Transport in Plants (2.21-2.24)
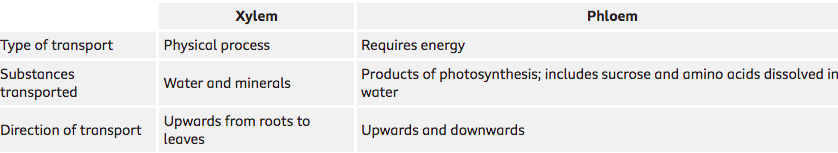
Xylem: Transports water and mineral ions. %%roots→stem→leaves (unidirectional)%%
Phloem: Transports ‘food’ (sucrose and amino acids) made by photosynthesis from phtosynthesisng region to non photosynthesisng region %%source → sink (bidirectional)%%
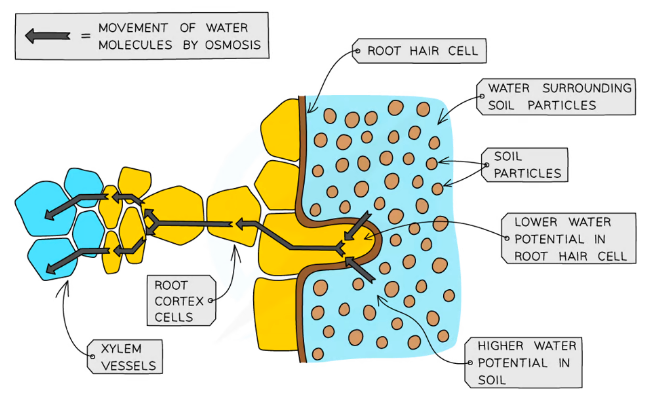
Root hair cells: Single celled extension in the epidermis which grow between soil particles and absorb water by osmosis and mineral ions by active transport
- The water potential in the soil is higher than the water potential in the cells cytoplasm
- Root hair cells %%increase the surface area of the cell,%% increasing the rate of absorption of water and mineral ions
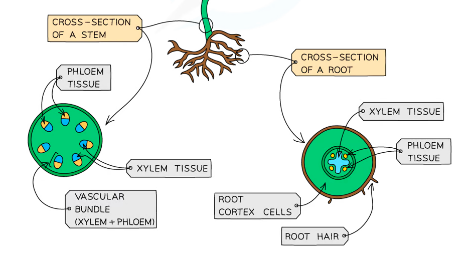
Pathway
%%Root Hair cells →Root cortex cells→Xylem→Mesophyll%%
Adaptation of xylem
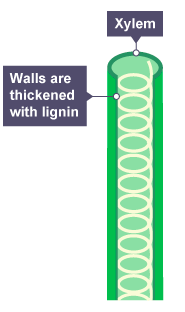
Lignin deposited in the cells to kill xylem cells
Cells are hollow and joined together end to end to form a continous tube
Lignin strengthens plant to withstand pressure
Transpiration: Loss of water vapor from the leaves by evaporation of water on the surface of the mesophyll followed by diffusion down a concentration gradient through the stomata
Functions of transpiration
1. Transporting mineral ions
2. Keep cells turgid (supports the structure)
3. Water for photosynthesis
4. Keeps leaf cool (Cooling effect from evaporation)
- The many interconnecting air spaces between spongy mesophyll and stomata increase the surface area for transpiration
Transpiration stream
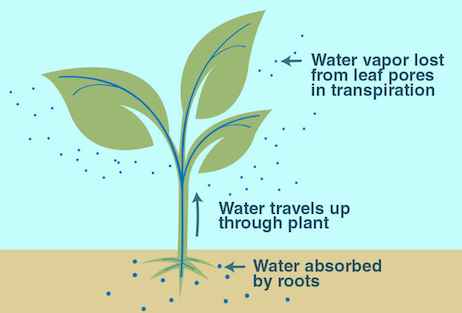
- Water molecules are attracted to each other by cohesion - creating a %%continuous column of water up the plant%%
- Water moves through the xylem vessels in a continuous transpiration stream from roots to leaves via the stem
- Transpiration produces a tension or ‘pull’ on the water in the xylem vessels by the leaves
- As water molecules are held together by cohesive forces (each individual molecule ‘pulls’ on the one below it), so water is pulled up through the plant
- If the rate of transpiration from the leaves increases, water molecules are pulled up the xylem vessels quicker
%%Factors that affect transpiration rate are:%%
- Temperature
- Higher temperatures result in faster moving molecules and therefore increases diffusion rate, which in turn, increases transpiration rate
- Humidity
Higher humidity results in a lower concentration gradient and thus reduces diffusion rate, which in turn, reduces transpiration rate
Wilting: More water evaporated from leaves than water absorbed from soil
Cells are flaccid so the plant collapses
Translocation: Movement of sucrose and amino acids in the phloem from the source to the sink.
- Source: region of production
- Sink: Region of storage or use
Many plants do not have leaves during the winter, so dissolved sucrose and amino acids can be transported from storage organs to other parts of the plant.
When a plant is growing (e.g. in spring), the storage organs (e.g. roots) would be the source and the many growing areas would be sinks
During the summer, the leaves are photosynthesizing and making large quantities of sugars; so they supply the plant with sugars, whereas the roots store starch until the plant needs it.
- %%Sources and sinks change as the seasons change%%
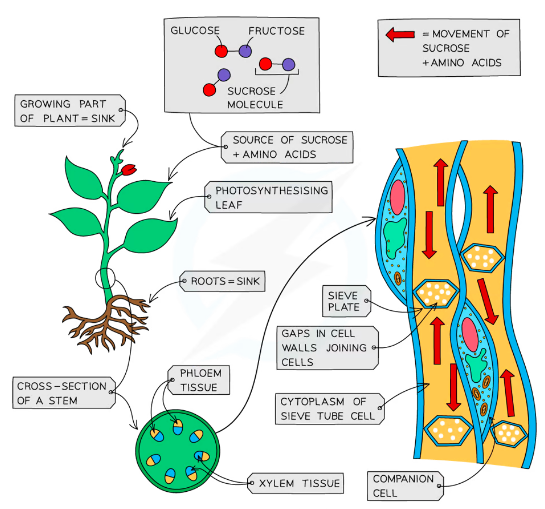
Phloem tubes are made of living cells
The cells are joined end to end and contain holes in the end cell walls (called sieve plates) which allow easy flow of substances from one cell to the next