Protists and Fungi
Protists
What is it?
- It is an organism that is not an animal, plant, fungus, or prokaryote
- Kingdom: Protista
- “The Very First” (the very first eukaryotes)
Evolution
- First eukaryotic organisms on earth
- 1.5 billion years ago (bya)
- Endosymbitotic Theory: Eukaryotic cells may have evolved when multiple cells joined together into one.
Classification(s)
- Animal-like
- Plant-like
- Fungus-like
Animal-like Protists (Unicellular):
Characteristics:
- All Heterotrophs
- 4 phyla: These are determined by movement
- Some are decomposers
- Base of some food chains
- Some cause disease
Types:
Zooflagellates:
- They’re apart of the Phylum: Zoomastigina
- They swim using flagella
- Can either have 1 or 2
- Absorb food through their cell membrane
- Reproduce sexually (conjugation) or asexually
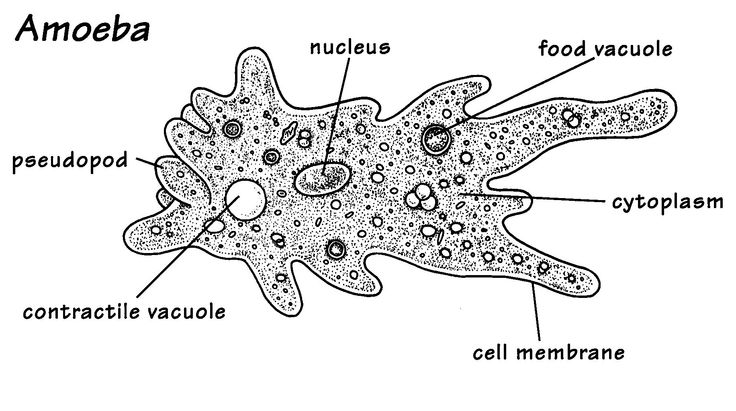
Sarcodines:
Phylum: Sarcodina
Moving cytoplasmic extensions called psuedopods
Amoeboid movement
Capture food with psuedopods: food vacuole
Food Vacuole: an organelle where food is stored after it’s captured
Can cause disease (Pathogenic)
Entomoeba
Giardia causes disease that causes diarrhea
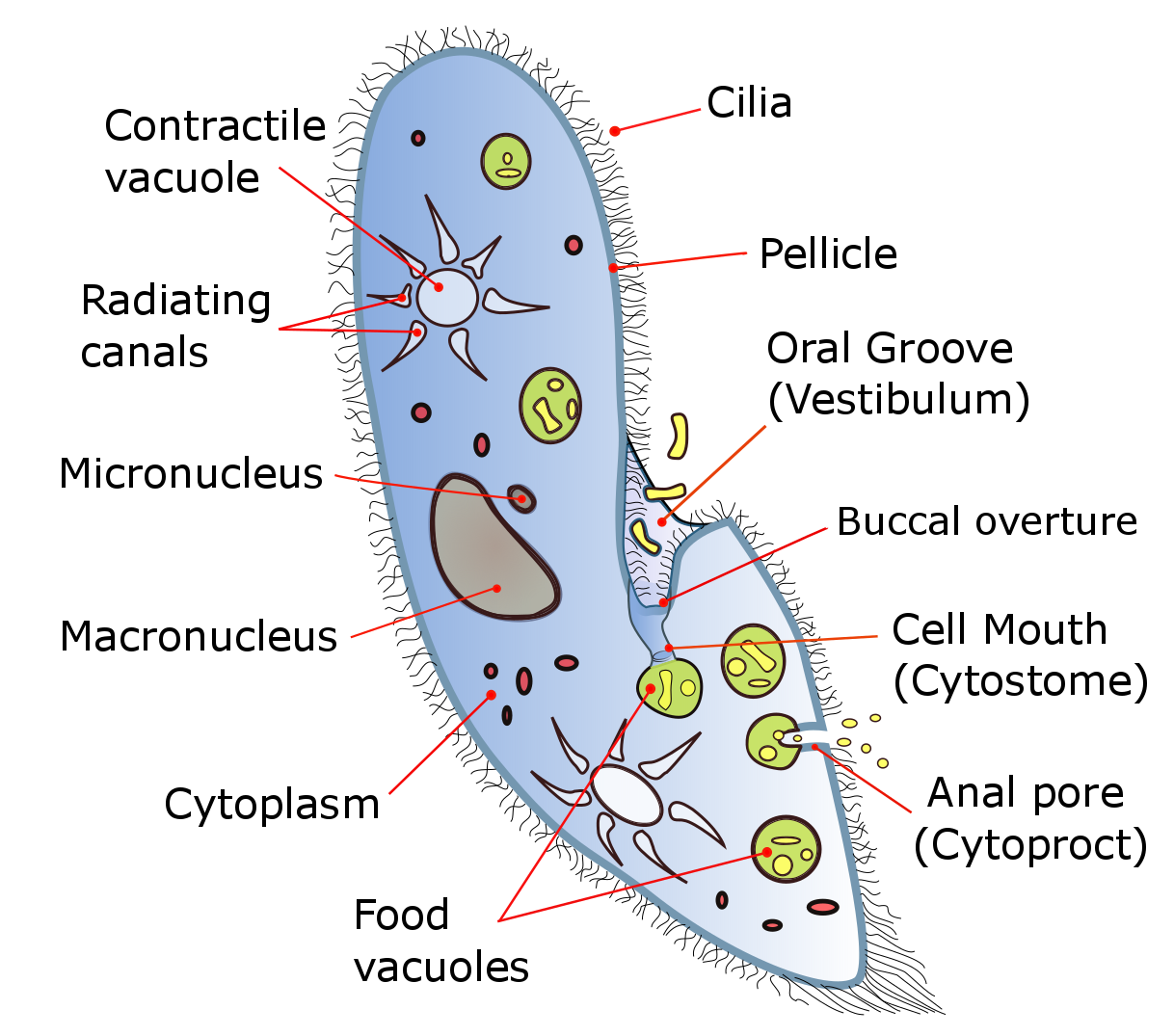
Ciliates:
- Phylum: Ciliophora
- Move through the use of cilia: hair-like projections that allows ciliates to move and get food
- Ciliate Anatomy (Paramecium)
- Trichocycts: structures used for defense
- Macronucleus: “working library” of genetic info (used for reproduction)
- Micronucleus: “reserve copy” of genetic info (used for reproduction)
- Gullet (Oral Groove): where food is trapped
- The food is collected here until it is stored in the food vacuoles
- Anal pore: where waste product is emptied
Contractile vacuole (sun shaped): collects/disperses water; maintains homeostasis
Ciliates Conjugation:
- Usually reproduce asexually: Mitosis
- Can exchange DNA through conjugation
- No NEW organisms are creates; simply an exchange of genetic info
- Occurs under stress (environmental pressures)
Sporozoans:
- Phylum: Sporozoa
- Do not move on their own
- They are parasitic
- Have complex life cycles
- Malaria: caused by a type of protist called. . .
- Plasmodium
Plant-like Protists: %%Unicellular Algae%%
Ecology:
- Phytoplankton: base of most aquatic food webs
- Algal blooms
- “red tides”
Types:
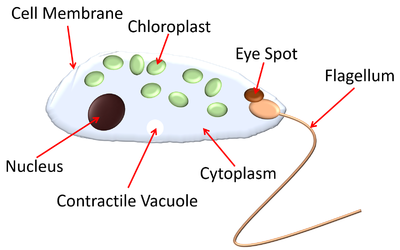
Euglenophytes:
- Phylum: Euglenophyta
- Phyta: “plant-like”
- Have two flagella
- ^^No cell wall; instead they have Pellicle^^
- Have eyespot: helps organism find sunlight to aide in photosynthesis
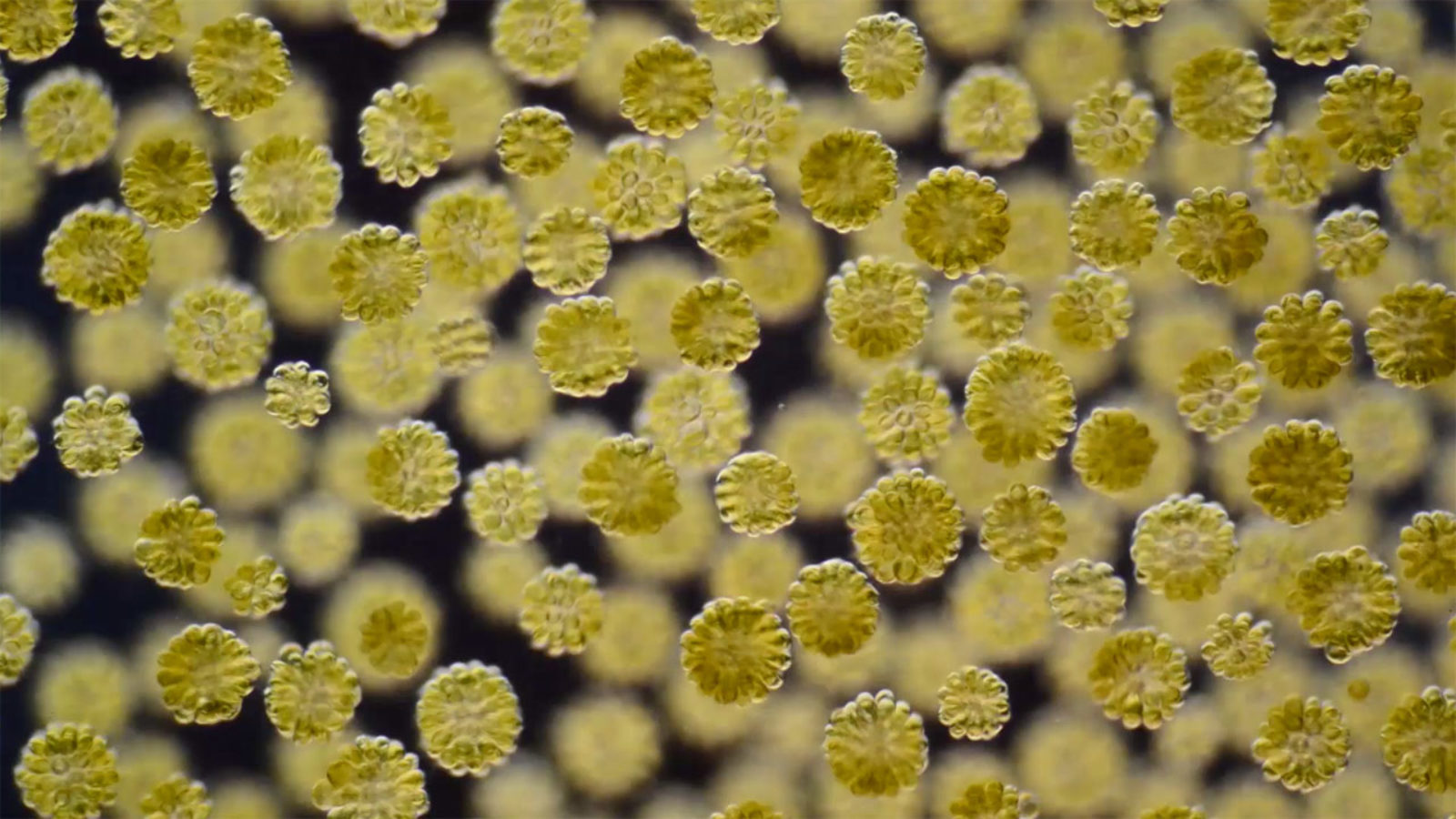
Chrysophytes:
- Phylum: Chrysophyta
- Gold-colored
- Cell walls have carbohydrate Pectin rather than cellulose
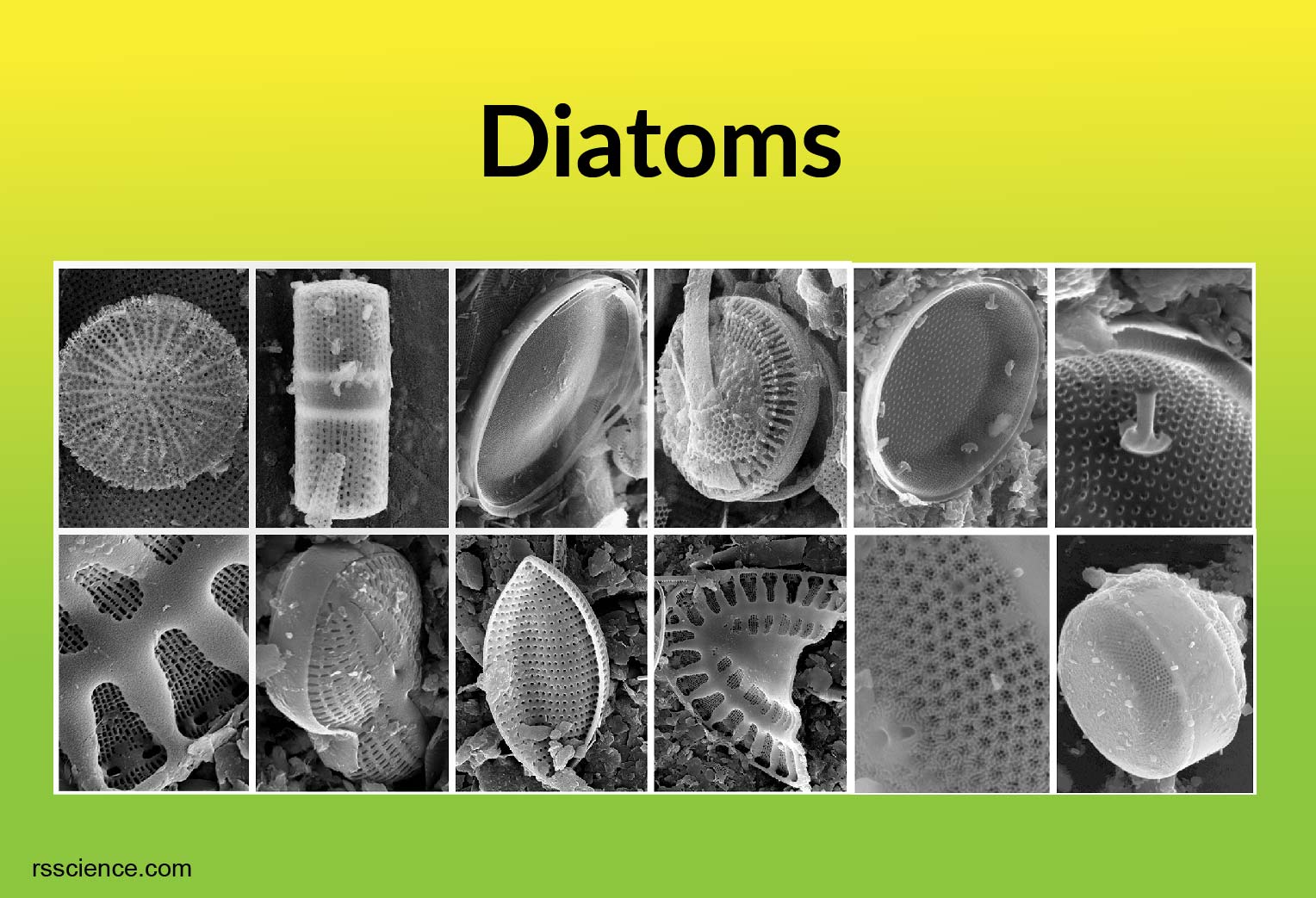
Diatoms:
- Phylum: Bacillarophyta
- Cell walls of Silicon (Si)

Dinoflagellates:
Phylum: Pyrrophyta
Usually luminescent
Plant-like Protists: ==Multicellular Algae==
Red Algae:
- Phylum: Rhodophyta
- “Red plants”
- Live at great depths
- Contain chlorophyll as well as Phycobillins (extra pigment) (absorb blue light, give off reddish color)
@@Brown Algae:@@
- Phylum: Pheophyta
- “Dusty plants”
- Have chlorophyll and fucoxanthin
- @@Largest and most complex algae@@
- Marine
Green Algae:
- Phylum: Chlorophyta
- “green plants”
- Share many characteristic with plants
- Cell wall of cellulose
- Chlorophyll a and b
- Hypothesized to be the ancestor of modern plants
Human Use of Algae:
Medications:
- Treat ulcers, arthritis, and blood pressure
Food:
- Sushi wrap
- Algin (thickener) in candy bars, ice cream, pudding, salad dressing
Industry:
- Used to make plastics and waxes
Fungi-like Protists:
- Heterotrophs
- Decomposes
- Lack cell wall
- Have centrioles
- Plant diseases: potato famine
- Two Groups
- Slime Molds
- Free-living cells in soil on the surface
- Water Molds
- Thrive on dead or decaying organic material in water, or plant
- (parasite)(on land)
Fungi:
- Eukaryotic
- Heterotrophs
- Digest food on the outside of their body (external digestion), then absorb it
- All are multicellular, except yeasts
- Cell walls
- Made of chitin
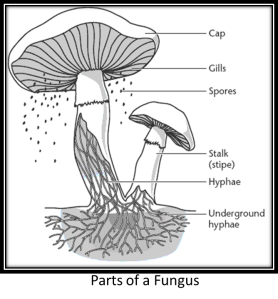
Structure:
- Hyphae: thin filaments that make up fungi
- Each hypha are only one cell thick
- Can form cross-walls
- Fungi bodies are composed of many hyphae tangled into a mass called:
- Mycelium: where food is absorbed (buried underground)
- Fruiting Body: reproductive structure above the soil (“mushroom” part)
Reproduction:
- Asexually
- Hyphae break off and grow on their own
- Spores: a reproductive cell that scatters and grow new organisms
- Sexually
- Fusion of (+) and (-) nuclei that happens inside the fruiting body
- There are no males or females
Spreading:
- Spores are carried through wind or attached onto animals for them carry
Classification:
- Common
- Sac
- Club
- Imperfect
Common:
- Phylum: Zygomycetes
- Life cycle includes a Zygosporangium: resting spore that contains zygotes (until conditions become favorable to spread)
- Bread Mold:
- Structure and Function of Bread Mold:
- Rhizopus Stolonifer
- Rhizoids (mycelium): rootlike hyphae that penetrate the bread’s surface
- Stolons: stem like hyphae that run along surface
- Sporangiophores: hyphae that push into air
- Contain 40,000 spores; each able to grow new fungus
Sac Fungi:
- Phylum: Ascomycota
- Ascus: reproductive structure that contains spores
- Largest phylum of fungi
- Yeasts:
- Unicellular fungi
- Used for baking and brewing
- Dry granules are ascospores
- Budding: asexual reproduction
Club Fungi:
- Phylum: Basidiomycota
- Specialized reproductive structure that resembles a club
- Basidium (spores): the whole cap itself
- Life Cycle:
- Mushroom cap; has gills; lines with basidia
- 2 haploid nuclei fuse creating diploid zygote
- Undergoes meiosis, producing haploid basidiospores
- Basidiospores are then scattered
- Edible and Inedible
- Many wild mushrooms are poisonous
- Can look identical to edible types
- Don't eat the shrooms
Imperfect Fungi:
- Phylum: Deuteromycota
- Varied
- Placed in this phylum because a sexual phase has never been documented by researchers
- Majority of them resemble ascomycetes
- Penecillium
Fungi Ecology: Decomposers
- All Heterotrophs
- Most are saprobes: obtain food from dead or decaying organic matter
- Maintain equilibrium in every ecosystem
- Parasites:
- Plant
- Wheat rust
- Corn smut
- Human
- Ringworm
- Athlete’s Foot
- Animal
- Cordyceps in grasshoppers in Costa Rica