Introduction to Canine Anatomy and Physiology
1/262
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
263 Terms
Anatomy
The branch of morphology dealing with the form, structure, topography and the functional interaction of tissues and organs that make up the body.
Systemic anatomy
Anatomy that has to do with 'systems', in other words, with structures and organs that perform a common function.
Species
A group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes and interbreeding.
Physiology
The branch of biology dealing with the functions and activities of living organisms and their parts, including all physical and chemical processes.
Macroscopic anatomy
The examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight.
Gross anatomy
A branch of anatomy that includes the examination of body parts with the naked eye.
Surface anatomy
The branch of gross anatomy that refers to the morphology and anatomical landmarks.
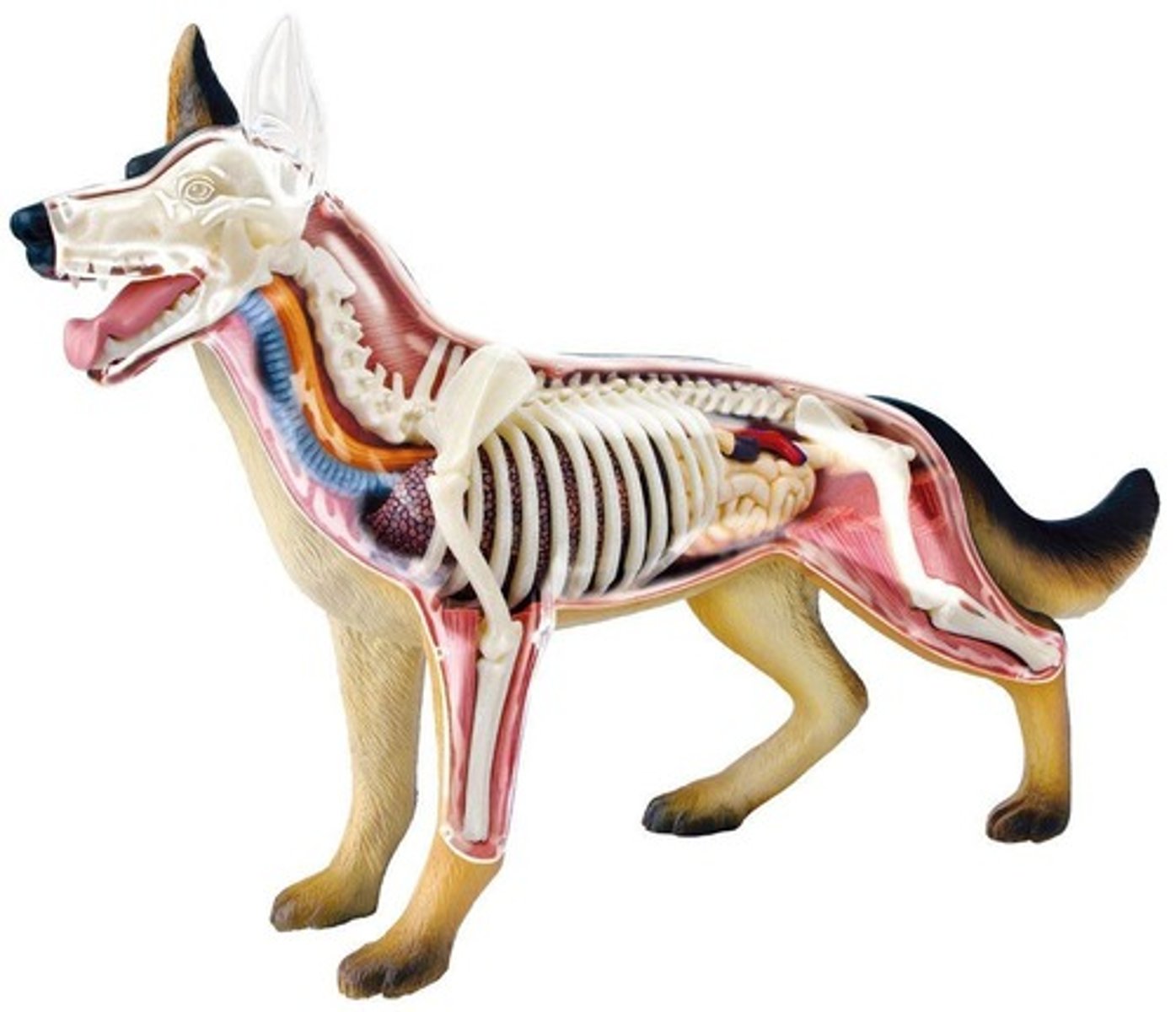
Nervous System
The system that includes the organization, central nervous system, reflexes, peripheral nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system, neurons and other nervous system cells.
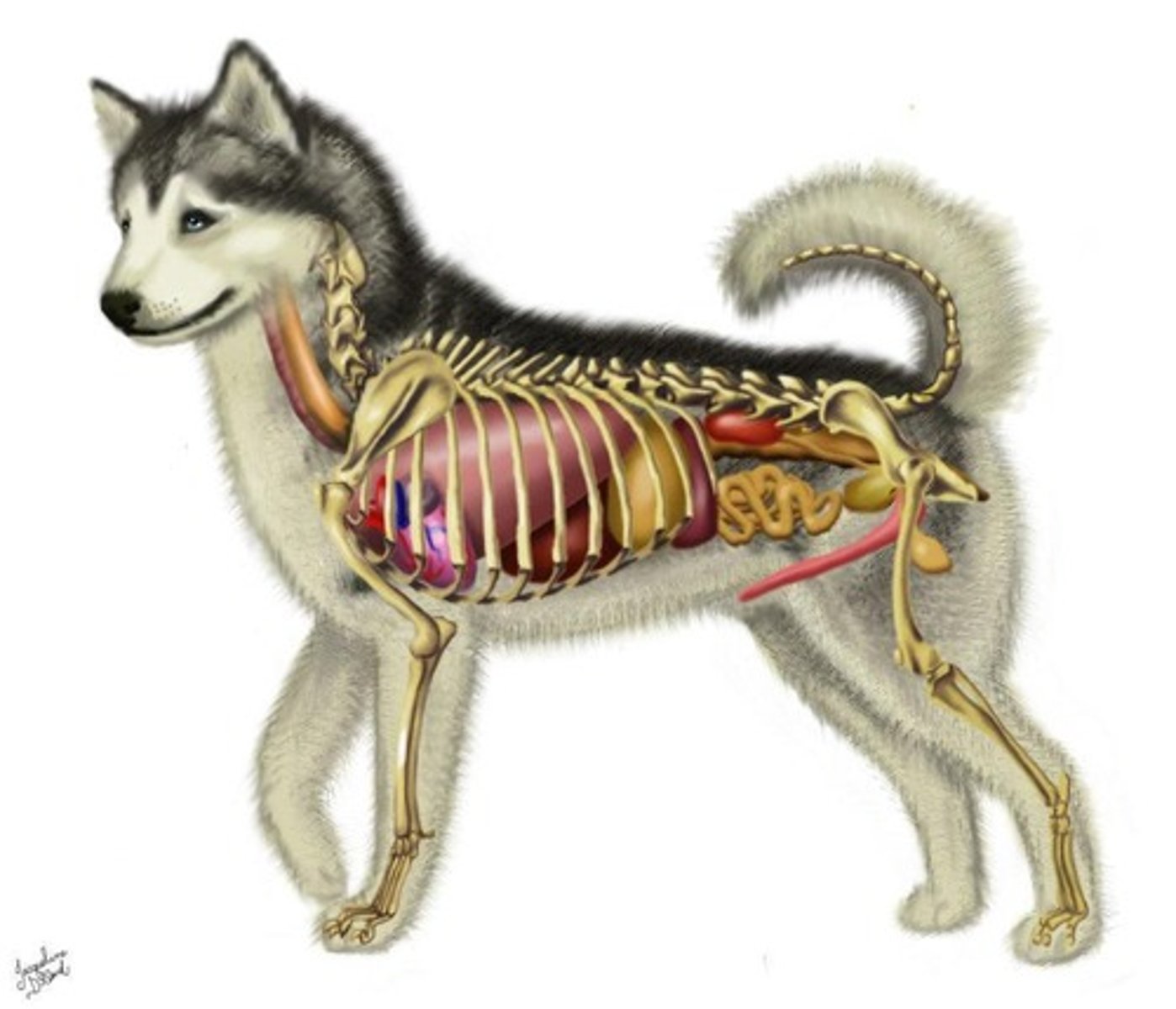
Body Cavities
Spaces within the body that contain organs.
Digestive System
The system responsible for the organization, cranial portion, abdominal portion, and accessory glands involved in digestion.
Cardiovascular System
The system that includes the organization, the blood, the heart, blood vessels, and circulation.
Respiratory System
The system responsible for the organization, conduction system, exchange system, and respiration.
Urinary System
The system that includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Reproductive System
The system that includes the female reproductive system, the heat cycle, male reproductive system, and testosterone.
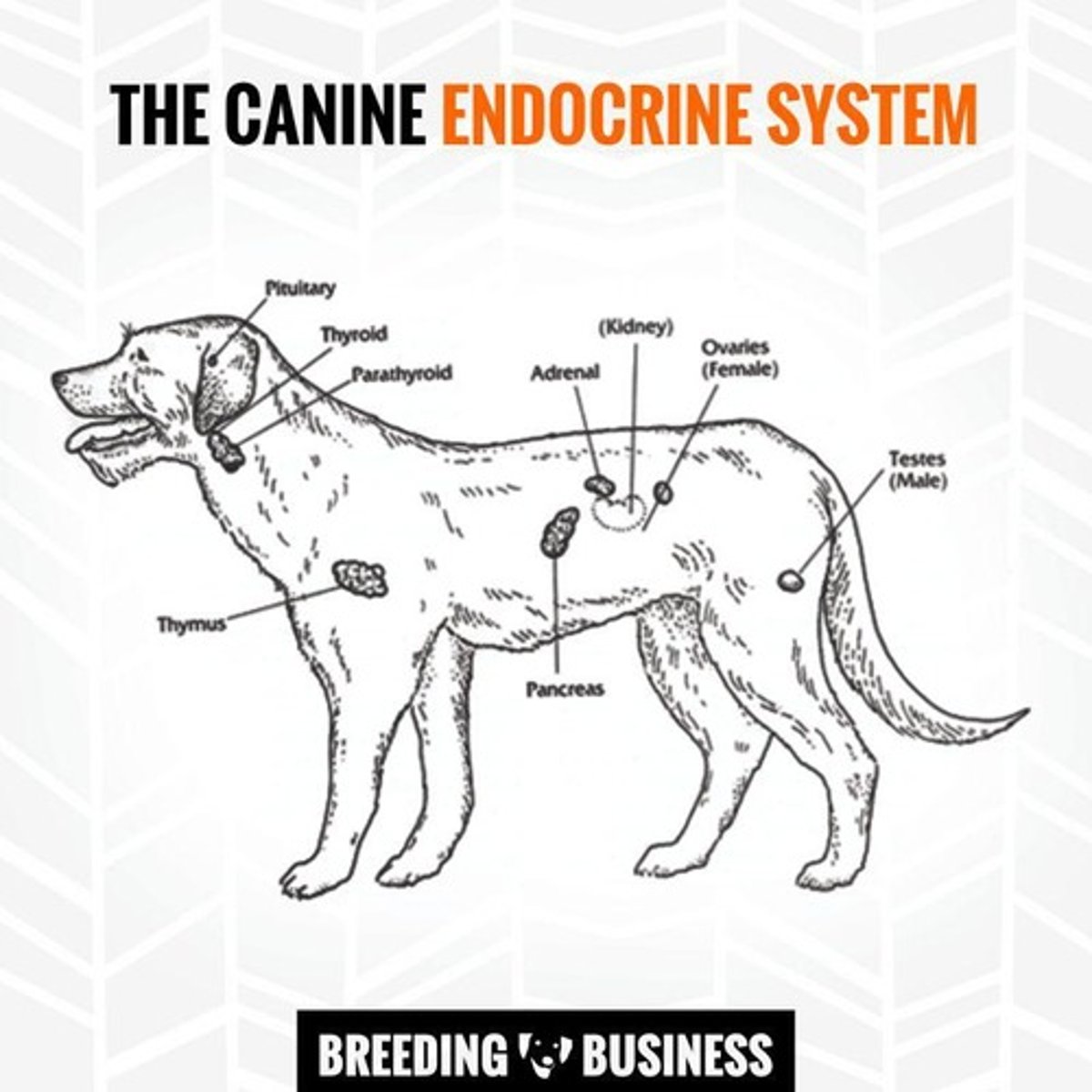
Endocrine System
The system that includes endocrine glands.
The Senses
Includes the sense of sight, hearing, and smell.
Cranial Portion
The part of the digestive system located in the head.
Abdominal Portion
The part of the digestive system located in the abdomen.
Accessory Glands
Glands that assist in the digestive process.
The Blood
The fluid that circulates in the cardiovascular system.
The Heart
The organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
Blood Vessels
The tubes through which blood flows in the cardiovascular system.
Circulation
The movement of blood through the heart and blood vessels.
Microscopic Anatomy
Involves the use of optical instruments in the study of tissues of various structures, known as histology, and also in the study of cells, known as cytology.
Cranial
Towards the head.
Caudal
Towards the tail.
Dorsal
Towards the back.
Ventral
Towards the abdomen or belly.
Medial
Towards the spine, or the central axis of the animal.
Lateral
Away from the spine or the central axis of the animal.
Proximal
Towards the trunk.
Distal
Away from the trunk.
Rostral
Towards the nose.
Palmar
Towards the palm, only used in the front paw.
Plantar
Towards the sole, only used in the hind paw.
Supine
An anatomical position where the body is lying face up.
Prone
An anatomical position where the body is lying face down.
Median Plane
Virtual plane dividing the body in two equal parts.
Paramedian Plane
Any plane parallel and located near to the median plane.
Sagittal Plane
Any plane parallel and located distal to the median plane.
Dorsal, Frontal or Horizontal Plane
Any plane parallel to the dorsal surface.
Transverse Plane
Any plane perpendicular to the long axis.
Nervous System (NS)
A very complex network consisting of Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Comprised of the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord; controls most bodily functions, both voluntary and involuntary.
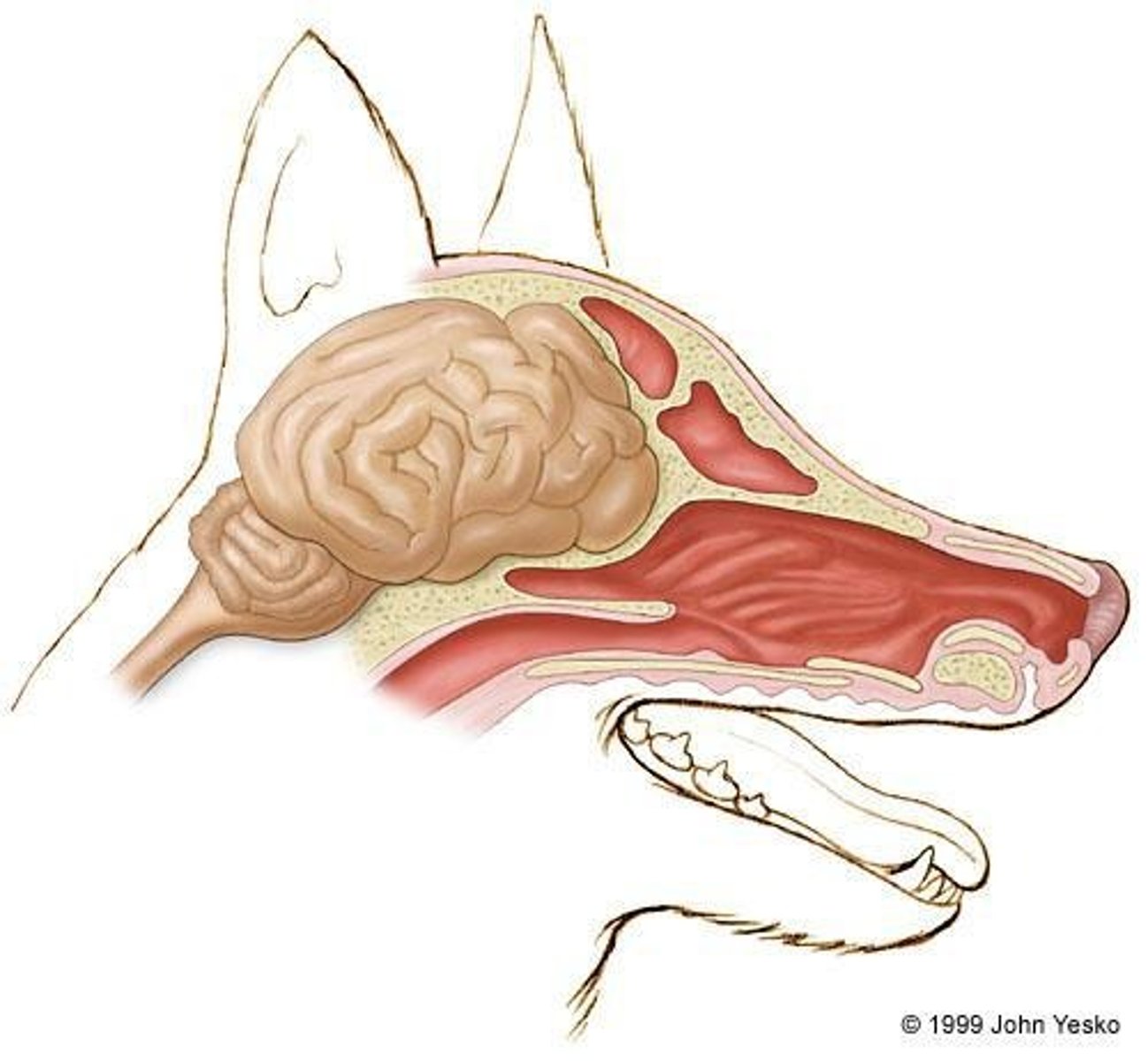
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Includes cranial nerves running from the brain to head and neck and spinal nerves exiting and entering the spinal cord.
Motor Nerves
Peripheral nerves that go from the brain or spinal cord, affecting muscles and carrying information such as pain sensation from the body structure back to the CNS.
Sensory Nerves
Peripheral nerves that return to the brain or spinal cord, carrying information such as pain sensation from the body structure to CNS.
Brain
The brain is where all of the conscious information is processed, and contains the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
Cerebrum
Where most of the voluntary movements and decisions occur, and also where the memory, the consciousness and the learning is saved.
Cerebellum
Responsible for movement coordination and equilibrium.
Brainstem
Controls most of the involuntary or autonomic responses, including eating, sleeping, breathing and the heart rate.
Grey Matter
The cortex (outside) of the cerebrum and cerebellum.
White Matter
The medulla (inside) of the cerebrum and cerebellum.
Spinal Cord
Transmits signals from the peripheral nerves of the body to the brain and communicates the response to the effector organs.
Vertebral Column
Protects the spinal cord and forms the spinal column along with ligaments and muscles.
Meninges
Protective layers surrounding the spinal cord.
Cervical Spinal Cord
Processes the reflexes of the superior limb and where most of the parasympathetic nerves originate.
Thoracic Spinal Cord
This segment is where most of the sympathetic tracts are originated.
Lumbar Spinal Cord
Where the lumbar intumescence is formed, and the nerves of the inferior limb originate.
Sacral Spinal Cord
Some of the parasympathetic nerves originate here.
Caudal Spinal Cord
The terminal filament that innervates the tail.
Reflex
An involuntary activity in an effector organ caused by the stimulation of a receptor organ.
Components of Reflexes
Receptors, sensory neurons, internuncial neurons, motor neurons, and effector organs.
Innate Reflex
A reflex that the animal was born with.
Conditioned Reflex
A reflex that is learnt through repetitive behaviour.
Withdrawal Reflex
An example of an innate reflex.
Myotatic Reflex
An example of an innate reflex.
Pavlov's Experiment
An example of a conditioned reflex.
Peripheral Nervous System
Consists of all the nerves and ganglia outside the brain and the spinal cord.
Somatic Nervous System
Carries stimuli and responses back and forth to the voluntary muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates involuntary body functions such as respiration, circulation, and digestion.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Controls the 'Fight or flight' responses in stressful situations where the animal needs to be alert and perform physical activity.
Origin of Sympathetic Nervous System
Thoracolumbar (all the way from the thoracic section of the spinal cord to the lumbar section).
Preganglionic Neurons in Sympathetic Nervous System
Short preganglionic neurons, as the ganglia are near the spinal cord or just beside it.
Postganglionic Neurons in Sympathetic Nervous System
Long postganglionic neurons.
Principal Neurotransmitter of Sympathetic Nervous System
Noradrenaline (NE), used in the postganglionic neurons, but it also uses acetylcholine (AcH) in its preganglionic neurons.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Controls the 'rest and digest' responses, where the animal is relaxed and/or processing food.
Origin of Parasympathetic Nervous System
Craniosacral (originates in the cranial section of the spinal cord, the sacral portion and the brainstem).
Constituents of Parasympathetic Nervous System
Mostly constituted by the cranial nerves 3, 7, 9 and 10 (being the 10th the most important), and the pelvic nerve.
Preganglionic Neurons in Parasympathetic Nervous System
Long preganglionic neurons.
Postganglionic Neurons in Parasympathetic Nervous System
Short postganglionic neurons, as the ganglia are located really near the effector organ.
Neurotransmitter of Parasympathetic Nervous System
Only neurotransmitter is acetylcholine (AcH), and its inhibition can be lethal.
Neurons
The basic, functional units by which the nervous system is constructed. They're elongated cells with a body and several extensions, that can receive the nervous impulse (dendrites) or transmit them (axons).
Classification of Neurons
The arrangement of extensions allows to classify the neurons as unipolar, bipolar or multipolar neurons.
Communication between Neurons
They communicate with each other through synapses (chemical contact between axon and dendrite).
Glial Cells
Maintain the neurons protected, nourished and gives them support.
Myelin
A substance formed by glial cells that insulates the axon from the extracellular fluid and speeds up the signal on the nerve fiber.
Pelvic Cavity
A direct continuation of the abdominal cavity, barely divided by the pelvic inlet, which is marked with the beginning of the sacrum bone, the top of the dog's hip.
Function of Body Cavities
Inside the cavities lie the organs, with fluid inside the small clefts between them, to allow the movement of the organs without much friction, essential for some organs to function properly.
Diaphragm
Separates the thoracic and abdominal cavity and communicates by 3 openings in it.
Esophageal Hiatus
Where the esophagus, its blood vessels and the vagus nerve pass.
Caval Foramen
Where the caudal vena cava passes.
Aortic Hiatus
Where the aorta and some other veins pass.
Pleural Cavity
The serous membranes within the thoracic cavity that cover the lungs forming two complete sacs, called pleural cavities, one on either side.
Pericardial Cavity
Formed by serous membranes that also cover the heart.
Abdominal Cavity
The abdominal cavity is upholstered by another serous membrane, with intern and extern layers.
Visceral Layer
The intern (or visceral) layer recovers the guts and some organs, and forms the peritoneal cavity.
Digestive System (DS)
The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of food into smaller portions, so that it can be utilised for energy, growth and cellular renewal.
Functions of the Digestive System
Breaks down complex food molecules to simple substances, serves as a protective barrier, contributes to immunologic defenses of the body, contributes to hydroelectric balance of the body, and serves as important blood storage in rest.
Differences in Dog's DS
The dog's DS is really similar to the human's DS, with a few differences, including teeth and the large intestine.