Psych Test 2
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Creative Thinking
Keeping an open mind past the obvious answer
What are the four Gestalt Principles?
Closure, proximity, similarity, and good continuation

Closure
When we look at a stimulus, we tend to see it as a closed shape rather than lines
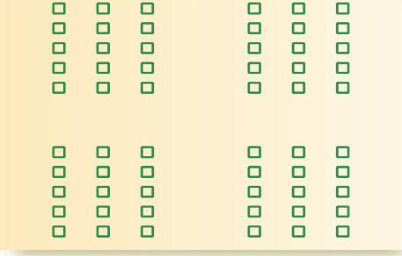
Proximity
Tendency to group close objects together during perception
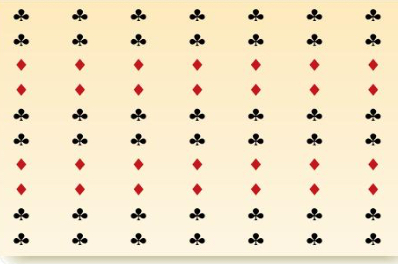
Similarity
Tendency to group like objects together during perception
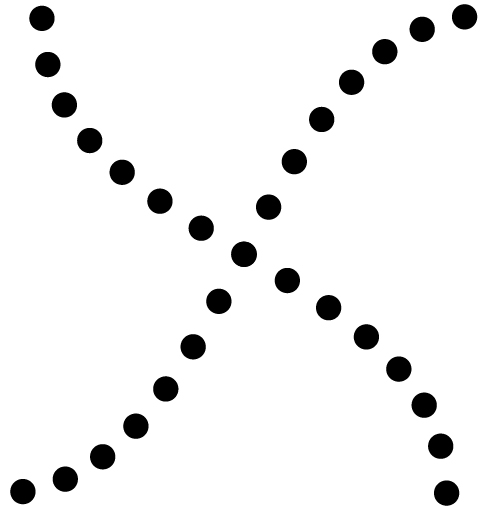
Good Continuation
Preferences for perceiving stimuli that seem to follow one another as part of a continuing pattern
Perceptual Constancies
Tendency to have certain perceptual experiences regardless of the relevant input from our senses (color, shape, and size)
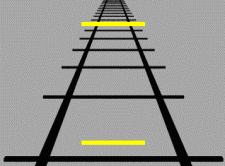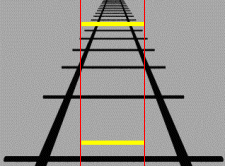
Size constancy
Perception of the size of familiar on objects as roughly constant regardless of the changes in the sizes of the retinal image or distance

Shape Constancy
No matter where you look from, an object will remain the same shape

Color Constancy
Tendency of people to perceive an object as a certain color because they know that the object is supposed to be that color, even if the object is not that color at all
Forer Effect
Believing that a general personality description is unique to oneself (ex: horoscopes, zodiac signs)
Availability Error
Occurs when people base their judgment on evidence that is vivid or memorable instead of reliable or trust worthy (ex: amusement park accidents, airplane crashes> car crashes)
Confirmation Bias
Ignore and misinterpret evidence that conflicts with our own views (watching news channels that share the same values as us)
Pareidolia
Projecting human physical features onto non-human objects
Recall
A memory task that is used when a person needs to previously learned information from storage
Recognition
A memory task employed when a person needs to identify certain items that have been presented as familiar
Proactive Interference
When information that was learned at a previous time interrupts the learning of new information
Retroactive Interference
When the learning of new information disrupts
Time-based prospective memory
When a person intends to do something after a specified amount of time has passed (ex: make a call at 12)
Event-based prospective memory
When a person intends to do something that is elected by some external event or cue (ex: remember to send a letter when you pass by a post office)
Bottom-up processing
When information from external environment is registered and sent up to the brain for interpretation (when encountering with information for the first time)
Top-down processing
Occurs with higher levels of cognitive processing (information that is already learned)
Attention
Conscious awareness; can be focused on events that are taking places in the environment or inside our minds
Thinking critically about truth
AVOID
Thinking everyone makes his or her own truth
Coming to conclusions before having enough information
Denying information contrary to personal beliefs
Opinion
To tell others what we think about something
Evidence
To show others what we think makes sense
Different kinds of evidence:
Personal experience
Unpublished + published reports
Eyewitness + celebrity testimony
Expert Opinion
Research Review
Inquiry
Seeking answers to questions, investigating issues, and gathering info to help us draw conclusions
Inquiry helps beyond our:
1st impressions
Feelings
Preconceived notions
Personal preferences
Introspection
Assessing one’s internal thoughts, feelings, and motivation
Runination
Negative cycle of thoughts
Growth mindset
Life as a learning process
Resilience
See failure as an opportunity to learn and grow
Welcomes challenges
Mistakes are a part of learning
Open to constructive feedback
Effort is key
Affective empathy
ability to understand another person’s emotions and respond appropriately
Somatic empathy
ability to have some type of physical reaction in response to what someone else is experiencing
Cognitive empathy
the ability to understand another person’s mental state and what they might be thinking in a given situation
Obstacles to empathy
Need to pay attention
time consuming
self-esteem/ self perception becomes a hurdle
history between the individual
Benefits of Empathy
Builds social connection with others
Regulate social connections with others
Promotion of altruistic behaviors
Observational learning
learning that takes place when an individual observes and then imitates another’s behavior (Albert Bandera’s Bobo Doll Experiment)
Becoming More Observant
Use all 5 senses
Being less self-absorbed
Try to notice things you would normally miss
Factors involved in observational learning
Attention
Retention in memory
Motivation
The four sources of knowledge:
Perception
Introspection
Memory
Reason
Perception
EXTERNAL source of knowledge
Introspection
INTERNAL source of knowledge
Memory
Rely on out memory to preserve and retrieve information
Reason
Reveals “how things are”
Obstacles to Knowing:
Assuming and Guessing
Assuming
Taking something for granted; accepting something as true that has not been proven or can easily be disputed
Guessing
Offering a judgement on a hunch or taking a chance on an answer without ant confidence that it is correct
Naturalistic Fallacy and its Variants
Common = good/ bad
Uncommon= bad/good
Knowledge
based on reality, not on fantasy, illusion, or wishful thinking
Commonsense Skepticism
Anything that lacks certainty is not suspect BUT anything that lacks evidence is suspect
Appeal to Intuition
Considered a source of knowledge: “knowing” due to feeling or perceiving
Appeal to Mystical Experience
Belief b based on having a privileged source of information
Appeal to Faith
Believing in something in spite of, or even because of, the fact that we have insufficient evidence for it
Actively
through direct experience, by testing and proving an idea or by reasoning
Passively
being told something by someone else; acquisition of knowledge without active effort