Ch 1 Dev Psych
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:18 PM on 5/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1
New cards
development
the pattern of movement or change that begins at conception and continues through the human life span
2
New cards
life-span perspective
a view that development is lifelong, multidimensional, multidirectional, plastic, multidisciplinary, and contextual, and as a process that involves growth, maintenance, and the regulation of loss (Paul Bates)
3
New cards
lifelong
Early adulthood is not the endpoint of development; rather, no age period dominates development. Development is _________.
4
New cards
multidimensional
Development consists of biological, cognitive, and socioemotional dimensions. Even within each of those dimensions, there are many components. Changes in one dimension affect development in others. Development is ____________.
5
New cards
multidirectional
Throughout life, some dimensions or components of a dimension expand and others shrink. Development is ______________.
6
New cards
plastic
Capable of change. Development is _________.
7
New cards
multidisciplinary
psychologists, sociologists, anthropologists, neuroscientists, and medical researchers all share an interest in unlocking the mysteries of development through the life span. Development is _________.
8
New cards
context
the setting in which development occurs, which is influenced by historical, economic, social, and cultural factors
9
New cards
Contextual
All development occurs within a context, or setting. Contexts include families, schools, peer groups, churches, cities, neighborhoods, university laboratories, countries, and so on. Each of these settings is influenced by historical, economic, social, and cultural factor. Development is ___________.
10
New cards
Normative age-graded influences
Influences similar for individuals in a particular age group. Includes puberty and menopause
11
New cards
Normative history-graded influences
Influences common to people of a particular generation because of historical circumstances
12
New cards
Nonnormative life events
unusual occurrences that have a major impact on the individual’s life. Don’t happen to all people, and when they do occur they can influence people in different ways
13
New cards
growth, maintenance, and regulation of loss
The three goals of human development according to Baltes
14
New cards
culture
encompasses the behavioral patterns, beliefs, and all other products of a particular group of people that are passed on from generation to generation
15
New cards
cross-cultural studies
compare the aspects of two or more cultures. Comparison provides information about the degree to which development is similar, or universal, across cultures or is instead culture-specific
16
New cards
ethnicity
rooted in cultural heritage, nationality, race, religion, and language
17
New cards
Socioeconomic status
refers to a person’s position within society based on occupational, educational, and economic characteristics. Implies certain inequalities
18
New cards
gender
the characteristics of people as females and males, is another important aspect of sociocultural contexts
19
New cards
social policy
a government’s course of action designed to promote the welfare of its citizens. Values, economics, and politics all shape a nation’s social policy
20
New cards
Minnesota Family Investment Program
a program designed in the 1990s primarily to influence the behavior of adults - specifically to move adults off welfare rolls and into paid employment
21
New cards
biological processes
produce changes in an individual’s physical nature. Genes inherited from parents, the development of the brain, height and weight gains, changes in motor skills, nutrition, exercise, the hormonal changes of puberty, and cardiovascular decline are all examples of biological processes that affect development
22
New cards
cognitive processes
changes in an individual’s thinking, intelligence, and language
23
New cards
Socioemotional processes
changes in the individual’s relationships with other people, changes in emotions, and changes in personality.
24
New cards
prenatal period
the time from conception to birth. tremendous growth - from a single cell to a complete organism with a brain and behavioral capabilities. 9 month period
25
New cards
infancy
the developmental period from birth to 18 or 24 months when humans are extremely dependent on adults. During this period, many psychological activities - language, symbolic thought, sensorimotor coordination, and social learning are just beginning
26
New cards
early childhood
the developmental period from the end of infancy to age 5 or 6. This period is sometimes called the “preschool years.” During this time, young children learn to become more self-sufficient and to care for themselves. They also develop school readiness skills, such as the ability to follow instructions and identify letters, and they spend many hours playing with peers. First grade typically marks the end of early childhood.
27
New cards
middle and late childhod
the developmental period from about 6 to 11 years of age, approximately corresponding to the elementary school years. During this period, children master the fundamental skills of reading, writing, and arithmetic. They are formally exposed to the world outside the family and to the prevailing culture. Achievement becomes a more central theme of the child’s world, and self-control increases
28
New cards
adolescence
the transition from childhood to early adulthood, entered at approximately 10 to 12 years of age and ending at 18 to 22 years of age. Adolescence begins with rapid physical changes—dramatic gains in height and weight, changes in body contour, and the development of sexual characteristics such as enlargement of the breasts, growth of pubic and facial hair, and deepening of the voice. At this point in development, the pursuit of independence and an identity are prominent themes. Thought is more logical, abstract, and idealistic. More time is spent outside the family.
29
New cards
emerging adulthood
from 18 to 25 years of age and is a time of considerable exploration and experimentation, especially in the areas of identity, careers, and lifestyles.
30
New cards
early adulthood
the developmental period that begins in the late teens or early twenties and lasts through the thirties. For young adults, this is a time for establishing personal and economic independence, becoming proficient in a career, and for many, selecting a mate, learning to live with that person in an intimate way, starting a family, and rearing children
31
New cards
middle adulthood
the developmental period from approximately 40 years of age to about 60. It is a time of expanding personal and social involvement and responsibility; of assisting the next generation in becoming competent, mature individuals; and of achieving and maintaining satisfaction in a career.
32
New cards
late adulthood
the developmental period that begins in the sixties or seventies and lasts until death. It is a time of life review, retirement from the workforce, and adjustment to new social roles involving decreasing strength and health. Usually the longest of the periods of development
33
New cards
Chronological age
the number of years that have elasped since birth
34
New cards
biological age
age in terms of biological health
35
New cards
psychological age
an individual’s adaptive capacities compared with those of other individuals of the same chronological age
36
New cards
social age
connectedness with others and the social roles individuals adopt. Individuals who have better social relationships with others are happier and tend to live longer than individuals who are lonely
37
New cards
normal aging
most individuals, for whom psychological functioning often peaks in early middle age, remains relatively stable until the late fifties to early sixties, and then shows a modest decline through the early eighties
38
New cards
pathological aging
individuals who show greater than average decline as they age through the adult years
39
New cards
succesful aging
characterizes individuals whose positive physical, cognitive, and socioemotional development is maintained longer, declining later in old age than is the case for most people
40
New cards
nature-nurture issue
concerns the extent to which development is influenced by nature and nurture
41
New cards
nature
an orgnaism’s biological inheritance
42
New cards
nurture
an organisms environmental experiences
43
New cards
stability-change issue
the degree to which early traits and characteristics persists or change over time
44
New cards
continuity-discontinuity issue
focuses on the degree to which development involves either gradual, cumulative change (continuity) or distinct changes (discontinuity)
45
New cards
theory
an interrelated, choherent set of ideas that helps to explain phenomena and make predications
46
New cards
hypotheses
specific assertions and predictions that can be tested
47
New cards
psychoanalytic theories
theories that describe development primarily in terms of unconscious processes that are heavily colored by emotion. Behavior is merely a surface characteristic and a true understanding of development requires analyzing the symbolic meanings of behavior and the deep inner workings of the mind SIGMUND FREUD EW
48
New cards
Sigmund Freud
This person developed psychoanalysis and believed peoples' problems were the result of experiences early in life. Five stages of psychosexual development; oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital. CRITICIZED FOR OVEREMPHASIZING SEUAL INSTINCTS

49
New cards
Erik Erikson
A person who believed Freud misjudged some aspects of development. Believed motivation is social and reflects a desire to affiliate with other people. Personality changes throughout life span
50
New cards
Erkison’s theory
eight stages of development unfold as we go through life. At each stage there is a crisis that needs to be resolved for development to occur
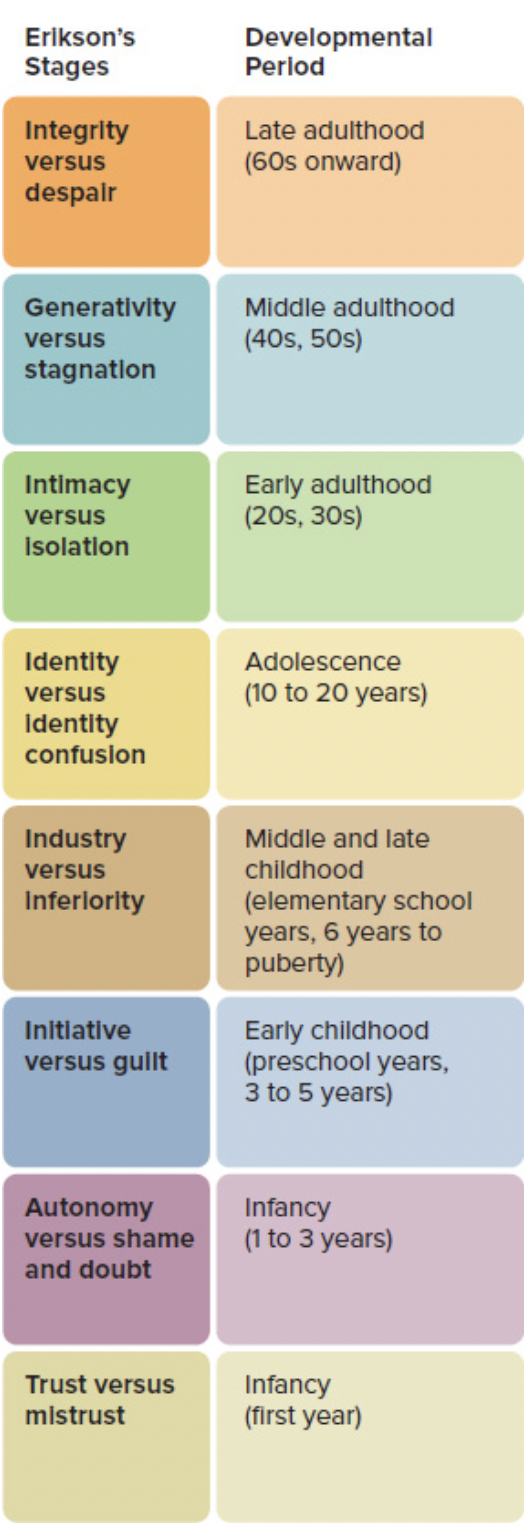
51
New cards
trust vs mistrust
the first psycho social stage, which is experienced in the first year of life. Trust during infancy sets that stage for a lifelong expectation that the world will be a good and pleasant place to live
52
New cards
autonomy vs shame and doubt
second stage that occurs in late infancy and toddlerhood (1-3). After gaining trust in caregivers, infant begin to discover that their behavior is their own. The start to assert their sense of independence or autonomy. They realize their will. If infants and toddlers are restrained too much or punished too harshly, they are likely to develop a sense of shame and doubt
53
New cards
initiative vs guilt
third stage during preschool years. children face new challenges that require active, purposeful, responsible behavior. Feelings of guilt may arise, though, if the child is irresponsible and is made to feel too anxious
54
New cards
industry vs inferiority
4th stage in elementary school. Children now need to direct their energy toward mastering knowledge and intellectual skills. The negative outcome is that the child may develop a sense of inferiority
55
New cards
identity vs identity confusion
5th stage during adolesents. ppl face finding out who they are, what they are all about, and where they are going in life
56
New cards
intimacy vs isolation
6th stage that occurs in early adulthood
faced with forming intimate relationships. If young adults form healthy friendships and an intimate relationship w a partner, intimacy will be achieved; if not, isolation will result
faced with forming intimate relationships. If young adults form healthy friendships and an intimate relationship w a partner, intimacy will be achieved; if not, isolation will result
57
New cards
generatively vs stagnation
7th stage during middle adulthood
the primary concern is helping younger generation develop and lead useful lives. The feeling of having done nothing to help the next generation is stagnation
the primary concern is helping younger generation develop and lead useful lives. The feeling of having done nothing to help the next generation is stagnation
58
New cards
integrity vs despair
8th and final stage in late adulthood. person reflects on the past. integrity is a life well spent which despair is gloom
59
New cards
Piaget’s Theory
theory that children go through 4 stages of cognitive development as they understand the world
\
\

60
New cards
sensorimotor stage
brith to 2 yr age
infants construct an understanding of the world by coordinating sensory experiences with physical, motor actions
infants construct an understanding of the world by coordinating sensory experiences with physical, motor actions
61
New cards
preoperational stage
2-7 yr of age
children are able to represent the world with words, images, and drawings. But children still lack the ability to perform operations, or internalized mental actions that allow children to do mentally what could only be done physically
children are able to represent the world with words, images, and drawings. But children still lack the ability to perform operations, or internalized mental actions that allow children to do mentally what could only be done physically
62
New cards
concrete operational stage
7-11 yr age
children can perform operations that involve objects, and they can reason logically about specific or concrete examples. They cant imagine the stems to complete an algebraic equation bc doing so would be abstract
children can perform operations that involve objects, and they can reason logically about specific or concrete examples. They cant imagine the stems to complete an algebraic equation bc doing so would be abstract
63
New cards
formal operational stage
11-15 to adulthood
move beyond concrete experiences and think in abstract and more logical terms. develop images of ideal circumstances
move beyond concrete experiences and think in abstract and more logical terms. develop images of ideal circumstances
64
New cards
Vygotsky’s theory
a sociocultural theory that emphasizes how culture and social interaction guide cognitive development.
65
New cards
information-processing theory
individuals manipulate info, monitor it, and strategize about it. Does not describe info as stage-like. Individuals develop a gradually increasing capacity for processing information, which allows them to acquire increasingly complex knowledge and skills
66
New cards
behavioral and social cognitive theories
theories that hold that development can be described in terms of behaviors learned through interactions with out surroundings. must be observable
67
New cards
operant conditioning
the consequences of a behavior produce changes in the probability of the behavior’s recurrence. Ex: Behavior followed by a rewarding stimulus is more likely to occur SKINNER
68
New cards
Social cognitive theory
behavior, environment, and person/ cognitive factors are the key factors in development BANDURA and observational learning
69
New cards
ethology
the study of the behavior of animals in their natural habitat. Ethological theory stresses that behavior is strongly influenced by bio LORENZ
70
New cards
imprinting
the rapid, innate learning that involves attachment to the first moving object seen
\
\
71
New cards
72
New cards
Brofenbrenner’s ecological theory
the theory that development reflects the influence of several environmental systems; microsystem, mesosystem, ecosystem, macrosystem, and chronosystem
73
New cards
microsystem
the setting in which an individual lives. family, peers, school, and neighborhood. most direct interactions w social agents
74
New cards
mesosystem
relations between microsystems or connections btwn contexts. ex relation of family experiences to school experiences
75
New cards
exosystem
links btwn a social setting in which the individuals does not have an active role and the individual’s immediate context. husband influenced by mothers experience at work
76
New cards
macrosystem
the culture in which individuals live
77
New cards
chronosystem
the patterning of environmental events and transition over the life course as well as sociohistorical circumstances
78
New cards
eclectic theoretic orientation
does not follow any one theoretical approach but rather presents what are considered the best features of each theory
79
New cards
laboratory
controlled setting where many of the complex factors of the “real world” are absent
80
New cards
naturalistic observation
observing behavior in real-world settings and making no effort to manipulate or control the situation
81
New cards
standardized test
uniform procedures for administration and scoring
82
New cards
case study
in-depth look at a single individual
83
New cards
descriptive research
research that aims to observe and record behavior
84
New cards
correlational research
research that aims to describe the strength of the relationship between two or ore events or characteristics
85
New cards
correlation coefficient
a number baed on statistical analysis that is used to describe the degree of association between two variables
86
New cards
experiment
a carefully regulated procedure in which one or more factors believed to influence the behavior being studied are manipulated while all other factors are held constant
87
New cards
cross-sectional approach
research approach that compares individuals of different ages
88
New cards
longitudinal approach
approach where the same individuals are studied over time
89
New cards
cohort effects
effects due to a person’s time of birth, era, or generation but not to actual age