital capacity.
E) expiratory reserve volume.
D) Vital Capacity
T/F: When a person hyperventilates there are lower than normal levels of CO2 and hydrogen ions in arterial blood, a condition called respiratory acidosis.
False, lower CO2 and H+ ions would result in respiratory alkaidosis
Jill lives in St. Louis, which is close to sea level. She decides to spend a month of her summer vacation working in the mountains outside of Denver. After a week in the mountains, what kinds of changes would you expect to see as Jill adapts to the higher altitude?
a)decreased hematocrit.
b)decreased blood presssure.
c)decreased alveolar ventilation rate.
d)decreased Po2 in the alveoli.
e) all of the above.
d)decreased Po2 in the alveoli.
Affinity for hemoglobin for oxygen is decreased by
increased temperature
Hyperventilation results in
Decreased carbon dioxide in the blood, and thus reducing carbonic acid (alkalosis)
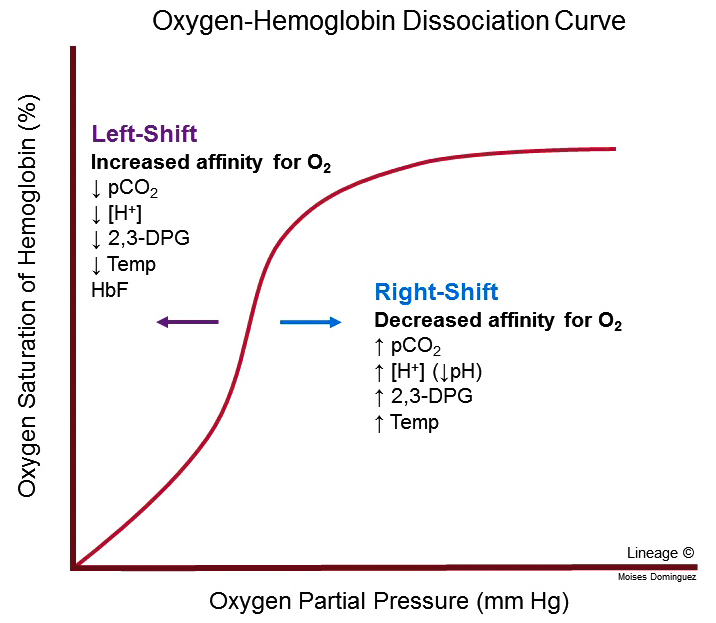
Which of the following would make the oxygen-hemoglobin curve shift right?
A) increased H+ concentration
B) increased pH
C) decreased temperature
D) decreased CO2
E) None of the answers are correct.
A) Increased H+ concentration (I.E lower pH/more acidic conditions)
intrapulmonary pressure must be ________ than interpleural pressure
more
Inspiratory capacity is ________.
A. The total amount of air that can be inspired after a tidal expiration
B. The total amount of exchangeable air
C. Functional residual capacity
D. Air inspired after a tidal inhalation
A. The total amount of air that can be inspired after a tidal expiration
Suppose that a mountaineer climbs to the top of Pikes Peak, which has an elevation of 14,000 ft above sea level, and finds herself breathing heavily, even at rest. Which of the physical factors explains the change in minute ventilation rate?
A.diminished partial pressure of oxygen
B.decreased airway diameter
C.diminished lung compliance
D.lower alveolar surfactant production
A.diminished partial pressure of oxygen
For maximum efficiency in loading oxygen at the lungs:
a. the temperature should be slightly lower than normal body temperature.
b. the PO2 should be about 70 mm.
c. the pH should be slightly acidic.
d. DPG levels in the red blood cells should be high.
e. All of the answers are correct.
a. the temperature should be slightly lower than normal body temperature.
The lungs remain inflated because:
A. intrapulmonary pressure is less than intrapleural pressure.
B. intrapleural pressure is less than intrapulmonary pressure.
C. intrapleural pressure is exactly equal to intrapulmonary pressure.
D. intrapleural pressure is exactly equal to atmospheric pressure.
B. intrapleural pressure is less than intrapulmonary pressure.
The lung volume that represents the total volume of exchangeable air is the ________.
a. tidal volume
b. expiratory reserve volume
c. inspiratory capacity
d. vital capacity
d. vital capacity
Place the structures of the respiratory tree in the order that air passes through them.
1. Secondary bronchi
2. respiratory bronchioles
3. primary bronchi
4. alveoli
5. terminal bronchioles
3
1
5
2
4
Which of the following has the highest partial pressure of carbon dioxide?
a: The alveoli of the lungs
b: The blood circulating in systemic arteries
c: The systemic cells
c: The systemic cells
What changes in the blood levels of respiratory gases result from hyperventilation?
A) Oxygen and carbon dioxide levels rise
B) Oxygen and carbon dioxide levels fall.
C) Oxygen levels rise and carbon dioxide levels fall.
D) Oxygen levels do not change but carbon dioxide levels fall.
D) Oxygen levels do not change but carbon dioxide levels fall
An actively contracting muscle will cause local temperature to rise and will produce acidic molecules. Warmth and lower pH cause the oxygen-hemoglobin saturation curve to shift ______ reflecting that hemoglobin releases ______ oxygen.
A) right; less
B) left; less
C) left; more
D) right; more
D) right; more
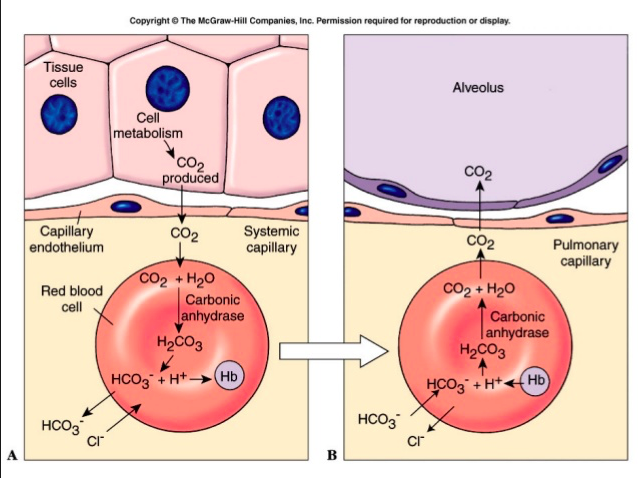
About 70% of the CO2 that diffuses into systemic capillaries:
combines with water to form carbonic acid, which dissociates to bicarbonate and hydrogen ions
The anatomic features of the respiratory membrane that make alveolar gas exchange so efficient are
A) The high degree of moisture and the large ratio of volume to surface area.
B) Its hearty thickness and the presence of oxygen transport pumps.
C) Its thinness, high water content, and scarcity of capillaries.
D) its large surface area and minimal thickness.
D) its large surface area and minimal thickness.
According to Boyle's law, the pressure of a gas _________ if the volume of its container increases.
decreases
(T/F) Inspiratory capacity is greater than inspiratory reserve volume.
True
The most common cell making up the alveolar wall is the
A) alveolar type 1 cell
B) alveolar type 2 cell
alveolar type 1 cell
Which is not part of the conducting portion of the respiratory system?
A) Alveoli
B) Trachea
C) Larynx
D) Nasal cavity
E) Bronchi
A) Alveoli
Ventilation refers to the
a. movement of air into and out of the lungs
b. gas exchange between the blood and the tissues.
c. transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
d. gas exchange between the air in the lungs and the blood.
e. respiration at the cellular level.
a. movement of air into and out of the lungs
Renal plasma clearance:
a) is lower than GFR for substances that are both filtered and secreted
b) is the same as GFR for substances that are both filtered and secreted
c) is the volume of plasma that can be entirely cleared of a substance in one minute
d) is the amount of plasma that passes through the kidney per minute
c) is the volume of plasma that can be entirely cleared of a substance in one minute
T/F: The countercurrent multiplier is a negative feedback mechanism
False, more of a positive feedback as there is no shut-off switch
It keeps balancing out the osmolarity as urine is made
If there is an increase in systemic BP (blood pressure) the resulting stretch of afferent arterioles results in reflexive:
a) vasoconstriction of efferent arterioles to raise GFR.
b) vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles to keep GFR normal.
c) vasodilation of efferent arterioles to lower GFR.
d) vasodilation of afferent arterioles to keep GFR normal.
b) vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles to keep GFR normal
As glomerular filtrate moves through the ascending loop of Henle, the filtrate becomes more dilute: why?
a.The ascending loop of Henle is permeable to water and ions
b. The ascending loop of Henle is permeable to ions but impermeable to water
c. The ascending loop of Henle is impermeable to water and ions
d. The ascending loop of Henle is permeable to water but not to ions
b
Macula densa cells monitor the concentration of
a. glucose in the blood.
b. antidiuretic hormone in the urine.
c. sodium chloride in the fluid within the distal convoluted tubule.
d. calcium in the fluid of the proximal convoluted tubule.
e. aldosterone in the afferent arteriole.
2) The macula densa cells respond to ________.
1) c. sodium chloride in the fluid within the distal convoluted tubule.
2)
- changes in Na+ content of the tubular fluid (filtrate)
- signals to afferent or efferent arteriole to influence vasoconstriction and vasodilation
T/F: The anatomic arrangement of juxtamedullary nephrons in the kidneys is such that the glomerulus, proximal tubule, and distal convoluted tubule are in the renal cortex, while the loop of Henle and collecting ducts lie mainly in the renal medulla.
True
T/F: If the GFR is too low, needed substances may pass so quickly through the renal tubules that they are not absorbed and instead are lost in the urine.
False, GFR would need to be too high
Constriction of the __________ decreases hydrostatic pressure in __________.
afferent arteriole, glomerulus
Which step(s) in the process of urine formation occur in the renal tubule?
A) Secretion and reabsorption
B) Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption
C) Reabsorption
D) Filtration
E) Secretion
a) secretion and reabsorption
what would happen if the hydrostatic pressure inside the Bowman's capsule increased above normal?
a) capsular osmotic pressure would
b) net filtration would increase above normal compensate so that filtration would not change.
c) filtration would increase in proportion to the increase in capsular pressure.
d) net filtration would decrease
d) net filtration would decrease
The amount of substance that is excreted in the urine is equal to the amount that is _________ + __________ - _____________.
filtered, secreted, absorbed
Shortcut: remember FSA
Substances that are co-transported into proximal convoluted tubule cells include
a.urea with water.
b.potassiumwith amino acids.
c.glucose molecules with sodium ions.
d.amino acids with bicarbonate ions.
e.chloride with potassium.
c
If the following hypothetical conditions exist in the nephron, calculate the net filtration pressure.
glomerular capillary pressure = 100mmHg
blood colloid osmotic pressure =30 mmHg
capsular hydrostatic pressure = 10 mmHg
a.120 mmHg
b.80 mmHg
c.60 mmHg
d. 30 mmHg
e.20 mmHg
c
NFP = (GCHP) - (BCOP) + (CHP)
NFP = 100 mmHg - (30 mmHg + 10 mmHg) = 60 mmHg
In the tubuloglomerular feedback and autoregulation, what is the response to an increase in blood pressure in the afferent arteriole?
a. constriction of the glomerulus
b. constriction of the afferent arteriole
c.dilation of the afferent arteriole
d. dilation of the efferent arteriole
b
The collecting ducts and distal convoluted tubules
a.reabsorb glucose.
b. collect filtrate from Bowman's capsule.
c.actively transport sodium ions but not chloride ions.
d. vary in their
permeability to water relative to the amounts of ADH present.
e. do not alter their permeability to water.
d
What percent of filtrate
becomes urine?
a. less than 1%
b. 5%
c. 10%
d.80%
e.90%
a
The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin ________.
a.when the peritubular capillaries are dilated
b. when the pH of the urine decreases
c. by an increase in blood pressure
d. by a decrease in the blood pressure
d
What would happen if the hydrostatic pressure in
capillaries of the glomerulus were increased above normal?
a. Net filtration would decrease.
b. net filtration would increase above normal
c. Filtration would increase in proportion to the increase in capsular pressure.
d. Capsular osmotic pressure would compensate so that filtration would not change.
b
Lasix is a diuretic that blocks the reabsorption of sodium in the ascending Loop of Henle. The
result of giving this drug would be
a. decreased aldosterone production.
b. decreased osmolality of the filtrate.
c. increased osmolality of the urine.
d. increased urine output.
e. decreased urine volume.
d
Angiotensin II
a. is a potent vasodilator.
b.acts on the collecting ducts to increase reabsorption of water.
c.decreases blood pressure.
d.stimulates aldosterone secretion.
d
How are the processes of reabsorption and secretion related?
a. They both involve movement of material from the blood into the tubular fluid.
b. Materials move in opposite
directions: reabsorption moves materials into the
blood, whereas secretion removes them from the blood.
c. Materials move in opposite directions: secretion moves materials into the blood, whereas reabsorption removes them from the blood.
d. They both involve movement of material from the tubular fluid into the blood.
b
The descending limb of the loop of Henle ________.
a. is permeable to sodium
b.pulls water by osmosis into the lumen of the tubule
c. is permeable to water
d.contains fluid that becomes less concentrated as it moves down into the medulla
c
The renal system does not play a direct role in regulating which of the following?
a.Blood solute concentrations
b.Blood temperature
c.Blood pressure
d.Blood pH
b
Which of the following is NOT an action of angiotensin II?
a.vasoconstriction of arterioles
b.decreases resistance in the PCT
c.increases ADH secretion
d.increases aldosterone secretion
b
Which of the following anatomical portion of a nephron connects the Bowman’s capsule to the loop of Henle?
a.Distal convoluted tubule
b.Connecting tubule
c.Proximal convoluted tubule
d.Collecting duct
c
Urine is formed in a three-step process: which of the following gives the correct order in which these steps take place in the nephron?
a.Tubular secretion, tubular reabsorption, glomerular filtration
b.Tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, glomerular filtration
c.Glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion
d.Glomerular filtration, tubular secretion, tubular reabsorption
c
The movement of water, small molecules, and ions from the plasma into Bowman's space to be sent to the tubule is called
a) excretion
b) filtration
c) secretion
d) reabsorption
a) excretion
True or false? Moving of substances from the blood into the tubule is called reabsorption.
true
false
false
Which of the following does not play a role in repelling molecules during filtration, keeping substances out of the filtrate?
a) parietal layer of Bowman's capsule
b) visceral layer of Bowman's capsule
c) capillary fenestrations
d) basement membrane
a) parietal layer of Bowman's capsule
Which of the following locations is NOT a critical location for water reabsorption in the nephron?
A. Descending loop of Henle
B. Collecting duct
C. Distal convoluted tubule
D. Proximal convoluted tubule
d
Which of the following is NOT a critical part of the filtration membrane?
A. Fenestrated endothelium
B. Visceral layer of the glomerulus
C. Basement membrane
D. Podocytes
E. Renal capsule
e
Generally, negatively charged plasma proteins are:
A. Repelled by the negative charge of the filtration membrane.
B. Moved across the filtration membrane by active transport pumps
C. Attracted by the positive charge of the filtration membrane
D. Engulfed by endocytosis and reabsorbed at the filtration membrane
a
Glomerular hydrostatic pressure is the pressure of
A. Filtrate in the glomerular capillaries.
B. Blood in the nephron capsule.
C. Blood in the glomerular capillaries.
D. Tubular fluid in the glomerular capsule.
E. Solutes in the tubular fluid.
c
If the filtration membrane were made more porous, how would you expect the glomerular filtration rate to change?
A. Increase
B. No Change
C. Decrease
a
Jim's experience in a particularly scary haunted house initiated a panic attack leading to hyperventilation. As the blood pH changes, how will the renal tubules respond?
A. Secrete bicarbonate and H+
B. Secrete H+ while reabsorbing bicarbonate in exchange
C. Absorb bicarbonate and H+
D. Secrete bicarbonate while reabsorbing H+ in exchange
d
A young woman is brought by ambulance to the ER after attending a party where she consumed alcohol. She is showing signs of severe dehydration despite insisting that she drank water in addition to alcohol during the night. Which of the following explains the mechanism by which she most likely became dehydrated?
A. Alcohol blocks the release of ADH, leading to a sharp decrease in water reabsorption in the collecting duct
B. Alcohol interferes with the adrenal gland causing an increase release of aldosterone leading to excessive water loss
C. Alcohol decreases GFR by acting on the efferent arteriole leading to increased water retention
D. Alcohol blocks the Na+/K+ ATPases is the ascending loop of Henle, leading to water reabsorption
a
A 24-year old college student with a history of Crohn's disease presents to the hospital with complaints of four days of bloody and watery diarrhea and lightheadedness. Her blood pH is 7.28 and she has a notably increased breathing rate. Which of the following is most likely true about her condition?
A. She is suffering from respiratory acidosis brought on by hyperventilation. The diarrhea is a compensatory mechanism by which loss of bicarbonate can return the pH to normal range.
B. The patient is suffering from metabolic acidosis likely brought on by an excessive loss of intestinal bicarbonate. Her hyperventilation is a compensatory mechanism.
C. She is suffering from metabolic alkalosis brought on by loss of intestinal H+. Her hyperventilation is a compensatory mechanism.
D. She is suffering from respiratory alkalosis brought on by hyperventilation. The diarrhea is a compensatory mechanism by which loss of bicarbonate can return the pH to normal range.
b
Which of the following causes a rise in blood pressure in response to hormonal stimulus?
A. Tubuloglomerular response
B. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism
C. Myogenic mechanism
D. Countercurrent multiplier
E. Adrenergic response
b
If the afferent arteriole has a normal diameter while vasoconstriction occurs in the efferent arteriole, what would you expect to happen to glomerular filtration rate?
A. Decrease
B. Stay the same
C. It is impossible to tell from the info given
D. Increase
d
The concentration within the interstitium of the renal medulla ______ with increasing depth leading to a(n) ______ in water reabsorption. This concentration gradient is primarily established by the movement of _____ via active transport out of the ________________.
Increases; increase; Na+; ascending loop of Henle
Select all of the following that are true about the countercurrent multiplier system.
A. Juxtaglomerular nephrons, which have longer loops of Henle that travel deep into the renal medulla are critical for water reabsorption and concentrating urine
B. The directed movement of cations from the distal convoluted tubule is critical to establishing the driving force gradient in the countercurrent multiplier system
C. The descending loop of Henle is only permeable to ions which the ascending loop of Henle is only permeable to water
D. The vasa recta are able to reabsorb sodium and water released from the loop of Henle by both active and passive processes
E. In the countercurrent multiplier system, sodium moves into the interstitial space via active transport but water moves via osmosis
a & e
An individual has an excessive urine output while exhibiting signs of dehydration. Select all of the following possible causes of this presentation. Note: all of the following statements are true by themselves.
A. Low renin hypertension with a failure to activate the RAAS pathway
B. Diabetes insipidus which is caused by a deficiency in ADH leads to suboptimal water reabsorption from the collecting ducts
C. Hyperaldosteronism caused by an adrenal tumor leading to high levels of sodium and water reabsorption while increasing potassium secretion
D. renal specific glucocorticoid resistance in which hormones like aldosterone and cortisol are unable to bind to their receptors and activate signaling cascades
a, b & d
In the myogenic mechanism of autoregulation, what is the response to an increase in blood pressure in the afferent arteriole?
constriction of the afferent arteriole