Economics Theme 2 - Edexcel A
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/93
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
1
New cards
Actual Growth
Economic growth measured by changes in real GDP.
2
New cards
Aggregate Demand (AD)
The total level of demand in an economy at any given price level at any given moment in time. Consumer Spending + Investment + Government Spending + (Exports Value - Imports Value).
3
New cards
Aggregate Supply (AS)
The total amount of output in an economy at any given price at any given moment in time.
4
New cards
Animal Spirits
The level of confidence of business owners.
5
New cards
Balance of Payments
A record of all financial dealings over a period of time between economic agents of one country and all other countries.
6
New cards
Base Year
A year chosen as a good comparison in a series of data when building an index; it is automatically given an index figure of 100.
7
New cards
Boom
The peak of the business cycle, when growth is high.
8
New cards
Budget
Where the government lays out their spending and taxation plans.
9
New cards
Budget Deficit
When the government spends more money than it receives.
10
New cards
Budget Surplus
When the government receives more money than it spends.
11
New cards
Circular flow
A model of the economy which shows the flow of goods and services, the factors of production and money around the economy.
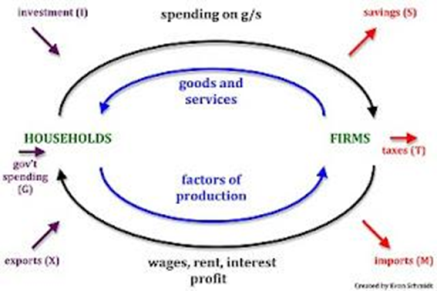
12
New cards
Claimant Count
A measure of unemployment; the number of people receiving benefits for being unemployed.
13
New cards
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Official measure used to calculate rate of inflation, using a weighted basket of goods.
14
New cards
Consumption
Consumer spending on goods and services.
15
New cards
Cost Push Inflation
Inflation caused by a decrease in AS.
16
New cards
Current Account
A record of the payments for the purchase and sale of goods and services as well as income and transfers.
17
New cards
Current Account Deficit
When more money leaves the country than enters, so the current account is negative.
18
New cards
Current Account Surplus
When more money enters the country than leaves, so the current account is positive.
19
New cards
Cyclical Unemployment
Unemployment caused by a lack of AD.
20
New cards
Deflation
A persistent fall in prices of goods and services. Inflation is negative.
21
New cards
Deflationary/Contractionary Policy
Fiscal or monetary policy which is aimed at reducing AD.
22
New cards
Demand Pull Inflation
Inflation caused by an increase in AD.
23
New cards
Depreciation
The reduction in the value of machinery over time.
24
New cards
Direct Tax
Taxes paid straight to the government by the individual taxpayer.
25
New cards
Disinflation
A reduction in the rate of inflation.
26
New cards
Disposable Income
The money consumers have left to spend, after taxes have been taken away and benefits added.
27
New cards
Economic Growth
An increase in the long term productive potential of the economy; an increase in the amount of goods and services which are produced, measured by an increase in real GDP.
28
New cards
Employed
Someone who does more than 1 hour of paid work a week or is temporarily away from work, on a government supported training scheme or does a minimum of 15 hours unpaid work for the family business. (International Labour Organisation (ILO) Definition).
29
New cards
Expansionary Policy
Fiscal or monetary policy which is aimed at increasing AD.
30
New cards
Exports
Goods and services sold to foreigners that bring income into the country.
31
New cards
Export-Led Growth
Economic growth arising from an increase in exports.
32
New cards
Fiscal Policy
The use of borrowing, government spending and taxation to manipulate the level of AD and improve macroeconomic performance.
33
New cards
Frictional Unemployment
Unemployment caused when people move between jobs and enter the job market.
34
New cards
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The value of goods and services produced in a country over a given period of time.
35
New cards
GDP Per Capita
Total GDP divided by the population.
36
New cards
Gross Investment
Investment both to replace old machinery that has depreciated and to create/buy new ones.
37
New cards
Gross National Income (GNI)
The value of goods and services produced by a country over a period of time plus net overseas interest payments and dividends.
38
New cards
Gross National Product (GNP)
The value of goods and services produced by citizens of a country, whether the live in the country or not.
39
New cards
Government Spending
Spending by the government on the provision of goods and services.
40
New cards
Imports
Goods and services bought from foreigners that takes income out of the country.
41
New cards
Inactive
Those neither employed nor unemployed; those not participating in the job market.
42
New cards
Income
A flow of assets
43
New cards
Index Number
Numbers allowing accurate comparisons to be made over time. The base year value is typically 100.
44
New cards
Indirect Tax
Tax where the person charged with paying the money to the government is able to pass the cost onto someone else.
45
New cards
Inflation
The general rise in prices of goods and services that erodes the purchasing power of money.
46
New cards
Injection
Spending power entering the circular flow of income resulting from investment, government spending and exports.
47
New cards
Interventionist Supply Side Policies
Policies designed to correct market failure, where the government intervenes in the market.
48
New cards
Investment
Spending by businesses on capital goods, which leads to the creation of real goods.
49
New cards
Labour Force Survey
A measure of unemployment which surveys people to class them as unemployed, employed or inactive under the ILO definitions.
50
New cards
Living Standards
The quality of life enjoyed by people in a country.
51
New cards
Long run
When all factors of production are variable.
52
New cards
Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)
The total output an economy can produce when operating at full output
53
New cards
Long Run Trend Rate of Growth
The average sustainable rate of economic growth over a period of time.
54
New cards
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
The proportion of an increase in income spent on consumption. Change in Consumption/Change in Income.
55
New cards
Marginal Propensity to Import (MPM)
The proportion of an increase in income spent on imports. Change in Imports/Change in Income.
56
New cards
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
The proportion of an increase in income that is saved. Change in Savings/Change in Income.
57
New cards
Marginal Propensity to Tax
The proportion of an increase in income that is taken away in tax. Change in Taxation/Change in Income.
58
New cards
Marginal Propensity to Withdraw (MPW)
\`The proportion of an increase in income that is withdrawn from the circular flow. MPW = MPS+MPT+MPM
59
New cards
Market-based Supply-side Policies
Policies which are designed to remove anything which prevents the free market system working efficiently.
60
New cards
Monetary Policy
The attempts of the central bank/regulatory authority to control the level of AD by altering base interest rates or the amount of money in the economy (QE).
61
New cards
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)
9 Economists who meet monthly to set the Bank rate as well as other monetary instruments.
62
New cards
Monetary Supply
Stock of money in the economy.
63
New cards
Multiplier
An increase in an injection will lead to an even greater increase in national income. 1/(1-MPC).
64
New cards
National Expenditure
The value of spending by households on goods and services.
65
New cards
National Income
The value of money paid by firms to households in return for land, labour, capital and enterprise.
66
New cards
National Output
The value of the flow of goods and services from firms to households.
67
New cards
Negative Output Gap
When GDP is lower than predicted; the economy is producing below full output.
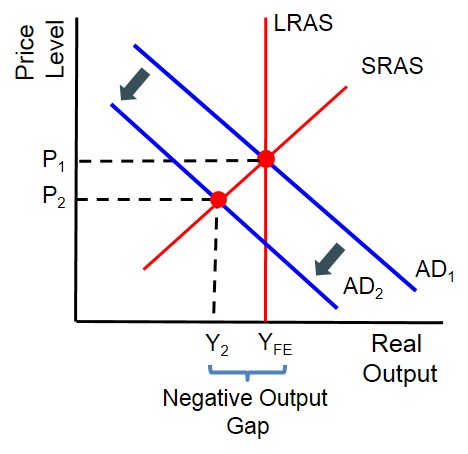
68
New cards
Net Exports
Exports - Imports
69
New cards
Net Investment
Investment adjusted for depreciation; gross investment minus depreciation.
70
New cards
Nominal GDP
GDP which does not take inflation into account; GDP at current prices.
71
New cards
Output Gap
The difference between the long term trend rate of growth and actual growth.
72
New cards
Positive Output Gap
When GDP is higher than predicted; the economy is producing above full output.
73
New cards
Potential Growth
A change in the productive potential of the economy.
74
New cards
Purchasing Power Parity
Exchange rate of one currency to another that compares the cost of living in different countries through comparing a typical basket of goods.
75
New cards
Quantitative Easing (QE)
When the central bank buys assets (bonds) from banks in exchange form money in an attempt to increase the money supply. The banks loan the money out.
76
New cards
Real GDP
GDP which strips out the effect of inflation.
77
New cards
Real Wage Unemployment
Unemployment caused when wages are set above the equilibrium wage rate.
78
New cards
Recession
The trough of the business cycle, when growth is low.
The government defines it as where real GDP falls in at least two successive quarters.
The government defines it as where real GDP falls in at least two successive quarters.
79
New cards
Retail Price Index (RPI)
An old measure of inflation which has lost its national statistic status. Includes housing costs and council tax.
80
New cards
Savings
The decision by consumers to postpone consumption.
81
New cards
Seasonal Unemployment
Unemployment caused when an industry only operates during certain times of the year.
82
New cards
Short Run
When at least one factor of production is fixed.
83
New cards
Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
Aggregate supply when at least one factor of production is fixed.
84
New cards
Short Run Phillips Curve
Shows the relationship between unemployment and inflation: higher levels of unemployment lead to lower levels of inflation.
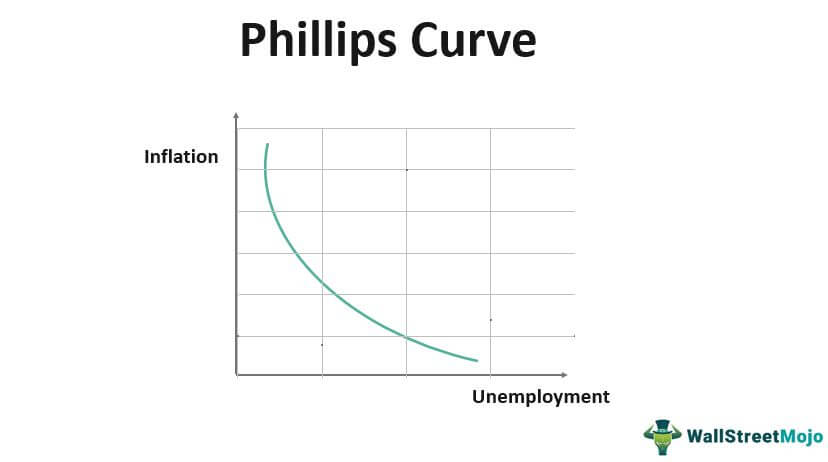
85
New cards
Structural Unemployment
Unemployment caused by the long term decline of an industry.
86
New cards
Supply-Side Policies
Government policies aimed at increasing the productive potential of the economy and shifting LRAS to the right.
87
New cards
Total GDP
The GDP of the whole country.
88
New cards
Trade (Business) Cycle
The tendency of economic growth to rise and fall above the trend rate of economic growth, causing booms and busts.
89
New cards
Underemployment
Those who are working part time, on zero hour contracts or on government training schemes but would prefer to be fill time or those employed in areas below their skill level.
90
New cards
Unemployed
Those who are without work, able to start work in the next 2 weeks and have actively sought work for the last 4 weeks (ILO definition).
91
New cards
Value of GDP
Nominal values of GDP; GDP at current prices.
92
New cards
Volume of GDP
Real values of GDP; the size of the basket of goods.
93
New cards
Wealth
A stock of assets.
94
New cards
Withdrawal
Spending power leaving the circular flow of income resulting from savings, taxation and imports.