DNA HISTORY, STRUCTURE, DNA REPLICATION, & RNA Types
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, nucleic acid that contains the hereditary information and information to make proteins
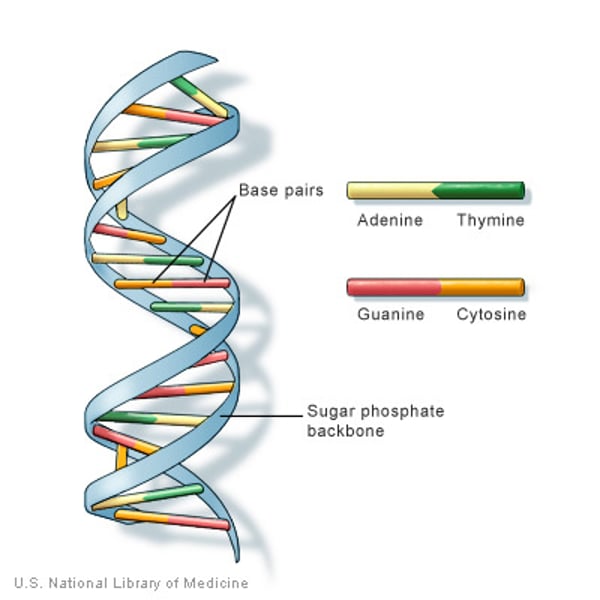
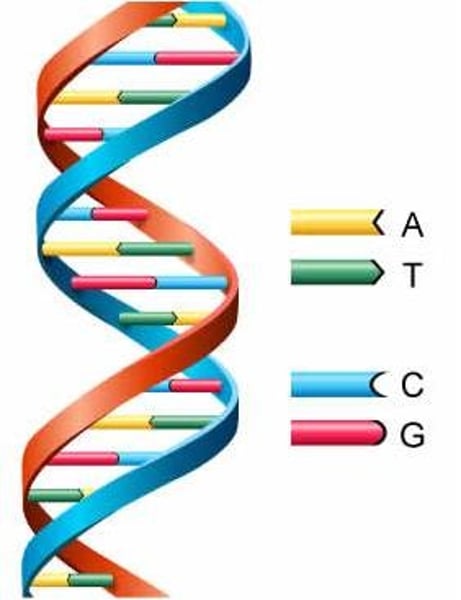
double helix
twisted ladder structure or shape of DNA, model created by Watson and Crick
Watson and Crick
Developed the double helix model of DNA.
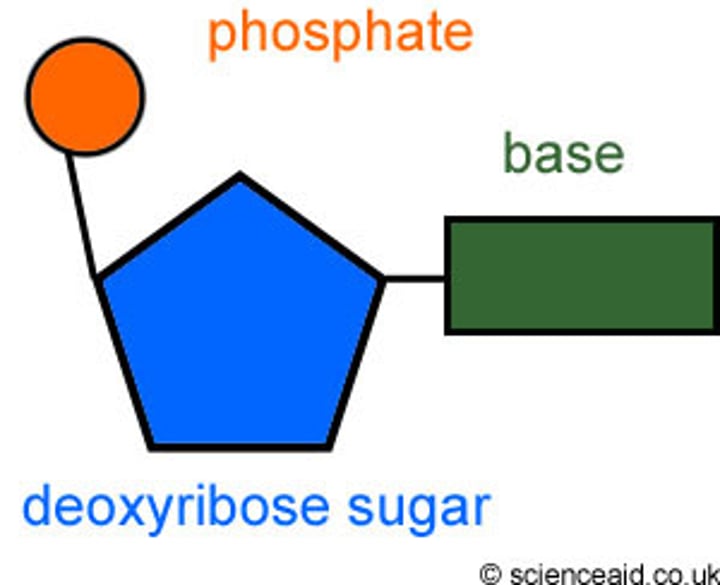
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
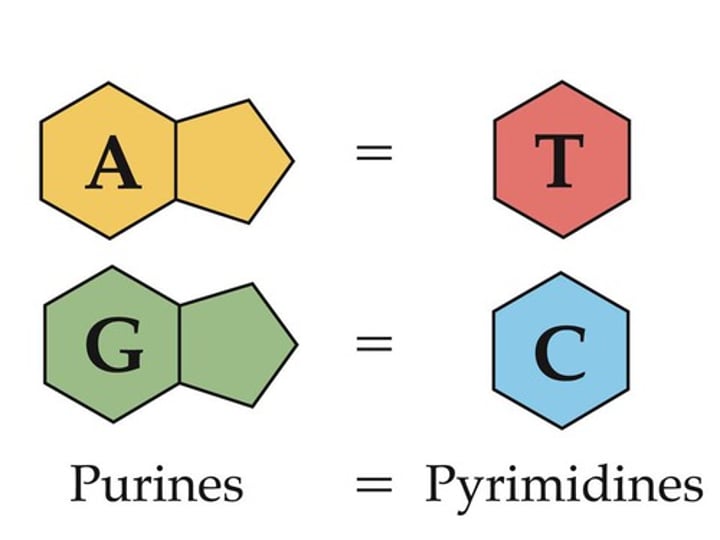
adenine
The nitrogenous base that pairs with Thymine in DNA
thymine
The nitrogenous base that pairs with Adenine in DNA
cytosine
The nitrogenous base that pairs with Guanine with DNA
guanine
The nitrogenous base that pairs with Cytosine in DNA
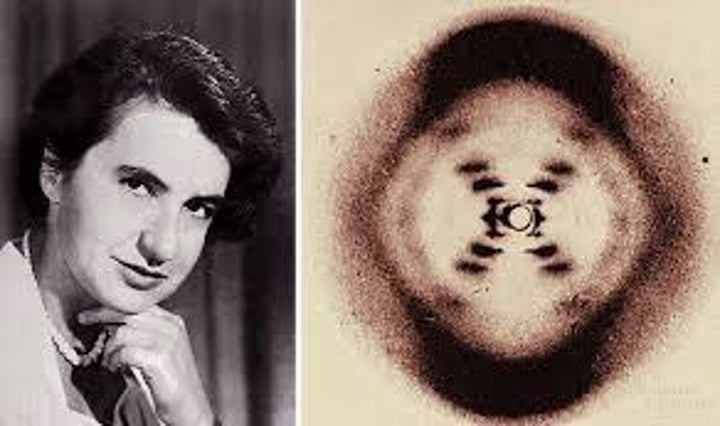
Rosalind Franklin
Woman who generated x-ray images of DNA, she povided Watson and Crick with key data about DNA

hydrogen bond
a weak bond that holds the base pairs together in the DNA double helix
Chargaff's Rule (Erwin Chargaff)
base pairing rules that state the nitrogen bases A=T and C=G, always equal amounts of A -T and C -G in a DNA molecule
nucleic acid
macromolecule containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus Ex: DNA and RNA
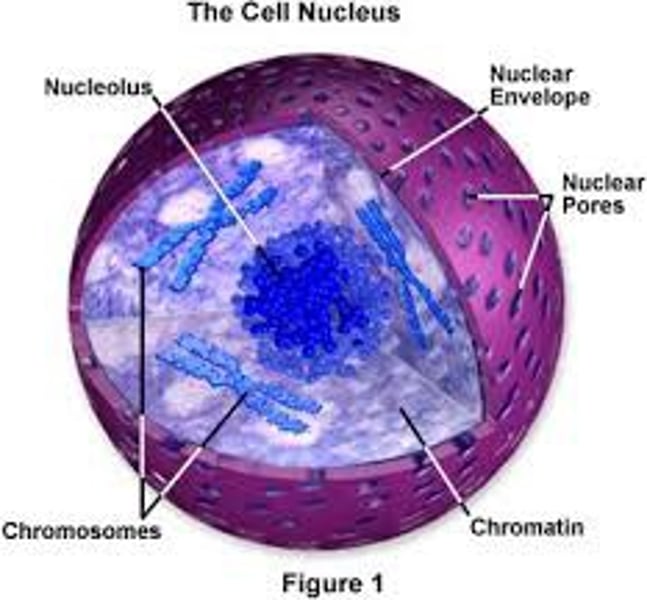
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for controlling everything in eukaryotes
Deoxyribose
5-Carbon sugar in DNA
Site or Location of DNA replication
nucleus
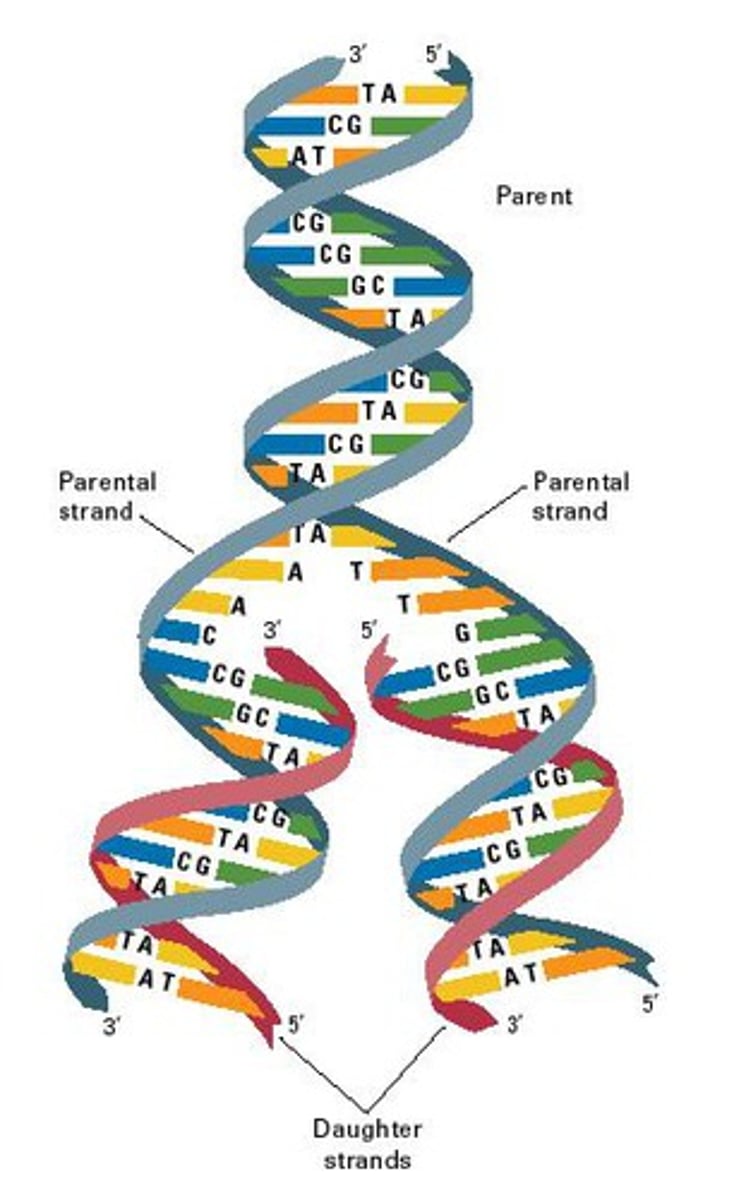
DNA replication
the process of making a copy of DNA, happens during the S-phase of the cell cycle
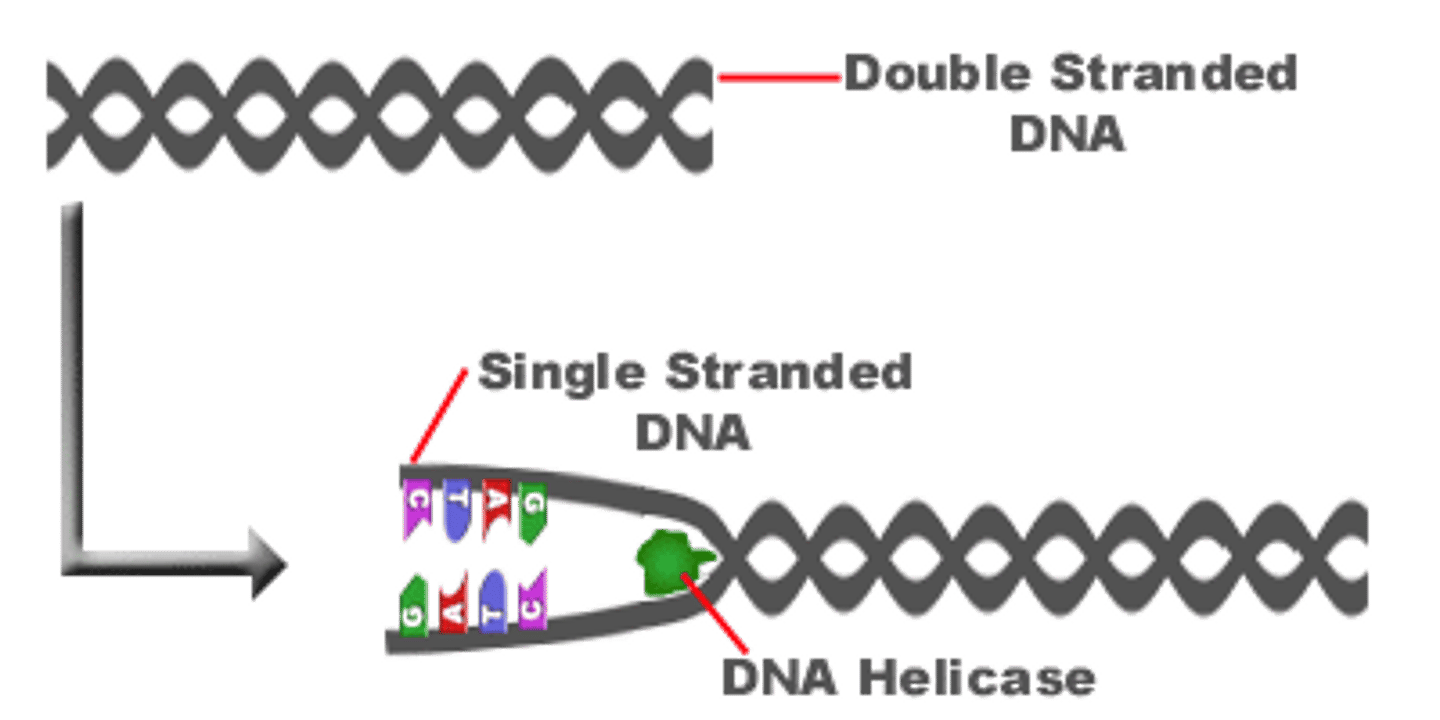
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists or unzips the double helix of DNA at the replication forks by breaking the hydrogen bond that holds the two strands together
DNA polyermase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
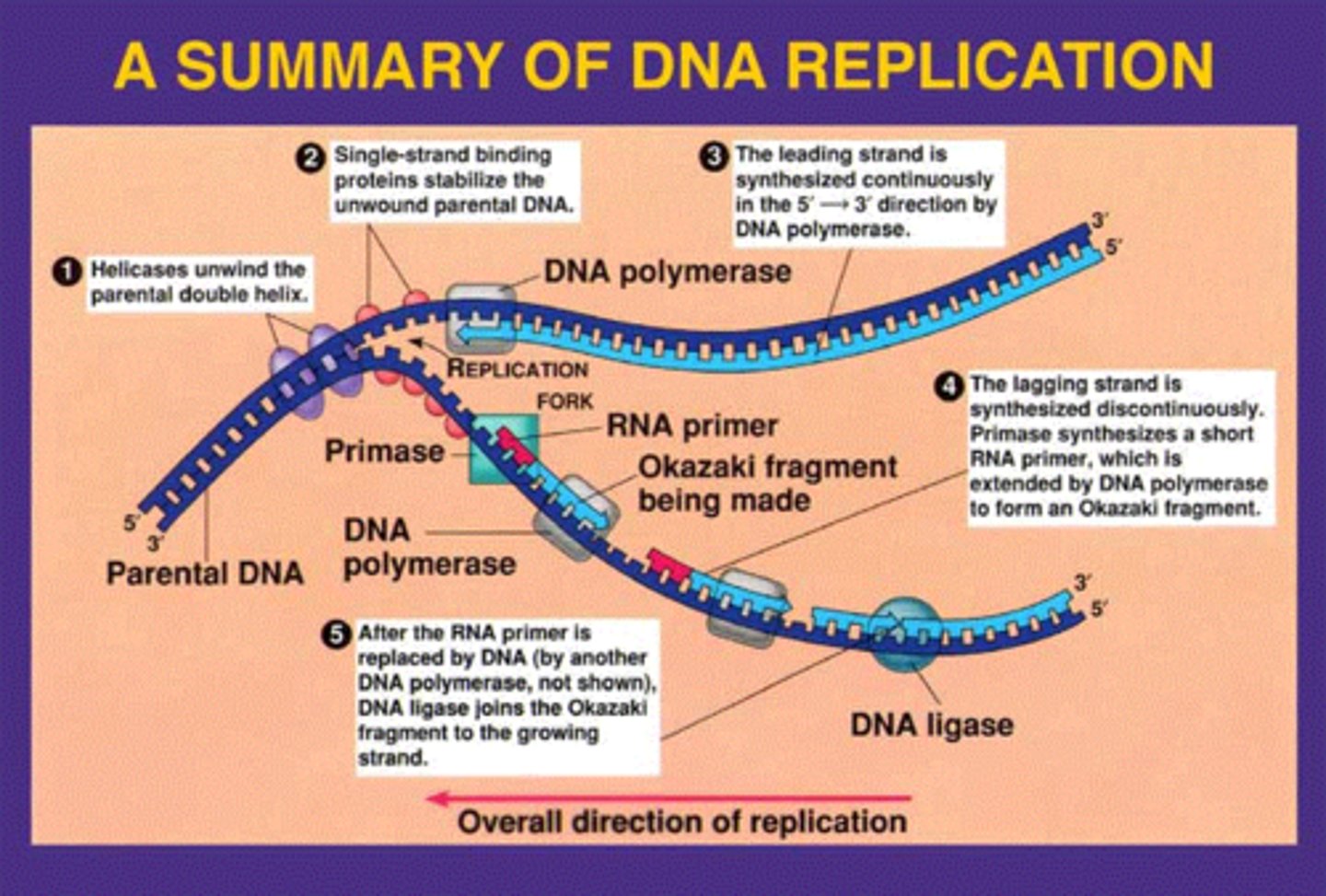
leading Strand
the new complementary DNA strand synthesized continuously along the template strand toward the replication fork in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction
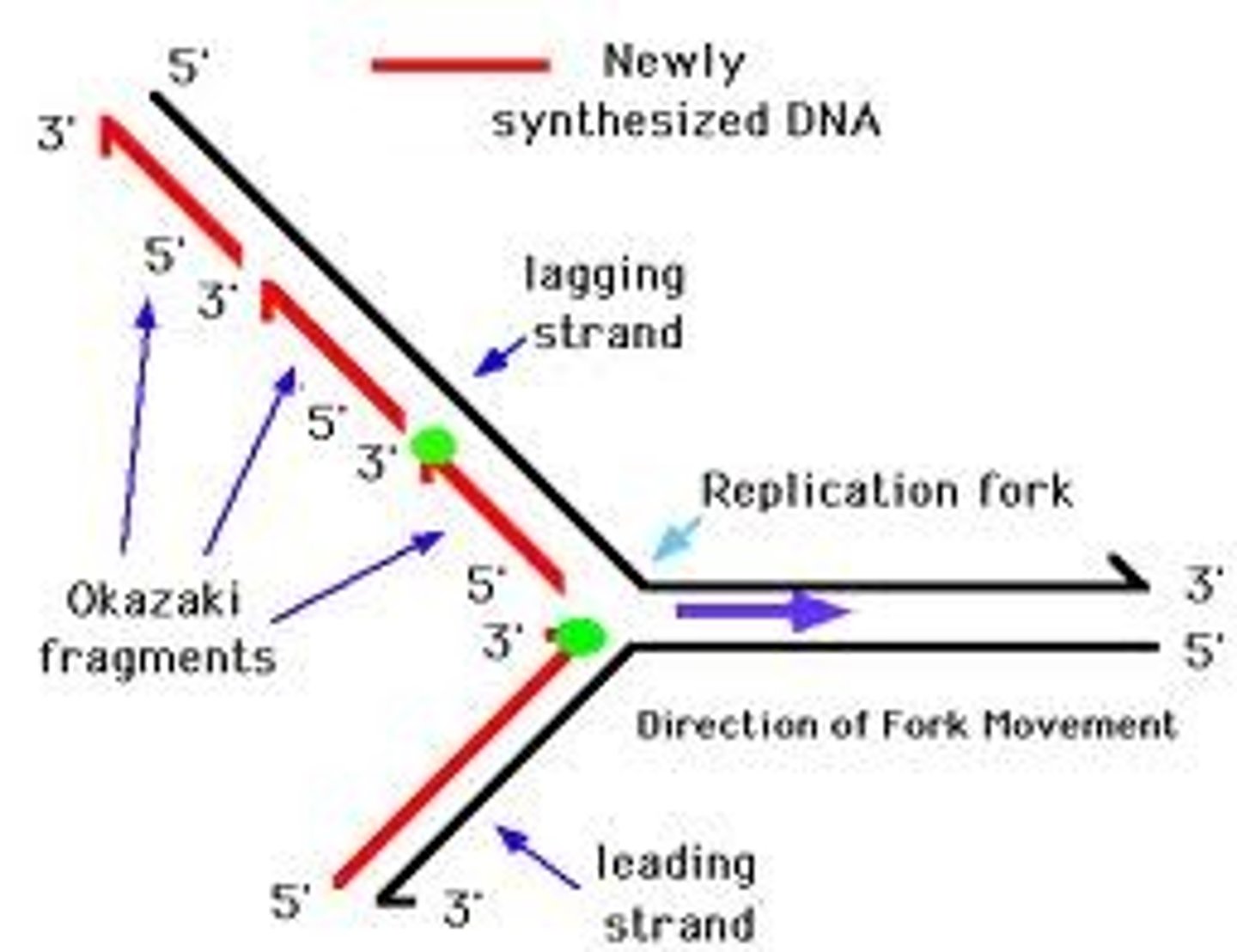
lagging strand
The strand that is synthesized in fragments or discontinuously using individual sections called Okazaki fragments
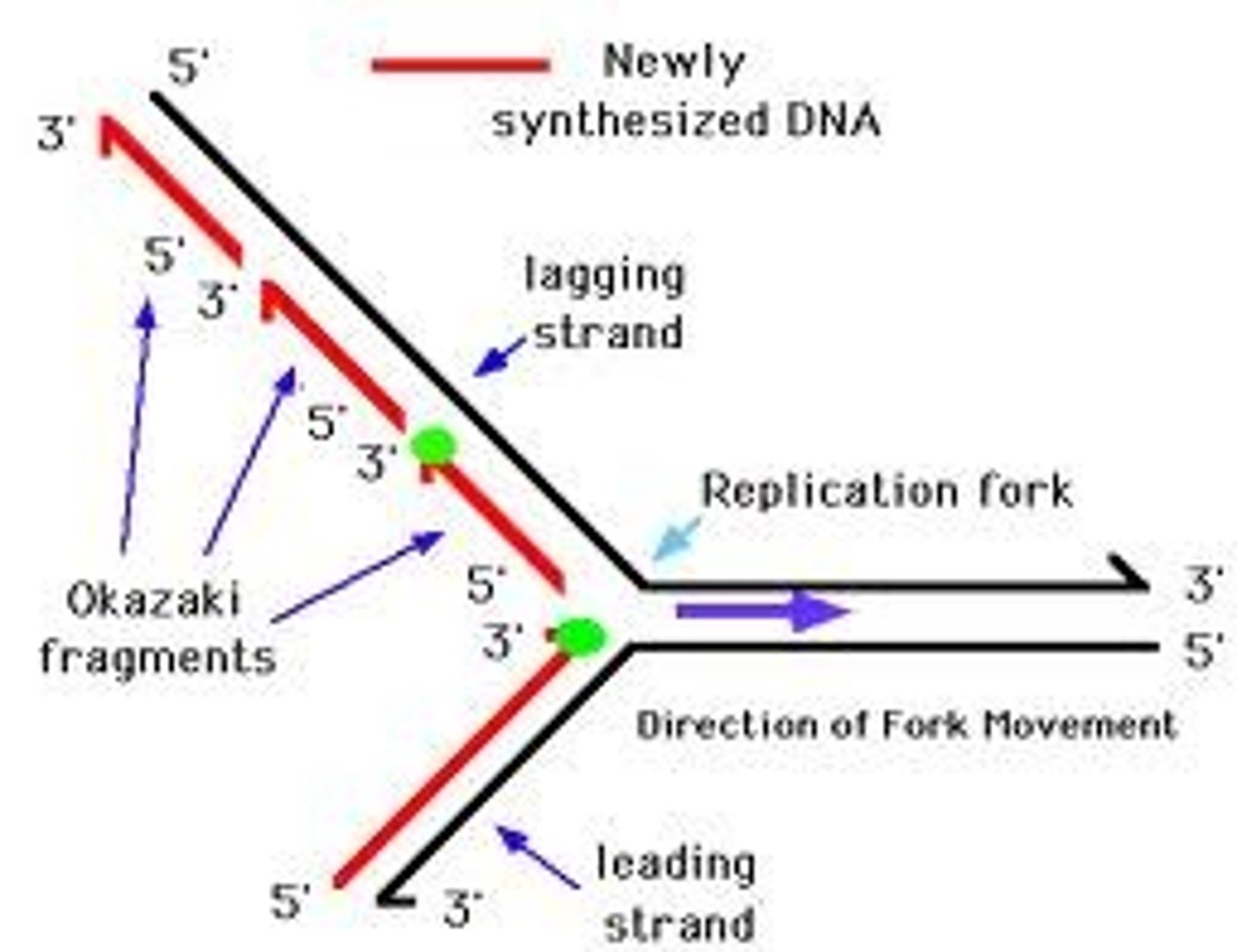
Anti-parallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix. One strand runs 5' to 3' while the other runs 3' to 5'.
semi-conservative replication
Each half of an original DNA molecule serves as a template for a new strand, and the two new DNA molecules each have one old and one new strand.

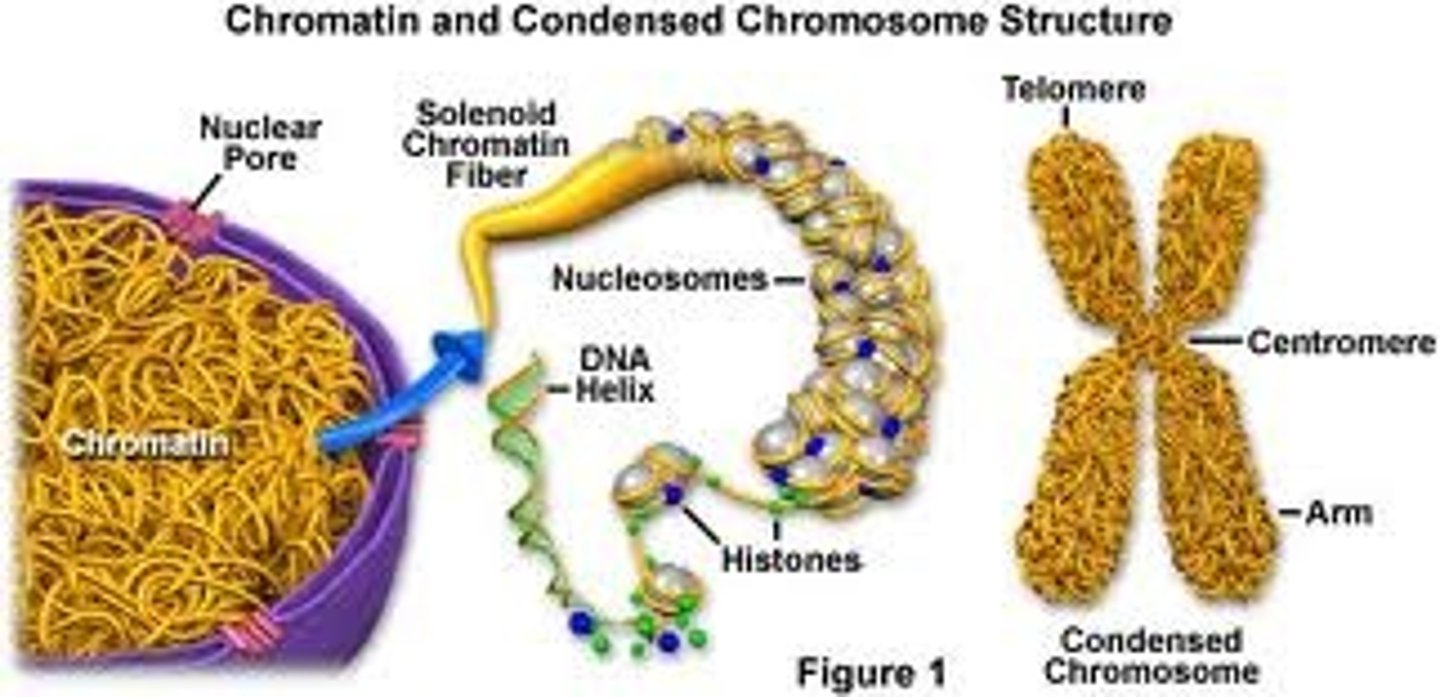
Chromosomes
tightly coiled, threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
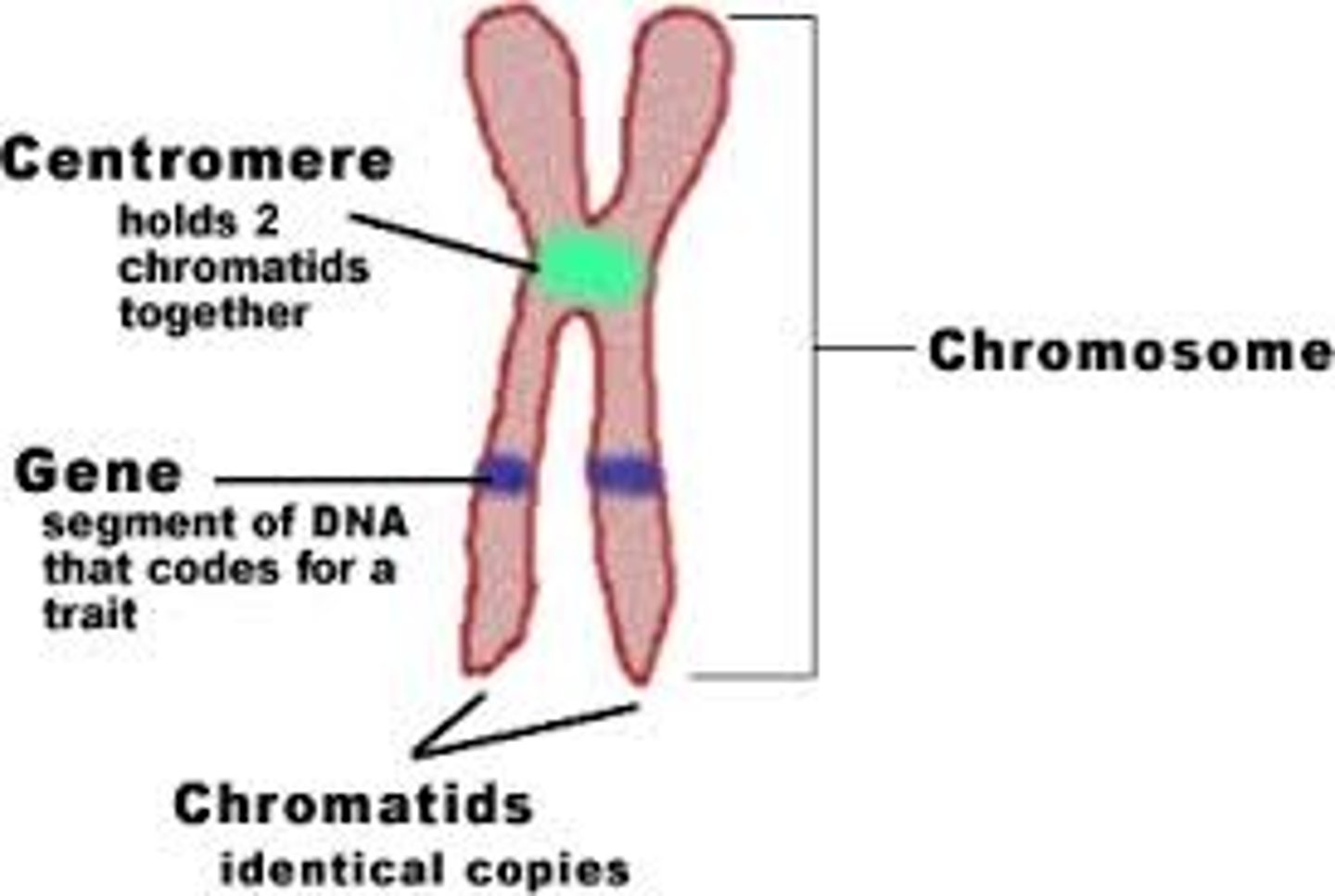
Chromatin
granular material (uncoiled) visible within the nucleus; consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins
RNA
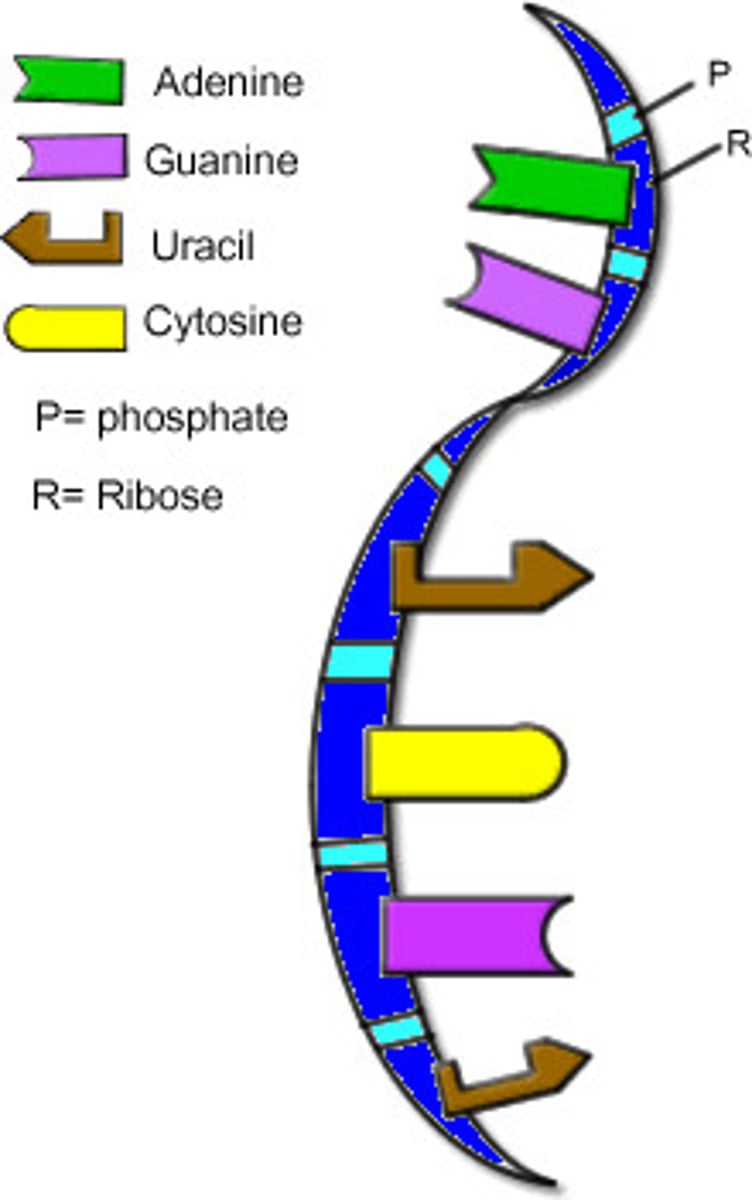
ribonucleic acid
Ribose
sugar in RNA
Uracil
a nitrogen-containing base found in RNA (but not in DNA) and derived from pyrimidine
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome-contains the codon
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
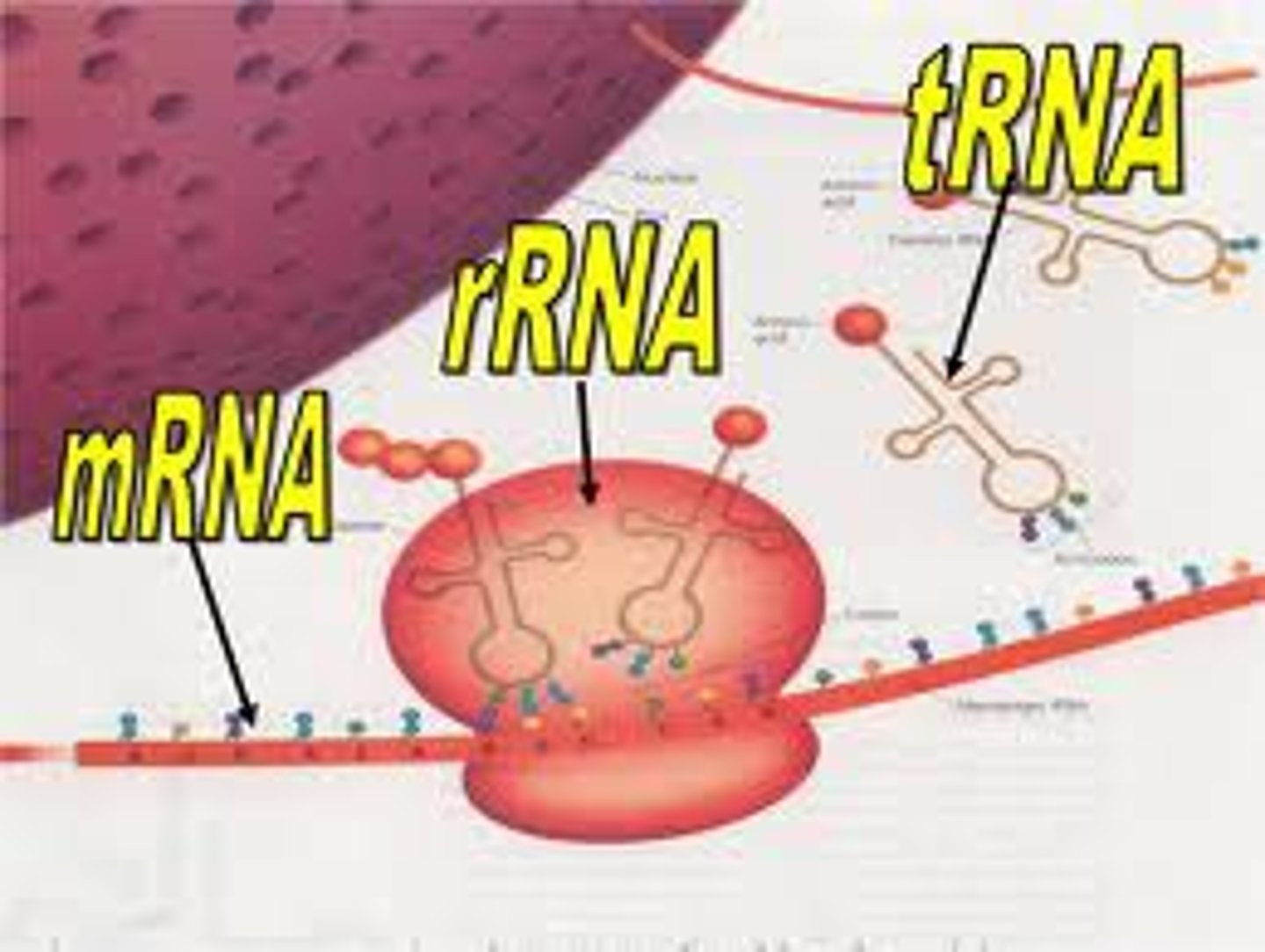
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome-contains the anti-codon