12 UT2 Kidneys and incontinence
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Be able to discuss the surgical anatomy of the kidneys and when/how to perform a nephrectomy • Be able to discuss how to work up an incontinent dog to achieve a diagnosis of USMI vs ectopic ureters • Be able to discuss the surgical treatment options for USMI, understand the limitations of each option and understand how to manage a patient with this condition • Understand the difference in management options for USMI between female and male dogs and feline patients
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
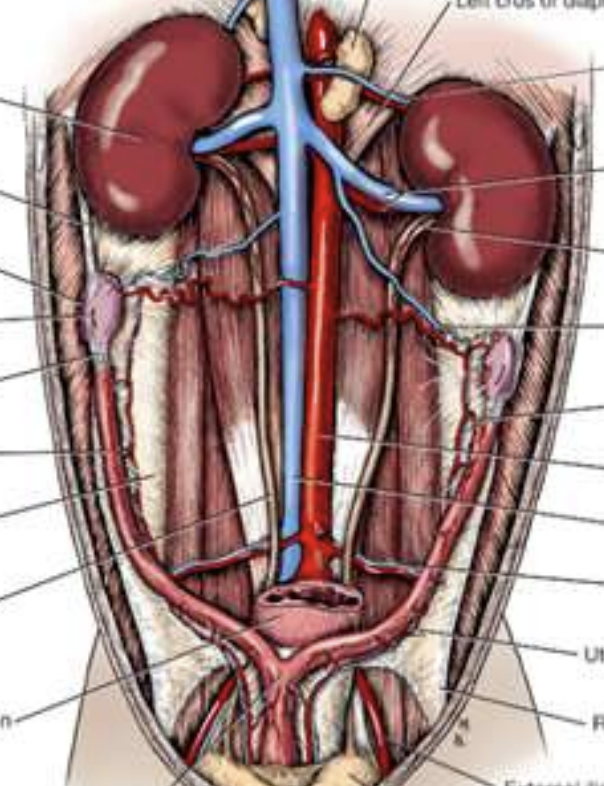
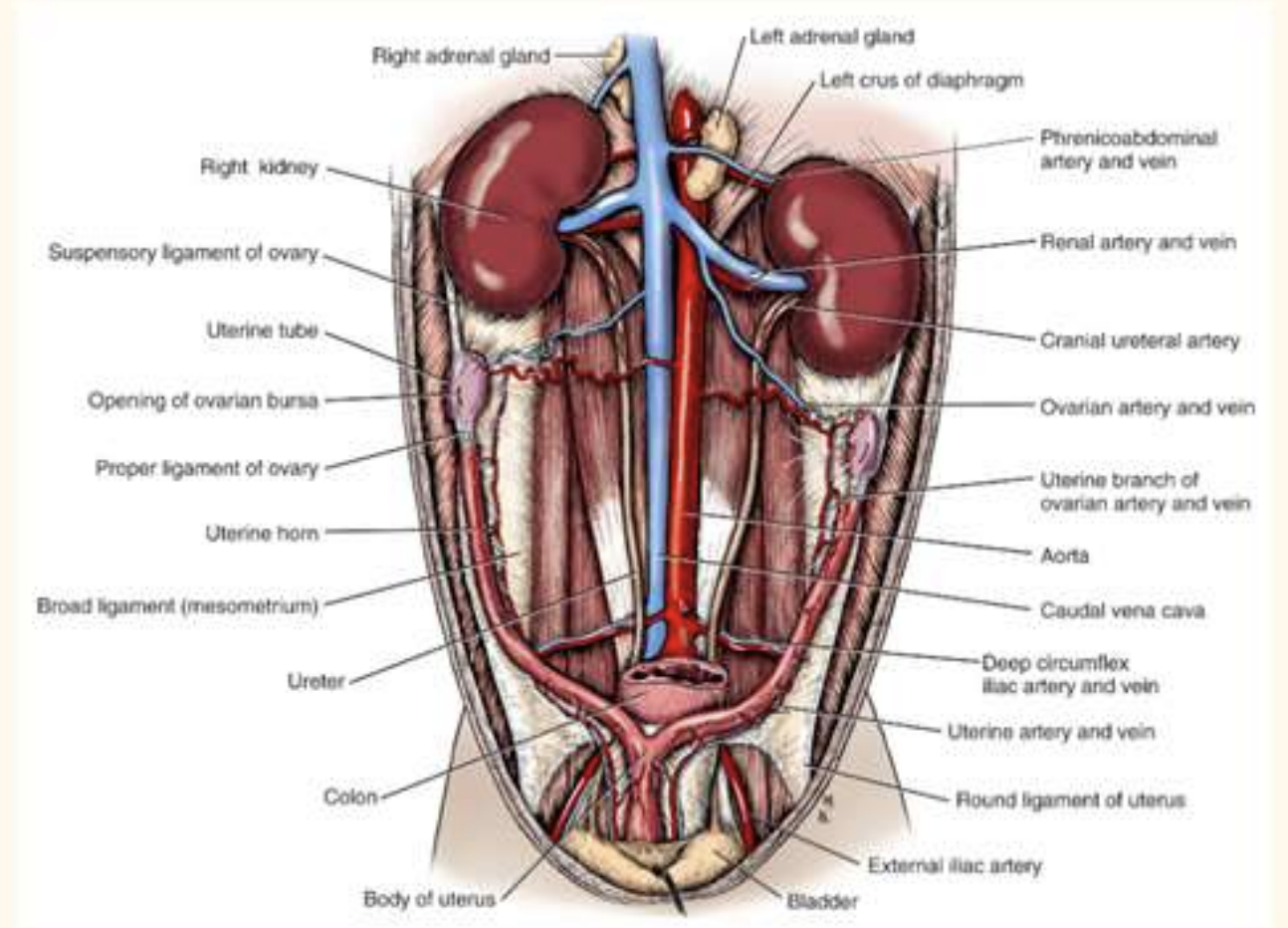
surgical anatomy of kidney
R kidney more cranial to L
ureter from kidney to urinary bladdder, hook, enter trigone region
one more renal artery/vein for each kidney
left ovarian gonard artery comes off renal artery
Uretero-nephrectomy indications
Unilateral renal disease • Neoplasia • Irreparable trauma • Persistent pyelonephritis – e.g. associated with nephroliths
Hydronephrosis
Ureteral abnormalities – Obstructive calculi
nephtolithiasis (uncommon)
usually medical meange or leave unless causing problem
Nephrolithiasis prevalence
• 5 to 10% of all uroliths •
Generally incidental
May be amenable to dissolution• Treatment options:
Nephrolithiasis tx
most common
– Shock wave lithotripsy (refer to RVC)
Nephrotomy ( if clinical sign)
Uretero-nephrectomy
ususllly end stage and non functional kidney
Severely hydronephrotic
Persistent infection
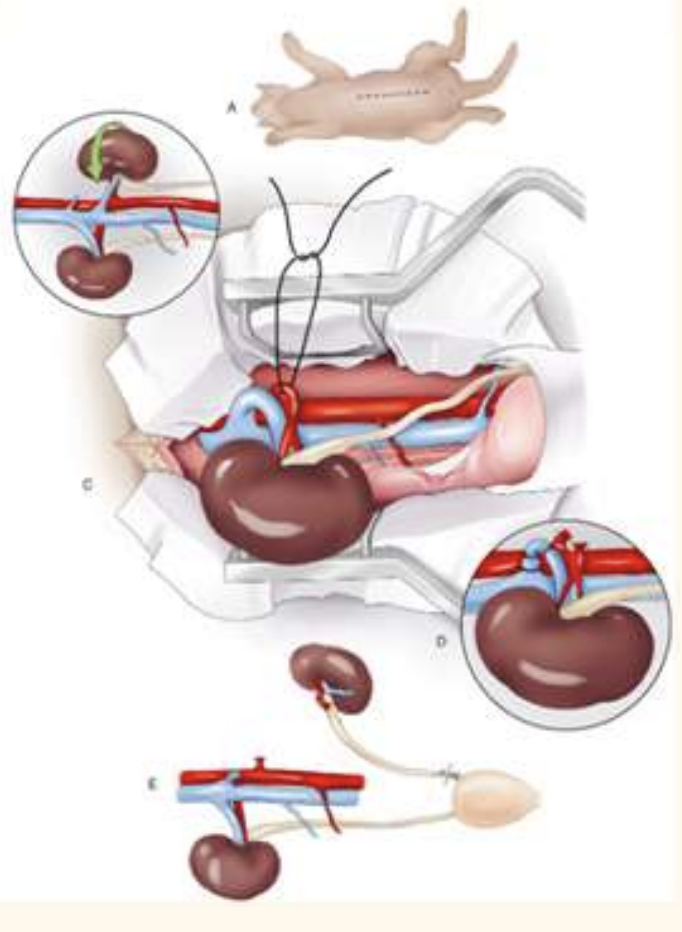
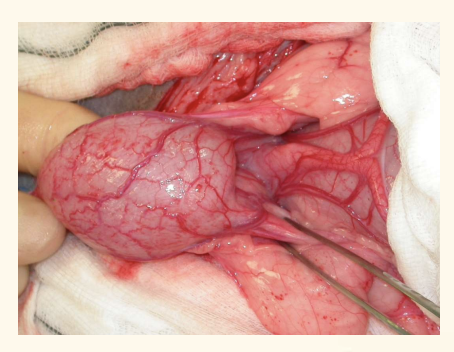
Uretero-nephrectomy
ventrla midline approach
identify kidney with duodenal/ colonic nerves
kidney sit in fatty pounch (retoperitoneal flat)—> blunt dissect kidney w digit
identify arterys and veins. —> thicker is artery, ;
circumfrential/ transfixing suture to ligate ligate a first (prevent engorgement)
remember to place ligature on each side and resect in between
elevate kidney, dry swap all the way down ureter down bladder
suture x2, resection as close to bladder as possible
Urinary incontinence ddx
• Congenital abnormalities
Ectopic ureter
Congenital urethral sphincter incontinence
Urethral sphincter mechanism incompetence (USMI)
Inflammation
Neurogenic abnormalities
Behavioural problems
Ectopic ureter
prevalence: sex
breed
Congenital, incontinent since birth. Occasional adult-onset
Females > males
Retrievers, Poodles, Huskies
Ectopic ureter - 2 types
can empty into urethra, vagina or uterus. can be unilateral or bilateral.
extramural : completely bypass bladder
intramural: enter bladder at region of trigone but not into luman. carryon submucosally and enter into urethra
Ectopic ureter - presentation 4
Continual dribbling of urine
Urine scald
Unilateral: can pass stream of urine: bilateral may have no bladder filling
Ectopic ureter • Associated urogenital abnormalities:
Urethral sphincter incompetence
Congenital renal abnormalities (esp retriever)
Bladder hypoplasia
UTI + pyelonephritis
Hydroureter
ureter peristaltic rate
one a minute
Ectopic ureter - diagnosis
Evaluate renal function – CBC/chem, urinalysis
Evaluate for UTI – urine C&S
CT excretory urography – most sensitive method
Contrast radiography – IV urogram with pneumocystogram
Cystoscopy (fancy)
Ultrasonography
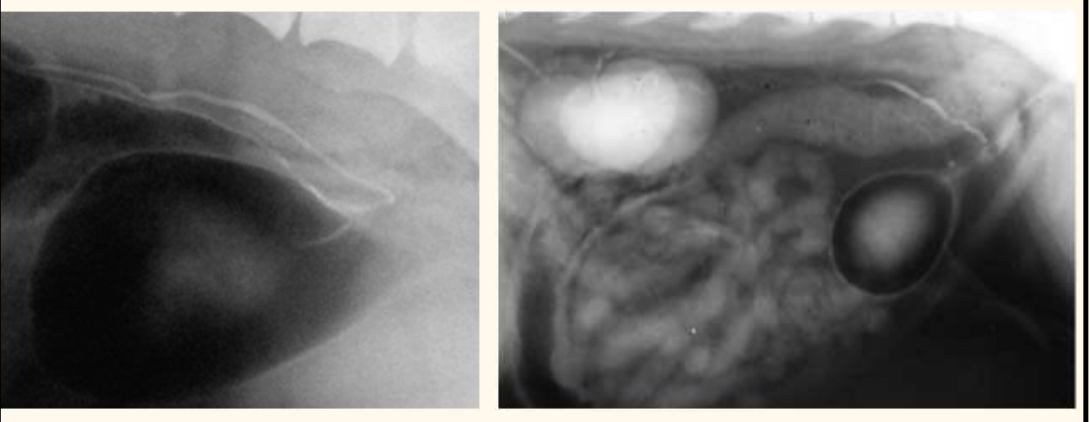
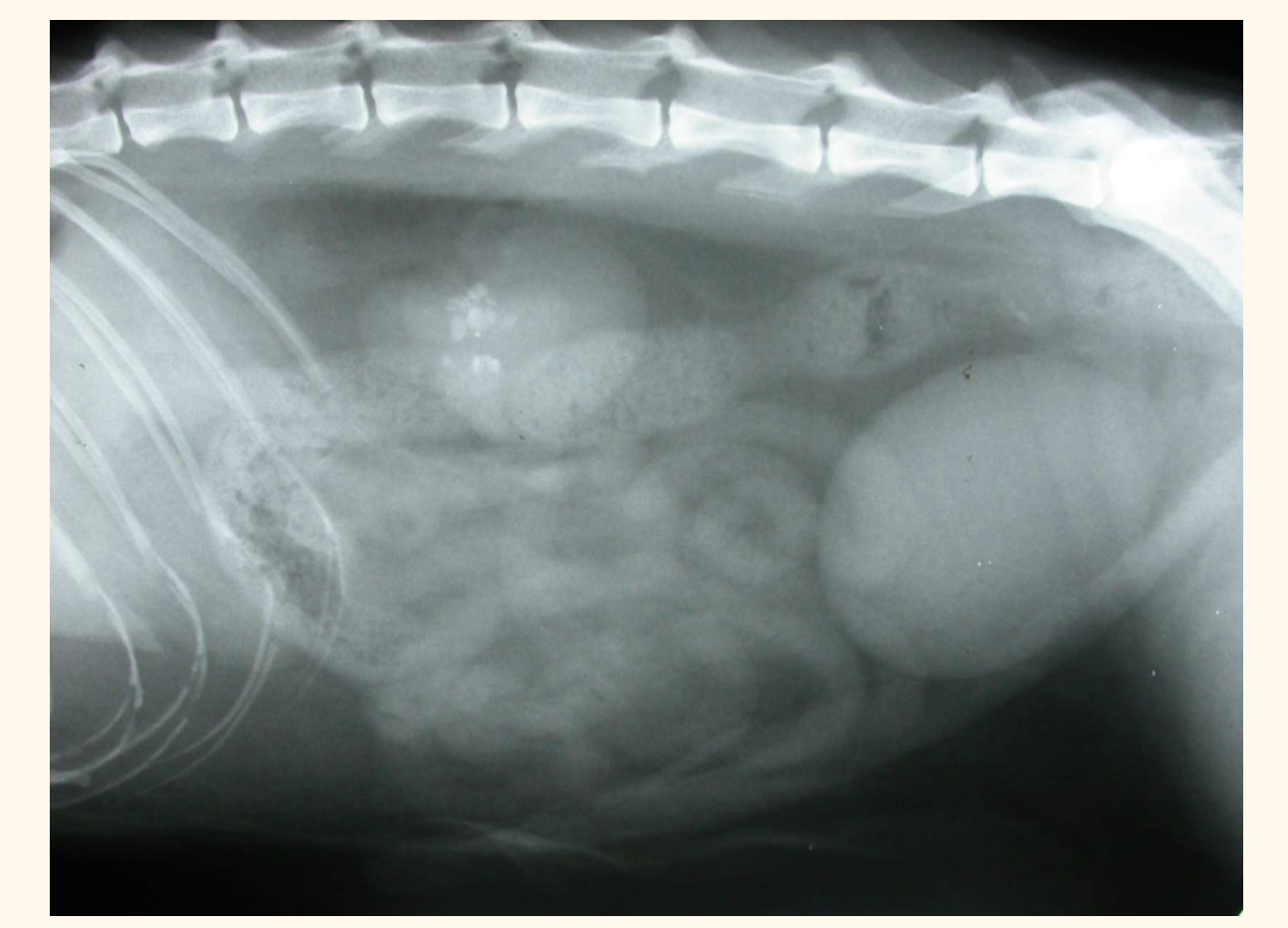
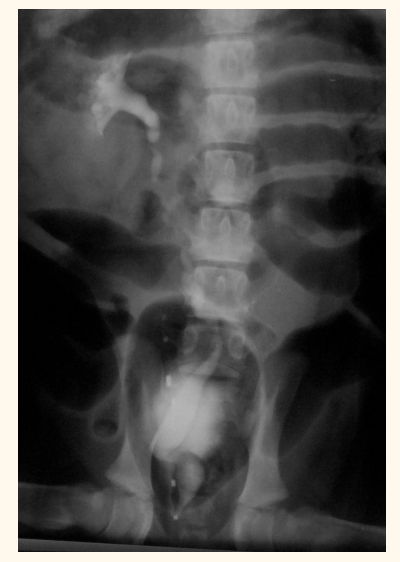
contrast radiography. what does this px have
air -ve contrast
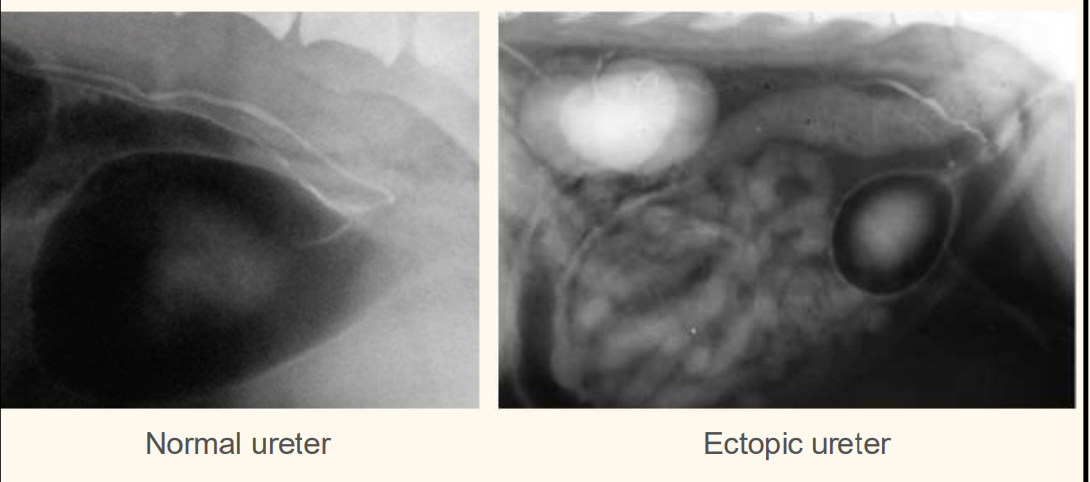
whats wrong with this patient
ectopic ureter— hydroureter
ectopic ureter treatment of choice
surgery
Ectopic ureter – surgical treatment
Intramural
Laser ablation
Neoureterostomy
Ureteroneocystostomy
Extramural
Ureteroneocystostomy
Unilateral end-stage renal disease
Uretero-nephrectomy
INtramural tx: Neoureterostomy – new stoma
creaete incision over oureter
create a new home: suture urothelium of ureter to the urothelium of the bladder
pass urinary cat through distal segment, pass suture between submucosal shelf and outside wall
take cat out, tighten suture
extramural ureter: Ureteroneocystostomy
stay suture at diatl portion of ureter
suture up defect region in urethra
create a hole
pull ureter through into urinary bladder lumen
create spatulation to make surface area of hole larger
simple interupted suture—> urothelium to urothelium
—> refer
USMI Urinary sphincter mechanism- Pathophysiology
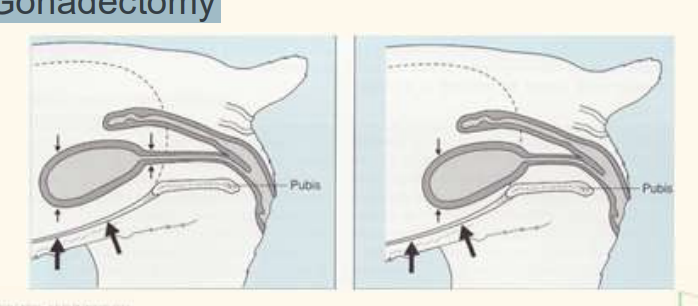
Urethral tone and length – Bladder neck position – Body size and breed – Gonadectomy
neck of urinary bladdder within abdomen: pressure is the same
older—> shorter urethra—> neck is out of abdo cavity—> incontinence
— usually older, F, N
USMI - diagnosis
History – Predominantly incontinent when recumbent – May occur after spay •
Rule out other causes incontinence– CBC/chem, urinalysis, urine C&S– repirical Medical management – CT excretory urography – Cystoscopy
USMI – medical management
4 treatment, which one to try
cure rate of single therapy treatment
do not become continent but often improve
Oestrogens *
a-adrenergic agonists : Phenylpropanolamine *
Weight loss *
Control of urinary tract infections
*reduce dose, side effect; increase response
cure rate of ~50%
USMI – surgical management approached
indication: if no response to medical treatment
common
Colposuspension
Pexy: Urethropexy / Cystourethropexy
Submucosal urethral bulking agent injections— collagen (6months effect)
Artificial urethral sphincter
Transobturator vaginal tape
USMI – surgical management: Colposuspension
goal
Increase urethral length
Relocate bladder neck to intraabdominal position
Increase pressure at bladder neck
USMI – surgical management: Colposuspension
outcome
50% cure, 40% improve, 10% no response
Colposuspension- referrla
• Sutures from the cranial vagina to the prepubic tendon on either side of the proximal urethra—> increase pressure
permenant, nonabcsorbable suture
Colposuspension normal complication: 11-15%
Pollakisuria— if it is pulled really tight
Recurrent UTIs
Slight tenesmus
Pain during first defaecation
USMI – surgical management: (Cysto)urethropexy (uncommon)
what is it? 2
complications
outcome 2
Pexy bladder more cranial to abdominal wall
Suture ventral wall of proximal urethra to prepubic tendon
Complications – Pollakisuria – Dysuria
Outcome:
Sole technique: 53% complete continence
Combined colposuspension: 70% complete continence
USMI – surgical management: Bulking agents
goal
Endoscopic submucosal injections of collagen to increase urethral resistance
USMI – surgical management: Bulking agents
success rate
recurrence?
50-70%
recurrence 1m-1y
USMI – surgical management: Artificial urethral sphincter
name 1 advantage
increase urethral resistance
Cuff placed around proximal urethra
Urethral compression can be increased by injecting saline into subcutaneous port
advantage: can monitor and manage subcutaneously post op if needed
disadvantage: FB complication, have to dissect around urethra: damage to BS—> necrosis
Artificial urethral sphincter • Complications:
UTI up to 67%
Urethral obstruction 7-17%
Infection port site
Accidental puncture device
Artificial urethral sphincter: Outcome:
36-56% complete continence
67-92% functional continence
USMI is rare in male dogs.
aetiology
Congenital – Pelvic urethral dilatation – Prostatic diverticulum
Acquired – Larger breeds – Neutering – Intrapelvic bladder
USMI in male dogs - treatment outcome vs cat
Treatment less successful than in females
USMI in male dogs - treatment
medical
– a-adrenergic agonists
USMI in male dogs - treatment 3
Vas deferens pexy to abdominal wall
Prostatopexy to prepubic tendon
artificail urethral sphincter
USMI in cats is very rare why?
Continent zone’ longer and stronger in cats
Smooth muscle
Striated muscle
Fribroelastic tissues
USMI in cats treatment— surgery
Artifical urethral sphincter
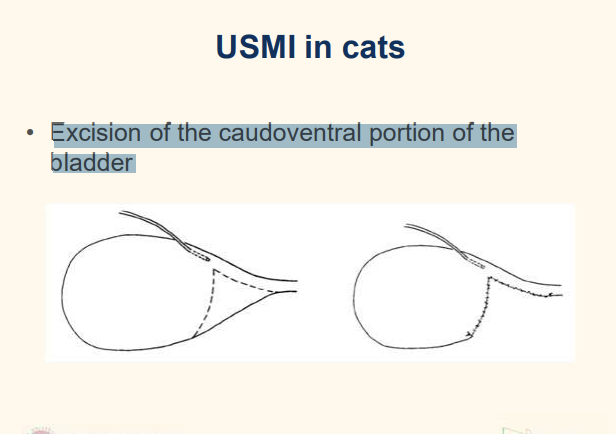
Excision caudal portion ventral wall bladder
Excision of the caudoventral portion of the bladder
uncommon
basically creater longer urethra and increase resistance