All of Higher Physics
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
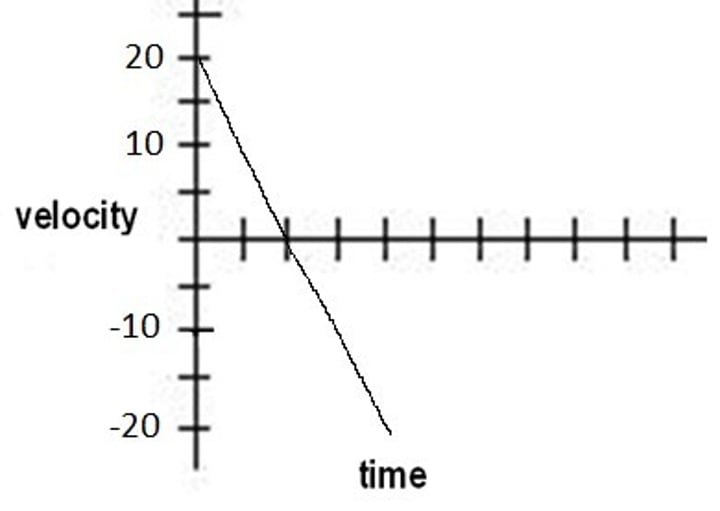
sketch the velocity-time graph for a ball thrown vertically upwards that falls back down to earth (neglecting air resistance) look like?
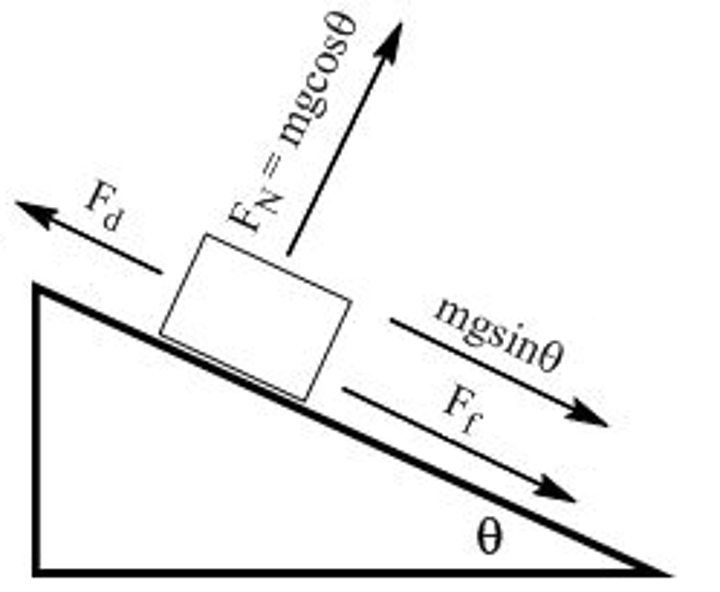
how do you calculate the magnitude of the force of friction acting on an object moving down a slope?
f=(mgsinθ) - friction
what is the area underneath a force-time graph equal to
impulse / change in momentum
initial vertical component (u) of a velocity v at angle theta
u = vsinθ
initial horizontal component (u) of a velocity v at angle theta
u = vcosθ
law of the conservation of momentum
total momentum before a collision is equal to total momentum after a collision in the absence of external forces
how do you show that a collision is elastic
kinetic energy before equals kinetic energy afterwards
how do you show that a collision is inelastic
kinetic energy before does not equal kinetic energy afterwards
direct current
a flow of electrons in one direction from negative to positive terminals of a power supply
alternating current
an electric current that constantly reverses its direction and instantaneous value over time
what is an oscilloscope used to display
voltage wave forms
what does the y-axis on an oscilloscope show
voltage across a component
how do you get the period of a wave from an oscilloscope
wavelength in boxes x timebase
how do you get the frequency from an oscilloscope
1/period
how do you get the peak voltage from an oscilloscope
amplitude x Y-gain
current in a series circuit is...
the same at all points
when resistors are connected in series, how do you calculate the total resistance?
Rt = R1 + R2 +....
in a parallel circuit the supply current is equal to...
the sum of the currents through each branch
if components are in parallel what is the same across all of the branches
potential difference
in a potential divider, the ratio of the resistor values is equal to...
the ratio of the potential differences
what is the gradient of a "Vtpd" versus "current from a cell" graph equal to?
negative internal resistance
emf
the electrical energy supplied to each coulomb of charge which passes through the source
short circuited cell
a cell that has two terminals connected together with just a wire which has (almost) zero resistance
what is the y-intercept of a "Vtpd" versus "current from a cell" graph equal to?
the emf
what is a scalar quantity
a quantity that has only magnitude
what is a vector quantity
a quantity that has both magnitude and direction
for displacement what must always be stated
distance and a direction (most likely a bearing)
how would you work out a resultant vector
add the vectors tip-to-tail and the use pythagoras to calculate the length. SOHCAHTOA to find angle.
the meaning of the individual letters of SUVAT
displacement, initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration, time
what is the gradient of a displacement-time graph equal to
velocity
what is the area under a speed-time graph equal to
total distance traveled
what is the area under a velocity-time graph equal to
displacement
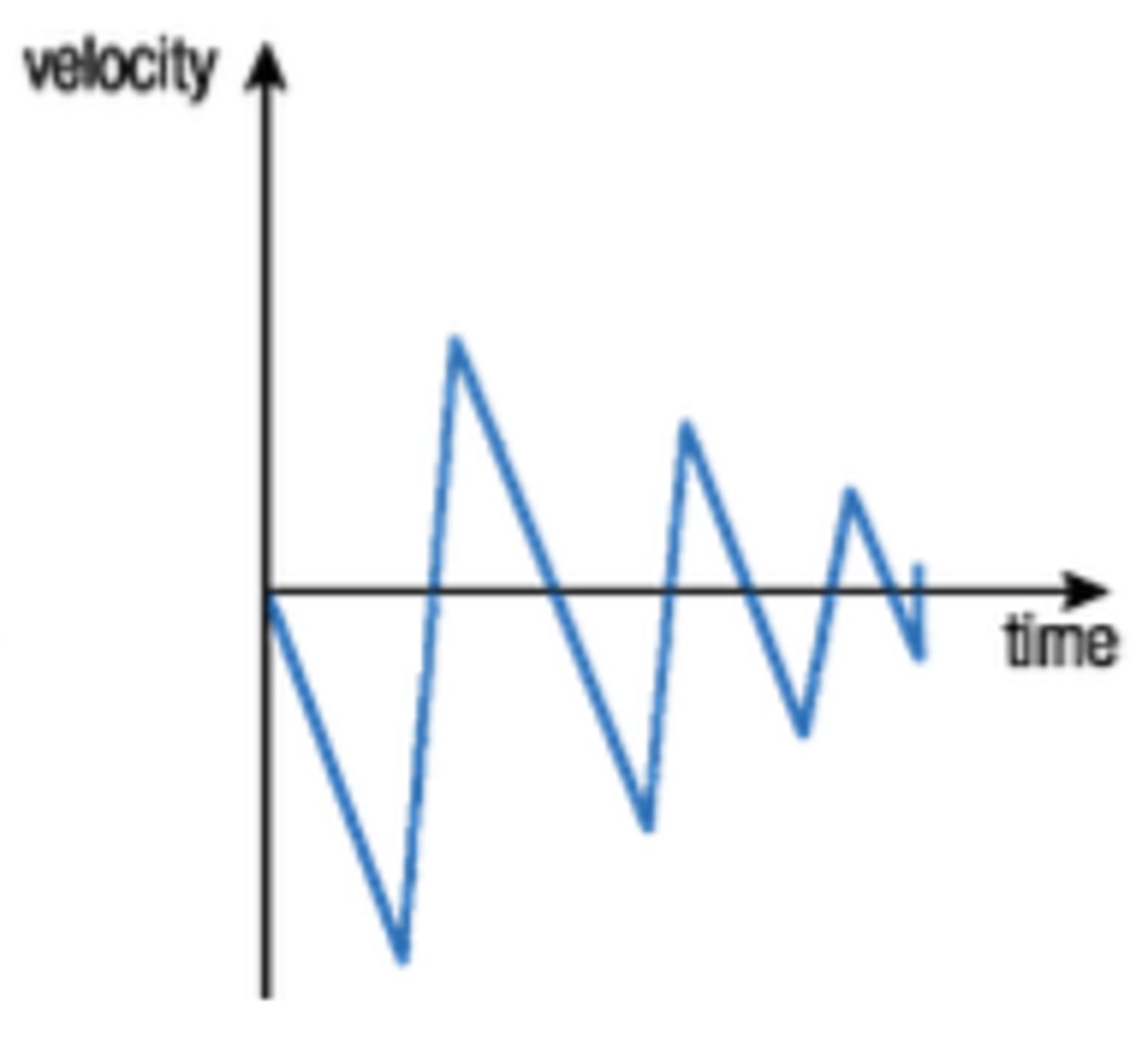
what does the velocity-time graph for a bouncing ball look like
acceleration for a freefalling object on Earth
-9.8 m s⁻²
vertical acceleration of a projectile
-9.8 m s⁻².
newtons first law
if an object is at rest or moving at a constant velocity in a straight line then the forces acting on the object are balanced
newtons second law
the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the unbalanced force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass (f=ma)
newtons third law
every action has an equal but opposite reaction
what happens to your apparent weight when accelerating upwards
apparent weight is greater
if a lift is moving down at constant speed what will your apparent weight be
apparent weight is the same
what happens to your apparent weight when accelerating downwards
apparent weight is greater
impulse
the change in momentum during a collision or explosion
newton's universal law of gravitation
each body with a mass will exert a force on each other body with mass
two postulates for special relativity
the laws of physics are the same in all frames of reference / the speed of light in vacuum has the same value c in all frames of reference
what is a light year
the distance light can travel in a year
what is length contraction
the observed decrease in length of an object moving relative to an observer compared to that when they are in a stationary frame of reference
what is time dilation
the observed increase in time interval of an object moving relative to an observer compared to that when they are in a stationary frame of reference
what is the doppler effect
the change in frequency observed when a source of sound waves is moving relative to an observer
what happens to the frequency of a wave as a source moves towards an observer
the frequency increases
what happens to the frequency of a wave as a source moves away from an observer
the frequency decreases
what is the relationship between speed of the galaxy (v) and distance form an observer (d)?
v is directly proportional to d. / v = H₀d
what evidence is there for the expansion of the universe
galaxies farther away from us are moving faster
what is the dark matter
the matter in the universe that is not visible
what is dark energy
something that is overcoming the force of gravity to cause the universe to expand at an ever greater rate.
what evidence is there for the big bang
the relatively uniform cosmic microwave background radiation is the remains of energy created just after the Big Bang. the universe is expanding, the other galaxies are moving away from us
milli
x10⁻³
micro
x10⁻⁶
nano
x10⁻⁹
equation for the energy gained by an electron when passing through a potential difference of V
W=QV
how much energy is stored in a capacitor of capacitance C with a potential difference of V applied across it
E=½ CV²
which energy band is full of electrons in an intrinsic semiconductor
valence band
charge on an n-type semiconductor
neutral (no charge)
random uncertainty
(max - min) divided by number of readings
reading uncertainty of digital scale
one in the least significant digit of the display
reading uncertainty of analogue scale
half the smallest division
overall uncertainty (single quantity)
the largest out of the reading, random and calibration uncertainties
overall uncertainty (calculated quantity)
the largest percentage uncertainty in the data being calculated
percentage uncertainty
(Absolute uncertainty / measurement) x 100
systematic uncertainty
a problem with the apparatus or method which causes an error in every single reading
intrinsic semiconductor
undoped group 4 semiconductor eg silicon
extrinsic semiconductor
semiconducting group 4 material with impurities of group 3 or group 5 material
doping
when very small amounts of impurities are added to the intrinsic semiconductor, this changes the properties of the material
diode
a component made of n-type and p-type material grown together. It is a device that allows current in one direction only
p-n junction
where the n-type and p-type materials are joined, this allows electrons and holes to diffuse across the gap
conductor
solid material that has electrons in the conduction band
insulator
solid material with no electrons in the conduction band and a large energy gap between the valence and conduction bands
valence band
the highest occupied band containing electrons. The band containing electrons with the highest energies and still be associated with a particular atom of a solid material
conduction band
The first unfilled band above the valence band, allowing the electron to dissociate from a particular atom and become a free charge carrier in the material
capacitance
the ratio of electric charge to potential difference between any two conductors separated by an insulating material. The capacitance of a system of conductors describes the ability of the system to store electric charge
capacitor
two (or more) conductors separated by an insulator that can be used to store charge
depletion layer
the area surrounding the p-n junction of a diode where the electrons have combined with the holes leaving no free charges
electric current
a net flow of charged particles
electromotive force
the electromotive force of a source is the electrical potential energy that is given to each unit of charge that passes through the source
forward-biased
a diode connected in a circuit such that the p-type terminal is more positive than the n-type terminal
frequency
the number of complete cycles of a wave passing a given point in a given time, usually per second. measured in hertz (Hz) where 1 Hz = 1 wave per second.
fundamental unit of charge
the magnitude of charge carried by one electron or one proton. Equal to 1.60 x 10-19 coulombs
instantaneous
at one point in time or at one particular instant in time
internal resistance
the opposition to current in a source of electrical energy
leakage current
the tiny current in a reverse-biased diode
load resistor
the resistor, or combination of resistors, that forms the external part of an electrical circuit
lost volts
the potential difference that is used to drive a current through the internal resistance of a source. given by the expression Ir where r is the internal resistance of the source
monochromatic
one energy, one frequency, one wavelength, one colour
ohm's law
the current in a conductor at constant temperature is directly proportional to the potential difference across it
open circuit
a circuit in which the current is zero. In the circuit there is a gap or an infinite resistance
period
the time to make one complete wave. measured in seconds
photodiode
a type of p-n junction diode that responds to light intensity
photovoltaic mode
the mode of operation of a photodiode where it can supply power to a load. This is the basis of a solar cell
potential divider
a circuit consisting of a number of resistors (often only two) in series, connected across a supply, that is used as a source of fixed or of variable p.d
p-type semiconductor
semiconductor material that has an excess of free holes
resistance
the opposition that a conductor offers to a current through it. Defined as the ratio of potential difference across the conductor to the current through it