Motivation at work (+ book week 4)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
What is motivational science?
\~ subfield of psychology and neuroscience, interested in why people do what they do (the direction, intensity and persistence of behaviour)
\
→ concerned w/needs, goals, effort, and rewards
\
→ concerned w/needs, goals, effort, and rewards
2
New cards
What is hedonic axiom?
\~ organisms try to obtain positive outcomes and avoid negative ones
\
→ basic assumptions of motivation science
→ __axiom__ \~ fundamental assumption that cannot be tested(bc it is so fundamental it is just common sense sort of)
\
→ basic assumptions of motivation science
→ __axiom__ \~ fundamental assumption that cannot be tested(bc it is so fundamental it is just common sense sort of)
3
New cards
What are the general principles of motivational science?
a. needs
b. goals
c. efforts
d. rewards
\
→ consistent across the fields studying motivation
b. goals
c. efforts
d. rewards
\
→ consistent across the fields studying motivation
4
New cards
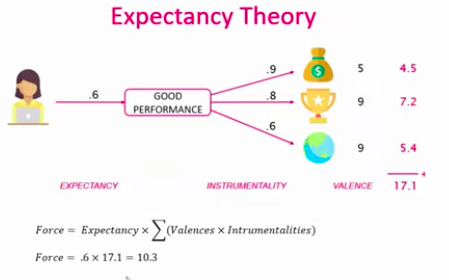
What is valence, instrumentality, and expectancy?
__valence__ \~ idea of how valuable the outcomes of a good performance are (scale 1-10)
\
__instrumentality__ \~ the probability with which people expect their performance to have the outcomes (scale 0-1)
\
__expectancy__ \~ are people able to perform to the level required (probability of reaching that; scale 0-1)
\
force = expectancy \* the sum of (all valence times all instrumentality)
\
→ ppl can choose to perform well or just good enough
\
__instrumentality__ \~ the probability with which people expect their performance to have the outcomes (scale 0-1)
\
__expectancy__ \~ are people able to perform to the level required (probability of reaching that; scale 0-1)
\
force = expectancy \* the sum of (all valence times all instrumentality)
\
→ ppl can choose to perform well or just good enough
5
New cards
when do people choose for the more difficult tasks?
__when__
i. valence is higher
ii. instrumentality is higher
iii. valence \* instrumentality is higher
\
→ supports expectancy theory
→ linked to dopamine systems and mood disorders
→ maybe linked to melatonin-dopamine interaction (decisions made differently in the evening as compared to during the day)
\
\
i. valence is higher
ii. instrumentality is higher
iii. valence \* instrumentality is higher
\
→ supports expectancy theory
→ linked to dopamine systems and mood disorders
→ maybe linked to melatonin-dopamine interaction (decisions made differently in the evening as compared to during the day)
\
\
6
New cards
What is Adam's equity theory?
\~ having a job is similar to being in a relationship (give and take)
\
__que__ → do I get enough in return for all my work?
i. outcomes
ii. inputs
→ own outcomes and inputs compared to the outcomes and inputs of others (outcome/input of self vs outcome/input of a reference => can be our past selves or smb else)
\
__research__ w/monkeys & cucumber/grapes, planes w/business and economy classes & number of fights
\
→ based on cognitive dissonance
\
\
__que__ → do I get enough in return for all my work?
i. outcomes
ii. inputs
→ own outcomes and inputs compared to the outcomes and inputs of others (outcome/input of self vs outcome/input of a reference => can be our past selves or smb else)
\
__research__ w/monkeys & cucumber/grapes, planes w/business and economy classes & number of fights
\
→ based on cognitive dissonance
\
7
New cards
What are the critical notes on equity theory?
i. only about __distributive justice__ (how the outcomes are distributed) as opposed to including also __procedural justice__ (how do you get to the outcome)
\
ii. __non-specific about inputs and outcomes__ → treats money, recognition, … as the same (while they are psychologically different)
\
\
ii. __non-specific about inputs and outcomes__ → treats money, recognition, … as the same (while they are psychologically different)
\
8
New cards
What is goal setting theory?
\~ says that motivation comes from within the person but that the environment can shape motivation and behaviour as well
\
→ behaviour motivated by intentions, motives, and/or goals
\
__important factors for it to be effective__
i. goal commitment
ii. feedback
iii. the more difficult the goal, the better the performance
iv. specific hard goals > vague do your best goals
v. self-set goals > organisationally assigned ones
\
→ behaviour motivated by intentions, motives, and/or goals
\
__important factors for it to be effective__
i. goal commitment
ii. feedback
iii. the more difficult the goal, the better the performance
iv. specific hard goals > vague do your best goals
v. self-set goals > organisationally assigned ones
9
New cards
Why is the word motivation not so useful in science?
\~ bc it is quite general and therefore doesn’t pinpoint a specific psychological process (motivation is a cause of behaviour is super broad)
\
\
\
\
10
New cards
how can expectancy theory be described?
\
\~ analytical way of making predictions of human behaviour based on expectancy, instrumentality and valence
\
__basic assumption__ → brain predicts outcomes of potential actions by making computations which help in decision making
\
__main que__ → what happens in the mind when trying to answer is this worth working for? Is the outcome worth the effort?
\
ppl have some degree of understanding how well they perform and what will happen if they do well
\~ analytical way of making predictions of human behaviour based on expectancy, instrumentality and valence
\
__basic assumption__ → brain predicts outcomes of potential actions by making computations which help in decision making
\
__main que__ → what happens in the mind when trying to answer is this worth working for? Is the outcome worth the effort?
\
ppl have some degree of understanding how well they perform and what will happen if they do well
11
New cards
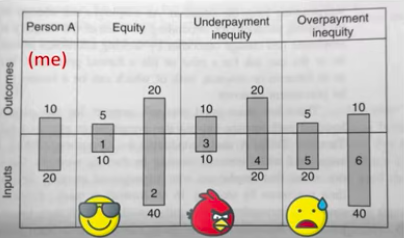
how is (in)equity divided?
a. __equity__ \~ compared to others, I get the same amount of reward for my effort (content)
\
b. __underpayment inequity__ \~ others get more money for the same amount of effort (anger)
\
c. __overpayment inequity__ \~ others get less money for the same amount of effort (shame)
\
__social__ (how fair is it in comparison to others doing the same job) vs __personal__ (did you get as much as you deserved?) equity
\
b. __underpayment inequity__ \~ others get more money for the same amount of effort (anger)
\
c. __overpayment inequity__ \~ others get less money for the same amount of effort (shame)
\
__social__ (how fair is it in comparison to others doing the same job) vs __personal__ (did you get as much as you deserved?) equity
12
New cards
what are the levels of needs assessment and how is it conducted?
\~ done to determine who needs training and what kind of training
\
__levels & how__
i. __organisation level__ \~ analysing the organisation’s objectives and how those are related to the employee performance
\
ii. __job level__ \~ analysing what is the nature of tasks of jobs (major tasks and the KSAOs needed for them)
\
iii. __person level__ \~ analysing how well are people able to do the job tasks
\
\
__levels & how__
i. __organisation level__ \~ analysing the organisation’s objectives and how those are related to the employee performance
\
ii. __job level__ \~ analysing what is the nature of tasks of jobs (major tasks and the KSAOs needed for them)
\
iii. __person level__ \~ analysing how well are people able to do the job tasks
\
13
New cards
what is transfer of training and which factors affect it?
\~ the expectation that employee will apply what they have learnt during the training on the job itself
\
**model of transfer**
\~ how the training design features affect how well trainees learn and therefore how well the training transfers to the job itself
i. __trainee characteristics__
ii. __training design__
→ feedback
→ general principles \~ why and how; framework of learning)
→ identical elements \~ responses in the training should be identical w/those on the job)
→ overlearning \~ overlearning the material so that it consolidates so well that it becomes almost automatic)
→ sequencing \~ *part vs whole* (learning it in parts vs all in one go), *massed vs spaced* (long sessions w/i short period of time vs short sessions over longer period of time)
iii. __work environment__
\
**model of transfer**
\~ how the training design features affect how well trainees learn and therefore how well the training transfers to the job itself
i. __trainee characteristics__
ii. __training design__
→ feedback
→ general principles \~ why and how; framework of learning)
→ identical elements \~ responses in the training should be identical w/those on the job)
→ overlearning \~ overlearning the material so that it consolidates so well that it becomes almost automatic)
→ sequencing \~ *part vs whole* (learning it in parts vs all in one go), *massed vs spaced* (long sessions w/i short period of time vs short sessions over longer period of time)
iii. __work environment__
14
New cards
What are the eight different training methods and their advantages?
a. __audiovisual construction__ \~ electronic presentation of materials (audio, video, …)
\
b. __autoinstruction__ \~ self-paced training method w/o an instructor (e.g., *programmed instruction* → chunks/frames of material w/questions and feedback that a person goes through on their own)
\
c. __conference__ \~ trainer meets w/trainees and can discuss the material and ask questions (active learning)
\
d. __lecture__ \~ trainee gives a presentation to a group of trainees (efficient)
\
e. __modelling__ \~ watch smb perform a task and then model what has been seen (live/recorded; effective/ineffective behaviour)
\
f. __on the job training__ \~ showing how to do a job while the employee is doing it (e.g., apprenticeship)
\
g. __role play__ \~ pretending to do a task as if it was real (part of the modelling procedure)
\
h. __simulation__ \~ pretending as if the situation is real, with all the same equipment and all, carrying out the tasks as they would in real life
\
→ __computer games__ also found to be effective
\
b. __autoinstruction__ \~ self-paced training method w/o an instructor (e.g., *programmed instruction* → chunks/frames of material w/questions and feedback that a person goes through on their own)
\
c. __conference__ \~ trainer meets w/trainees and can discuss the material and ask questions (active learning)
\
d. __lecture__ \~ trainee gives a presentation to a group of trainees (efficient)
\
e. __modelling__ \~ watch smb perform a task and then model what has been seen (live/recorded; effective/ineffective behaviour)
\
f. __on the job training__ \~ showing how to do a job while the employee is doing it (e.g., apprenticeship)
\
g. __role play__ \~ pretending to do a task as if it was real (part of the modelling procedure)
\
h. __simulation__ \~ pretending as if the situation is real, with all the same equipment and all, carrying out the tasks as they would in real life
\
→ __computer games__ also found to be effective
15
New cards
how are trainings evaluated?
__**five steps**__
i. __define criteria for evaluation__
→ __training-level criteria__ (*reaction* - how much they liked it, *learning* - what they have learnt)
→ __performance-level criteria__ (*behaviour* - do they do what they were taught, *results* - did the training have the intended effect)
ii. __choose design__ \~ how do you collect the data (pre/post test, control group, …)
iii. __choose measures of the criteria__ \~ reaction criteria → questionnaire; learning criteria → test at the end
iv. __collect data__
v. __analyse and interpret data__
\
→ if training works at both training and performance level, it is effective
i. __define criteria for evaluation__
→ __training-level criteria__ (*reaction* - how much they liked it, *learning* - what they have learnt)
→ __performance-level criteria__ (*behaviour* - do they do what they were taught, *results* - did the training have the intended effect)
ii. __choose design__ \~ how do you collect the data (pre/post test, control group, …)
iii. __choose measures of the criteria__ \~ reaction criteria → questionnaire; learning criteria → test at the end
iv. __collect data__
v. __analyse and interpret data__
\
→ if training works at both training and performance level, it is effective
16
New cards
How can work-motivation theories be divided?
a. __expectancy theory__ \~ relates environmental rewards to behaviour
b. __self-efficacy theory__ \~ looks at how ppl’s beliefs about their capability affect their behaviour
c. __justice theories__ \~ concerned w/ppl’s values, presuming they generally value fairness (unfairness motivates ppl to resolve it)
d. __goal-setting theory__ \~ how ppl’s goals and intentions lead to behaviour
e. __cognitive control theory__ \~ focus on goal w/attention on feedback and how discrepancies between goals and current situation motivate behaviour
f. __action theory__\~ explains self-motivated and voluntary (volitional) behaviour at work
\
→ __distal__ (processes far from behaviour, needs) vs __proximal__ (processes close to the behaviour, goals/intentions) __motivational theories__
b. __self-efficacy theory__ \~ looks at how ppl’s beliefs about their capability affect their behaviour
c. __justice theories__ \~ concerned w/ppl’s values, presuming they generally value fairness (unfairness motivates ppl to resolve it)
d. __goal-setting theory__ \~ how ppl’s goals and intentions lead to behaviour
e. __cognitive control theory__ \~ focus on goal w/attention on feedback and how discrepancies between goals and current situation motivate behaviour
f. __action theory__\~ explains self-motivated and voluntary (volitional) behaviour at work
\
→ __distal__ (processes far from behaviour, needs) vs __proximal__ (processes close to the behaviour, goals/intentions) __motivational theories__
17
New cards
What are the two needs theories?
\~ motivation is seen as a result of people’s desires for smth
\
a. __need hierarchy theory__ \~ Maslow, needs fulfilment necessary for overall health/wellbeing (need must be unmet to be motivating)
\
b. __two-factor theory__ \~ motivation comes from the nature of the job, not the rewards
\
a. __need hierarchy theory__ \~ Maslow, needs fulfilment necessary for overall health/wellbeing (need must be unmet to be motivating)
\
b. __two-factor theory__ \~ motivation comes from the nature of the job, not the rewards
18
New cards
how are job satisfaction and organisational commitment different?
\~ organisational commitment focuses on the attachment of the individual to the organisation rather than on whether or not they are satisfied w/the job
\
→ job satisf. assessed w/questionnaires or an interview (que > interv)
\
→ job satisf. assessed w/questionnaires or an interview (que > interv)
19
New cards
what are the types of organisational commitment?
a. __affective__ \~ emotional attachment as a motivation to stay in a job
b. __continuance__ \~ need of the benefits/lack of alternatives motivating the person to stay in the job
c. __normative__ \~ ppl believe they owe it to the organisation to stay as it is the right thing to do
\
→ assessed based on these three subtypes w/a questionnaire
b. __continuance__ \~ need of the benefits/lack of alternatives motivating the person to stay in the job
c. __normative__ \~ ppl believe they owe it to the organisation to stay as it is the right thing to do
\
→ assessed based on these three subtypes w/a questionnaire
20
New cards
how are emotional states different from moods?
\~ __emotional state__ is the immediate experience of an emotion while a __mood__ is a long-term, less specific state w/a positive or negative direction