Week 3- Self Regulation
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Sensory integration is a function of the brain and body that occurs in all humans….
Across the life span
What 3 components to know about sensory integration as it relates to OT
A specific clinical frame of reference for the assessment and treatment of people who have functional disorders in sensory processing
Multi sensory integration is used in basic science and neuroscience but does not reflect a behavioral or clinical OT perspective
Sensory processing has become common language in OT to differentiate from Ayer’s sensory integration and neuroscience constructs
What are the core concepts of sensory processing according to Dunn?
Sensory processing patterns apply to everyone, not just people with disabilities
Every has some amount of each sensory pattern; some are seen more intensely expressed in neurodiverse populations
Context and activities provide unique sensory experiences; differences in sensory processing is NOT A DISORDER
What are the core concepts of sensory processing according to Miller?
Sensory processing disorder is a complex disorder that affects the brain; the daily lives of 1 in 20 child read are affected by SPD
The disorder has unique symptoms not explained by other known conditions and is often misdiagnosed
Initiative to include SPD in the DSM-V as a novel diagnosis- FAILED
What theory regarding sensory processing what OT operates within?
Winnie Dunn’s
What is the low registration or bystander category according to Winnie Dunn’s theory?
An individual has a high threshold and needs a lot of sensory input but is passive when it comes to addressing their low threshold
What is the seeker category according to Dunn’s theory?
An individual has a high threshold and requires a lot of sensory input, this individual seeks out sensory stimulation in response to their low threshold
What is the sensor/sensitivity category according to Dunn’s Theory?
An individual has a low threshold and detects sensory stimuli sooner and at a higher rate than others, the individual is passive and does not do anything in response to their overstimulation
What is the avoider category according to Dunn’s theory?
An individual with a low threshold and detects sensory stimuli earlier and at a higher rate, they actively will remove themselves or get away from the stimuli to address their sensitivity
What sensory category does this sentence describe:
“These individuals are great at creating new ideas but can get distracted by their higher need for input”
Seeker
What category of sensory processing does this sentence describe:
“They are very easy going because they don’t notice all the details, but this can create a challenge when noticing details is important to a situation”
Bystander
What sensory processing category does this sentence describe:
“They are great at organizing and creating systems but can be challenged when something disrupts the routine”
Avoider
What sensory processing category does this sentence describe:
“They are great at noticing details that others miss and can get overwhelmed by this awareness”
Sensor
What is the process of evaluating sensory processing skills?
Review record
Occupational interview with the individual, family, teacher
Conduct skilled observations when: participation is successful and when participation is challenging
Complete formal assessments; performance based testing and informant questionnaires
What is important to know regarding “rarely”, “frequently”, and “sometimes”
Each phrase has a percentage tied to it that indicates how often the occurrence is, so its more subjective than objective
What are things you want to look at during the clinical observation portion of a sensory processing assessment?
Distinguish patterns of sensory processing behaviors in natural context
Assessment of occupational performance; supplemental information provided by standardized testing
Assessment of component skills
Group meaningful clusters of behaviors that are indicative of a pattern of function/dysfunction
What kind of information does standardized measures provide?
Information regarding sensory-related skills
Provide information about the child’s functional level in comparison to other children
Supplement the information provided by your other measures
What are examples of standardized measures used to assess sensory processing skills?
Sensory integration and praxis test
Sensory profile
Sensory processing measure
Preschool SENSE
Why would we evaluate sensory processing skills but not be considered sensory integrationist?
We want to identify sensory skills that affecting the child’s participation and performance in occupations; we are gathering this info to inform us but we will not be solely addressing it
In the North Carolina school setting, when is the OT required to complete a sensory processing evaluation
If the team is considering autism as an educational diagnosis
What is social emotional learning (SEL)?
The process through which children and adults understand and manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions
What are the dimensions of SEL?
Self-awareness
Self-management
Social awareness
Relationship skills
Responsible decision making
What is self-awareness?
Know your strengths and limitations, with a well grounded sense of confidence, optimism, and a growth mindset
What is self-management?
Effectively manage stress, control impulses, and motivate yourself to set and achieve goals
What is social awareness?
Understand the perspectives of others and empathize with them, including those from diverse backgrounds and culture
What are relationship skills?
Communicate clearly, listen well, cooperate with others, resist inappropriate social pressure, negotiate conflict constructively, and seek and offer help when needed
What is responsible decision making?
Make constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions based on ethical standards, safety, and social norms
What are some SEL approaches?
School-wide
RTI/MTSS
Individual
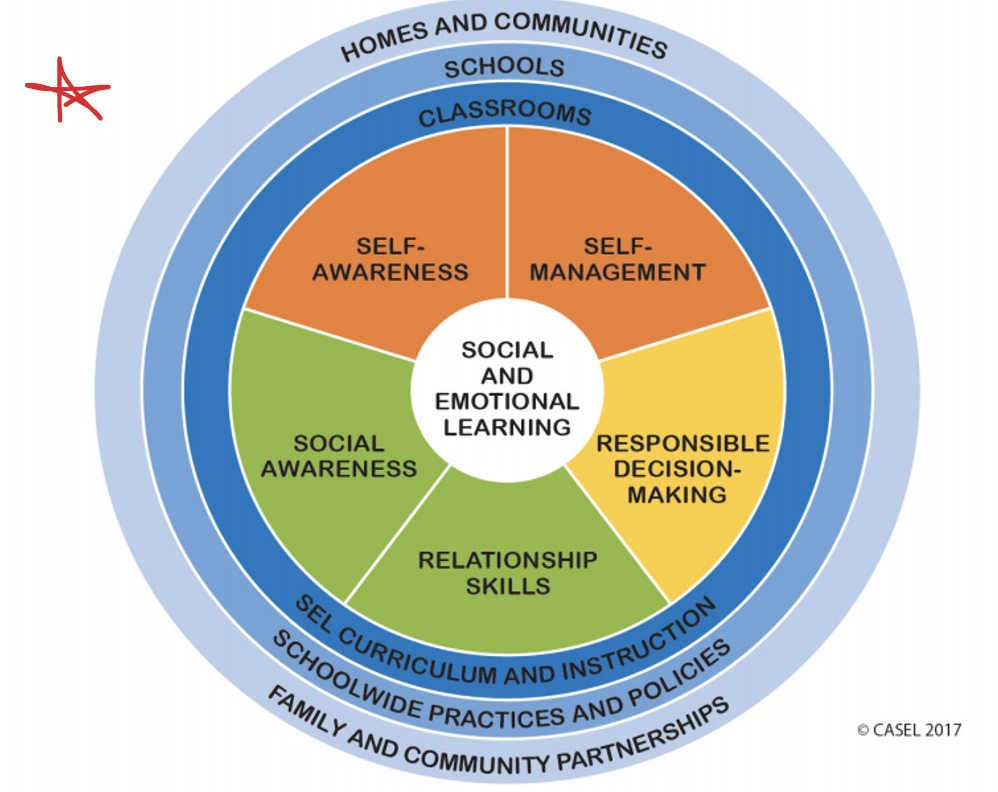
What does this chart demonstrate regarding SEL?
These are the environments we want to evaluate to identify factors that affecting a person’s SEL skills and identify how they use their SEL skills across multiple environments and settings
What SEL skills is a 2 month old exhibiting?
Start to smile and look directly at you
Cry to get needs met
Occasionally self-soothe by sucking on hands and fingers
What SEL skills is a 4 month old exhibiting?
Smile and play spontaneously
Cry when you stop playing
Begin to engage with you by imitating faces that you make
What SEL skills is a 9 month old exhibiting?
Start to show stranger anxiety
Start to prefer some toys over others
May cry when familiar faces are not around
What SEL skills is a 6 month old exhibiting?
Are more aware of which people are familiar and which are strangers
Can respond to your emotions by crying, smiling, or laughing
Enjoy looking at themselves in the mirror
What SEL skills would a 12 month old exhibiting?
Play favorites with familiar people
Are more interactive
Enjoy simple interactive games like patty cake and peak a boo
What are things that are hallmarks of SEL skills exhibited between 2- 12 months?
Attachment
Language exposure
Self-soothing
Routines
Shared interest
What SELs skills will a 18 months to 2 year old be exhibiting?
Have more temper tantrums and become more defiant as attempts at independence and communication increases
Begin simple pretend play, often by imitating what adults or other kids are doing
Becoming interested in having other kids around but are more likely to play alongside them (parallel play) than with them (cooperative play)
What SEL skills would a child between 3 and 4 being exhibiting?
Start to show and verbalize a wider range of emotion
Are interested in pretend play but may confuse real and “make believe”
Are spontaneously kind and caring
Start playing with other kids and separate from caregiver easier
May still have tantrums because of changes in routine or not getting what they want
What are the hallmarks of SEL skills for children between 18 months to 4 years?
Tantrums
Transitions
Independence
Wider range of emotions
Helpfulness
Separation anxiety
Routines
What SEL skills would a 5 to 6 year old be exhibiting?
Are aware of their gender and may prefer to play with same-sex peers
Enjoy playing with other kids and are more conversational and independent
Test boundaries but are still eager to please and help out
Begin to understand what it means to feel embarrassed
What SEL skills would a 7 to 8 year old child be exhibiting?
Are more aware of others’ perceptions
May complain about friendships and other kids’ reactions
Want to behave well, it aren’t as attentive to your directions
Try to express feelings with words, but may resort to aggression when upset
What SEL skills would a 9 to 10 year old child between exhibiting?
Start narrowing peer groups to a few close friends they share secrets and joke with them
May withdrawal from family activities and conversations to start developing their own identity
Are affectionate, silly and curious, but can also be selfish, rude, and argumentative
What are the hallmarks of SEL skills for children aged 5 to 10 years?
Gender roles
Initiating friendships
Awareness of perceptions
Even more complex emotions
Sense of humor
Trust, secrets, and boundaries
What are examples of SEL questionnaires?
Vineland adaptive behavior scale (VABS)
Devereux early childhood assessment (DECA)
Social skills improvement system rating scales (SSIS)
Social emotional assessment measure (SEAM)
What does the DECA assess?
Measures protective factors and resiliency; initiation, attachment, self-regulation
What are the different settings and age ranges the DECA can be used with?
Infant
Toddlers
Preschool
Student strengths K-8
Adults in the child’s life
What is the social skills improvement system?
3 to 18 years old
An intervention system/guide to assess social skills, problem behaviors, and academic competence (and how to address areas of concerns)
What are examples of social skills?
Communication, cooperation, assertion, responsibility, empathy, engagement, self-control
What are examples of problem behaviors?
Externalizing, bullying, hyperactivity and inattention, internalizing, autism spectrum
What are examples of academic competence?
Reading achievement, math achievement, and motivation to learn
What are active behaviors?
Direct refusals
Opposition
Aggression toward people or property
Self-injurious
What are passive behaviors?
No compliance
Withdrawal
Inattention
Lack of response
What are examples of why a child may be exhibiting a certain behavior?
For attention
To be alone/nonsocial
To escape
Tangible
Due to sensory stimuli
What are ways to manage behaviors during the evaluation process?
Have a preferred adult assist in the evaluation process
Use first and the language
Clear expectations
Incorporate occupational profile likes into the evaluation
Attempt to redirect
Encourage and uplift during challenging tasks
Stickers
Have the child determine the order of activities with you
Create a visual schedule
Use a time if transitions become challenging
What drives your approach regarding addressing a child’s behavior?
Differential assessment- identifying why that behaviors is occurring and getting to the root of the problem
What are the goals of addressing a child’s social emotional skills? (Skills they will improve or gain)
Awareness of social rules
Awareness of others
Self management or co-regulation
Problem solving
Self-awareness and self advocacy
What are the goals of addressing sensory regulation?
How participation in the activity or the environment that is causing the dysregulation is impacting them and their occupations
Self management and co-regulation
Self-awareness