1.3 Aquatic Biomes
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Characteristics of water that help organisms
Water has a high thermal capacity, so most aquatic organisms don’t rely much on temp. regulation
Water provides buoyancy and reduces organisms need for support structures(legs, trunks)
Water screens out UV radiation
Salinity
How much salt there is in a body of water, determines which species can survive and usability for drinking
Depth
Influence how much sunlight can penetrate and reach plants below surface for photosynthesis
Flow
Determines which plants and organisms can survive, how much O2 can dissolve in water(rapidly moving bodies of water allow for better mixing between Oxygen and water)
Temperature
Warmer water holds less O2 so it can support fewer aq. organisms
Why are lakes important?
They are standing bodies of fresh H2O(key drinking water source)
Why do rivers have high O2?
Due to flow(high mixing of air and water)
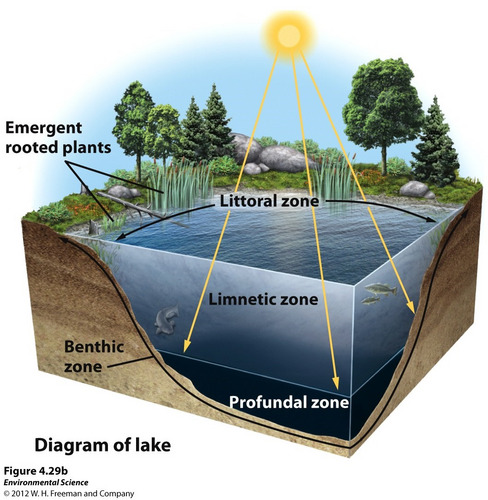
Littoral zone(lake zones)
shallow water w/ emergent plants
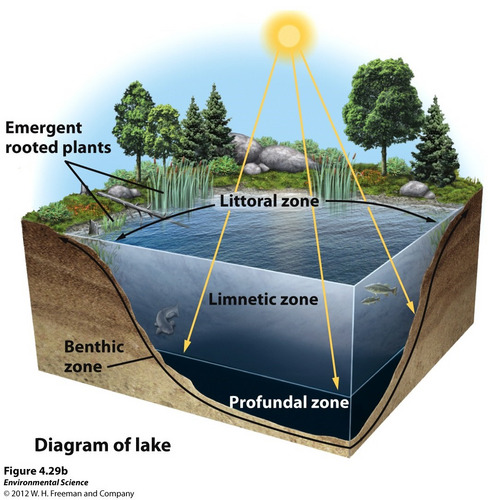
Limnetic zone(lake zones)
Where light can reach(photosynthesis)
No rooted plants, only phytoplankton
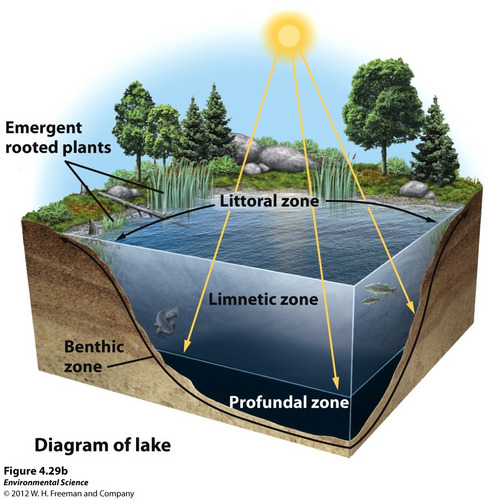
Profundal zone(lake zones)
Too deep for sunlight, no photosynthesis
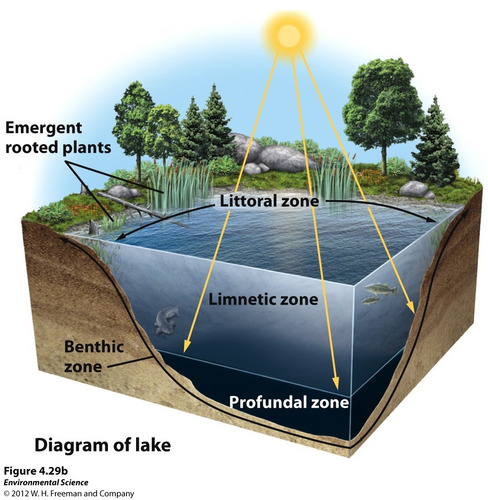
Benthic zone(lake zones)
Murky bottom where bugs live, nutrient rich sediments
Wetland
Area with soil submerged/saturated water in front for at least part of the year but shallow enough for emergent plants
Plants living here have to be adapted to living with roots submerged in standing water
Benefits of wetlands
Store excess water during storms, lessening floods
Recharges groundwater by absorbing rainfall into soil
Roots of wetland plants filter pollutants from water draining through
High plant growth due to lots of water and nutrients in sediments
Estuaries
areas where rivers empty into the ocean(ex: salt marsh, mangrove swamps,
Mix of fresh and salt water
High productivity due to nutrients in sediments deposited in estuaries by river
Coral Reef
Warm shallow waters beyond the shoreline; most diverse ocean biome on earth
Features mutualistic relationship between coral(animal) and algae(plants)
- Algae live in the reef and provide sugar for the corals and algae get a home and CO2 from the corals
Intertidal Zones
Narrow band of coastline between high and low tide
Organisms must be adapted to surviving crashing waves and direct sunlight during low tide
-Shells and tough outer skin can prevent drying out during low tides
Different organisms are adapted to live in different zones
Mangrove swamps(esutaries near coast):
stabilize shoreline
provide habitat for many fish and shellfish
Open Ocean
Low productivity per unit of area as only phytoplankton and algae can survive in most of ocean
Large size makes algae and phytoplankton a big producer of O2 and ocean also absorbs a good chunk of CO2
Ocean zones
Photic zone: Area where sunlight can reach
Aphotic zone: Area too deep for sunlight → many organisms in this area rely on bioluminescence to navigate and are also well adapted to sustain really high pressures
Ocean Conveyor Belt
A global system of ocean currents that circulates heat and nutrients around the Earth.
It is driven by differences in temperature and salinity
The conveyor belt begins in the North Atlantic, where warm, less dense water flows northward, cools, and sinks. This cold, dense water then spreads southward and eventually upwells in other parts of the world
Oligotrophic Lake(young lake)
Type of lake that has low nutrient levels, resulting in low productivity and limited plant growth
. These lakes are typically clear, deep, and have low concentrations of dissolved nutrients
have high oxygen levels
important source of drinking water and recreation
Mesotrophic Lake
A type of lake that falls in the middle range of nutrient levels.
has moderate levels of nutrients, which support a diverse range of plant and animal life.
are typically clear and have a balanced ecosystem.
they are considered to be healthier than eutrophic lakes (high nutrient levels) but less healthy than oligotrophic lakes (low nutrient levels).
Eutrotrophic lake
An eutrophic lake is a type of lake that has high levels of nutrients, which promote the growth of algae and other aquatic plants.
This excessive plant growth can lead to a decrease in water clarity and oxygen levels, as well as the potential for harmful algal blooms and weeds.
Eutrophication is often caused by human activities, such as agricultural runoff and sewage discharge.
Lake Stratification
Is the tendency of lakes to form separate and distinct thermal layers during warm weather
What is lake turnover?
Simply put, lake turnover is the seasonal mixing of the entire water column. For many lakes deeper than about 20 feet, distinct, thermally stratified layers of water form during the summer. These layers prevent the lake from mixing and aerating.