Chemistry - 3.1.11: Electrode Potentials and Electrochemical Cells
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What happens if you place two different metals in a salt solution and connect them together?
An electron current flows where the electrons pass from the more reactive metal to the less reactive
Why is a reference electrode needed whenever a standard electrode potential is measured?
Can only measure emf if a reference electrode is present
Standard electrode potential
The emf of a half cell compared to a standard hydrogen electrode - solutions at 1 moldm-3 concentration, gases at 100 kPa, temperature at 298 K
In what direction do electrons flow?
From the most reactive metal to the least reactive - from the more negative to the more positive
What happens when a rod of metal is dipped into a solution of its own ions? Write an equation for this.
An equilibrium is set up, e.g.:
Zn (s) ⇌ Zn2+ (aq) + 2e-
Electrode
An arrangement where a rod of metal is dipped into a solution of its own ions
Why is a salt bridge used in electrodes instead of a piece of wire?
Wires can only transfer electrons, while salt bridges can transfer ions
Draw an electrode
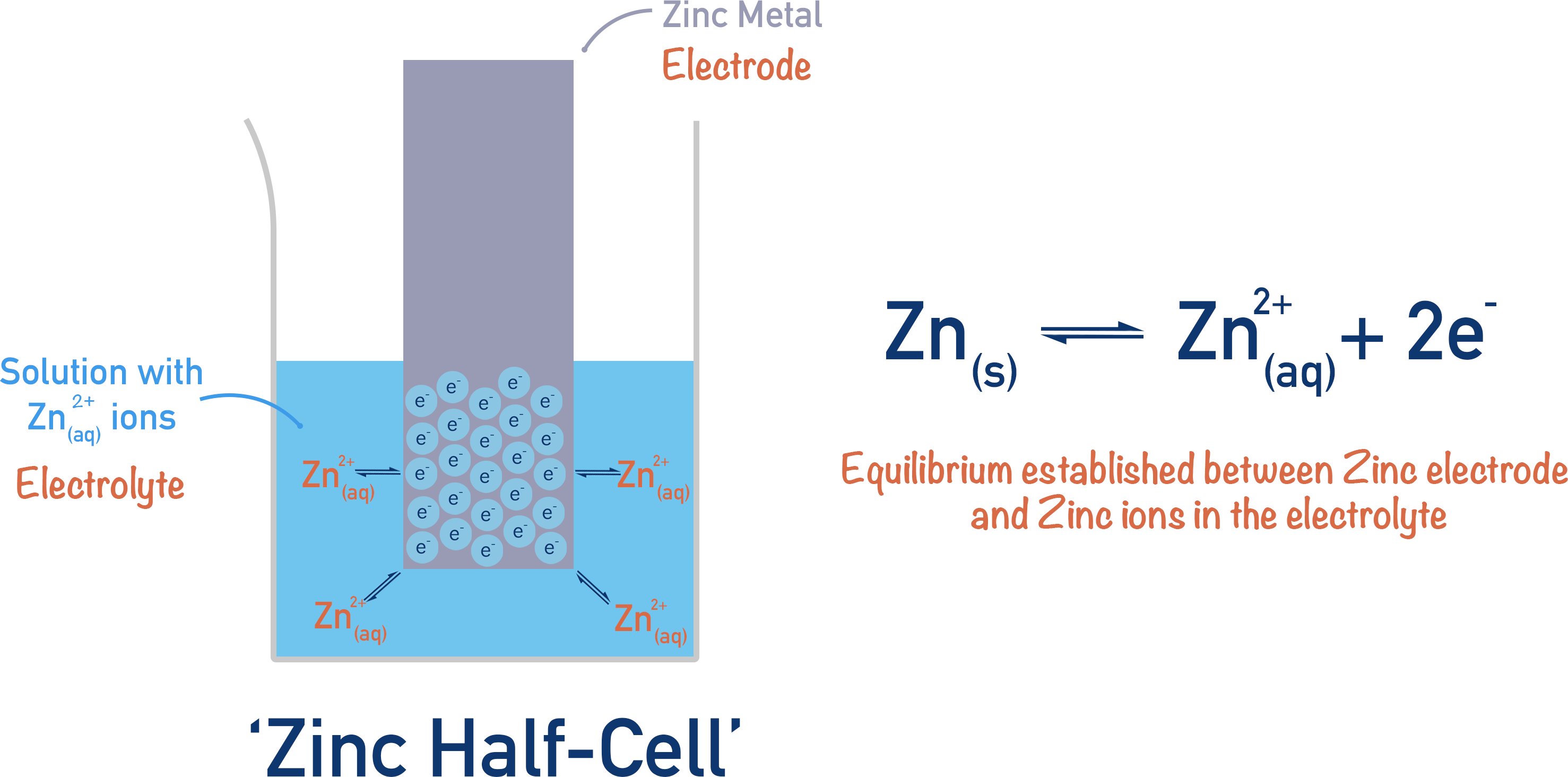
Draw two electrodes connected together to measure the potential difference.
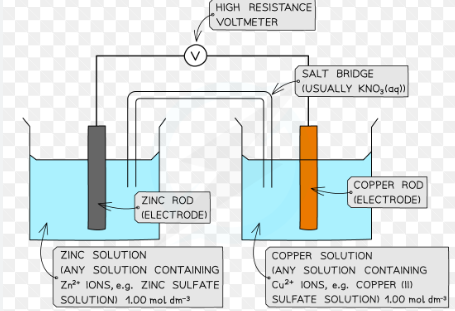
Why is a standard electrode needed?
To compare the tendency of different metals to release electrons - other half cells can be connected to it for comparison
Why is Pt used as the electrode for half cells with no solids? (2)
It is a conductor of electricity
It is unreactive
Describe the standard hydrogen electrode and its conditions (4)
Hydrogen gas is bubbled in
1.00 mol dm-3 solution of H+ ions
Platinum metal and wire used
298 K, 100 kPa
What is the potential of the standard hydrogen electrode?
0
The electromotive force
The potential of a cell connected to the standard hydrogen electrode
How do you represent the electromotive force?
E
EƟ
Standard electrode potential - the potential of the second cell at standard conditions
What does it mean if EƟ is negative?
The electrodes are better at releasing electrons (i.e. better reducing agents) than hydrogen
How can you change the electrical potential of an electrode?
By changing the conditions e.g. the concentration of ions, the temperature or the pressure
Do the number of electrons involved in a reaction affect EƟ?
No
How do you find the potential difference obtained by connecting two standard electrodes together?
By finding the difference between the two EƟ values
In a conventional cell diagram, how do you represent the phase boundary?
A vertical solid line
In a conventional cell diagram, how do you represent the salt bridge?
A double vertical solid line
In a conventional cell diagram, where is the species with the highest oxidation state written?
Next to the salt bridge
6 Features of a conventional cell diagram
ROOR
Reduced species on right, oxidised species on left
| to separate species in different states
, to separate species in the same state
|| to represent a salt bridge
Pt (s) electrode if species is not in the solid state
How can you tell the direction of a redox reaction from standard electrode potentials?
From the signs of the electrodes - electrons flow from the more negative (reducing agent / oxidised one) to the more positive (oxidising agent / reduced one)
Battery
A number of cells connected together
3 types of cells
Non-rechargeable, rechargeable or fuel cells
What is a risk associated with the use of non-rechargeable cells?
Electrolytes used may be acidic so corrosive - batteries must be disposed of properly
How are rechargeable batteries recharged?
By applying an external voltage greater than the voltage of the cell to drive the electrons in the opposite direction, reversing the cell reactions
What reaction takes place at the positive electrode of a lithium cell?
Li+ + CoO2 + e- → LiCoO2
What type of cell is a lithium cell?
Rechargeable, portable
What are the benefits associated with the use of lithium in lithium ion cells? (3)
Light as lithium is the least dense metal
Solid polymer electrolyte so cannot leak
Charge can be topped up at any time (doesn’t have to be fully discharged to recharge efficiently)
What are the electrodes made out of in lithium cells?
Positive: Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2)
Negative: Carbon
What reaction takes place at the negative electrode of a lithium cell?
Li → Li+ + e-
What overall reaction takes place in an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
What reaction takes place at the negative electrode of an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
2H2 (g) + 4OH- (aq) → 4H2O (l) + 4e-
What reaction takes place at the positive electrode of an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
O2 (g) +2H2O (l) + 4e- → 4OH- (aq)
What electrolyte is used in an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
NaOH solution
What metal is used for the electrodes in an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
A porous platinum-based material
In an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, how are the electrodes separated?
By a semi-permeable membrane
What are the benefits associated with the use of alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells? (3)
The only by-product is water, so can be used as drinking water by astronauts
It doesn’t produce carbon dioxide, so doesn’t contribute to global warming
Hydrogen and oxygen are supplied continuously - can be operated without stopping to recharge
What are the costs associated with the use of alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells? (4)
Hydrogen may be obtained from crude oil - a non-renewable resource
Hydrogen filling stations would have to be built so hydrogen-powered vehicles can be used
Hydrogen gas is highly flammable so would be difficult to store and transport
Hydrogen gas takes up a large volume, so would be difficult to be stored
How do you calculate the Emf of a cell?
E(reduced) - E(oxidised) = E(right) - E(left)
Why is the electrode potential for the standard hydrogen electrode equal to 0.00V?
By definition
Why do hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells operating in acidic and alkaline conditions have the same emf?
The overall reaction is the same
Why might the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell not be considered carbon neutral?
Hydrogen may be being made by an energy source that is not ‘carbon neutral’ (e.g. fossil fuels)
When drawing a conventional cell diagram, where must the standard hydrogen electrode always be?
On the left
Why might the actual EMF of a cell be different from the EMF calculated using standard electrode potentials?
The cell might not be under standard conditions
Electrochemical series
A list of electrode potentials in order OR a list of half cells in order of electrode potential
How do you set up electrodes to measure the electrode potential of a cell? (3)
Immerse strip of metal in the solution
Connect the solutions with a salt bridge
Use a voltmeter to measure the emf of the cell
Why is a salt bridge needed in cells?
To complete the circuit by allowing ions to flow
How might you change a circuit used to measure the emf of a cell so that the cell reaction will go to completion?
Replace the voltmeter with a lamp / wire / ammeter
Why would the EMF of a cell decrease to 0?
The concentration of ions in the two solutions become equal
What is an advantage of using a fuel cell instead of an internal combustion engine?
Internal combustion energy wastes more energy / fuel cell converts more of the available energy from combustion of hydrogen into kinetic energy of the car
Conventional representation for an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell
Pt (s) | H2 (g) | OH- (aq), H2O (l) || O2 (g) | H2O (l), OH- (aq) | Pt (s)
What type of reaction takes place at the positive electrode?
Reduction
What type of reaction takes place at the negative electrode?
Oxidation
Why might a salt solution not be suitable for the salt bridge?
One of the ions of the salt would react with the ions of the electrodes
Why are Pt / C rods used in cells without solid reactants?
To allow electrons to flow / to provide a reaction surface
Why might a cell not be rechargeable?
The reaction is not reversible
What happens to the EMF of a cell if the position of equilibrium shifts to the left?
EMF becomes less positive
What happens to the EMF of a cell if the position of equilibrium shifts to the right?
EMF becomes more positive