MSE Midterm 1 Set 4: Crystal Structure Fundamentals
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
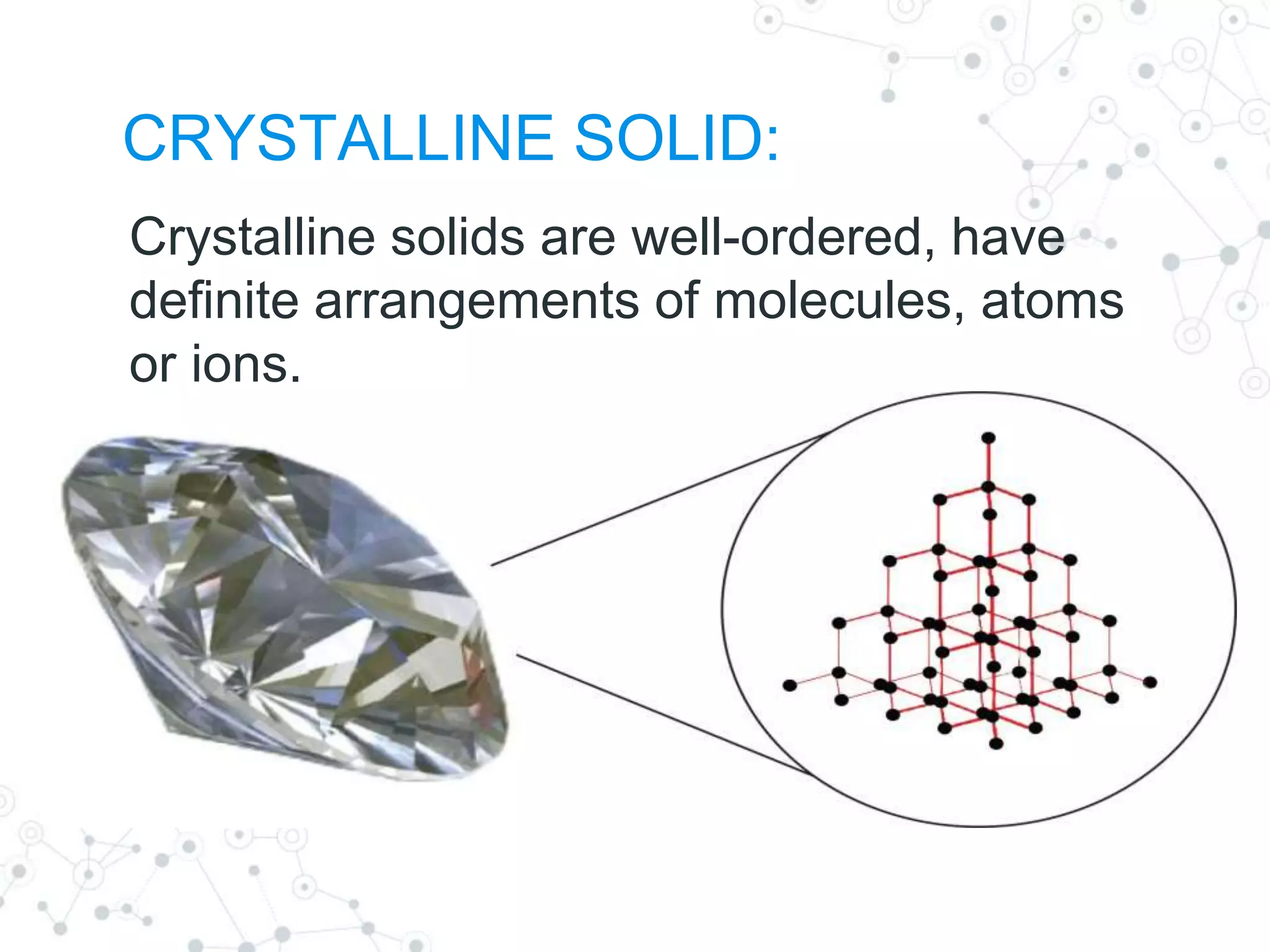
crystalline
The state of a solid material characterized by a periodic and repeating three-dimensional array of atoms, ions, or molecules.
crystal structure
For crystalline materials, the manner in which atoms or ions are arrayed in space. It is defined in terms of the unit cell geometry and the atom positions within the unit cell.
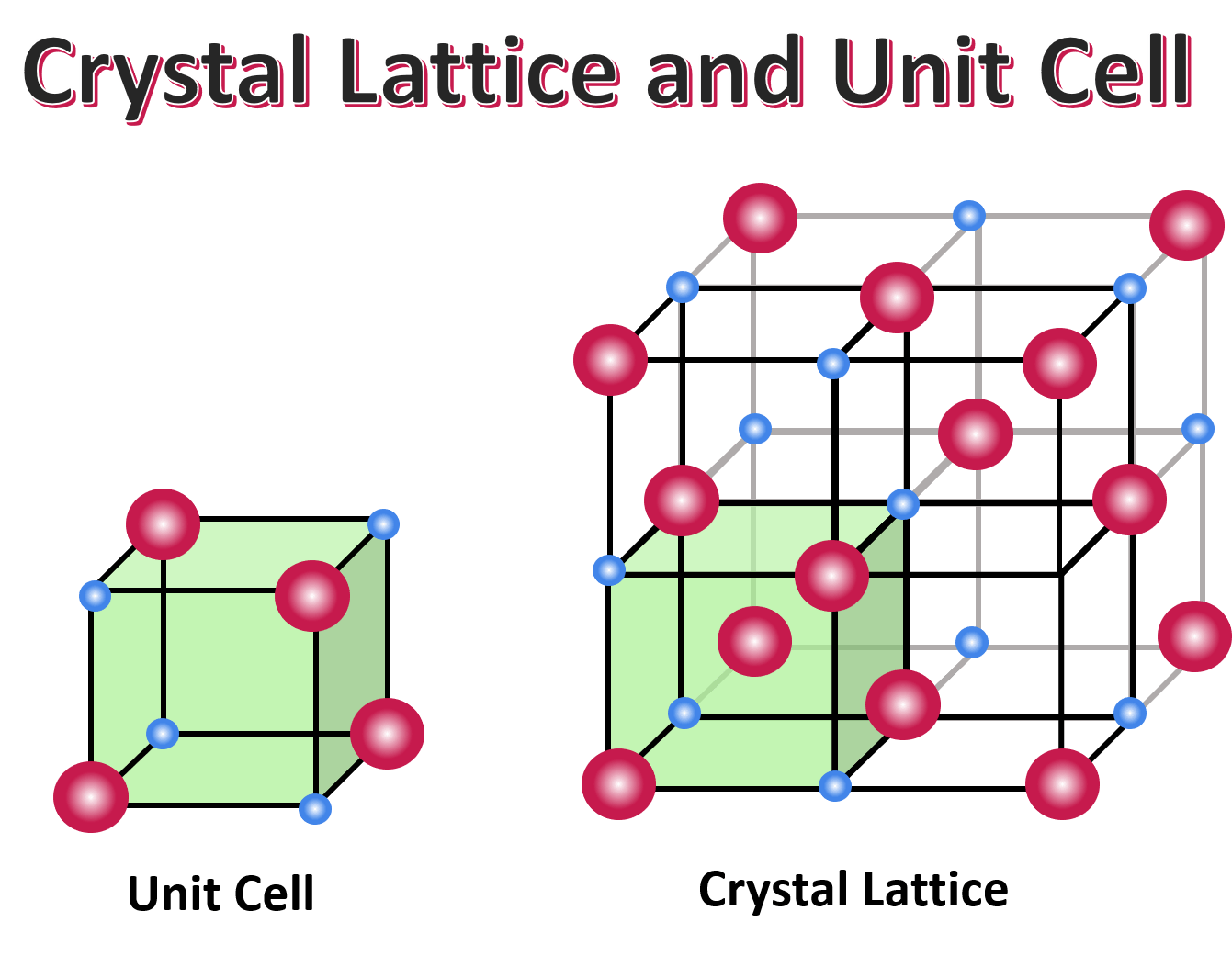
lattice
The regular geometrical arrangement of points in crystal space.
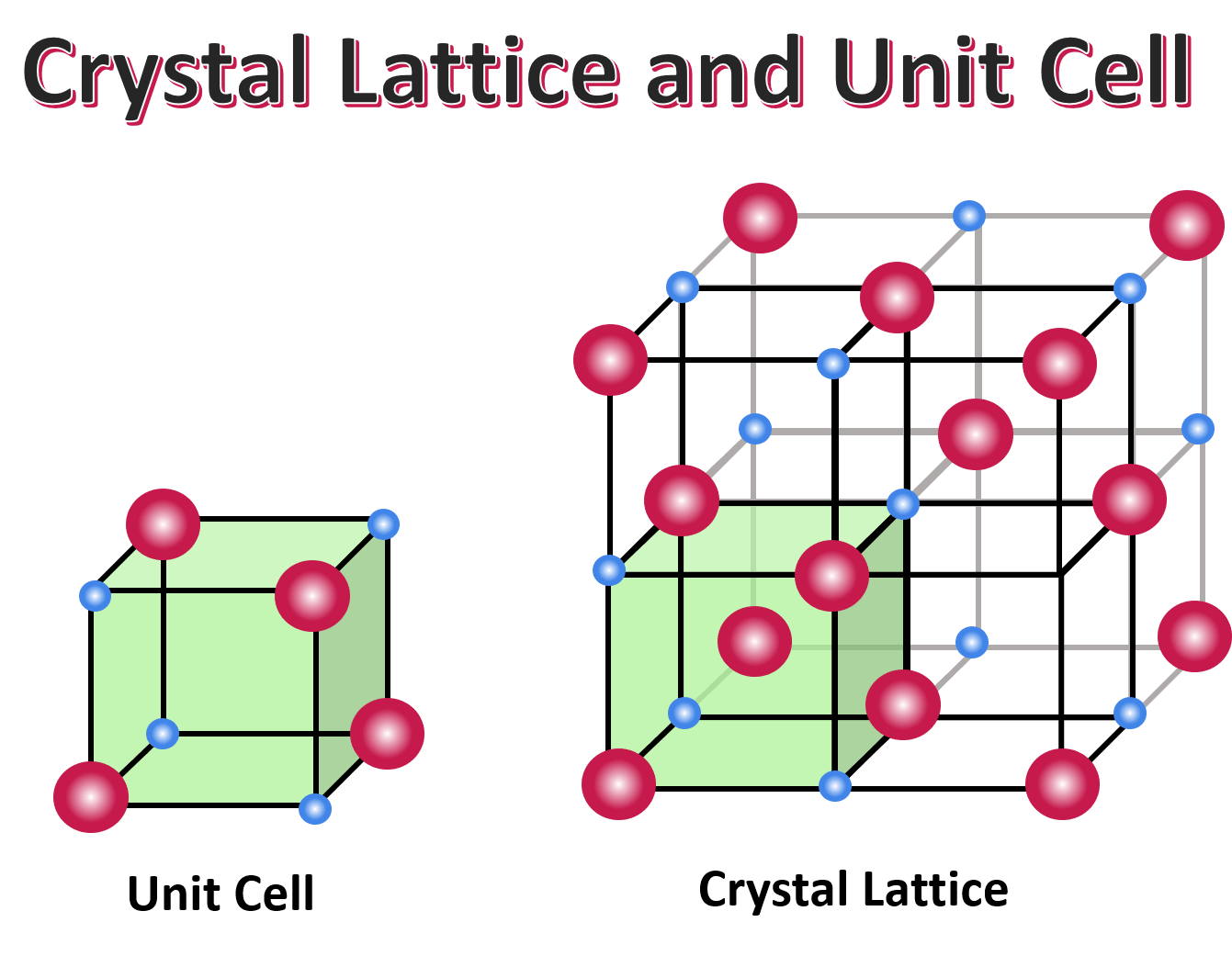
unit cell
The basic structural unit of a crystal structure. It is generally defined in terms of atom (or ion) positions within a parallelepiped volume.
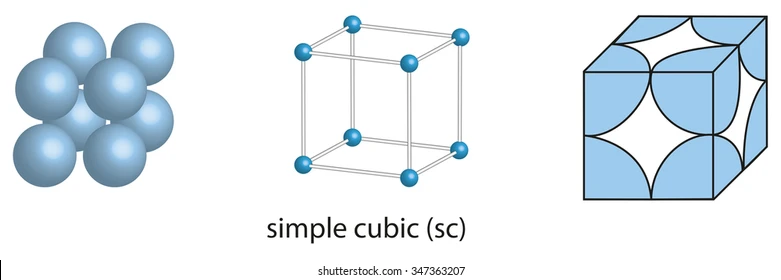
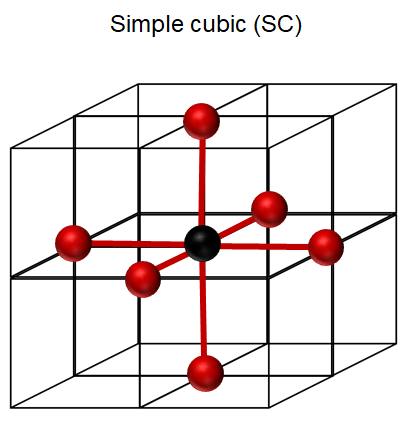
simple cubic (SC)
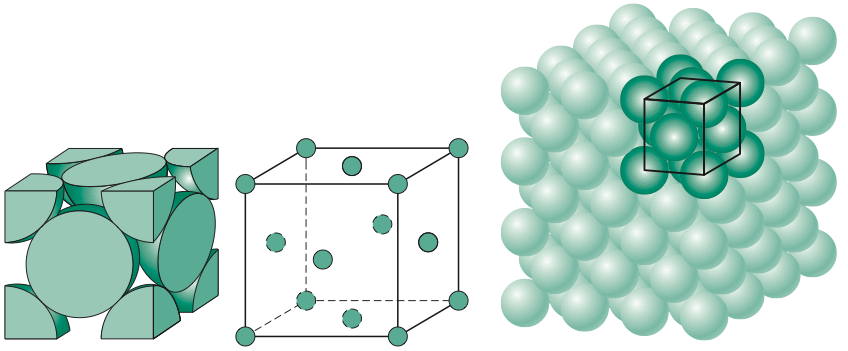
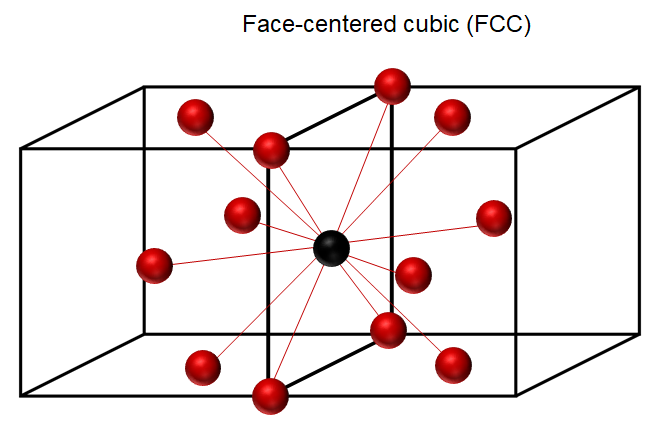
face-centered cubic (FCC)
A crystal structure found in some common elemental metals. Within the cubic unit cell, atoms are located at all corner and face-centered positions.
a * sqrt(2) = 4R
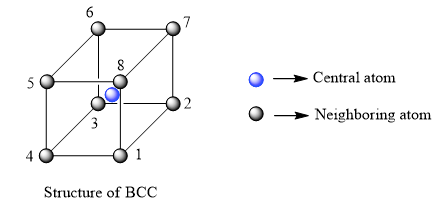
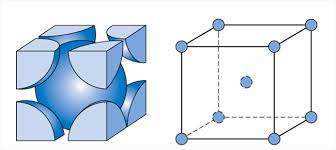
body-centered cubic (BCC)
A common crystal structure found in some elemental metals. Within the cubic unit cell, atoms are located at corner and cell center positions.
a * sqrt(3) = 4R
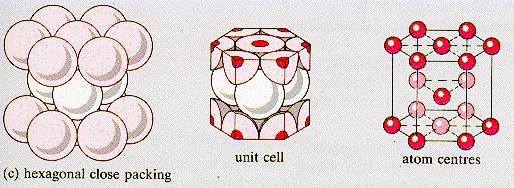
hexagonal close-packed (HCP)
A crystal structure found for some metals. The HCP unit cell is of hexagonal geometry and is generated by the stacking of close-packed planes of atoms.
SC coordination number
CN = 6, APF 0.52
coordination number
The number of nearest atomic neighbors equidistant to each other
atomic packing factor (APF)
The fraction of the volume of a unit cell that is occupied by hard-sphere atoms or ions.
FCC coordination number & APF
CN = 12, APF 0.74
BCC coordination number
CN = 8, APF 0.68