Forensic Science EXAM #1 (Evidence, Education, CSI, Blood, Body Fluids, DNA, Trace Evidence) (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/179
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
1
New cards
What cells are found in semen?
Sperm cells
2
New cards
Why would sperm count be lower in some males?
Due to genetics, drugs, alcohol, or a vasectomy
3
New cards
How does semen appear under alternate light?
Appears yellowish-white; glows under UV light
4
New cards
What is the presumptive test for semen?
Seminal Acid Phosphate (SAP) aka Brentamine Fast Blue Test or AP Spot Test
5
New cards
What are the two confirmatory tests for semen?
Christmas Tree Stain (of sperm cells) & Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA)
6
New cards
What is the method and color change for the AP Spot Test?
1. moisten swab with water
2. rub swab over semen stain
3. reagent is dropped on swab
4. PURPLE color reaction
7
New cards
What are some false positives for the AP Spot Test?
urine, vaginal secretions, sweat; old semen stain may produce weak reaction
8
New cards
What is the method for the Christmas Tree Stain?
1. take swab and tease apart fibers in a drop of water on a microscope slide
2. dry the slide
3. stain with red dye and rinse, then stain with green dye and rinse
9
New cards
What is the method for the PSA tests?
1. swab agitated in water
2. drop of this solution added to test well
3. liquid moves through result well
4. C and T line should show for positive result
10
New cards
What enzyme is detected in saliva tests?
Amylase (breaks down starch)
11
New cards
What is the presumptive test for saliva?
Phadebas Reagent
12
New cards
How to use Phadebas method?
1. place stain in a tube
2. add phadebas tablet; heat tube
3. sample is centrifuged
4. color is released into top liquid
5. look for dye at the top of the tube; blue color
13
New cards
What are the false positives for the Phadebas test?
urine or sweat
14
New cards
Why are saliva stains not usually tested before moving on to DNA testing?
We aren't questioning on whether it's blood or semen, saliva can be inferred
15
New cards
What does DNA stands for?
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
16
New cards
What does DNA do for a living thing?
contains genetic information; codes for the proteins our bodies make that are necessary for survival
17
New cards
What is the molecular appearance of DNA?
Double Helix structure
18
New cards
What are the building blocks of DNA?
\-Sugar Phosphate (Sides of double helix)
\-Nitrogenous Base (rungs of double helix)
\-Nitrogenous Base (rungs of double helix)
19
New cards
Where are the bases located in DNA?
Attached to a nucleotide in the ladder of DNA
20
New cards
What are the four bases of DNA?
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
21
New cards
How do the four bases pair with one another?
Adenine = Guanine (AG)
Cytosine = Thymine (CT)
Cytosine = Thymine (CT)
22
New cards
How many base pairs are in one copy of DNA?
Three Billion
23
New cards
What is the percentage of DNA sequence that is the same among humans?
99.8%
24
New cards
Where is DNA located in a cell?
In the nucleus (brain) and in the mitochondria
25
New cards
Where is the DNA located in the nucleus?
In chromosomes
26
New cards
How is DNA organized in cells?
In the chromosomes: -46 chromosomes, 23 pairs (mom and dad)
27
New cards
Where are cells located in different parts of the body?
White blood cells, sperm cells, cheek cells, saliva, tissue, bone, teeth, hair, maggot crops
28
New cards
What are the 3 ways DNA can be different among individuals?
1. base pairs can be different
2. base pairs can be added or removed
3. regions of DNA can be repeated
29
New cards
Which difference is used by FS to identify an individual?
Repeated DNA; look at a certain area of cells to determine how many times it's repeated
30
New cards
What is an unknown sample?
*any type of evidence found* blood stain, semen stains, saliva residue, hair, bones, teeth
31
New cards
What is an known samples?
blood or buccal swabs from suspect or victim or other known person (cheek swab)
32
New cards
How should DNA evidence be packaged?
\-Packaged individually
\-Paper bags, not plastic
\-Keep at room temperature, out of the sun
\-Paper bags, not plastic
\-Keep at room temperature, out of the sun
33
New cards
What are the forensic markers that are used in the FBI database?
Short Tandem Repeats (STRs) & Mitochondrial DNA
34
New cards
What are Short Tandem Repeats (STRs)?
Located in chromosomes; repeated sets
35
New cards
What is a locus?
the location of the STR on the chromosome
36
New cards
What is an allele?
it refers to the type of DNA; the number of repeats (Ex. 7,9)
37
New cards
What is an example of a locus?
D5S818
38
New cards
What makes up a locus?
DNA, chromosome \#, genome location
39
New cards
Why are there 13 loci used in the FBI database?
The 13 areas show a number of characteristics that are easily shown
40
New cards
What happens during extraction?
DNA is separated from sample
41
New cards
What happens during amplification (or pcr)?
Amplifies small portions of DNA (STR regions); creates up to 10 million copies
42
New cards
How would a FS present a matching profile in court?
The frequency of this DNA profile in a given population is 1 in 300 trillion...
43
New cards
When would a non-matching profile give a definite no?
If one of the 13 loci do not match; DNA does not change over time
44
New cards
How many base pairs are in the mtDNA genome?
16, 569 letters long
45
New cards
How many base pairs are analyzed in mtDNA?
900 base pairs
46
New cards
How is mtDNA analysis more useful than STR analysis?
\-can be used on old or degraded samples
\-can be amplified
\-multiple copies in each mitochondria in each cell
\-can be amplified
\-multiple copies in each mitochondria in each cell
47
New cards
What are the limitations of using mtDNA?
it can only be described by the 900 letters
48
New cards
Which cell is mtDNA found in?
the egg cell; from your mother
49
New cards
What two types of light are used with microscopes?
reflected or transmitted light
50
New cards
What is reflected light?
when light bounces off the surface of an object under the microscope
51
New cards
What is transmitted light?
when light is passing through the object on a microscope
52
New cards
What are the two types of microscopes?
Stereo Binocular Microscopes & Compound Microscopes
53
New cards
What objects can be viewed with a Stereo Binocular Microscope?
\-search for small fibers, hairs, etc
\-looking at 3D objects
\-using reflected light
\-looking at 3D objects
\-using reflected light
54
New cards
What objects can be viewed with a Compound Microscope?
\-transparent object; transmitted light
\-look through object
\-fibers, hair, glass, biological samples for sperm cells, microcrystalline tests
\-look through object
\-fibers, hair, glass, biological samples for sperm cells, microcrystalline tests
55
New cards
What type of light does a Stereo Binocular Microscope use?
Reflected Light
56
New cards
What type of light does a Compound Microscope use?
Transmitted Light
57
New cards
This is a Stereo Binocular Microscope
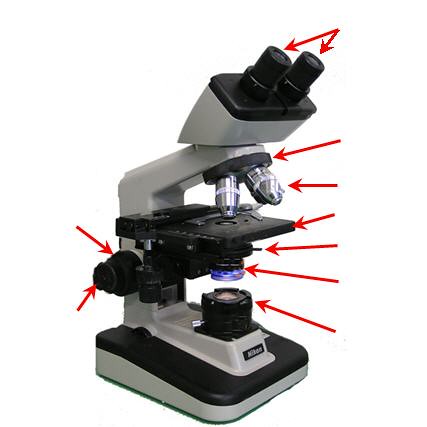
58
New cards
This is a Compound Microscope
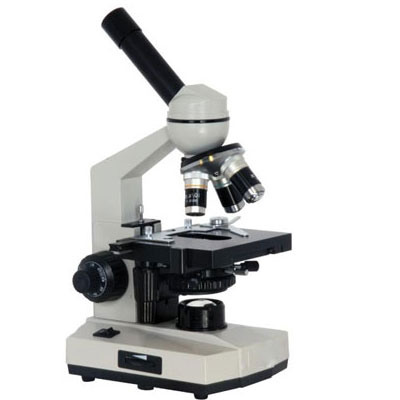

59
New cards
What is an Ocular Lens?
Lens in the eyepiece of a microscope
60
New cards
What is an Objective Lens?
Lens above the sample in a microscope
61
New cards
What is a micrometer?
a ruler int he eyepiece; allows for measurement of sample
62
New cards
What is magnification?
the amount the object is enlarged
63
New cards
What is working distance?
distance between the object and objective lens
64
New cards
What is a PLM Microscope?
Polarized Light Microscope
\-takes advantage of the optical properties of glass, crystal, and fibers
\-sample absorbs light differently ==depending== on its ==orientation== in polarized light
\-takes advantage of the optical properties of glass, crystal, and fibers
\-sample absorbs light differently ==depending== on its ==orientation== in polarized light
65
New cards
What is a Comparison Microscope?
\-an optical bridge allows viewing of evidence side by side
\-useful for comparing bullets, fibers, hairs
\-useful for comparing bullets, fibers, hairs
66
New cards
Why should evidence items be collected separately?
it prevents trace from being transferred to other objects
67
New cards
What is the Locard Exchange Principle?
whenever there is contact between two objects, they will leave or pick up debris from the other object
68
New cards
What are the 3 methods for collecting trace evidence?
1. Visual Inspection
2. Tape Lift
3. Vacuum
69
New cards
What is Visual Inspection?
\-using naked eye or hand lens
\-evidence removes and packages for later analysis
\-use bright light and forceps to collect
\-evidence removes and packages for later analysis
\-use bright light and forceps to collect
70
New cards
What is Tape Lift?
repeatedly apply clear tape to small area until most of the stickiness is gone
71
New cards
What is Vacuuming?
\-nozzle is short and transparent
\-debris collected on a filter or membrane
\-debris collected on a filter or membrane
72
New cards
Why is vacuuming often misused by investigators?
It often results in the collection of a lot of irrelevant materials
73
New cards
What are filaments?
long continuous fiber (silk)
74
New cards
What is a staple?
a filament that is cut into smaller pieces; staples are spun into thread (cotton)
75
New cards
What is a natural fiber?
found in nature; comes from and animal, plant, or mineral
76
New cards
What are examples of natural fibers?
wool (sheep), silk (silkworm), cotton (plant)
77
New cards
What are synthetic fibers?
made from a vat of chemicals that solidifies when it hits the air; mimics other fibers
78
New cards
What are examples of synthetic fibers?
nylon, polyester, acrylic
79
New cards
What is a refractive index?
a number that describes the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the fiber
80
New cards
What are the class characteristics of fibers?
chemical composition (nylon, polyester, acrylic); other elements (chlorine)
81
New cards
How are fibers analyzed?
Using Microspectrophotometry (IR) that determines the chemical make up of fibers
82
New cards
What is a radial crack?
cracks that began at the origin of impact and spread out (pizza slice)
83
New cards
What is a concentric crack?
cracks that form between radial cracks to connect them (spider web)
84
New cards
How do we measure the refractive index of glass?
Place glass in different oils that have different refractive indexes to make the halo around the glass disappear
85
New cards
What is a Beke line?
the thick outside line around a sample of glass that shows that the RI of glass and oil are different
86
New cards
What is a conchoidal line?
cylinder like lines that point back to the origin of the impact
87
New cards
How to help identify the order and direction of fractures in glass?
Look at where radial fractures end into other fractures; the ones it ends into was there first
88
New cards
What type of relief do we look for in the RI of glass?
Low Relief \= no Beke line means that the RI and oil are similar
89
New cards
How are the chemical components of paint measured?
Infrared Spectroscopy (layers of paint can be analyzed to find chemical composition)
90
New cards
How is GSR analyzed?
\-hand is swabbed
\-swab is analyzed using (SEM/EDS) & looking for high levels of barium and antimony
\-swab is analyzed using (SEM/EDS) & looking for high levels of barium and antimony
91
New cards
What are the two elements detected in GSR?
Barium & Antimony
92
New cards
What is GSR?
a mixture of materials that originate from the firing of a gun and fall onto shooter's hand or clothing
93
New cards
Why should we not testify about guilt or innocence?
FS obtain circumstantial evidence; only helping the jury understand what we did and help them understand it
94
New cards
What is the first career category?
Investigation
95
New cards
What is the second career category?
Laboratory Work
96
New cards
What do Investigation Jobs do?
\-police investigate crimes \n -receive the information \n -make an analysis \n -DO NOT question suspects
97
New cards
What are the degree requirements for an Investigation Job?
A degree is not always required
98
New cards
What do Crime Laboratory Jobs consist of?
Conduct lab analysis
99
New cards
What are the degree requirements for Crime Laboratory Jobs?
Degree is required; usually a natural science degree (BS in chemistry, biology)
100
New cards
What do forensic pathologists do?
\-Conduct autopsies;determine cause of death \n -Have an MD degree