DILD and DM- Austin- EXAM 3
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is a xenobiotic?
a foreign substance to the body (ex: drug)
Where is the primary site of metabolism? Where are other sites?
primary- liver
other: GI wall
How many phases to metabolism are there? What type of reactions belong to each?
Phase I- oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis
Phase II- conjugation
Phase I produces what kind of metabolites?
inactive, active, or TOXIC
Phase II produces what kind of metabolites?
inactive, NONTOXIC
What is the rate of phase I and phase II reactions? slow or fast
phase I- slow
phase II- fast
What is the capacity of phase I and phase II reactions?
phase I- infinite
Phase II- limited
What are the requirements for an oxidation reaction?
oxidizing agent (O2)
enzyme
substrate/drug
sometimes cofactor
What ENZYMES are used in oxidation reactions?
CYTOCHROME P450 SUPERFAMILY aka CYP enzymes
others: MAO, FMO, ADH
What are some common examples of oxidation reactions?
aliphatic/aromatic hydroxylation
N or S oxidation
N, O, S dealkylation
N-deamination
Why is there only N or S oxidation and not O oxidation?
can’t oxidize an oxygen
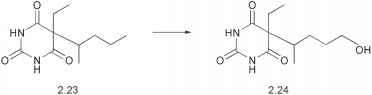
What type of reaction is this:
aliphatic hydroxylation
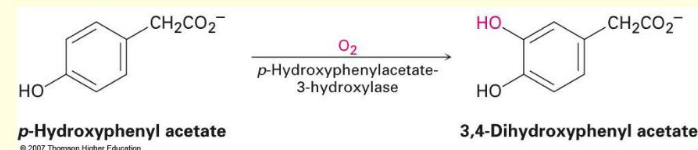
What type of reaction is this:
aromatic hydroxylation
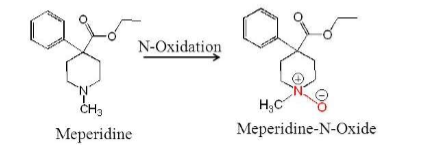
What type of reaction is this:
N-oxidation
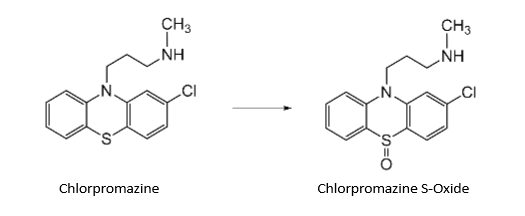
What type of reaction is this:
S-oxidation
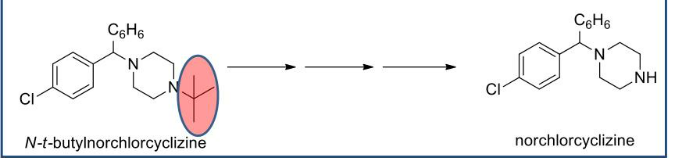
What type of reaction is this:
N-dealkylation
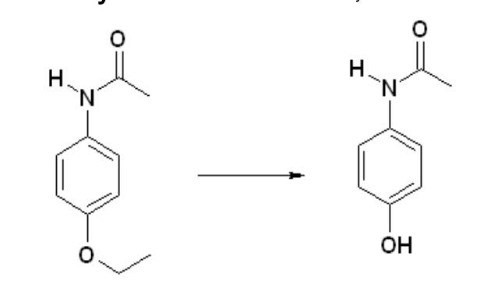
What type of reaction is this:
O-dealkylation
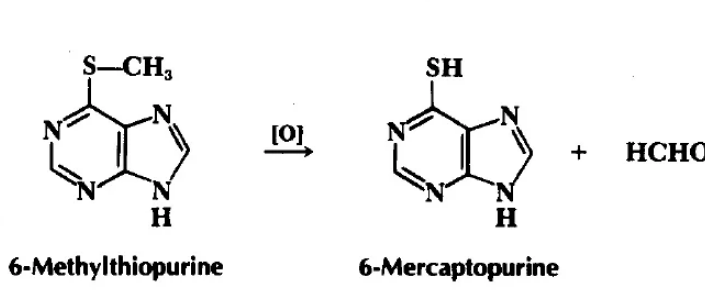
What type of reaction is this:
S-dealkylation
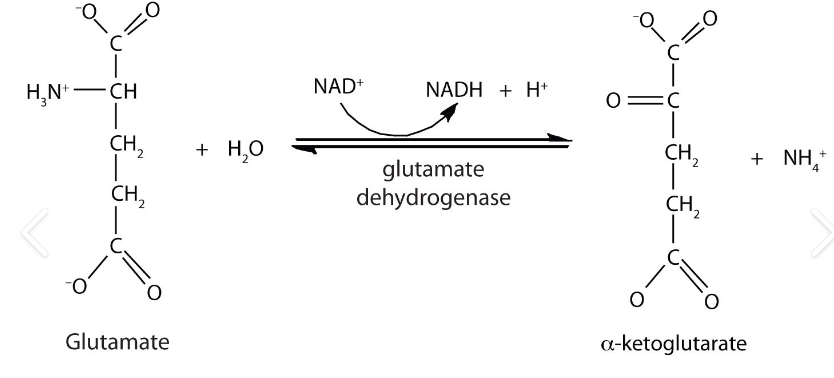
What type of reaction is this:
Deamination
Hydrolysis is another type of Phase I reaction. What groups does this usually occur on?
esters and amides
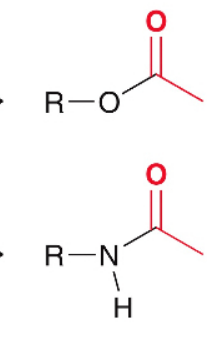
What type of reaction is this:
hydrolysis (ester)
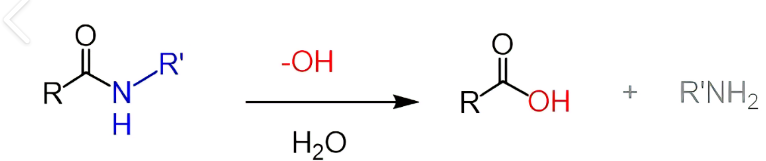
What type of reaction is this:
hydrolysis (amide)
What is a conjugation reaction?
attaching hydrophilic molecules to drug molecules/metabolites by formation of a covalent bond
In a phase II conjugation reaction, the conjugate usually replaces…
a hydrogen covalently bonded to a heteroatom
A conjugation reaction requires a ____________ enzyme.
transferase
What are some examples of conjugates?
glucuronate- MOST COMMON
glutathione
others: sulfate, AA, acetyl, methyl
What enzyme is needed in a glucuronidation?
UDP glucuronosyltransferase
What do phase II reactions require?
conjugate
drug
transferase enzyme
What are the 6 mechanisms of toxicity in DILD?
stimulation of autoimmunity
idiosyncratic rxns
disruption of Ca++ homeostasis & cell membrane injury, transport proteins & cell communities
cytochrome P450 mediated
mitochondrial injury
liver neoplastic disease
What are the 2 MECHANISMS that stimulate autoimmunity? (this leads to DILD)
enzyme-drug adducts migrate to cell surface and form neoantigens
happens immediately and are targeted by Kupffer cells and cytotoxic killer T-cells
chronic active hepatitis- takes long time
takes long time and formation of anti-organelle and antinuclear Abs
What drugs are associated acute autoimmune injury ?
TNF-a inhibitors
carbamazepine
fluoroquinolones
halothane
nevirapine
sulfamethoxazole
What drugs are associated with chronic active hepatitis?
dantrolene
isoniazid
methyldopa
nitrofurantoin
phenytoin
trazodone
What are the 2 types of idiosyncratic rxns? What are some examples of drugs that belong to each?
allergic (HLA phenotypes)- minocycline, augmentin, allopurinol
nonallergic- amiodarone, ketoconazole
What drugs can cause a disruption of Ca++ homeostasis and cell membrane injury and lead to DILD?
lovastatin and venlafaxine
What drugs can effect transport proteins and cell communities and lead to DILD?
glimepiride (inhibit BSEP) and metformin (MATE2)
What are Kupffer cells?
local immune cells—> macrophages that help remove debris and initiate the immune response
What are some drug examples of cytochrome P450 mediated DILD?
Acetaminophen
furosemide
diclofenac
How is APAP normally metabolized? (include all 3 pathways)
80-90% goes glucuronidation and conjugation
other 10% goes through OXIDATION and forms the toxic metabolite NAPQI
NAPQI is inactivated by glutathione
What happens in toxic/large doses of APAP?
phase II is saturated/ more APAP goes thru oxidation pathway
not enough glutathione to inactivate the toxic metabolite NAPQI
Why is the risk of hepatotoxicity with APA higher if you drink alcohol?
lowers toxic threshold
give preference to NAPQI
The max daily dose of APAP is ___ g.
4
What is the antidote to APAP? How does it act?
N-acetylcysteine- acts like glutathione
What are some drug examples that can cause mitochondrial injury and lead to DILD?
aspirin
valproic acid
What are some drug examples that can cause liver neoplastic disease and lead to DILD?
androgens, estrogens, and other hormone agents
THINK: HORMONE DRUGS