Lesson 3.2 Applied forces: Friction and tension
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is friction?
The resistance to motion of a surface moving relative to another, caused by electromagnetic attraction between charged particles in two touching surfaces. Symbol: Fᶠ, measured in newtons (N).
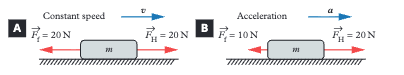
What happens to friction when an object moves at constant speed on a horizontal surface?
Net force is zero, so frictional force equals the applied horizontal force (Fᶠ = Fₕ).
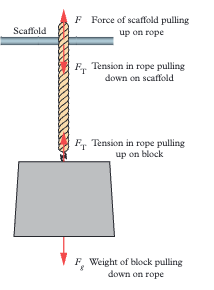
For a hanging object at rest, how does tension relate to weight?
Tension equals weight (Fₜ = Fᵍ) because net force is zero. The rope pulls up with the same magnitude as gravity pulls down.
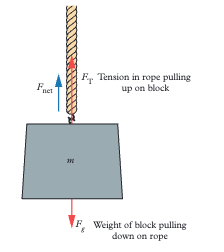
When an object is accelerating upwards, what is the relationship between tension and weight?
Tension is greater than weight. The net force equals Fₙₑₜ = Fₜ - Fᵍ, which can be rearranged to Fₜ = Fₙₑₜ + Fᵍ.
What does a frictionless pulley do to forces?
It redirects forces without changing their magnitude or losing energy. The tension in the cord remains the same on both sides of the pulley.
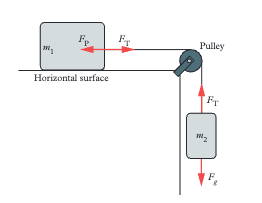
What is an applied force (Fₐ)?
A force applied to an object by a person or another object, can be a push or a pull. Example: pushing a desk or pulling a cart with a rope.
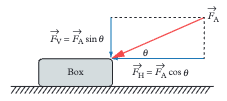
When pulling an object at an angle θ, what are the horizontal and vertical components of the applied force?
Horizontal: Fₕ = Fₐcos θ (moves object forward). Vertical: Fᵥ = Fₐsin θ (tends to lift object, reducing normal force).
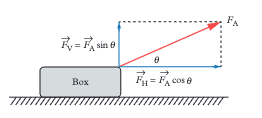
When pushing an object at an angle θ, how do the force components differ from pulling?
Horizontal: Fₕ = Fₐcos θ (moves object forward). Vertical: Fᵥ = Fₐsin θ (pushes object into ground, increasing normal force). This is why pulling is often easier than pushing.