Week 8: IP security
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What is a hop?
The journey a data packet takes from one router or network device to another, from the source to a destination
Why do we have no global domain of trust?
Because different subnets might or might not be trustworthy
How can we secure communications with no global domain of trust?
Secure applications over insecure channels
Pretty Good Privacy to encrypt and sign emails
Solutions involved protocols like SSH, TLS, IPsec
Why do we need security protocols in the Transport and Internet layer?
There is no authentication or confidentiality of information + integrity, so addresses can be spoofed and payloads can be read/modified
How can we secure internet connections?
End-to-end security (application layer)
SSL/TLS (between application and transport layers)
IPsec (between transport and internet layers)
How can we have end-to-end security in the application layer?
At the app layer, user-specific data like usernames, roles, perms, etc... are used to make security decisions
What are the advantages of end-to-end security (at the application layer)?
No assumptions needed about security of underlying protocols used, router, etc
Security decisions are based on user-ID, data, etc - individual basis
What are the disadvantages of end-to-end security (at the application layer)?
Applications must be designed to be "security aware"
What is SSL/TLS?
Secure Sockets Layers: A layer of security wrapped around a user's communications to prevent snooping or tampering
Transport Layer Security: Successor to SSL
What are the advantages of security between the application layer and transport layer?
No modifications are needed to the OS, and minimal changes to applications are made
What are the disadvantages of security between the application layer and transport layer?
Vulnerabilities when interacting with TCP, so this makes for an easy DoS attack
How can a DoS attack occur in SSL/TLS?
If an attacker sends data violating SSL security rules, then SSL rejects it and drops the connection, but TCP may still accept it - SSL will close the connection and cause the server to drop all packets
What is IPsec?
IP security - A suite of protocols for security at the IP layer
What does IPsec provide?
Provides Authentication, Confidentiality, and Key Management.
How does IPsec provide authentication?
Assures a received packet was transmitted by the source in the packet header, and that the packet was not altered in transit
How does IPsec provide confidentiality?
Enables communicating nodes to encrypt messages, prevents eavesdropping by third nodes
How does IPsec provide key management?
Secures exchange and distribution of keys needed for cryptographic algorithms
What does IPsec extend security to?
Works for both security-aware and security-ignorant apps
Where can IPsec be located at?
Can be in OS (end-to-end) or gateways (VPNs)
What are the applications of IPsec?
Securing distributing applications, like remote logon, client/server email, file transfer, web access, etc...
What are the advantages of IPsec?
Provides transport layer security without needing to modify applications -Transparent to end-users
Organisations can ensure secure networking for both security-aware and security-ignorant applications
Can secure individual users if needed
What are the disadvantages of IPsec?
It only authenticates devices/connections and not individual users
It has more potential, but requires changing the TCP API and applications
How does packet filtering with IPsec work?
IPsec maintains a policy database, when the packet arrives at the device this DB is checked in order to control whether the packet is allowed
Encryption policies are enforced to protect the data in transit
What does it mean when IPsec is transparent to end-users?
Applications are unchanged to end-users, so they do not need to be trained on security mechanisms
Manual key management is not needed on a per user basis
What is the IPsec standard?
Covers authentication headers, encapsulating security payload and internet key exchange protocol
What is an Authentication Header (AH)?
IPsec protocol that authenticates the entire IP packet, including the outer header
What is a Message Authentication Code (MAC)?
Proving the integrity and authenticity of a message by combining its hash with a shared secret.
What parts of the CIA triad do AHs cover?
Authenticity
What is a security association (SA)?
A one-way relationship between sender/receiver.
Defines security services for communication (algos, keys, modes).
What does an AH provide for the destination?
Enough info to identify SA between sender and receiver
How does an AH provide an anti-replay service?
Protects against attackers retransmitting old, valid packets by using a sequence number and a receiver sliding window to detect and discard replayed packets
How does the anti-replay service work in IPsec on the sender's side?
Set the sequence number to 0
Every time a packet is sent, increase the counter by 1 and place the value in the sequence number field
If the counter reaches 2^32 - 1, terminate the SA and negotiate a new SA with a new key
What is the Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)?
IPsec protocol for Confidentiality (encryption), protects the actual packet data
How does the anti-replay service work in IPsec on the receiver's side?
Implement a window of size W, ending at sequence number N
Mark the packet in the window, depending on the received packet sequence number
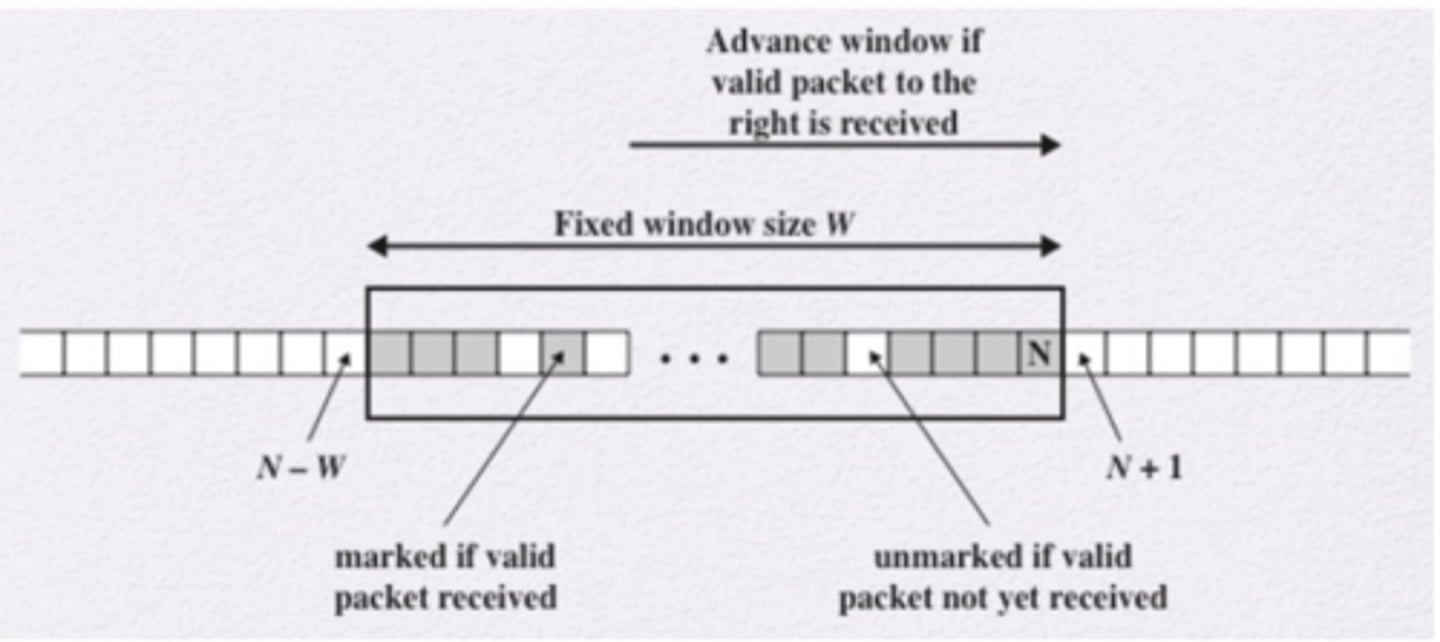
What happens in the anti-replay service if the received packet sequence falls within the window?
If the number is fresh, then we check the MAC for integrity
If the packet is authenticated, mark the corresponding slot
What happens in the anti-replay service if the received packet sequence is to the right of the window?
If authentication is successful, we mark the packet as valid and then the window shifts to the right by one space
What happens in the anti-replay service if the received packet sequence is to the left of the window, or authentication via MAC fails?
Discard the packet and audit the event
What does ESP provide as optional services?
Optionally provides authentication, integrity, anti-replay.
What does ESP authentication cover?
ESP authentication covers only the IP datagram portion, not the outer header
What are the steps of using ESP protection in IPsec?
When an IP packet is sent, it is checked against the SPD to find an SA
Based on the security settings in the SAD, source and destination exchange keys for secure comms
ESP encrypts the data for transit
What is an SA uniquely identified by?
SPI, Destination IP, and Protocol (AH or ESP)
What is a Security Association Database (SAD)?
Database that stores information about the SAs to ensure the communication uses the right key and encryption method
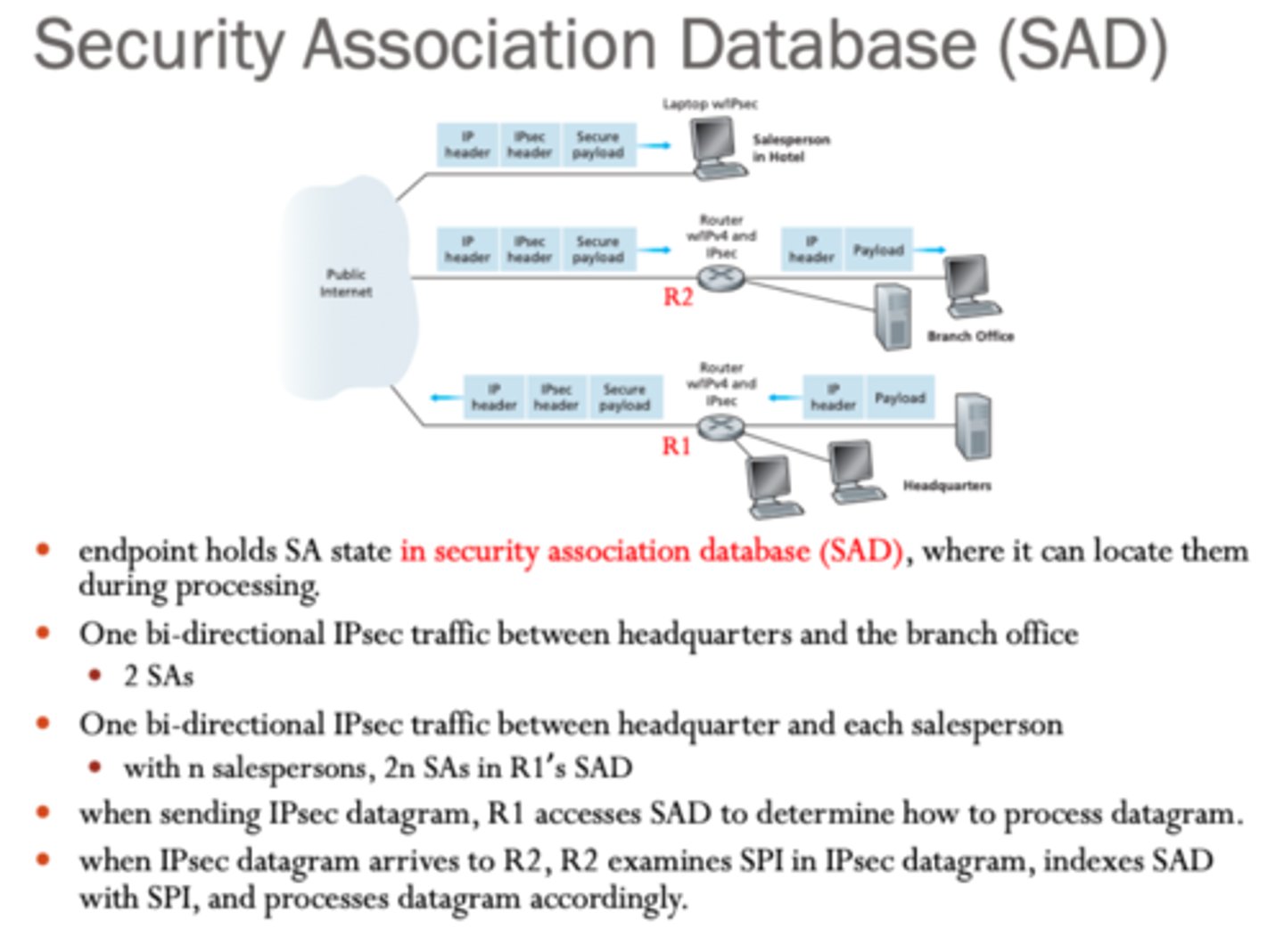
What is a Security Policy Database (SPD)?
Database that relates IP traffic to SAs or indicates bypass/discard

If an IP traffic has no SA related to it in the SPD, what does that mean?
That traffic is allowed to bypass IPsec
What does a SPD use to filter traffic?
Uses selectors (IP/protocol fields)
What is the typical mapping of an IP traffic to SAs?
In complex environments, this is many to many
There could be multiple entries relating to a single SA, or multiple SAs related to a single entry
What actions does an SPD determine?
Determines DISCARD, BYPASS, or PROTECT actions
How does key exchange occur in IPsec?
Happens through protocols like IKE, ensures that both nodes share a secret that is used to encrypt and decrypt packets securely
How is IPsec executed?
On a packet-by-packet basis
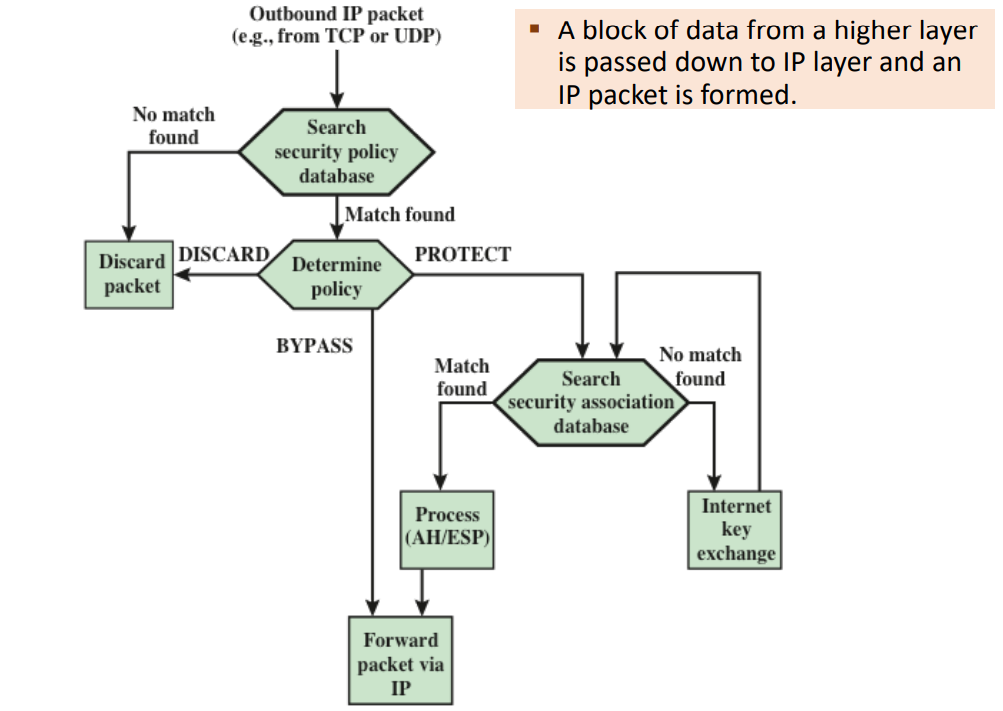
What are the steps of processing outbound IP traffic in IPsec?
Packet generated -> Check SPD.
No match: Discard
Match found:
DISCARD: Discard packet
BYPASS: No IPsec processing.
PROTECT: Check SAD for SA.
No SA: Use IKE to create one.
SA found: Apply security per SA (encrypt/auth, mode).
Processed packet sent
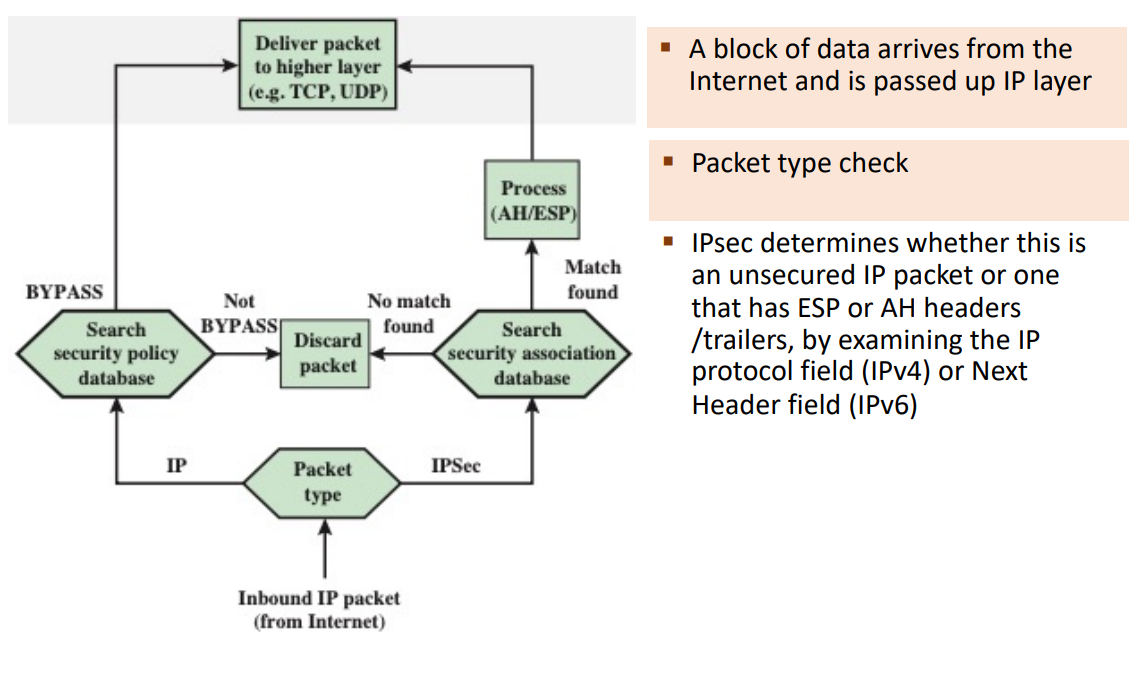
What are the steps of processing inbound IP traffic in IPsec?
Packet arrives -> Check if Secured (AH/ESP) or Unsecured.
Unsecured: Check SPD.
Match is BYPASS: Allow.
Match is PROTECT/DISCARD
or no match: Discard.
Secured (AH/ESP): Check SAD for SA.
No SA: Discard.
SA found: Apply AH/ESP processing (decrypt/auth), deliver payload
What is the distinction between being authenticated and being encrypted?
Authenticated = Integrity (verify content hasn't changed)
Encrypted = Confidentiality (hide content from eavesdroppers)
What is the AH transport mode?
AH header placed between original IP and payload for end-to-end authentication/integrity
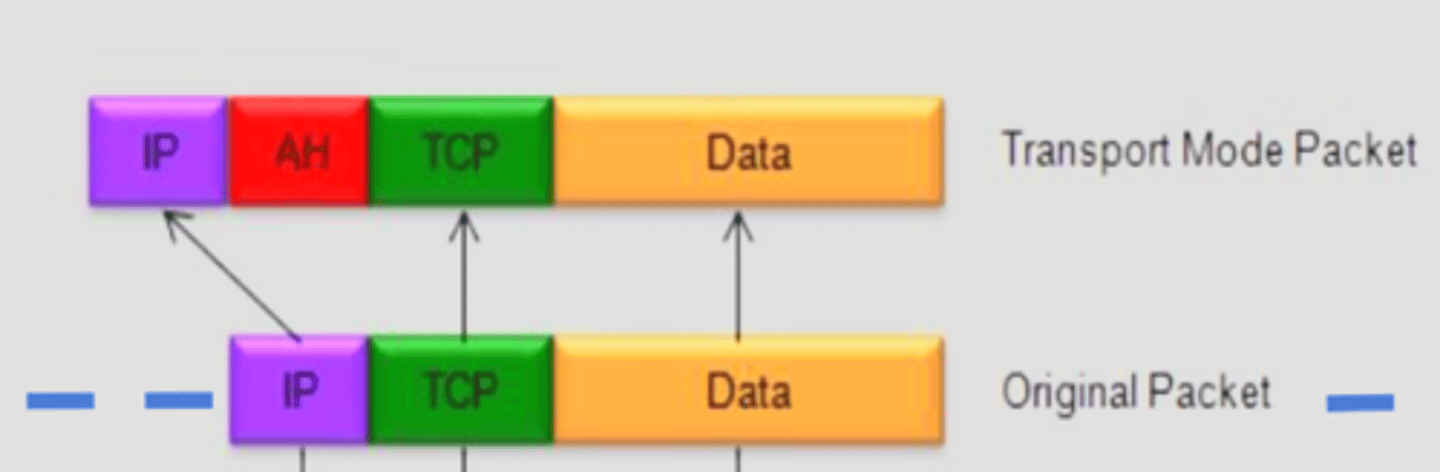
What does the AH transport mode authenticate?
Authenticates the entire packet (except mutable fields)
Where is the AH header located in AH transport mode?
After the IP header and before the payload
What is AH tunnel mode?
Authenticates the entire original IP packet and adds new outer IP header
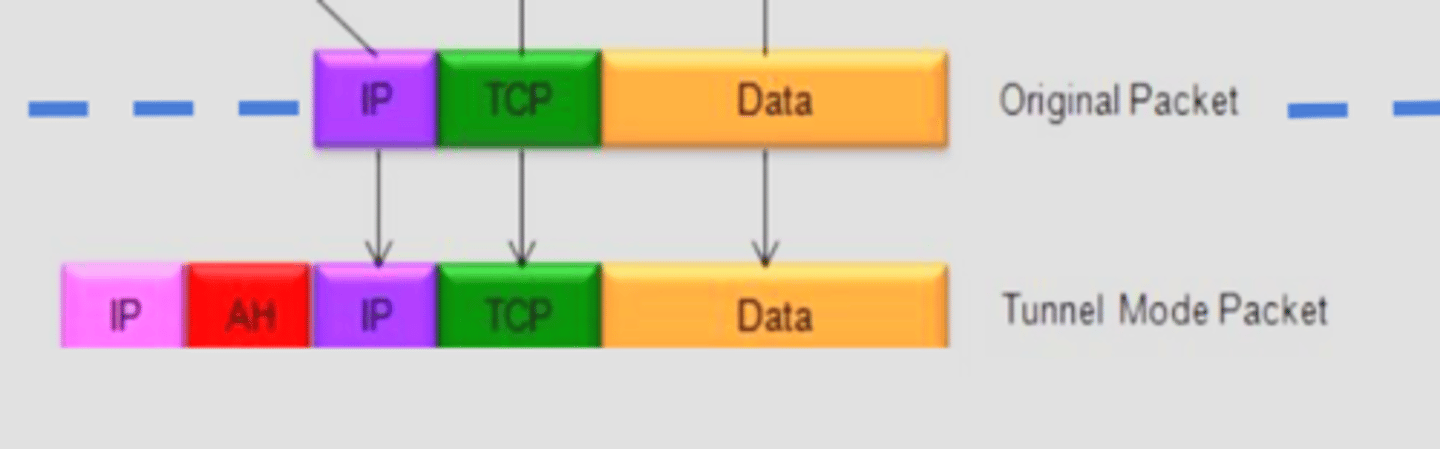
Why is AH tunnel mode used?
So that attackers cannot see the real communication endpoints, and only the secure tunnel endpoints are visible
Where is the AH header located in AH tunnel mode?
Between the new outer IP and the original packet
Where is AH tunnel mode used?
Used between gateways or end-station to gateway
What is the ESP transport mode?
Encrypts only the payload (transport segment + ESP trailer), and not the original IP header
Uses a transport mode SA
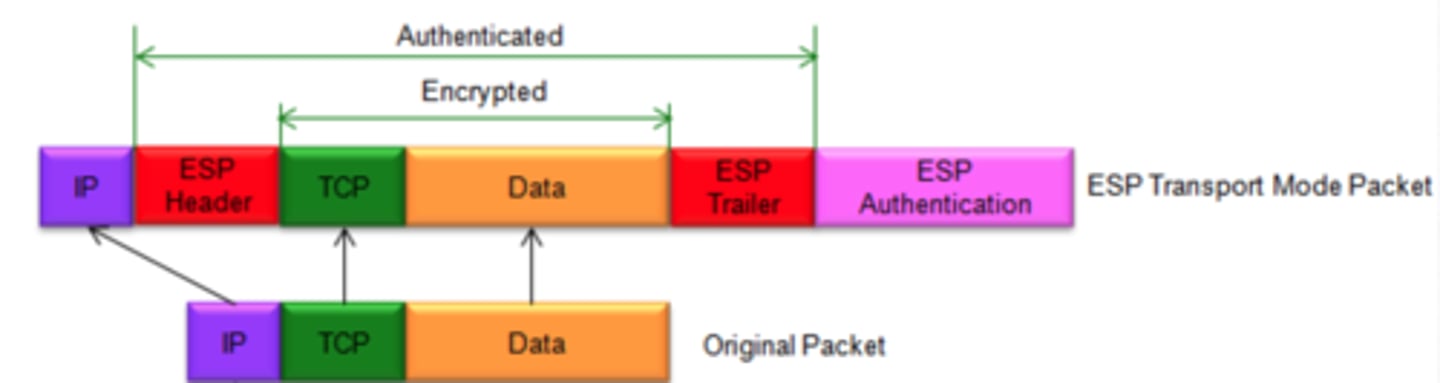
Can the use of an Authentication Header (AH) be considered the same as just using the ESP transport mode?
No - AH is authentication ONLY, but ESP is encryption AND optional authentication
AH authenticates the whole packet including outer header, but ESP authentication covers only the payload portion
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 packet structure?
IPv6 has extra headers for hop-by-hop, routing and fragment extensions before the payload
What is the IPv4 packet structure after applying ESP transport mode?
The ESP header is placed before the payload, and the ESP trailer + authentication (if selected) is placed after the payload
What is the IPv6 packet structure after applying ESP transport mode?
The ESP header is placed before the payload and after the extension headers, the ESP trailer (+ optional authentication) is placed after the payload
What does encryption cover in ESP?
The entire payload + the ESP trailer (+ the destination options header in IPv6)
What does authentication cover in ESP?
The entire ciphertext + the ESP header
How does routing work in ESP transport mode?
Intermediate routers examine and process the original IP header (and any plaintext IP extension headers in IPv6) but do not need to examine the ciphertext
How does the destination process the packet in ESP transport mode?
The destination node examines the IP header and uses the SPI in the ESP header to decrypt the remainder of the packet to recover the plaintext transport-layer segment
What is the benefit of using ESP in transport mode?
Provides confidentiality for any application that uses it, avoiding the need for application-specific confidentiality
What is the downfall of using ESP in transport mode?
We can still perform traffic analysis based on the ultimate destination address because the original IP header is not encrypted
What is the ESP tunnel mode?
Encrypts the entire original IP packet and adds a new outer IP header for routing
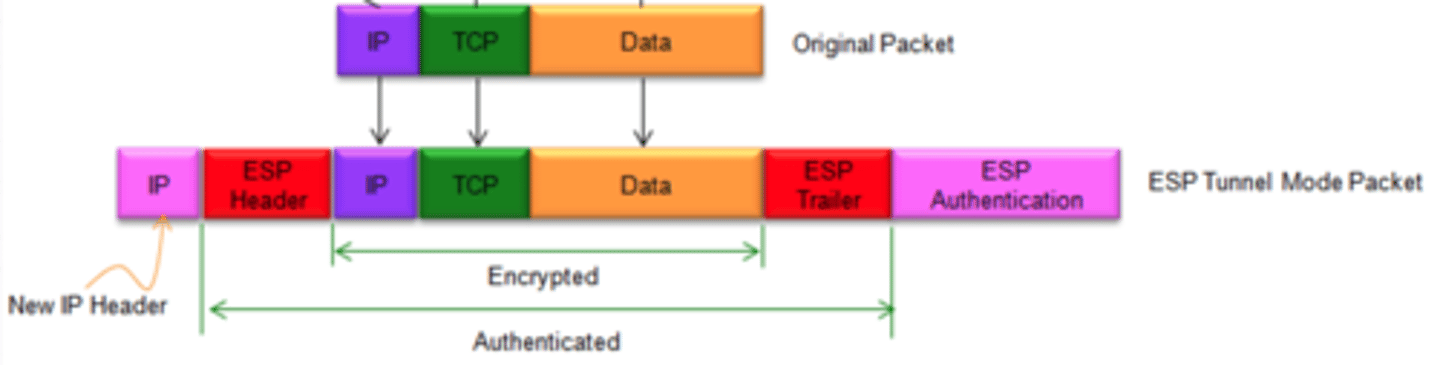
Why is a new IP header needed in an ESP tunnel mode packet?
Because the original IP header was encrypted, so we need to make a new header with sufficient information for routing whilst preventing traffic analysis
What are the benefits of using ESP in tunnel mode?
Prevents traffic analysis based on ultimate destination
Encryption only occurs between external host and security gateways/two security gateways, so the burden of processing encryption is lifted off of internal hosts
Less keys are needed, so it simplifies key distribution
What is Internet Key Exchange (IKE)?
Protocol used by IPSec to create keys for encryption and negotiate an SA
What SAs do IKE establish?
The protocol format used
Cryptographic and hashing algorithm used
The keys
What is phase 1 of IKE?
Phase 1: Parties negotiate an SA to agree on keying material and mechanisms
What is phase 2 of IKE?
Phase 2: the negotiated SA is used to create child SAs, used to encrypt and authenticate further communications
What are the benefits of IKE?
Flexible, e.g. it supports authentication based on pre-shared secrets
What are the downfalls of IKE?
It is complex - has many options and alternative subprotocols
What is a master key?
A pre-shared secret symmetric key
What types of keys can a master key be?
Public encryption key or public signature key for signing and signature verifications