BSC360 HW Quiz Exam 1
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
Living systems are incredibly diverse in size, shape, environment, and behavior. Despite this wide variety of organisms, it remains difficult to define what it means to say something is alive. Which of the following can be described as the smallest living unit?
DNA
organelle
protein
cell
cell
The central dogma provides a framework for thinking about how genetic information is copied and used to produce structural and catalytic components of the cell. From the choices below, select the order of biochemical processes that best correlates with the tenets of the central dogma.
replication, translation, transcription
translation, transcription, replication
replication, transcription, translation
translation, replication, transcription
replication, transcription, translation
Changes in DNA sequence from one generation to the next may result in offspring that are altered in fitness compared with their parents. The process of change and selection over the course of many generations is the basis of
mutation
heredity
evolution
reproduction
evolution
Scientists learned that cell death is a normal and even important part of life by studying the development of the nematode worm C. elegans. What was the most important feature of C. elegans for the study of programmed cell death?
Its genome was partially sequenced
The nematode is smaller and simpler than the fruit fly
Seventy percent of C. elegans genes have homologs in humans
The developmental pathway of each cell in the adult worm was known.
The developmental pathway of each cell in the adult worm was known.
Biologists cannot possibly study all living species. Instead, they try to understand cell behavior by studying a select subset of species. Which of the following characteristics are useful in an organism chosen for use as a model in laboratory studies?
rapid rate of reproduction
all of the above
amenability to genetic manipulation
ability to grow under controlled conditions
all of the above
Which of the following organisms was the simplest and the key model organism for the advancement of molecular biology (understanding DNA replication, decoding the DNA to make proteins, etc.)?
Fruit flies
C. elegans
E. coli
yeast
E. coli
Drosophila melanogaster is a/an __________. This type of animal is the most abundant of all animal species, making it an appropriate choice as an experimental model.
insect
bird
mammal
amphibian
insect
Caenorhabditis elegans is a nematode. During its development, it produces more than 1000 cells. However, the adult worm has only 959 somatic cells. The process by which 131 cells are specifically targeted for destruction is called
direct pruning
necrosis
apoptosis
autophagy
apoptosis
Zebrafish (Danio rerio) are especially useful in the study of early development because their embryos
are exceptionally large
are pigmented
are transparent
develop slowly
are transparent
Brewer's yeast, apart from being an irreplaceable asset in the brewery and in the bakery, is an experimental organism used to study eukaryotic cells. However, it does have some limitations. Select all the processes below that CANNOT be studied in yeast.
fermentation
cell cycle
tissue formation
exocytosis
tissue formation
Which statement is NOT true?
Light microscopy was essential in demonstrating the commonalities between plant and animal tissues
New cells arise from the growth and division of previously existing cells
Cells came to be known as the smallest universal building block of living organisms
New cells can form spontaneously from the remnants of ruptured cells.
New cells can form spontaneously from the remnants of ruptured cells.
What unit of length would you generally use to measure a typical plant or animal cell?
centimeters
millimeters
micrometers
nanometers
micrometers
Prokaryotic cells do not possess
membrane bilayers
a nucleus
replication machinery
ribosomes
a nucleus
The nucleus, an organelle found in eukaryotic cells, confines the __________, keeping them separated from other components of the cell.
ribosones
lysosomes
peroxisomes
chromosomes
chromosomes
Which of the following organelles has both an outer and an inner membrane?
peroxisome
mitochondrion
endoplasmic reticulum
lysosome
mitochondrion
You wish to explore how mutations in specific genes affecting sugar metabolism might alter tooth development. Which organism is likely to provide the best model system for your studies?
horses
mice
Arabidopsis
E. coli
mice
Which of the following is NOT a difference that would allow one to distinguish a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell?
Presence of a nucleus
Presence of membrane-bound organelles
Ribosomal subunit weight
Presence of a membrane on the outside surface of the cell
Presence of a membrane on the outside surface of the cell
The most reliable feature distinguishing an eukaryotic cell from a prokaryotic cell is the
presence of DNA
presence of a plasma membrane
eukaryotic cell's larger size
presence of a nucleus
presence of a nucleus
Which of the following is present in a prokaryotic cell?
mitochondrion
ribosome
ER
nuclear envelope
ribosome
All cells share the following features except
use energy to carry out metabolic activities
can respond to environmental stimuli
have mitochondria
reproduce themselves
have mitochondria
Which of the following is the strongest chemical interaction?
hydrogen bond
Van der Waals interaction
peptide bond
hydrophobic interaction
peptide bond
Select the answer that BEST completes the following statement: Chemical reactions in living systems occur in an __________ environment, within a narrow range of temperatures.
extracellular
organic
aqueous
optimal
aqueous
Which subatomic particles contribute to the atomic mass for any given element?
Protons and neutrons
protons and electrons
protons
neutrons
Protons and neutrons
About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter?
oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium
carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
A covalent bond between two atoms is formed as a result of the
sharing of electrons
loss of a proton from one atom
transfer of electrons from one atom to the other
loss of electrons from both atoms
sharing of electrons
An ionic bond between two atoms is formed as a result of the
transfer of electrons from one atom to the other
loss of electrons from both atoms
loss of a proton from one atom
sharing of electrons
transfer of electrons from one atom to the other
Polar covalent bonds are formed when the electrons in the bond are not shared equally between the two nuclei. Which one of these molecules contains polar bonds?
hydrogen molecules
NaCl
molecular oxygen
water
water
__________ play an important role in organizing lipid molecules with long hydrocarbon tails into biological membranes.
Hydrophobic interactions
Hydrogen bonds
Van der Waals attractions
Ionic bonds
Hydrophobic interactions
Which of the following monomer building blocks is necessary to assemble selectively permeable boundaries around and inside cells?
nucleotides
amino acids
sugars
fatty acids
fatty acids
Cells require one particular monosaccharide as a starting material to synthesize nucleotide building blocks. Which of the monosaccharides below fills this important role?
fructose
ribose
ribulose
glucose
ribose
Both DNA and RNA are synthesized by covalently linking a nucleoside triphosphate to the previous nucleotide, constantly adding to a growing chain. In the case of DNA, the new strand becomes part of a stable helix. The two strands are complementary in sequence and antiparallel in directionality. What is the principal force that holds these two strands together?
ionic interactions
van der Waals interactions
hydrogen bonds
covalent bonds
hydrogen bonds
Glucose, starch, cellulose, and glycogen are classified as:
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Nucleic Acids
Lipids
Carbohydrates
Macromolecules in the cell can often interact transiently as a result of noncovalent interactions. These weak interactions also produce stable, highly specific interactions between molecules. Which of the factors below is the most significant in determining whether the interaction will be transient or stable?
surface complementarity between molecules
the concentration of each molecule
the rate of synthesis
the size of each molecule
surface complementarity between molecules
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule is known as:
hydrolysis
denatration
condensation reaction
photosynthesis
condensation reaction
Polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are similar in that they
are synthesized from monomers by dehydration reactions
are synthesized from monomers by the process of hydrolysis
are synthesized as a result of peptide bond formation between monomers
are decomposed into their subunits by dehydration reactions
are synthesized from monomers by dehydration reactions
Which of the following is not a macromolecule ?
vitamin C
RNA
DNA
cellulose
vitamin C
When disaccharides are changed to monosaccharides, the common chemical process involved is:
denaturation
hydration
hydrolysis
dehydration
hydrolysis
Saturated fats:
Are associated with heart disease
Have many double bonds
are components of ribosomes
Have no double bonds
Have no double bonds
The main source of energy for human cells is
glucose
phospholipids
vitamin
hormones
glucose
Polymers of polysaccharides, nucleic acids, and proteins are all synthesized from monomers by
The addition of water to each monomer
Ionic bonding of the monomers
Connecting monosaccharides together
The removal of water
The removal of water
Polypeptides are synthesized from amino acid building blocks. The condensation reaction between the growing polypeptide chain and the next amino acid to be added involves the loss of
an amino group
a carboxylic acid group
a water molecule
a carbon atom
a water molecule
The variations in the physical characteristics between different proteins are influenced by the overall amino acid compositions, but even more important is the unique amino acid
bond
orientation
number
sequence
sequence
Complete the sentence with the best option provided below. The primary structure of a protein is the
amino acid composition
lowest energy conformation
average size of amino acid side chains
amino acid sequence
amino acid sequence
Proteins are important architectural and catalytic components within the cell, helping to determine its chemistry, its shape, and its ability to respond to changes in the environment. Remarkably, all of the different proteins in a cell are made from the same 20 __________. By linking them in different sequences, the cell can make protein molecules with different conformations and surface chemistries, and therefore different functions.
nucleotides
amino acids
fatty acids
sugars
amino acids
Which of the following statements is most likely to be true of nonpolar R groups in aqueous solution?
They are hydrophilic and found on protein surfaces
They are hydrophilic and found buried within proteins
They are hydrophobic and found on protein surfaces
They are hydrophobic and found buried within proteins
They are hydrophobic and found buried within proteins
An α-helix is most likely to be held together by:
hydrogen bonds
disulfide bonds
hydrophobic effects
ionic attractions between side chains
hydrogen bonds
Which of these amino acids has a side chain that can become phosphorylated in cells?
cysteine
Proline
Threonine
Leucine
Threonine
Complete the sentence with the best option provided below. The secondary structures of a protein are the
temporary, unstable protein folding conformations
chemical modifications of amino acid side chains
regular, repeated folds present in a lowest energy conformation
interactions between polar amino acid side chains
regular, repeated folds present in a lowest energy conformation
Some proteins have α helices, some have β sheets, and still others have a combination of both. What makes it possible for proteins to have these common structural elements?
hydrogen bonds along the protein backbone
the hydrophobic-core interactions
specific amino acid sequences
side-chain interactions
hydrogen bonds along the protein backbone
Protein conformation is defined as
the composition of amino acids
quaternary structure
the sequence of amino acids
the characteristic 3-dimensional shape of a protein
the characteristic 3-dimensional shape of a protein
A functional protein is made of 4 peptides, therefore, it has
quaternary structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
tertiary structure
primary and secondary structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
A hydrophilic amino acid R group (side chain) would be found where in a protein?
forming hydrogen bonds with other R groups
on the inside of the folded chain, away from water
forming a peptide bond with the next amino acid in the chain
on the outside of the folded chain, in the water
on the outside of the folded chain, in the water
Which of the following amino acid has a side chain that can form a disulfide bond?
serine
tyrosine
methionine
cysteine
cysteine
The portion of an amino acid that makes it unique among the 20 different amino acids is its
carboxyl group
peptide bonding
side chain or R-group
amino group
side chain or R-group
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Disulfide bonds are formed by the cross-linking of methionine residues
Disulfide bonds stabilize but do not determined the secondary structure of a protein
Disulfide bonds are more common in DNA than in proteins
Disulfide bonds are formed mainly in proteins that are retained within the
cytosol
Disulfide bonds stabilize but do not determined the secondary structure of a protein
Two amino acids of the standard 20 contain sulfur atoms. They are:
threonine and serine
cysteine and serine
cysteine and threonine
methionine and cysteine
methionine and cysteine
What is a peptide bond?
A bond that is formed by the sharing of electrons
A bond that holds the phosphate group of one nucleotide and a sugar of a
neighboring nucleotide
A bond that holds hydrogen and oxygen molecules together
A Bond that holds two amino acids together
A Bond that holds two amino acids together
The diagram shows a bond forming between two amino acids. What is the name of this reaction?
condensation reaction
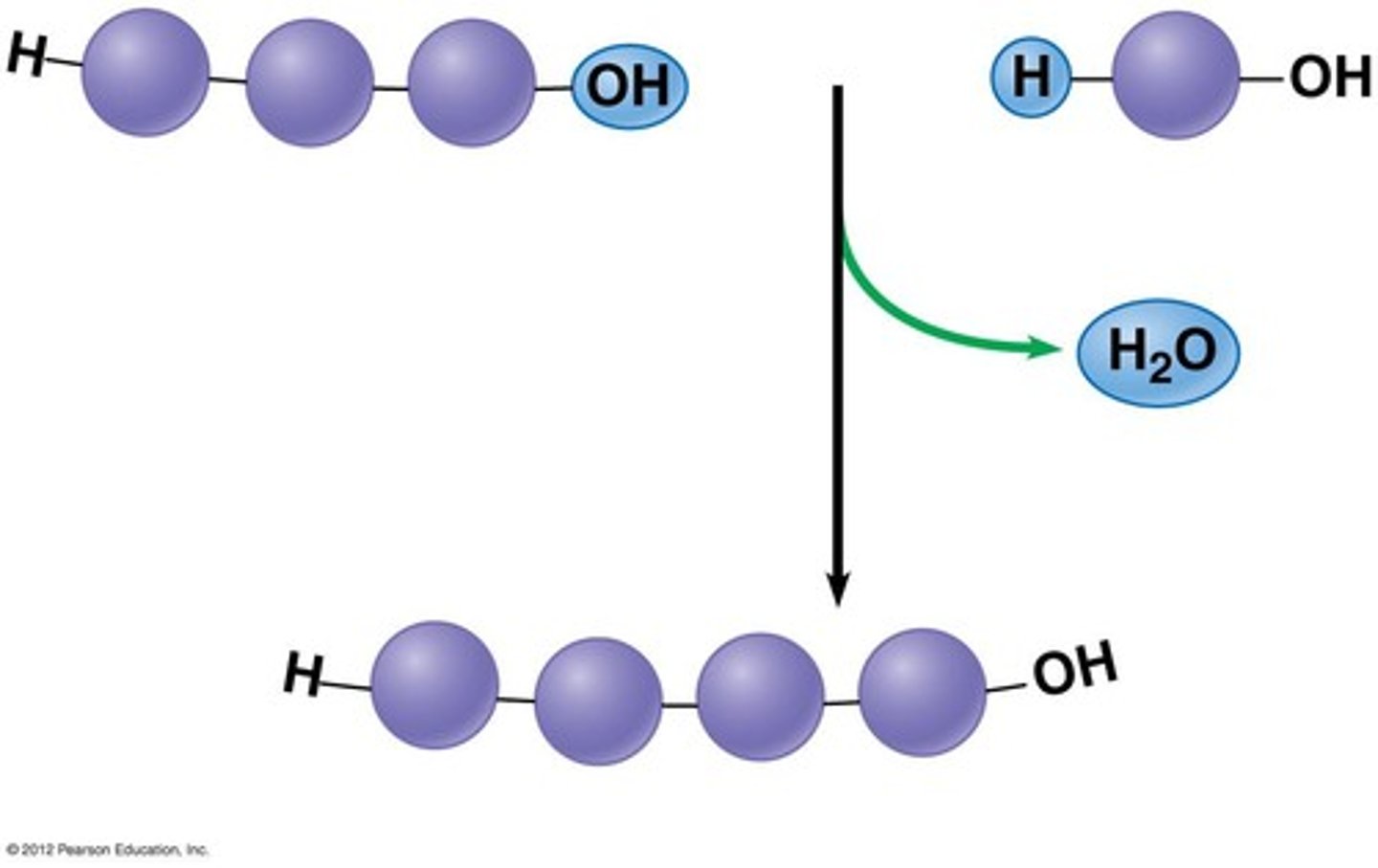
Which of the following levels of structure in a protein would not be disrupted by chemicals that break disulfide bonds and hydrogen bonds?
secondary structure
tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
Primary structure
Primary structure
Which level of protein structure is stabilized primarily by hydrogen bonding?
Primary structure
Quaternary structure
Tertiary structure
Secondary structure
Secondary structure
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
changes in the amino acid sequence of a protein can affect binding to a ligand
many proteins have more than one binding site for other molecules
the three dimensional structure of a protein dictates its function
binding between a protein and its ligand generally involves formation of strong covalent bonds
binding between a protein and its ligand generally involves formation of strong covalent bonds
Besides turning enzymes on or off, what other means does a cell use to control enzymatic activity?
all of the above
control the rate of protein synthesis
compartmentalization of enzymes into defined organelles
degradation by proteases
all of the above
Altering the three-dimensional structure of an enzyme might
change the nature of substrate that binds the enzyme's active site
change the amount of ATP needed for a reaction
change the type of product produced in the reaction
prevent the substrate from binding the enzyme's active site
prevent the substrate from binding the enzyme's active site
A bowl of glucose sugar water is very stable. But if you feed it to cells it is rapidly broken down into carbon dioxide and water. What is the best explanation for this observation?
Cells release energy to break down glucose
Enzymes in the cell catalyze the breakdown of glucose
Glucose is absorbed by the cell
Glucose becomes more chemically reactive inside a cell
Enzymes in the cell catalyze the breakdown of glucose
The active site of an enzyme is the region that
binds the products of the catalytic reaction
is inhibited by the presence of a coenzyme or a cofactor
binds allosteric regulators of the enzyme
is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme
is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme
All of the following statements about enzymes are true except:
multiple functional catalysts, typically react with many different substrates
increase the rate of a reaction
function in an aqueous environment
lower the activation energy of a reaction
multiple functional catalysts, typically react with many different substrates
Which of the following is a mechanism for regulating protein activity by covalent modification?
denaturation
phosphorylation
allosteric regulation
compartmentalization of enzymes into defined organelles
phosphorylation
Enzymes require specific conformation to perform their catalytic function. Which of the following conditions might alter the conformation and function of an enzyme?
high concentration of urea
temperature above 200 degree
all other answers
pH above 10
all other answers
Cell biologists use the term "ligand" to generally refer to any molecule that specifically binds to a protein for its specific function. In the case of an antibody, its ligand will be
T cells
light chain
the antigen
heavy chain
the antigen
Which of the following factors determine an enzyme's specificity?
The number of peptide bonds
The type of cofactor required for the enzyme to be active
The regulatory site of the enzyme
The three-dimensional shape of the active site
The three-dimensional shape of the active site
Catalysts are molecules that lower the activation energy for a given reaction. Cells produce their own catalysts called enzymes. Which of the following is an example of enzymes?
lysosome
lysozyme
ribosome
microsome
lysozyme
Protein folding can be studied using a solution of purified protein and a denaturant (urea), a solvent that interferes with noncovalent interactions. Which of the following is observed after the denaturant is removed from the protein solution?
The polypeptide forms solid aggregates and precipitates out of solution
The polypeptide is hydrolyzed.
The polypeptide could return to its original conformation.
The polypeptide remains completely denatured
The polypeptide could return to its original conformation.
Proteins bind selectively to small-molecule targets called ligands. The selection of one ligand out of a mixture of possible ligands depends on the number of weak, noncovalent interactions in the protein's ligand-binding site. Where is the binding site typically located in the protein structure?
In a hydrophobic cavity in the center of the protein
In the C-terminus of the protein
inside a cavity on the protein surface
buried in the interior of the protein
inside a cavity on the protein surface
Lysozyme is an enzyme that specifically recognizes bacterial polysaccharides, which renders it an effective antibacterial agent. Into what classification of enzymes does lysozyme fall?
nuclease
hydrolase
Synthase
protease
hydrolase
Which of the following mechanisms best describes the manner in which lysozyme speeds up hydrolysis of bacterial polysaccharides?
by altering the length of the substrate
by binding irreversibly to the substrate so that it cannot dissociate
by binding two substrate molecules and orienting them in a way that favors a reaction between them
by lowering activation energy required for the reaction to take place
by lowering activation energy required for the reaction to take place
Which of the following statements about allosteric regulation is TRUE?
Allosteric regulators are often products of other chemical reactions in the same biochemical pathway.
Enzymes are the only types of proteins that are subject to allosteric regulation.
Allosteric regulation is always used for negative regulation of enzyme activity.
Binding of an allosteric molecule to a protein usually uses covalent bonds.
Allosteric regulators are often products of other chemical reactions in the same biochemical pathway.
The Ras protein is a GTPase that functions in many growth factor-signaling pathways. In its active form, with GTP bound, it transmits a downstream signal that leads to cell proliferation; in its inactive form, with GDP bound, the signal is not transmitted. Mutations in the gene for Ras are found in many cancers. Of the choices below, which alteration of Ras activity is most likely to contribute to the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells?
a change that prevents Ras from being made
a change that decreases the rate of hydrolysis of GTP by Ras
a change that decreases the affinity of Ras for GTP
a change that increases the affinity of Ras for GDP
a change that decreases the rate of hydrolysis of GTP by Ras
The phosphorylation of a protein is typically associated with a change in activity. This reaction is catalyzed by
protein phosphatase
protein hydrolase
protein kinase
protein isomerase
protein kinase
Energy required by the cell is generated in the form of ATP. ATP is hydrolyzed to power many of the cellular processes, increasing the pool of ADP. As the relative amount of ADP molecules increases, they can bind to glycolytic enzymes, which will lead to the increased enzymatic activity. The best way to describe this mechanism of regulation is
phosphorylation
allosteric activation
dephosphorylation
feedback inhibition
allosteric activation
Which of these is most likely to be preserved when a protein is denatured
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
Primary structure
Primary structure
Why is ATP an important molecule in the cell?
Its terminal phosphate group is used for protein phosphorylation
all of the above
It is a monomer for the synthesis of nucleic acids
It provides energy for cellular activities
all of the above
In a DNA double helix,
the two DNA strands run antiparallel
the two DNA strands are identical
thymine pairs with cytosine
purines pair with purines
the two DNA strands run antiparallel
Which of the following chemical groups is NOT used to construct a DNA molecule?
six-carbon sugar
nitrogen-containing base
phosphate
five-carbon sugar
six-carbon sugar
Which of the following structural characteristics is NOT normally observed in a DNA duplex?
external sugar-phosphate backbone
uniform left-handed twist
antiparallel strands
purine-pyrimidine pairs
uniform left-handed twist
Which of the following DNA strands can form a DNA duplex by pairing with itself at each position?
5′-AAGCCGAA-3′
5′-AAGCGCAA-3′
5′-AAGCGCTT-3′
5′-AAGCCGTT-3′
5′-AAGCGCTT-3′
The DNA from two different species can often be distinguished by a difference in the
ratio of A + G to C + T
presence of bases other than A, G, C, and T
ratio of sugar to phosphate
ratio of A + T to G + C
ratio of A + T to G + C
You are a virologist interested in studying the evolution of viral genomes. You are studying two newly isolated viral strains and have sequenced their genomes. You find that the genome of strain 1 contains 25% A, 55% G, 20% C, and 10% T. You report that you have isolated a virus with a single-stranded DNA genome. Based on what evidence can you make this conclusion?
because double-stranded genomes have equal amounts of A and T
because single-stranded genomes always have a large percentage of purines
because single-stranded genomes have a higher rate of mutation
by using the formula G − A = C + T
because double-stranded genomes have equal amounts of A and T
The complete set of information in an organism's DNA is called its
genetic code
coding sequence
gene
genome
genome
The relationship between the nucleic acid sequence over a stretch of DNA and the order of amino acids in the resulting protein is referred to as the __________ code.
expression
transnational
protein
genetic
genetic
DNA is an information storage molecule, whose sequences serve as a template to make
protein
lipid
nucleotide
RNA
RNA
What is the total number of chromosomes found in each of the somatic cells in your body?
23
46
22
44
46
A nucleosome
contains RNA that is not being translated
is an extra nucleotide at the 3' end of chromosomes in the nucleus
contains DNA that is not being transcribed
is the most basic structural unit of chromatin
is the most basic structural unit of chromatin
What type of macromolecule helps package DNA in eukaryotic chromosomes?
carbohydrates
Lipids
proteins
RNA
proteins
Which of the following has beads on a string structure?
Telomeres
Chromosomes
Nucleosomes
Chromatids
Nucleosomes
The N-terminal tail of histone H3 can be extensively modified, and depending on the number, location, and combination of these modifications, these changes may promote the formation of heterochromatin. What is the result of heterochromatin formation?
degradation of DNA
no effect
decrease in gene expression
increase in gene expression
decrease in gene expression
Which of the following is NOT a chemical group commonly found on histones for chromatin regulation?
sulfhydryl
methyl
phosphoryl
acetyl
sulfhydryl
DNA replication is considered semiconservative because
each daughter DNA molecule consists of two new strands copied from the parent DNA molecule.
each daughter DNA molecule consists of one strand from the parent DNA molecule and one new strand.
new DNA strands must be copied from a DNA template.
after many rounds of DNA replication, the original DNA double helix is still intact.
each daughter DNA molecule consists of one strand from the parent DNA molecule and one new strand.
Why are chromatin are condensed to chromosomes during cell division?
To ensure accurate distribution of genetic material into daughter cells
To facilitate gene expression
To facilitate DNA replication
to increase transcription rate
To ensure accurate distribution of genetic material into daughter cells
Modifications of a histone that cause the interaction with the DNA to change in chromatin. What is this event called?
Chromatin condensation
chromatin modulation
chromatin remodeling
chromatin dehydration
chromatin remodeling
All of the following are different parts of a eukaryotic chromosome, except:
telomere
centromere
centrosome
chromatid
centrosome