Empirical Marketing - Week 4
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is offering?
Offering is a purposely broad term that captures tangible products and intangible services provided by firms.
What is innovation?
- Innovation is a creation of substantial new value for customers and the firm by creatively changing one or more dimensions of the business.
- Innovation is a critical precondition for all organizations to survive precondition: firms must have innovation in order to survive.
What are the key aspects of innovation?
· Broader than product or technology innovation
· Must generate new value for customer and seller
· Involves change leading to differentiation and SCA
· How did Starbucks, Dell, and IPod create value and SCA?
How can a firm innovate?
· Change what the firm offers: seeks new product, service, offering, platform or solution innovations.
· Changing who the customer is: seeking innovations related to customers, experiences, value capture.
· Changing how you sell to the customers: processes, organizations, supply chains that it uses.
· Changing where you sell to the customers: presence, networking, and brand innovations.
What is innovation radar?
A framework that captures the many ways a firm can innovate by defining the innovation space by what, who, how, and where aspects.
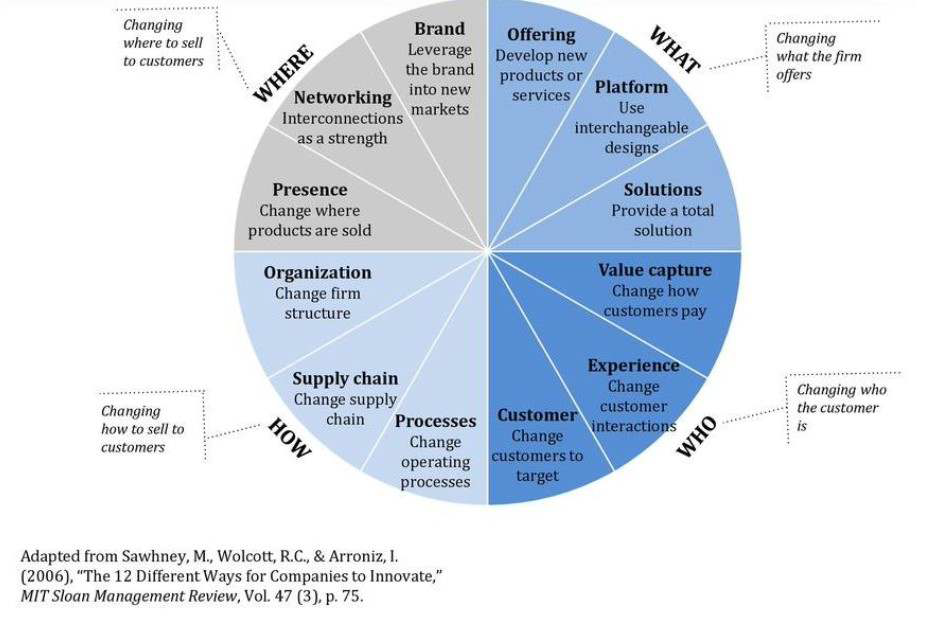
Describe the innovation radar Starbucks?
The red shape in the radar shows Starbucks’ relative strength across these dimensions. A more extended shape along a particular axis indicates greater innovation in that category. In the radar:
- Starbucks shows strong innovation in offering and customers (e.g., brand strength, customer experience).
- Presence and process innovation are moderately developed, reflecting ongoing but less emphasized innovations in these areas compared to the others.
How can marketing contribute to and define offering and innovation strategies?
Launch new offerings to generate sales with acceptable profit levels.
Develop innovative offerings by collecting customer input and forecasting market trends
Many good products fail to achieve their financial objectives due to poor product launches.
Extensive efforts go into test marketing and understanding the factors that will influence whether customers adopt a new offering and increase the likelihood of a successful launch.
To manage offering - based sustainable competitive advantages, we use launching and diffusing innovation strategies, what are the three drives of adoption?
People: users with different propensities to adopt new products
Psychology: what are the sources of persuasion?
Products: specific product characteristics may help or hinder adoption
In 3 drivers of adoption, what is people consist of?
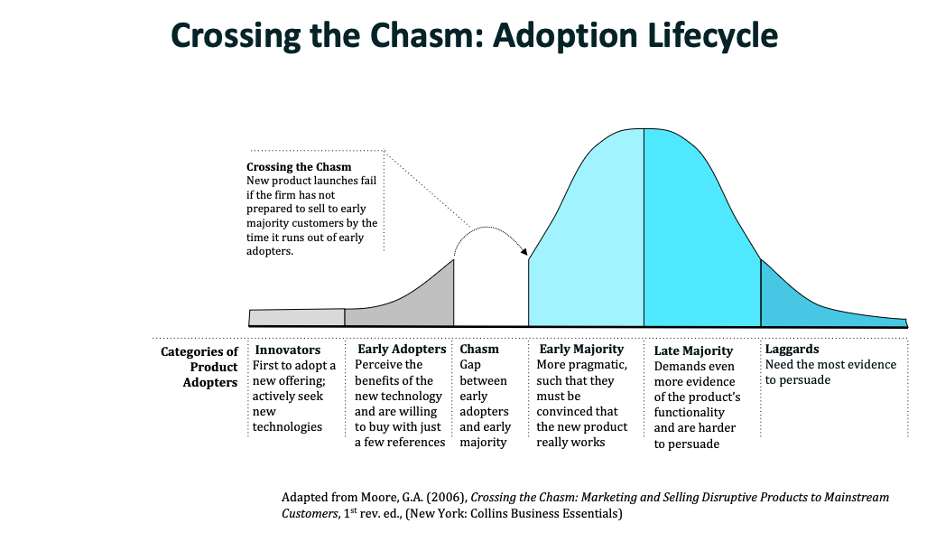
The adoption lifecycle: a model that describes the timeline and pattern of adoption of a new product, service, or innovation that generally follows a normal distribution.
The adoption cycle of an innovative offering suggests 5 groups of potential users:
- Innovators: first to adopt, often before the new offering even is officially launched
- Early adopters: see the benefits of the new technology and are willing to adopt it after just a few references.
- Early majority: pragmatic consumers, who need to be convinced that the new product really works. They demand evidence and a full range of supporting materials, unlike the previous two groups.
- Late majority & laggards: want more evidence and are especially hard to persuade.
What does it mean crossing the chasm in the people drivers of adoption?
Label given to the process of a new firm successfully moving from early adopters to majority groups.
In 3 drivers of adoption, what is psychology consist of?
Social proof: looking at others is a way we determine what to do.
More people, larger belief it is correct.
More similar people, larger impact on behavior.
Authority: we have a deep-seated sense of respect for authority and status.
Scarcity: things seem more valuable when their availability is limited.
Prospect theory: perceived value for an objective gain or lost.
In 3 drivers of adoption, what is product consist of?
- Relative advantage: degree to which an offering is perceived as being better than the ideas it supersedes:
· Economic: cost, price
· Status, prestige, etc.
· Although a relative advantage is a necessary condition for product adoption, it is not a sufficient one.
- Compatibility: degree to which an offering is perceived as consistent with existing values and experiences
· Often must break habits, perceptions, beliefs.
· ie plastic wine corks
- Complexity: degree to which an offering is perceived as relatively difficult to understand/use
· Education is key (online banking)
· Speed and easy use of Google
- Trialability: degree to which an offering may be experimented with a limited bias:
· Free samples, demo, test drive
· Especially salient for high cost, time, risky products
- Observability: degree to which the results of an offering are visible to others:
· Especially salient for status products
· Can be negative (parking by a “men’s club”)
If the firm can optimize the people-based and product-based factors associated with its new offering, it will greatly increase the likelihood of its launch success, as well as its offering equity.
In the offering and innovation strategies, what is repositioning and disruptive innovations
An innovative offering can result from dramatically repositioning an existing offering, such as removing some features or adding others, so that the total offering appeals to a different customer segment with a “new” value proposition
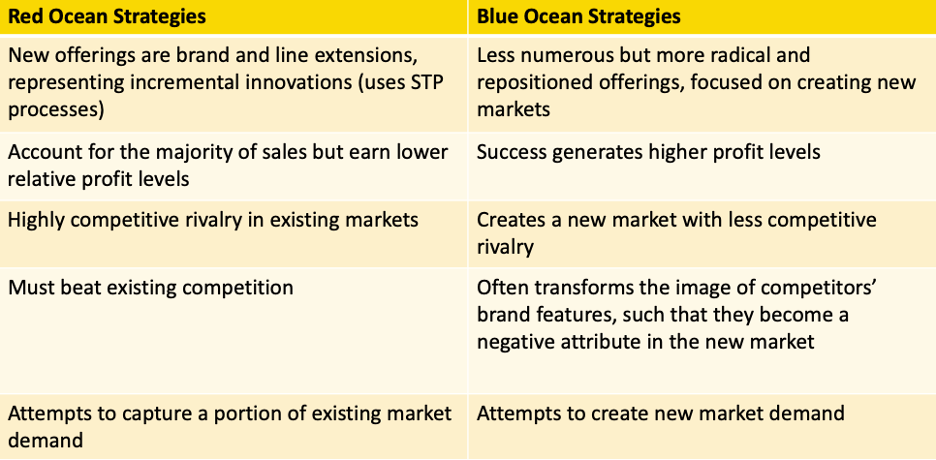
Classic STP focuses on red ocean strategies:
· Known market space, competitive rules and industry boundaries (lifecycle mindset).
· Product mature and become commodities.
· Can be managed, tested and analyzed.
Disruptive positioning focuses on the blue ocean:
· Market space does not exist (unknown boundaries)
· Demand is created rather than fought over (often no direct competition)
· Hard to test, more of an art, often requires intuition, high risk.
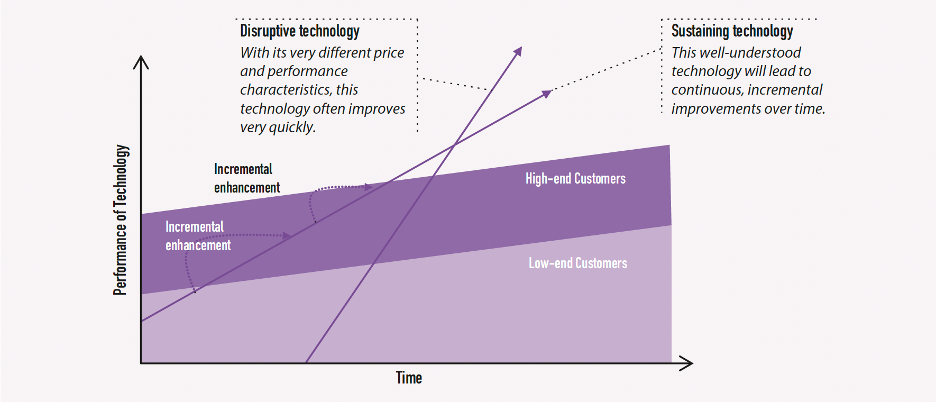
What is sustaining versus disruptive innovation?
They are technology based innovation strategies.
A technological innovation can undermine a firm’s leadership position in a market, even if that firm is doing everything else well.
What are the 2 main categories of these technologies?
· Sustainable technologies are well understood and typically exploited by market leaders, which produce continuous, incremental improvements over time.
· Disruptive technologies accordingly present highly different price and performance characteristics or value propositions.
Do sustainable technologies improve or worsen performance of firm?
Sustainable technologies improve performance of established products along dimensions valued by mainstream customers in major markets:
· Products often overshoot customer needs.
· Processes support incremental product improvements (lower risk).
Do disruptive technologies improve or worsen performance of firm?
Disruptive technologies result in “worse” performance in short term:
· Brings to market a different value proposition than available previously.
· Underperforms established products in mainstream markets.
· Typically cheaper, simpler, smaller, or more convenient to use.
· Small off-road motorcycles and transistor radios
· Eventually are good enough (servers vs mainframes)
Why do market leaders fall into this trap?
- Companies find it difficult to invest in disruptive innovations – lower margin opportunities that their customers don’t want.
- Growth targets bias firms toward larger markets
- Markets for disruptive innovations cannot be qualified
- Competition leads to oversupplying performance relative to what customers want.
Solution: set up an autonomous organization tasked with building an independent business around disruptive innovations in parallel.
What is the state gate design review process for effective product development?
This is the process that most firms rely on to increase the speed of their offering development and enhance their likelihood of success, while also reducing their development costs.
What are the steps in the state gate design?
- First, in each stage, the feasibility of the new development project is evaluated from multiple perspectives: customer, technology, financial, and operations, for example.
- Second, in each review stage, evaluators who determine if the project will continue cannot be members of the project team. This ensures the independence of the process and avoid bias. A designer’s curse: bias that once developers or designers accept some new feature, they perceive its great value – far more than would be assigned the feature by non-users. Behavioral insights:
· Endowment Effect: Once consumers adopt a feature, they tend to overvalue it.
· Loss Aversion: Consumers may resist new products if they fear losing existing features, even if the new product offers gains.
- Thirdly, projects that fail to meet criteria are canceled early, preventing resource waste. This allows firms to allocate resources more effectively and avoid development bottlenecks. But the challenges for radical innovation: incremental innovations pass stage-gate reviews more easily due to lower risks, radical innovations may struggle due to their novelty and higher uncertainty.
- Alternative approaches:
· Some firms create dedicated teams or skunk works for radical innovations, bypassing the rigid stage-gate process.
· Others adopt jugaad innovation, a flexible, frugal approach focused on quick, unconventional solutions for creative problem-solving.
What is conjoint analysis?
Conjoint analysis: process for determining the “unit-less” tradeoff among attributes and set of attributes that maximizes appeal (sales, share)
What are two main stages of conjoint analysis?
Conjoint design: attributes and levels, type of conjoint, selecting profiles.
Conjoint analysis: recovering part-worth utilities, identify segments