Mammology Lab Practical : Primates and Carnivores
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Primate Characteristics
Five digits on hands and feet
opposable thumbs and big toes
generalized heterodont dentition
Tactile pads on fingers, toes, and sometimes tails
nails used instead of claws
foreamen magnum under the skull
eyes facing forward, depth perception through stereoscopic vision
visual information processed by both hemispheres of brain
decreased sense of smell
Canine honing
main function: to engage in competition and display in sexually dimorphic species
groove is formed in upper canine where the lower one has worn it away
Canine diastema
Space for canine to fit in low jaw, usually more prominent in groups with higher sexual dimorphism
Haplorhini
Old world monkeys and new world monkeys
no rhinarium
more mobile, continuous dry upper lip
relatively short rostrum
plate separating orbitals from temoral fossa
Strepsirhini
Lemurs, lorises, Aye-Ayes
Rhinarium - moist, hairless fur patch of skin that surrounds the nostrils
Has grooming claw
Has dental comb
post orbital bar
No plate separating orbitals from temporal fossa
Grooming claw
made of keratin
used for grooming and scratching, cleaning, etc
Tarsiers from Haplorhini have this too
Dental Comb
incisors of the mandibular canine come together to form tooth comb
used for oral grooming
can also be useful for accessing various food resources
Ethology
Study of animal behavior
What causes animal behavior
External environment = rain, heat, cold, etc
internal environment = Hormones, disease, parasites
Ad lib sampling
Behaviors are recorded as their observed
Time | Behavior Category | Specific Behavior | Behavior Definition |
01:22- 01:54 | Feeding Behavior | Monkey 1 - Ingesting food (nut), Monkey 2- begging for food unsuccessfully | Begging for food- monkey approaches another monkey with food and stares at food item while in close contact with second monkey. |
01:54-02:15 | Feeding Behavior | Monkey 1- ingesting food (onion), Monkey 2- begging for food successfully |
|
Focal sampling
surveys just one individual in the group for a specific amount of time and their behavior is recorded
Focal Sampling Exercise “Popeye” | ||
Behavior Category | Specific Behavior | Behavior Definitions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scan Sampling
Surveys the entire group at regular intervals and each behavior is recorded during the scan
-Record what each animals is doing every 30 seconds for 5 minutes
Carnivore characteristics
Fourth upper premolar (P4) and first lower molar (M1)
Cylindrical canines
Mandibular condyle transverse nearly locked into socket
2 suborders of Carnivora
feliformia and Caniformia
Suborder: Feliforma
Felidae (cats)
Puma Concolor
Lynx Rufus
incisors are small, arranged in a transverse line, face short and broad
Divided bullae
Puma Concolor

Lynx rufus
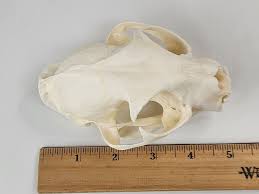
Bobcat
Suborder: Caniformia
Families: Canidae, Ursidae, Procyonidae, Mustelidae, Mephitidae,
Canidae
Elongated rostrum
Molars have a crushing surface
Canis lantrans
Canis lupus
Vulpus Vulpus
Vulpus Macrotis
Urocyon Cinereoargentus
Canis Latrans

Coyote
Canis Lupus

Grey Wolf
Vulpus Vulpus
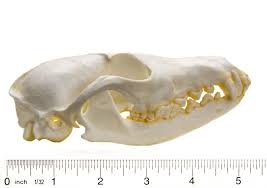
Red Fox
Vulpus Macrotis
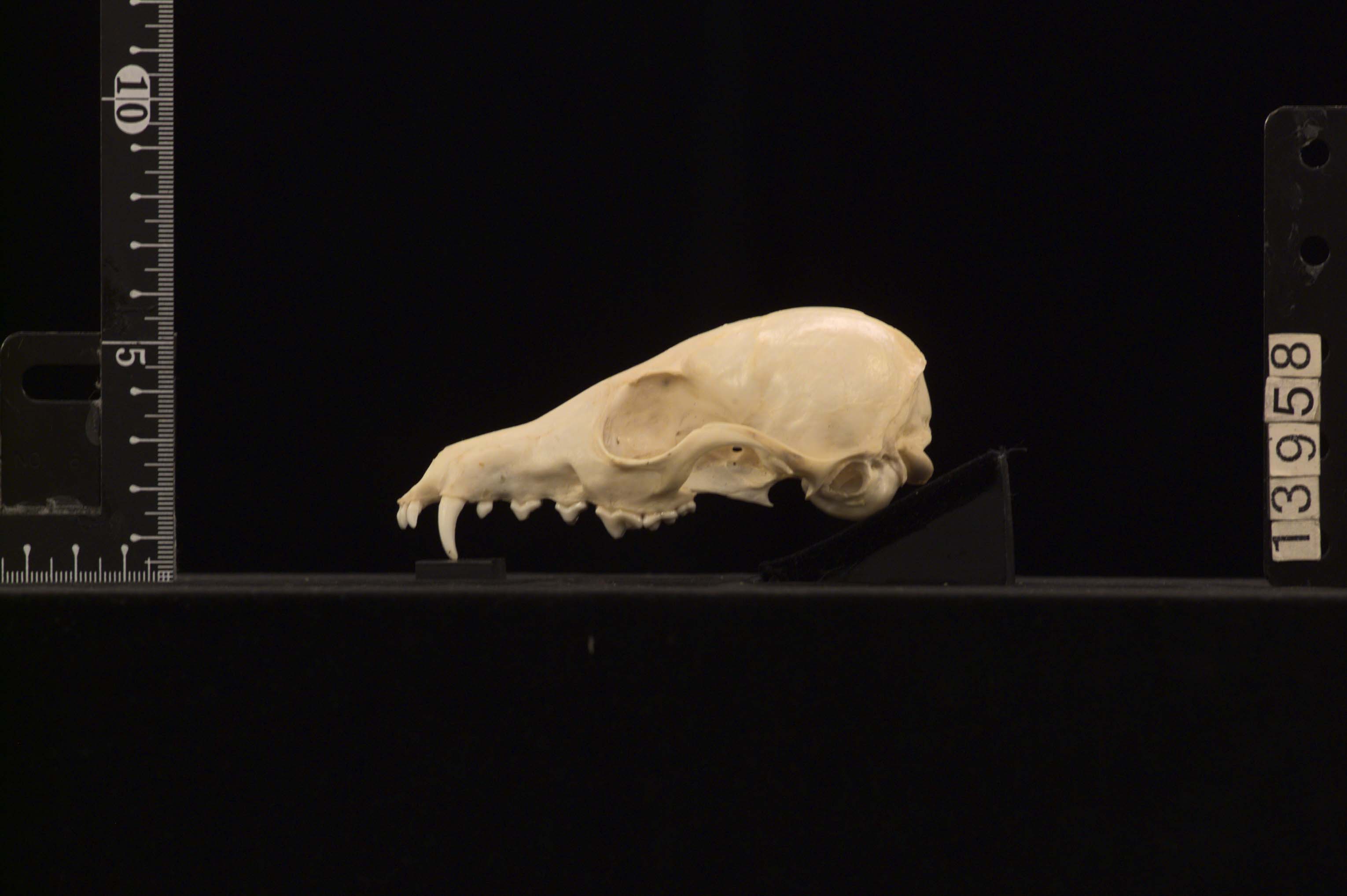

Kit Fox
Urocyon Cinereoargentus
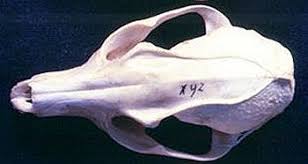
Gray Fox
Family: Ursidae
Molars Bunodont
First 3 molars are rudimentary or lost
weakly developed carnassial
Prominant sagittal crest
Ursus Americanus
Ursus Americanus

Black Bear
Family: Procyonidae
Canines oblong in cross-section
premolars pointed and small
Carnassial poorly developed
Molars broad and some what bunodont
Procyon lotor
Bassasariscus asustus
Procyon lotor

Raccoon
Bassariscus astutus

Ring Tail
Family Mustelidae
Facial region of the skull very short
Premolars small, Carnassial usually well-developed
Mustela frenata
Taxidae taxus
Lontra canadensis
Mustela frenata
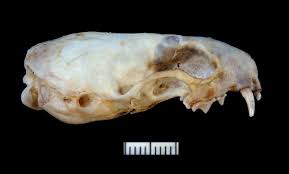
Long tailed weasel
Taxidae taxus

American Badger
Lontra canadensis
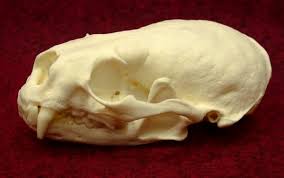
river otter
Family: Mephitidae
Cheek teeth tuberculo-sectorial (partially modified for omnivorous diet)
Mephitis mephitis
Spilogale gracilis
Conepatus leuconotus
Mephitis mephitis
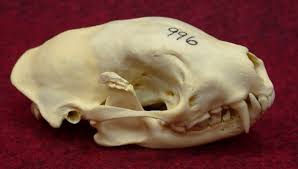
Striped Skunk
Spilogale gracilis
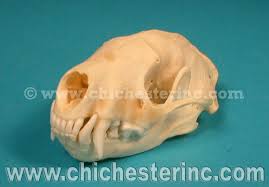
Western Spotted skunk
Conepatus leuconotus
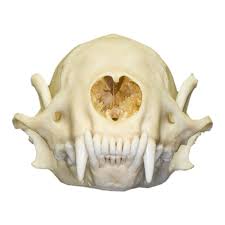
hog nosed skunk
Simple measurements from camera trapping
detection frequency - one image of an animal per day
activity patterns - when animals were active during different times of the day
detection rate - total number of photos of species divided by total time camera was running
Species richness - total number of species detected during the study
Relative abundance index - summing of all detections of each species for all camera traps multiplied by 100 and divided by total # of camera trap days
not-so-simple camera trap measurements
Density - mark-recapture - if animals can be identified
Large datasets - more practical to use computer program software programs to analyze data
camera trap field placement
-select trees that wont blow in the wind
-ground level w/ no obstructions
-avoid direct sunlight
-positions camera down the path, not perpendicular
-consider the height of animals
-make sure data and time stamp are visible in the frame
-secure camera in tree with wire and chains to prevent theft
-test your camera by walking in front of it