Histo Lab- Lymphatic System (Aughey)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
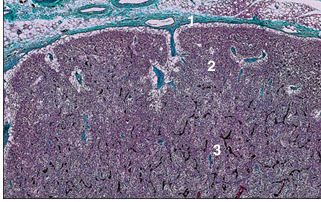
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Lymph node (dog). (1) Connective tissue capsule. Cortex with (2) lymphatic follicles and (3) paracortex. Masson’s trichrome. ×20.
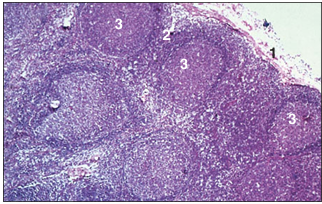
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Lymph node (sheep). (1) Connective tissue capsule. (2) Connective tissue trabeculae. (3) Lymphatic tissue. H & E. ×62.5.
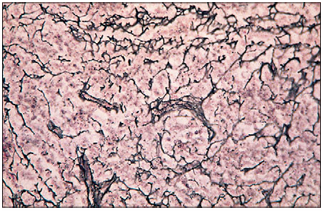
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Lymph node (cat). The reticular fibres form a black network and support the cells of the lymphatic tissue. Gordon and Sweet. ×100.
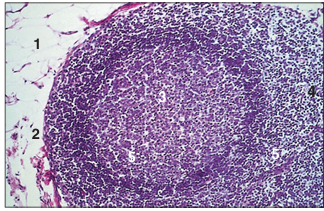
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Lymph node (dog). (1) Connective tissue capsule with some fat cells. (2) Subcapsular sinus. (3) Cortical follicle. (4) Parafollicular tissue. (5) Sinusoid. H & E. ×125.
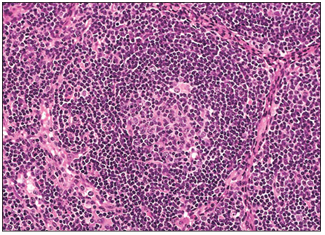
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
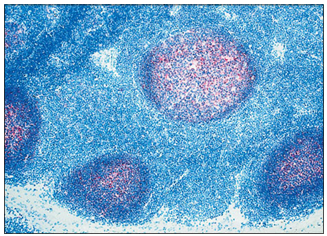
Lymph node. Cortex (dog). A single follicle is present. The central zone is the pale staining reactive germinal centre. There is an outer rim of closely packed small lymphocytes. H & E. ×125.
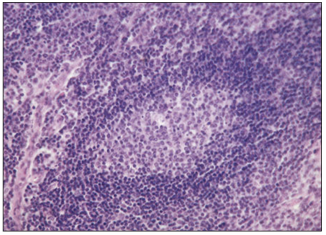
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Lymph node. Cortex (dog). The germinal centre is composed of lymphoblasts, reticular cells and macrophages. H & E. ×125.
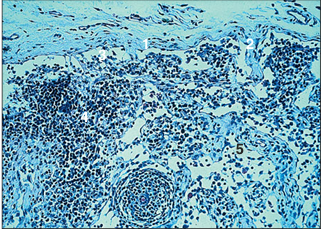
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__
Stain used:
Lymph node. Paracortex (pig). (1) Connective tissue capsule. (2) Connective tissue trabeculae. (3) Subcapsular sinus. (4) Thymus-derived T lymphocytes. (5) Sinusoid. Alcian blue. ×125.
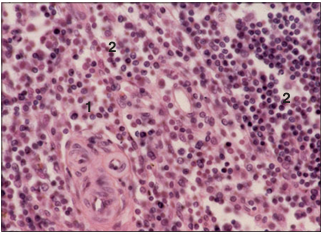
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Lymph node. Medulla (dog). (1) Loose aggregation of lymphoid tissue. (2) Open meshwork of sinusoids. H & E. ×250.
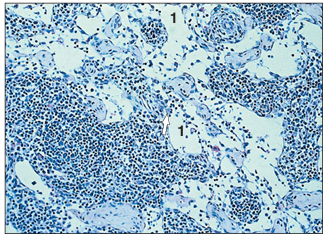
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__
Stain used:
Lymph node. Medulla (dog). (1) Sinusoid lined by macrophages. Also, clusters of small lymphocytes (arrowed). Alcian blue. ×125.
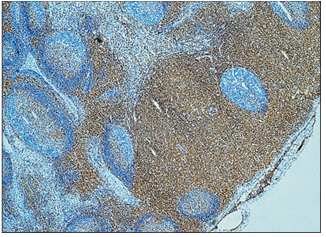
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Lymph node (cat). Anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody. The avidin/biotin method detects an exclusive population of T lymphocytes in the parafollicular and deep cortex of the lymph node; brown reaction. Avidin/biotin method. ×62.5.
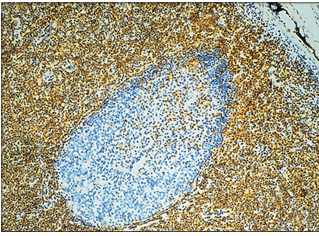
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Lymph node (cat). Anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody. The avidin/biotin method detects an exclusive population of T lymphocytes in the parafollicular and deep cortex of the lymph node; brown reaction. Avidin/biotin method. ×125.
name of histologic slide:
Stain used:
Lymph node. Cortex. Anti CD8/CD4 monoclonal antibody. This subset of positive cells are rarely present in the follicle germinal centre. Avidin/biotin method. ×100.
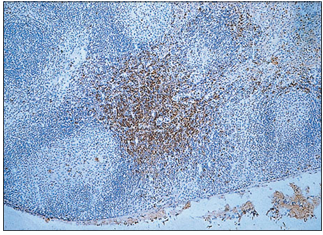
name of histologic slide:
Stain used:
Lymph node. Cortex. Anti-C.D.21 monoclonal antibody. This method recognizes the follicular dendritic cells and the cell processes; stained red. Avidin/biotin method.×62.5.
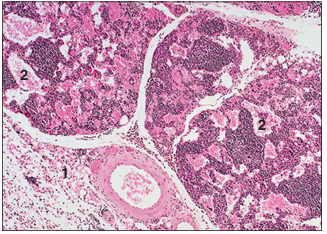
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Haemal lymph node (ox). (1) Connective tissue capsule. (2) Blood filled sinusoids. H & E. ×20.
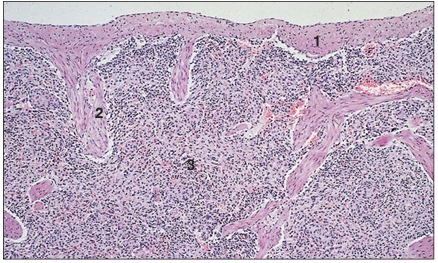
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Spleen (horse). (1) Fibromuscular capsule. (2) Fibromuscular trabeculae. (3) Splenic pulp. H & E. ×12.5.
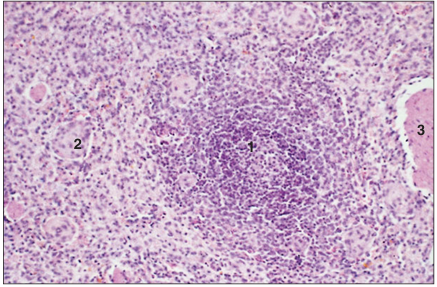
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Spleen (horse). (1) White pulp. (2) Red pulp. (3) Trabecula. H & E. ×62.5.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
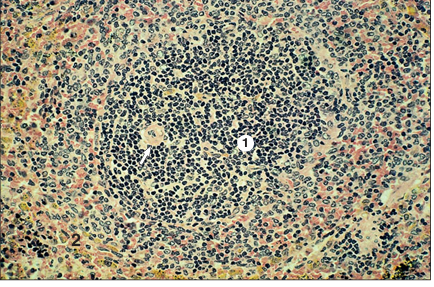
Spleen (dog). (1) White splenic corpuscle with an eccentric arteriole (arrowed). (2) Sinusoids of the red pulp filled with erythrocytes. H & E. ×125.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
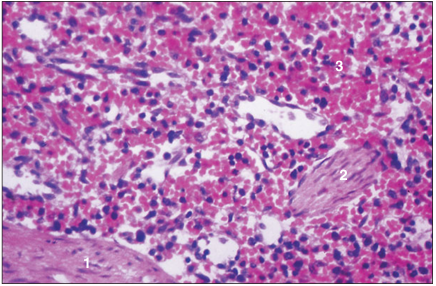
Spleen (cat). (1) Part of a trabecula. (2) Ellipsoid. (3) Blood filled sinusoids of the red pulp. H & E. ×250.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
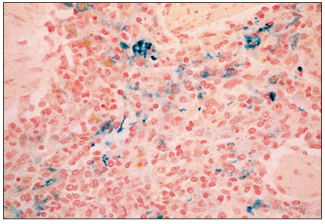
Spleen (dog). The site of iron deposits as a result of erythrocyte phagocytosis are blue. Perls’ Prussian blue. ×125.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
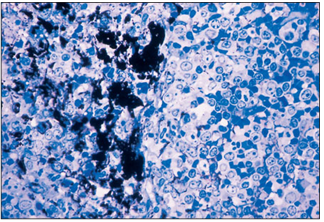
Spleen (dog). The marginal zone has a large population of macrophages. These are shown filled with phagocytosed carbon particles. Toluidine blue. ×250.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
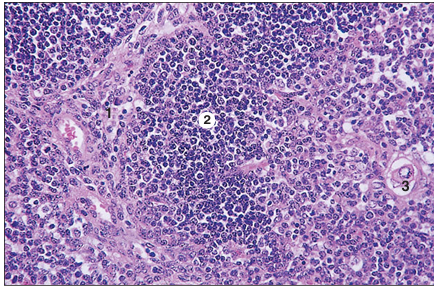
Thymus (ox). (1) The supporting epithelial cells derived from the pharyngeal endoderm. (2) Thymocytes. (3) Thymic corpuscle. H& E. ×125.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
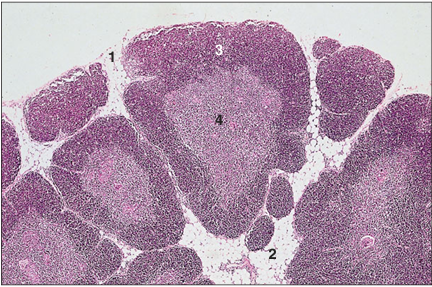
Thymus (ox). (1) Fine connective tissue capsule. (2) Fat laden interlobular connective tissue. Thymic lobule with (3) outer cortex of densely packed thymocytes, and (4) inner less cellular medulla. H & E. ×62.5.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
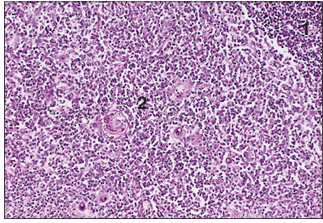
Thymus (ox). (1) Thymocytes in the cortex. (2) Medulla with epithelial cells and few thymocytes. H& E. ×125.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
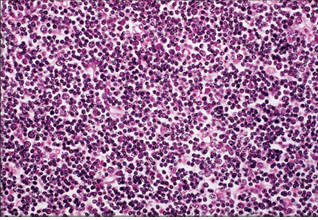
Thymus (ox). The small dark blue cells are the densely packed cortical thymocytes. H & E. ×250.
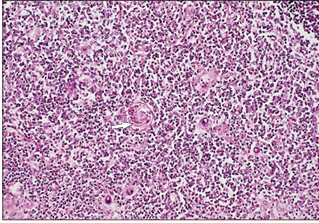
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Thymus (ox). The central medullary zone is less cellular; a thymic (Hassall’s) corpuscle is arrowed. H & E. ×125.
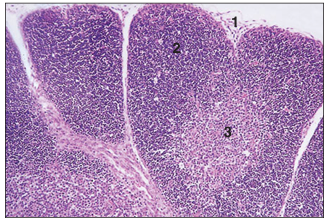
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Fetal thymus (ox). (1) The connective tissue of the capsule and the supporting trabeculae; there are no fat cells. Thymic lobules with (2) cortex and (3) medulla. H & E. ×62.5.
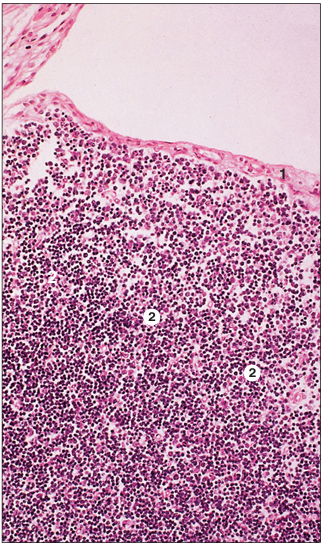
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Fetal thymus (ox). (1) Connective tissue capsule. (2) Cortical zone of the thymic lobule with loosely arranged thymocytes. The intercellular supporting framework is composed of epithelial cells. H & E. ×125.
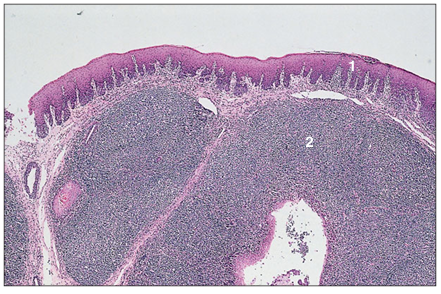
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Tonsil (dog). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium. (2) Dense aggregation of lymphoid tissue in the lamina propria. H & E. ×20.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
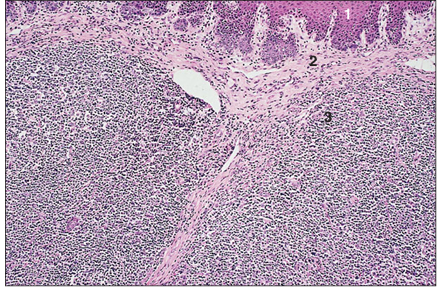
Tonsil (dog). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium. (2) Connective tissue lamina propria. (3) Lymphoid tissue. H & E. ×125.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
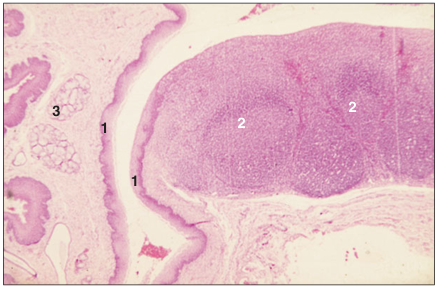
Tonsil (dog). (1) Stratified squamous epithelium lining the crypt. (2) Dense aggregations of lymphoid tissue in the lamina propria. (3) Mucus-secreting salivary glands. H & E. ×7.5.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
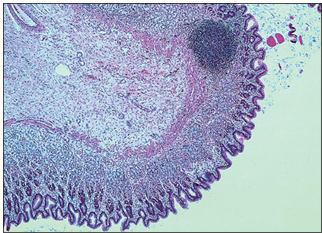
Stomach (cat). A lymph nodule is present in the mucosal/submucosal layer of the stomach. H & E. ×7.5.
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
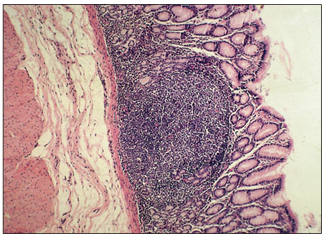
Abomasum (goat). A lymph nodule in the lamina propria of the mucosa. H & E. ×62.5.
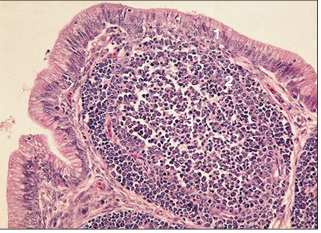
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Cloacal bursa (bird). (1) Simple columnar epithelium of the cloaca. (2) Cortical area of densely packed lymphocytes. (3) Sparsely populated medulla. H & E. ×62.5.
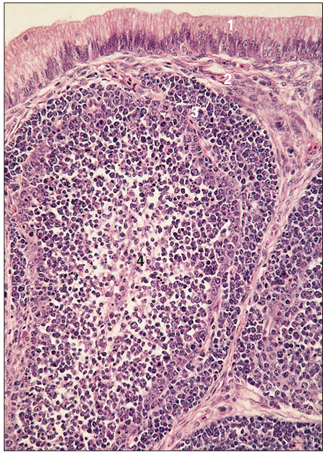
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Cloacal bursa (bird). (1) Simple columnar epithelium of the cloaca. (2) Connective tissue lamina propria. (3) Cortex. (4) Medulla. H & E. ×125.
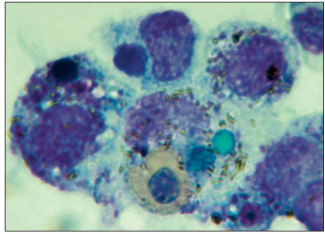
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Bone marrow specimen from an iguana. This section contains several macrophages with engulfed cellular material and bacteria. Note the green inclusion within the large macrophage which contains biliverdin, the degradation product of haemoglobin in amphibians, reptiles and birds. H & E. ×250.
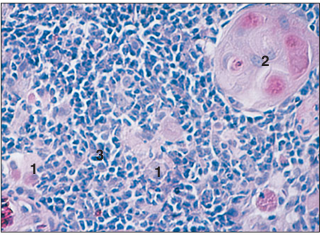
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Parts
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Section of cortical part of a thymic lobule from a desert tortoise (Xerobates agassizi). (1) Epithelial cells. (2) Concentric (Hassall’s) corpuscle. (3) Thymocytes. H & E.×125.
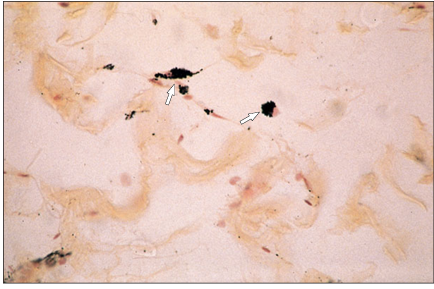
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Loose connective tissue (dog). The histiocytes have phagocytosed the injected carbon particles (arrowed). ×250.
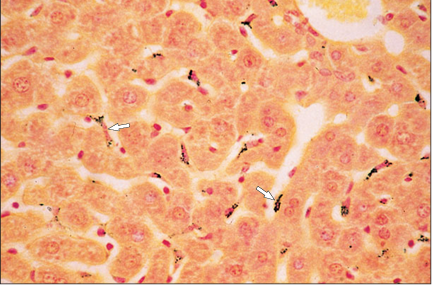
name of histologic slide:
Specie:
Stain used:
Liver (sheep). The macrophages lining the sinusoids have phagocytosed the injected carbon particles (arrowed). Safranin/haematoxylin. ×250.