Social Perception and Managing Diversity
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hr final
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Social Persception
The process whereby we process social info related to interactions with others
Decision making is affected by social perception
Staffing
Job assignment
Termination
Etc
Model of social info processing
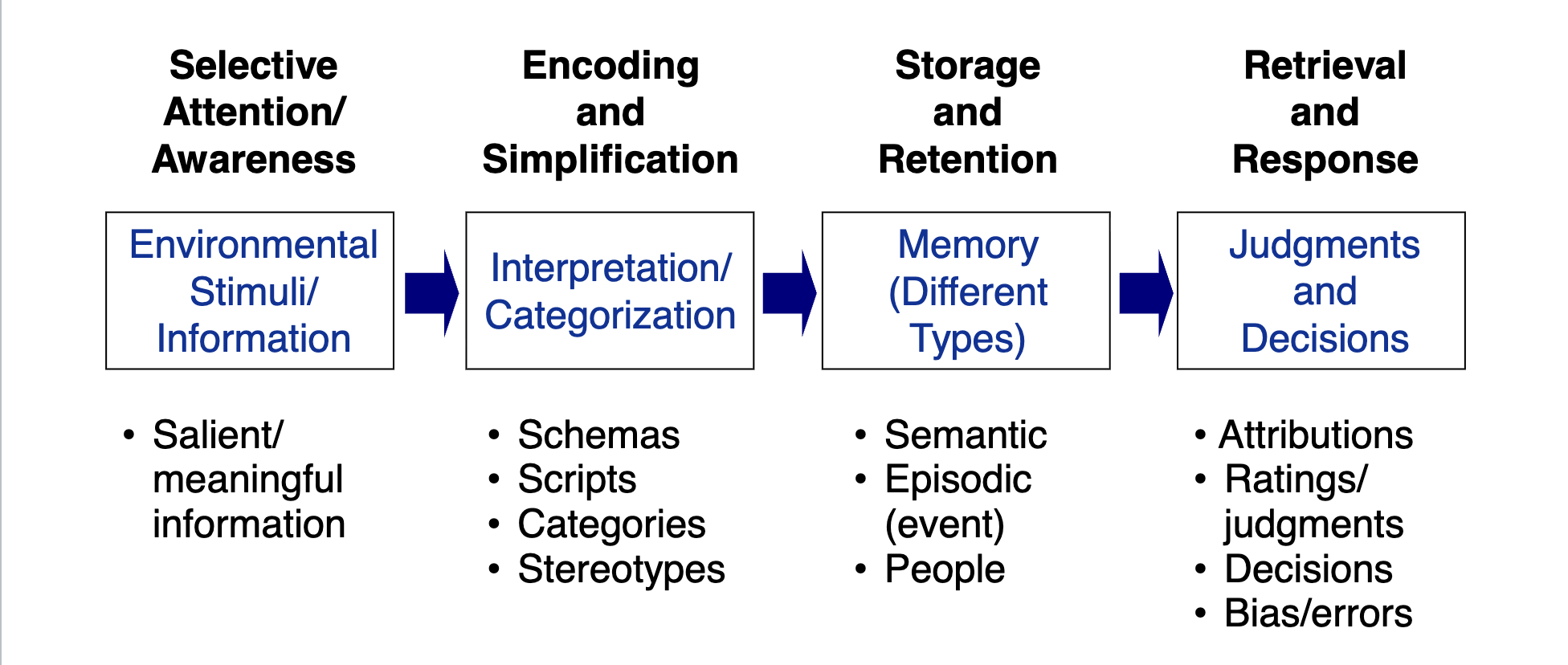
Different types of implicit bias: Fundamental Attribution Bias (FA Error)
The tendancy to make internal or external attributions (assumtions). Internal: they did bad on soemthing because they are lazy, bad at it, etc. External: they did bad on soemthing because they didnt get enough sleep, tehy were late, etc
Different types of implicit bias: Self Serving Bias
Making internal attributions for success (I pass because i studied) and external attribusions when you fail ( i failed because teh teacher is bad)
Different types of implicit bias: Halo Error
When one good characteristic about someone carries your view of them. They are very integral, so you assume they are very smart, a good person, etc.
Different types of implicit bias: Pitchfork Error
When one bad characteristic about someone carries your view on them. They are NOT integral so you believe they are a lair, dumb, a bad person, etc
Different types of implicit bias: Leniency Error
Thinking everyone is doing exceptional no matterwhat; VERY lenient about work
Different types of implicit bias: Severity Error
Thinking everyone sucks no matter if they may be excelling. No one is ever good enough
Different types of implicit bias: Central Tendency error
Different types of implicit bias: Recency and Primary Effect
Bing of on of the first (primary) or last (recency) to something makes you more memorable than the people in between.
To avoid this bias, be extra present at taking notes for people in the middle during things like interviews.
Different types of implicit bias: Steryotyping
Using assumptions to make decisions about people and situations
Different types of implicit bias: Contrast Effects
Being contrasted to someone who looks better or more successful
Different types of implicit bias: “Similar to me” error
Tending to be the most comfortable with people who are more similar to you. You KNOW that you fel comfortable and probably choose to be / work with people similar to you. THIS CAN BE BAD
Different types of implicit bias: Projection
ASSUMING someone is similar to you even when you dont know anything about them or dont know this is true
Attribution Theory (Fritz Heider, Harold Kelly)
An Attribution is made as to whether actions and/or behaviors resulted from internal factors (ex. ability, amount of work, etc) or external factors (task difficulty). This attribution is based on 3 demsions of observed behavior.
3 demensions of observed behaviors
Consensus: Compares an individual behavior with their peers
-is the behavior similar to their peers?
Distinctiveness: Compares an individuals behavior on a task with their behavior on other tasks at the time
-is the behavior in the this situation different from behavior in different situations happening simultaneously
Consistency: Compares an individuals behavior on a task with their performance on other tasks overtime
-Is their behavior in the same situation similar over time?
Most frequent attributions
H Concen
H Dis
L Consist
=External causes
L Concen
L Dis
H Consist
=Internal Causes
Example:
Concen: How did roommate test score compare to others in the class?
Dis: How does roommate performance compare to their other classes that semester
Consist: How does roommates performance compare to their performance the last two years?
Diversity V Inclusion
Diversity: The multitude of individual differences and similarities that exist among people
-Can tend to focus on differences
-Easy to find segregation of groups within organization
-Isnt automatically a plus
Inclusion: The extent to which the vast diversity of organization members are brought together in a meaningful way to increase success (individual, group, org)
-Recognizes diversity of organization members
-Primary focus is on brining those differences together, not just pointing them out
4 layers of diversity
-Personality is at the core, its a key source of identity
-Internal diversity (surface level characteristics) are quickly obvious to outsiders and relatively unchangeable
-External dimensions and organization dimensions (deep level characteristics) take time to emerge through attitudes, values, etc
—-
-The more peripheral, the more likely it is changeable
-many more aspects of diversity
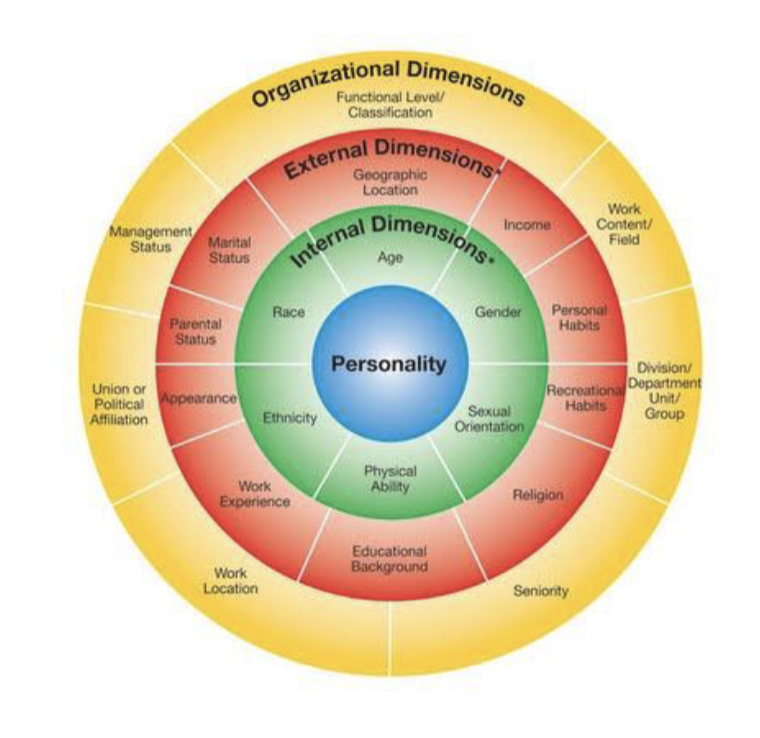
Model of Diversity

Benefits of diveristy and inclusion
-Increasing creativity
-Less likely of group think
-Increased awareness of broad customer base
-More interesting
Affermative action vs “managing diversity”
AA: Artificial interventions that allow companies to
correct imbalances, address diversity problems, etc.
- Required for organizations that are federal contractors
- Can be seen as more of an “enforcement” approach to diversity
- Can be divisive as well as not necessarily beneficial
“Managing diversity”: focuses on changing organizational systems,
culture, etc. to drive an inclusive work environment
Research from Ann Morrison suggests three basic strategies exist for managing diversity (THREE E’s)
- Educational: Help people develop for success in a diverse
workplace (works but not quickly enough; need additional strategies)
- Enforcement: Accountability mechanisms to change the system, etc.
- Exposure: Expose people to others with different backgrounds
Other concepts about diversity and inclusion
-Discrimination
-Affirmative Action (again)
-The “Glass Ceiling”:Cutting minorities off from getting to a certain place in an organization
-Glass Walls and Glass Elevators/Escalators: Social barriers keeping you from certain positions, like you cannot be a teacher with tattoos
-Psychological safety
-On-ramping: Getting people with big work gaps up to speed with modern work environment. Like being a stay at home mom or dad and then getting back into the office years later, veryyy big work gap it will NOT be the same