Unit 9: Forces
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Force
A push or a pull
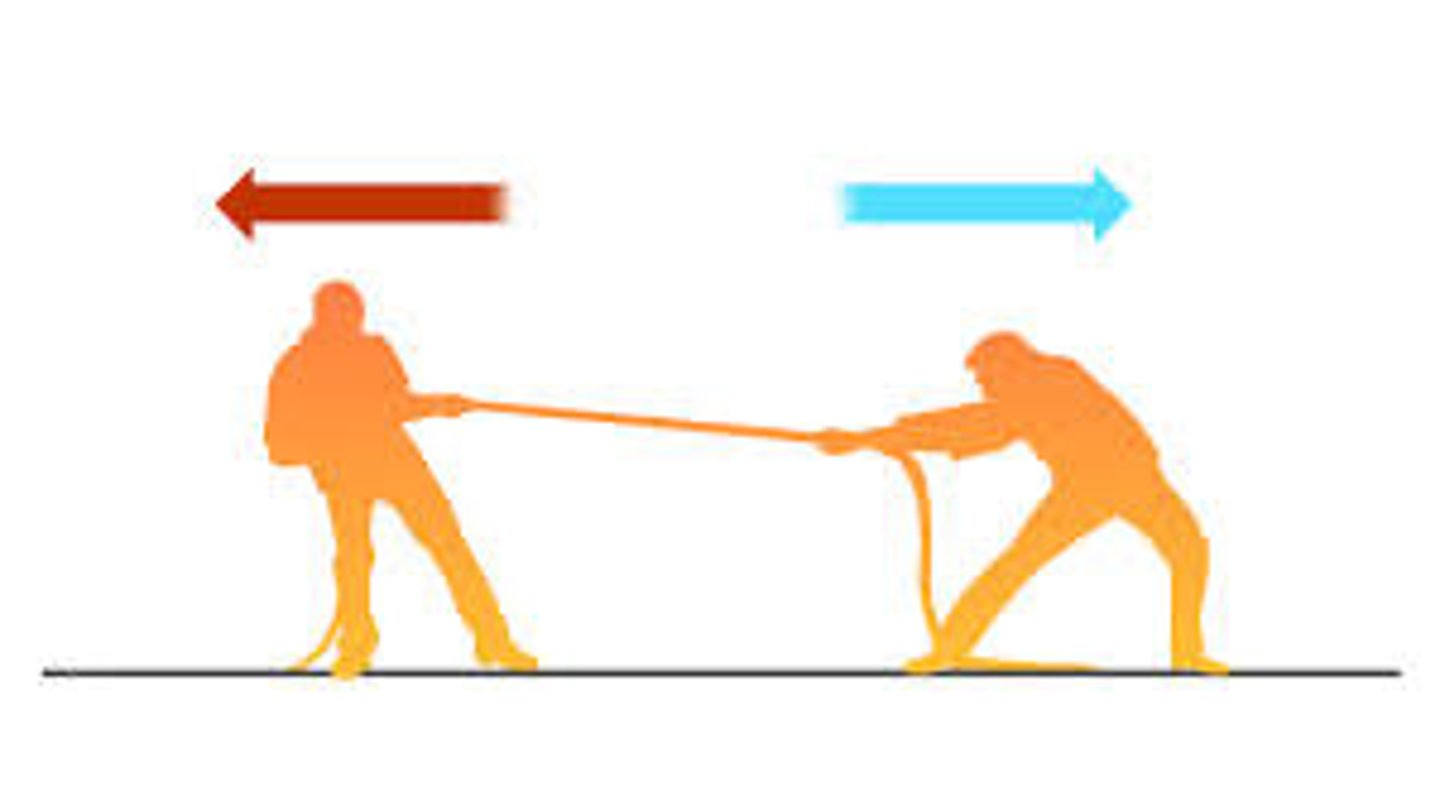
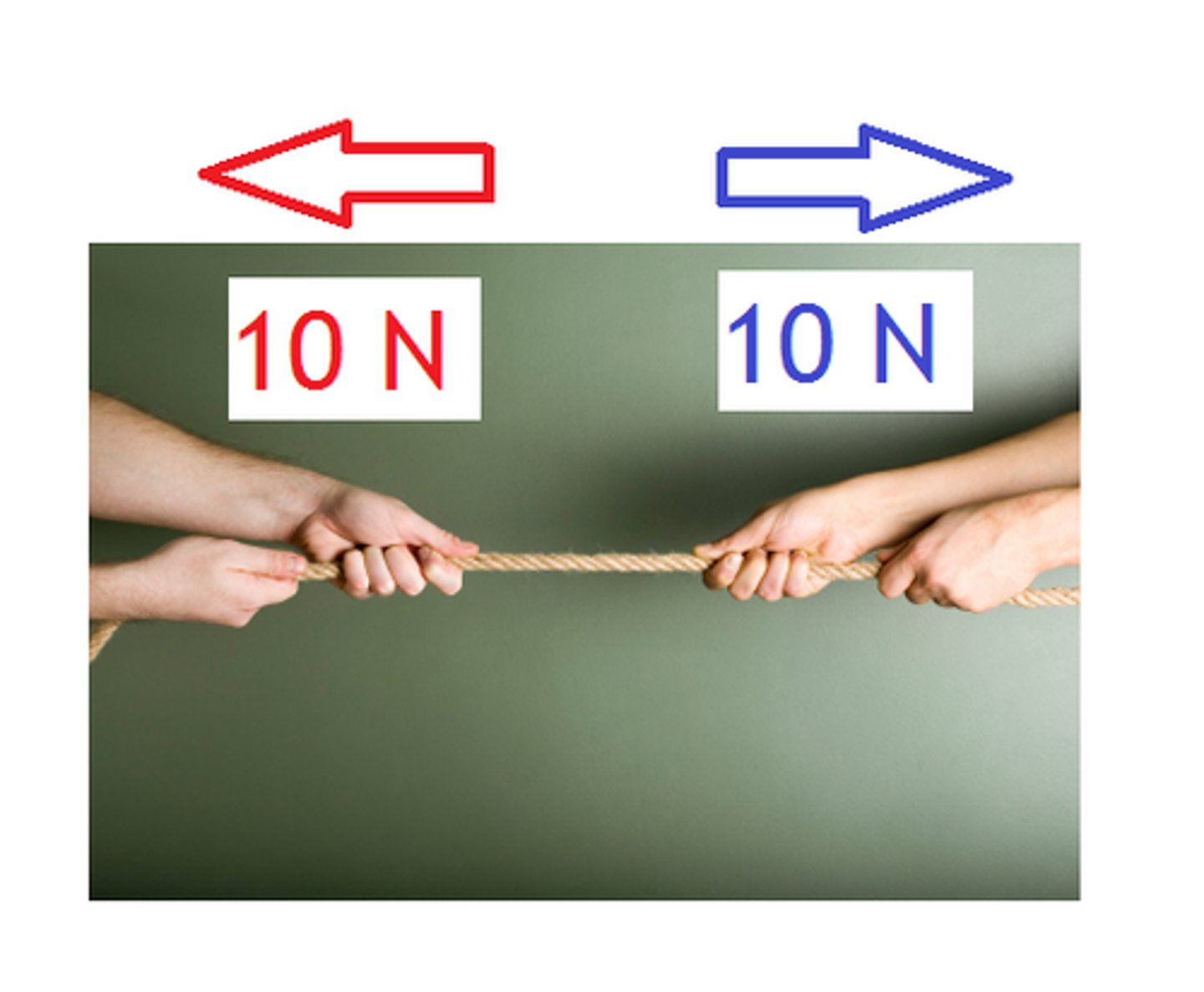
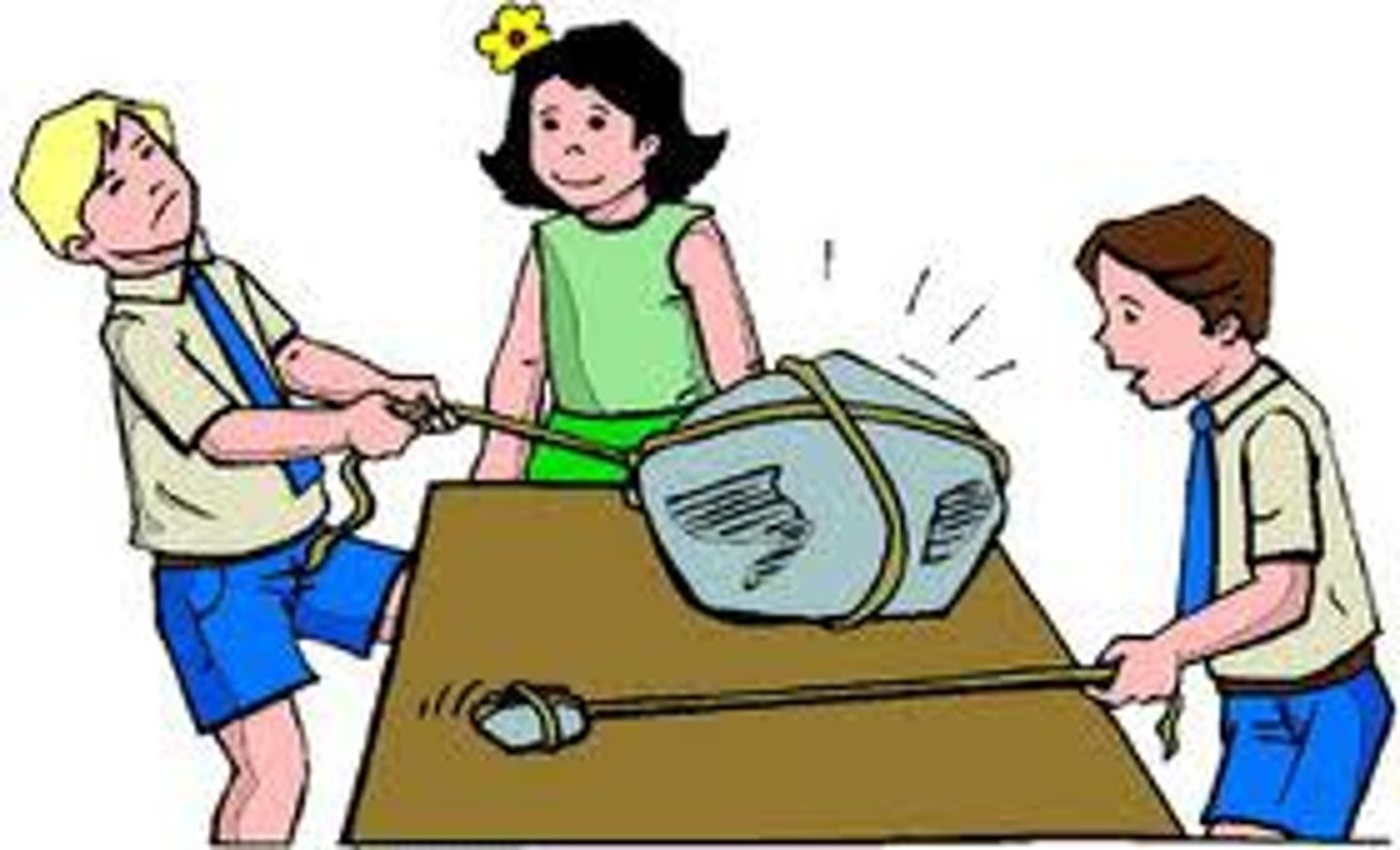
balanced forces
Equal forces acting on an object in opposite directions
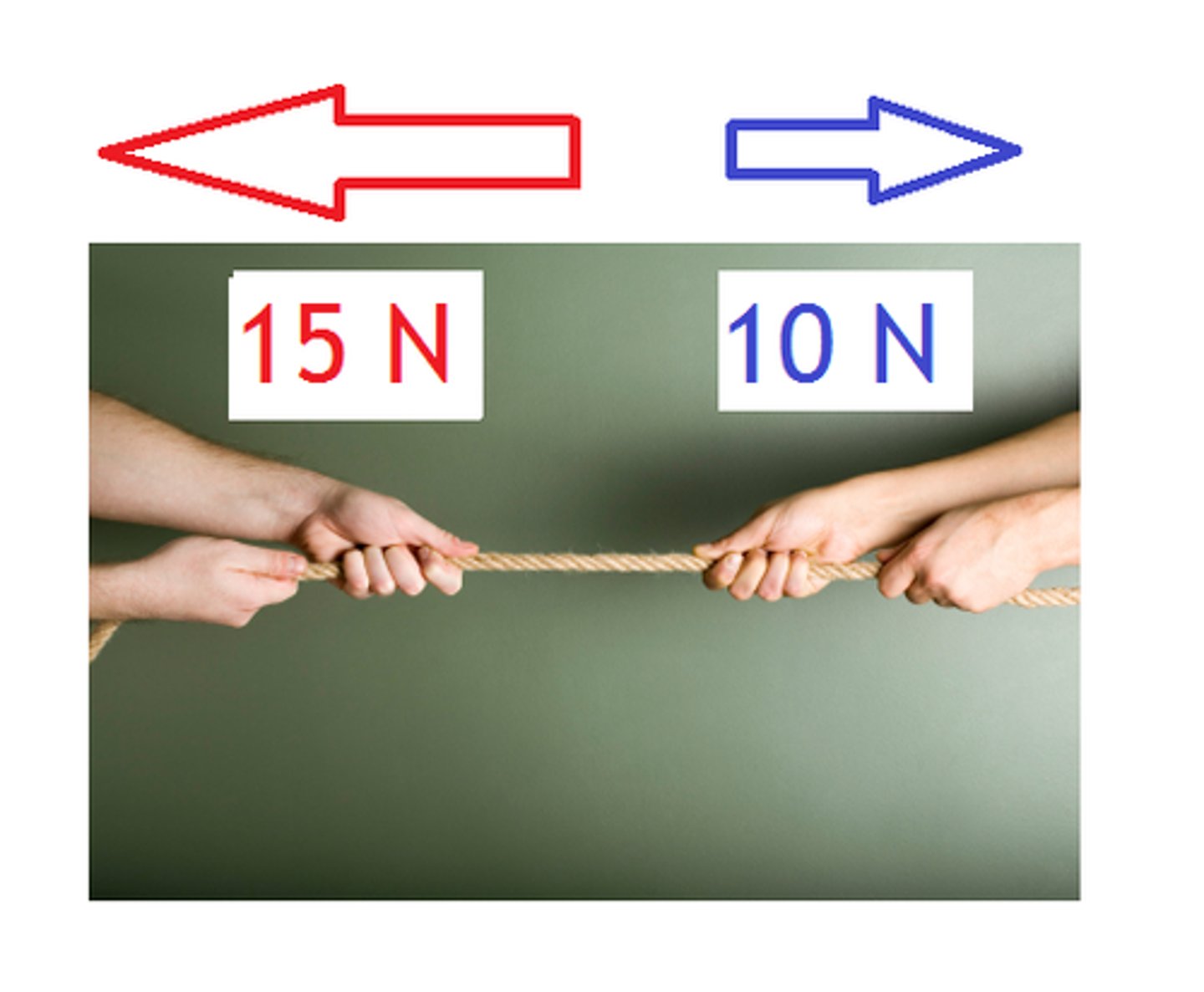
unbalanced forces
Forces that cause a change in the motion of an object
Friction
A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact

Gravity
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses.
Inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion

net force
The combination of all forces acting on an object
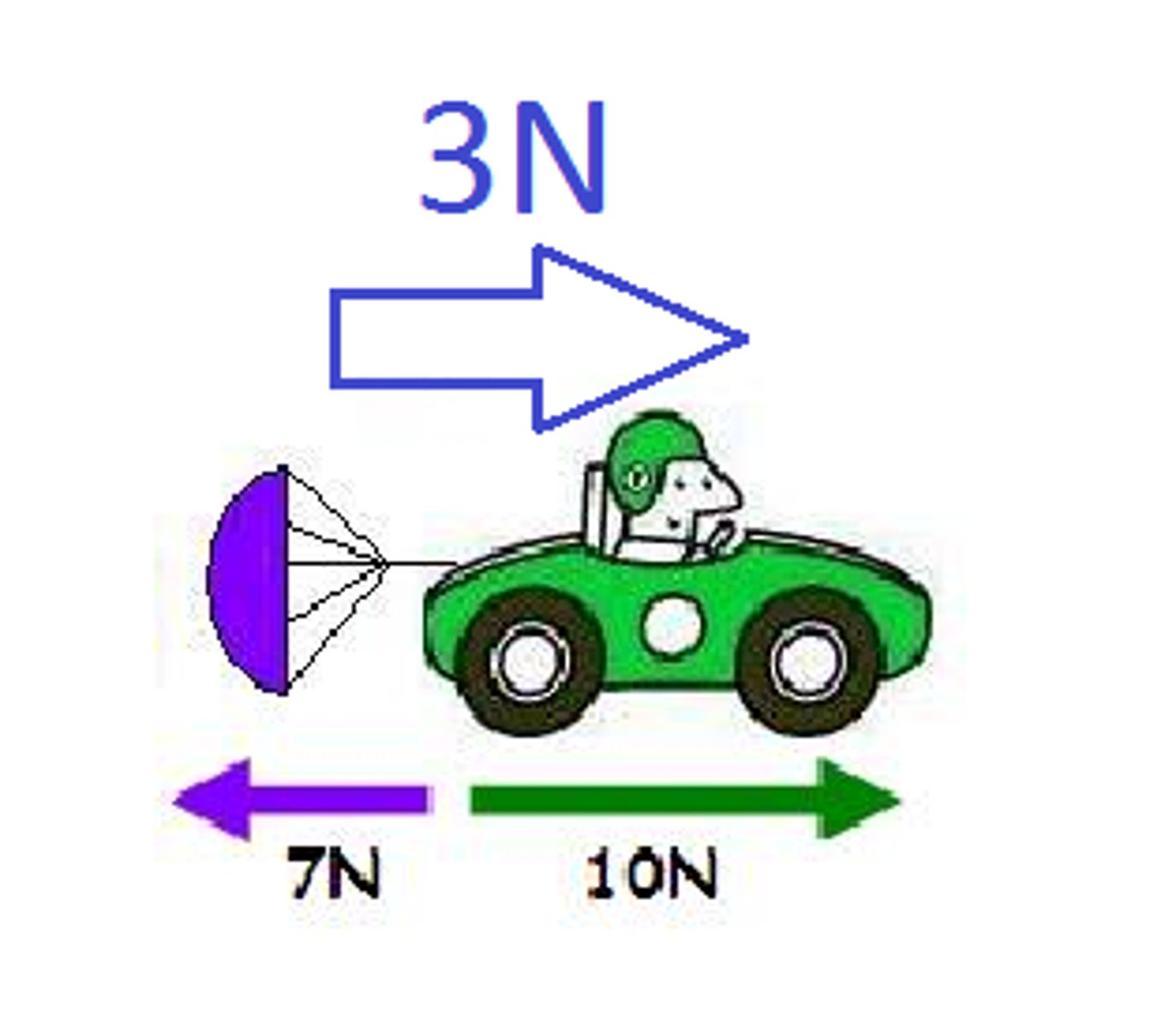
action force
the initial push or pull of one object on another object

reaction force
force acting in the opposite direction

Newton's 1st law of motion
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
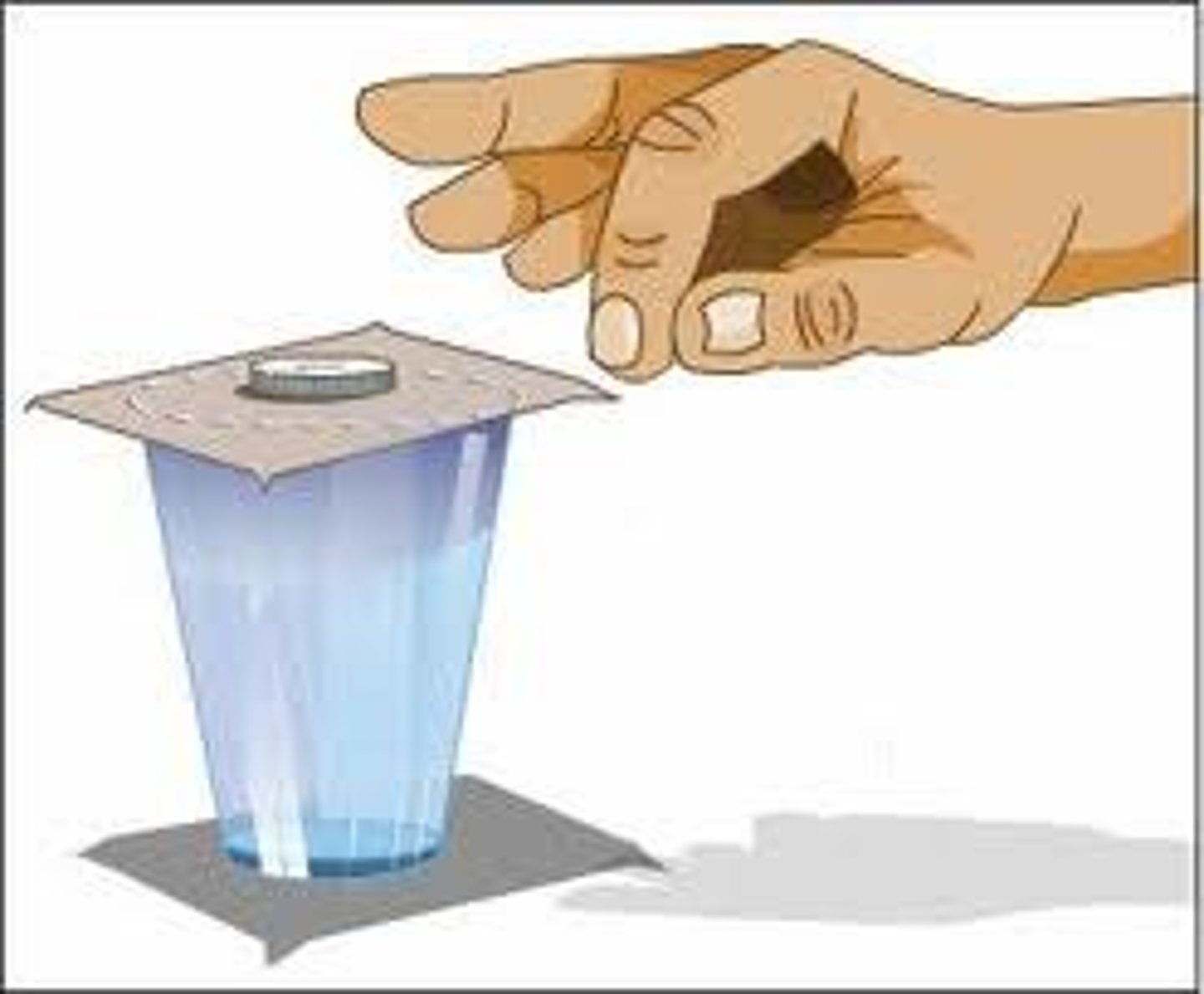

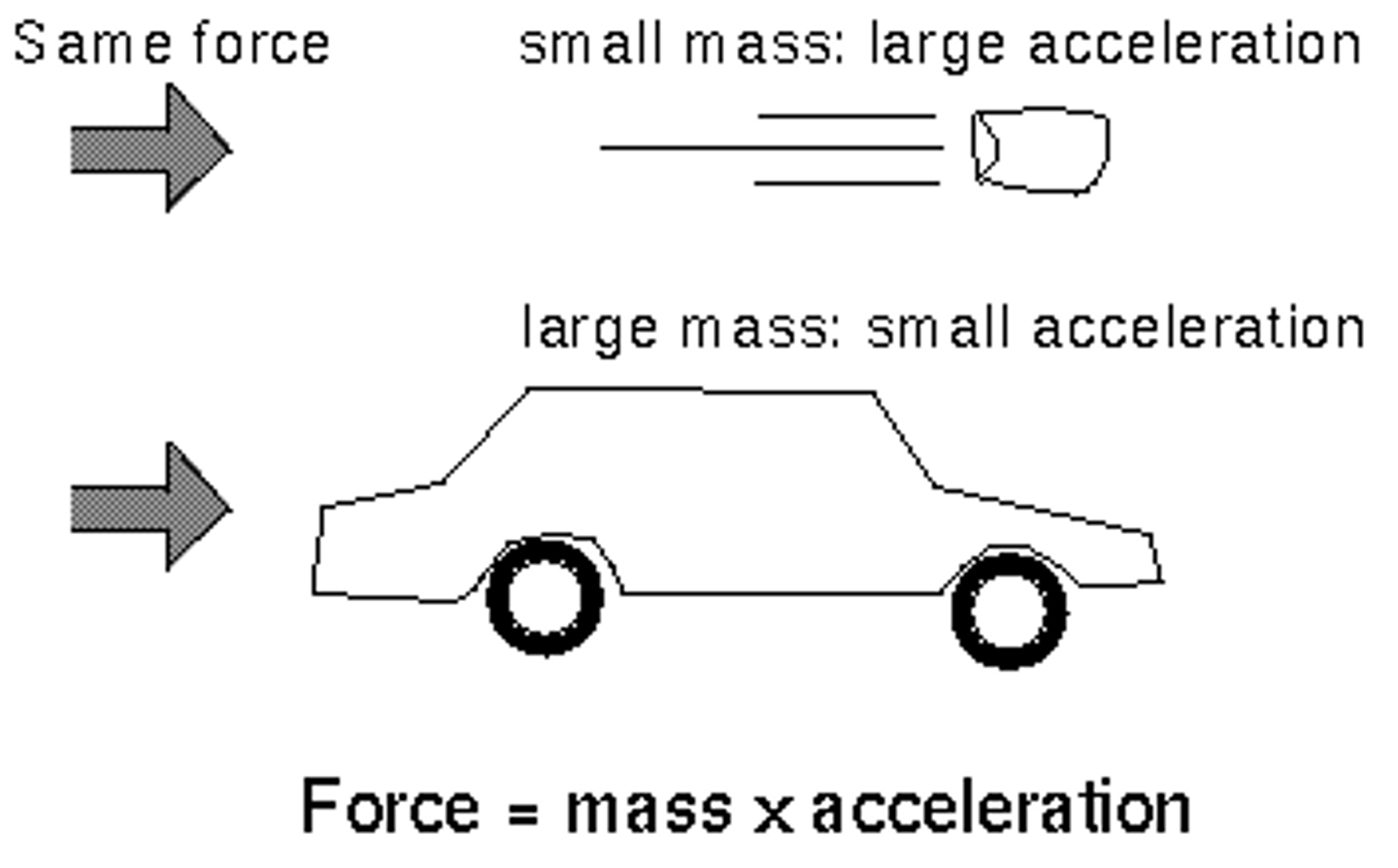
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion
Force equals mass times acceleration; f=ma
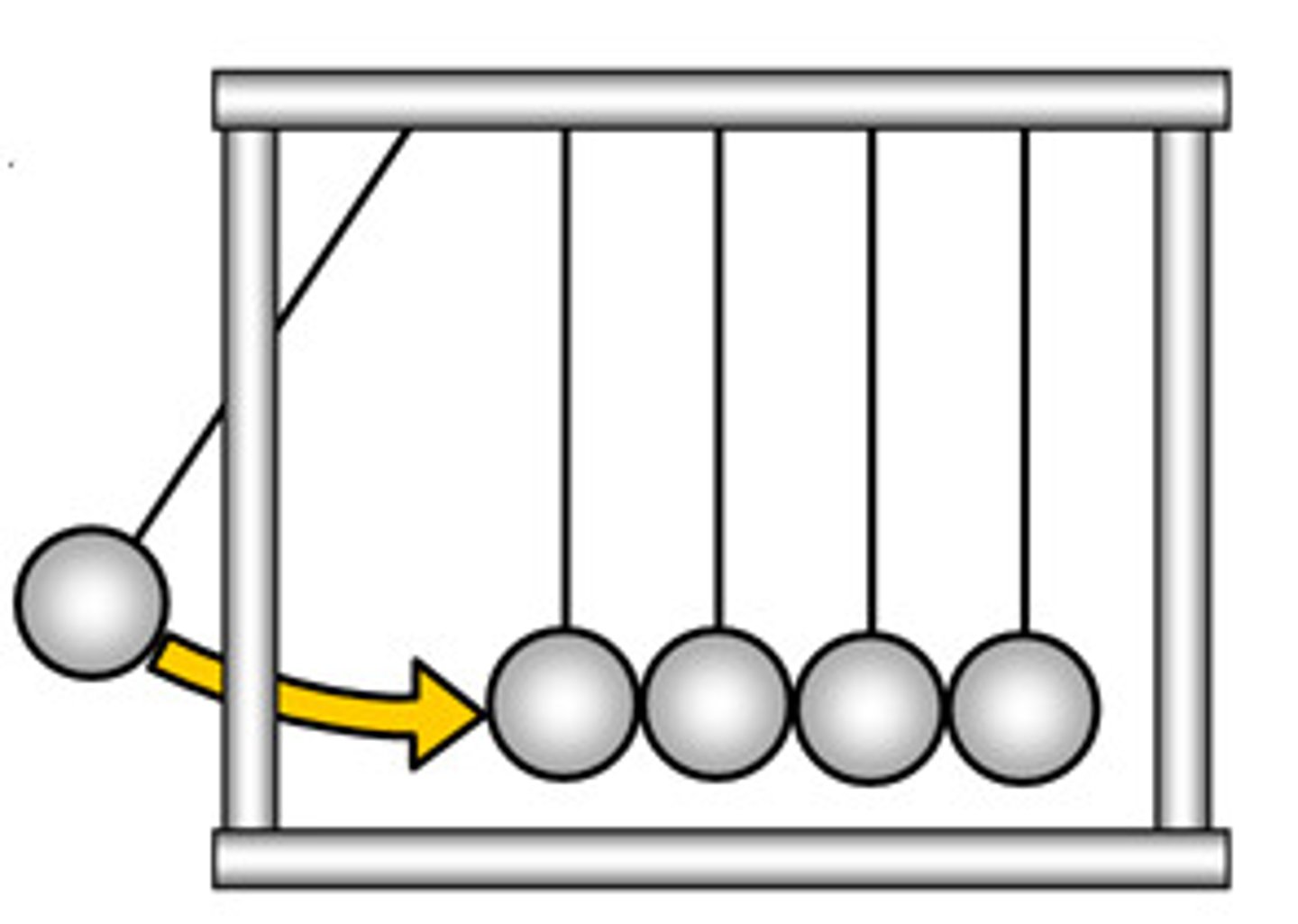
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
air resistance
force that opposes the motion of objects that move through the air

Newton's Second Law
It requires more force to make a more massive object accelerate. It takes less force to make a less massive object accelerate.

acceleration
the rate of change of velocity

fluid friction
the friction between layers of a viscous fluid (liquid or gas) that are moving relative to each other
free fall
an object that is falling under the sole influence of gravity

friction
the force that resists motion when the surface of one object comes in contact with the surface of another

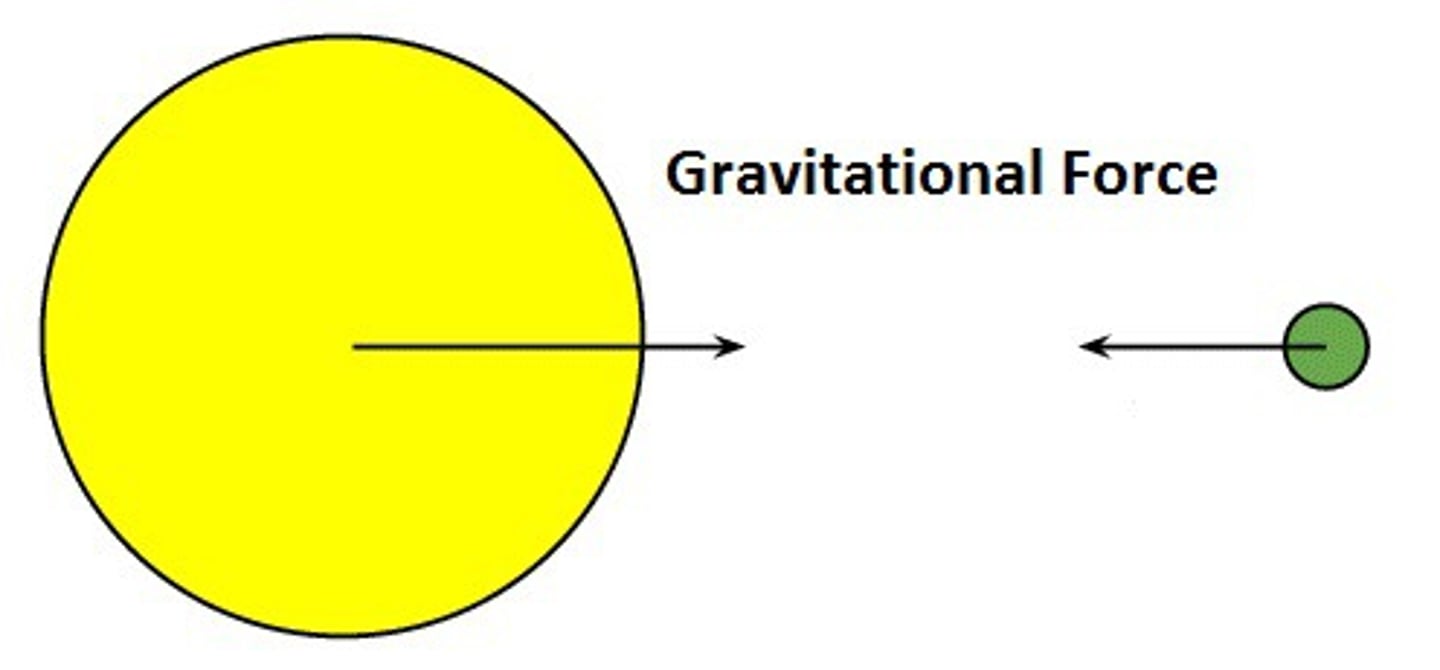
gravitational force
is a force between any two objects. The strength of the force is related to the mass of the objects and the distance between them.
mass
the amount of matter in a substance

Newton
the unit used to measure force
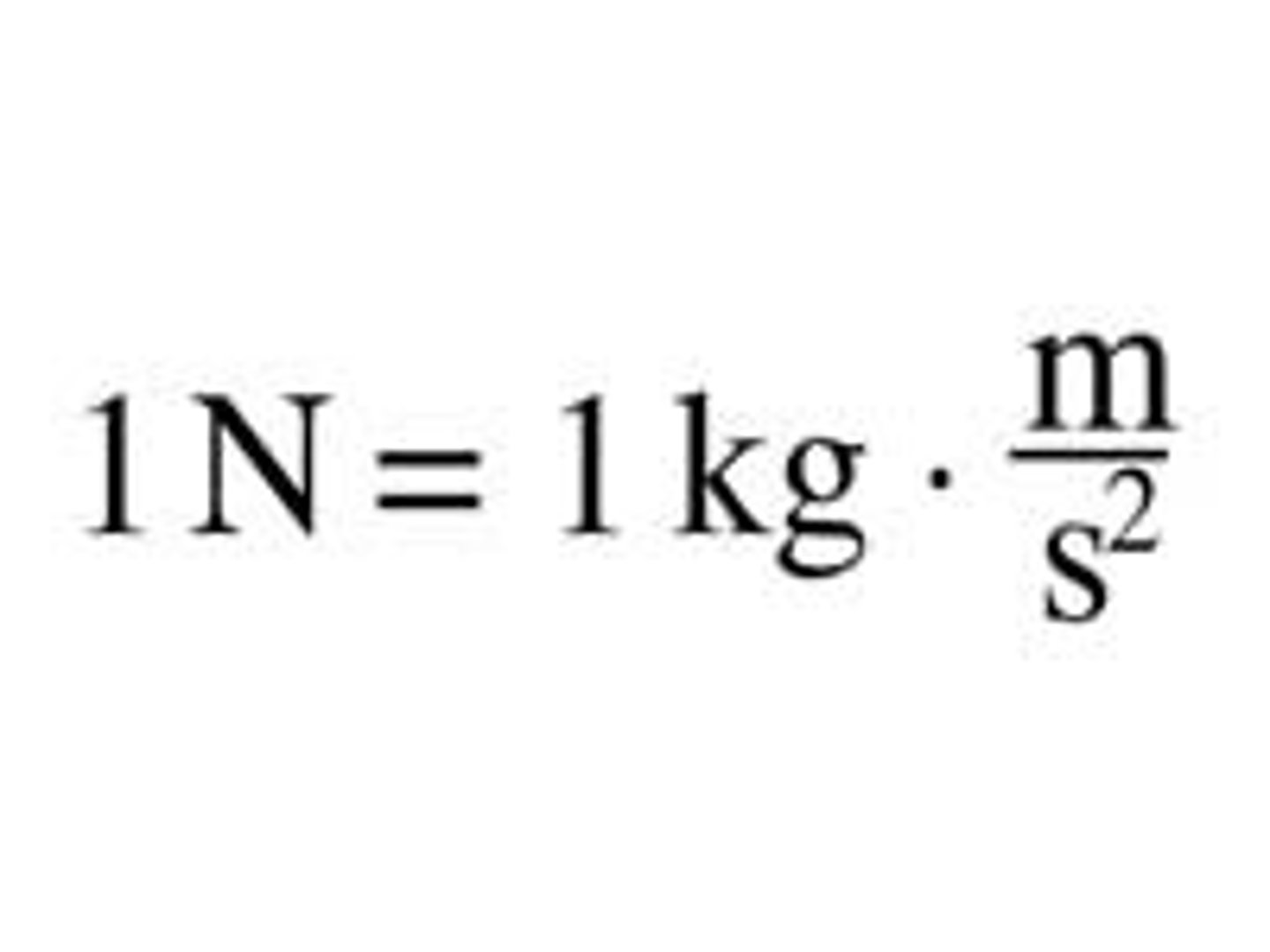
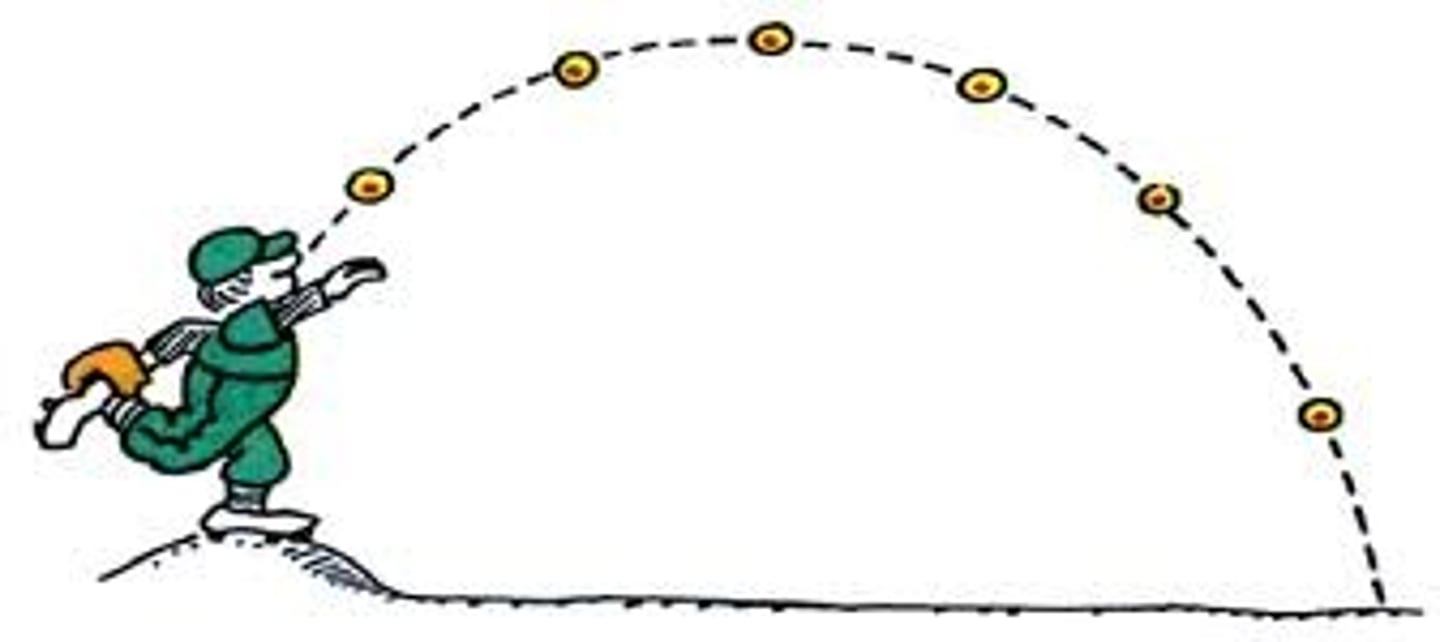
projectile motion
the motion of an object projected vertically upward into the air and moving under the influence of gravity
rolling friction
a type of force that opposes the motion of a rolling body

sliding friction
the force that resists an object as it slides or starts to slide along a surface
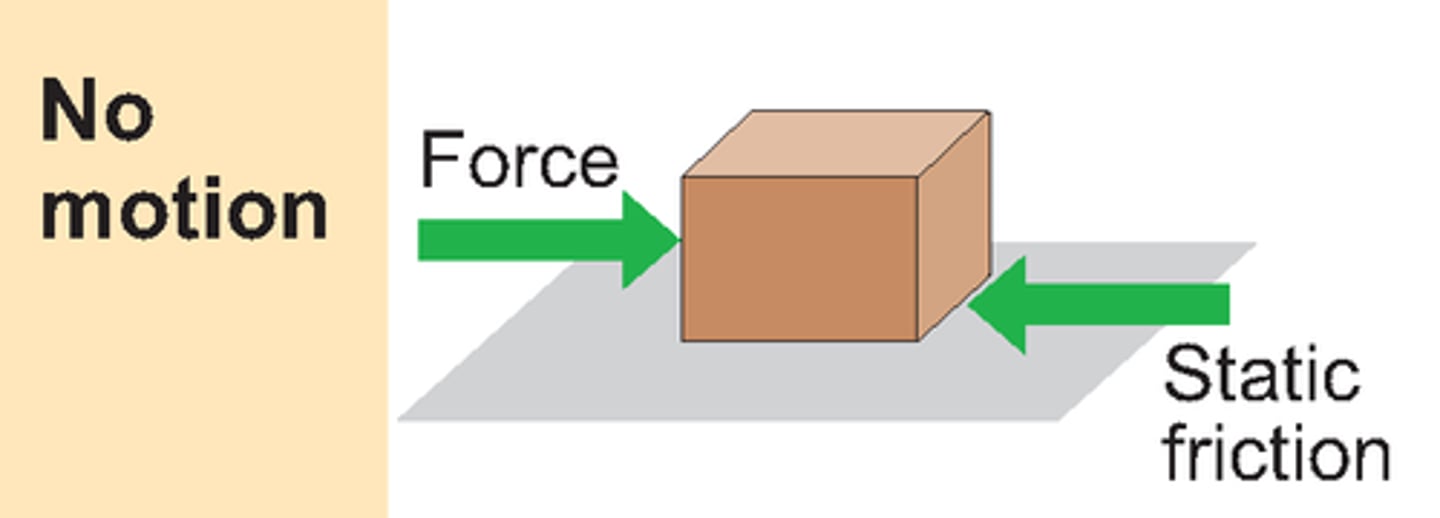
static friction
a force that opposes the initiation of motion between two bodies at rest
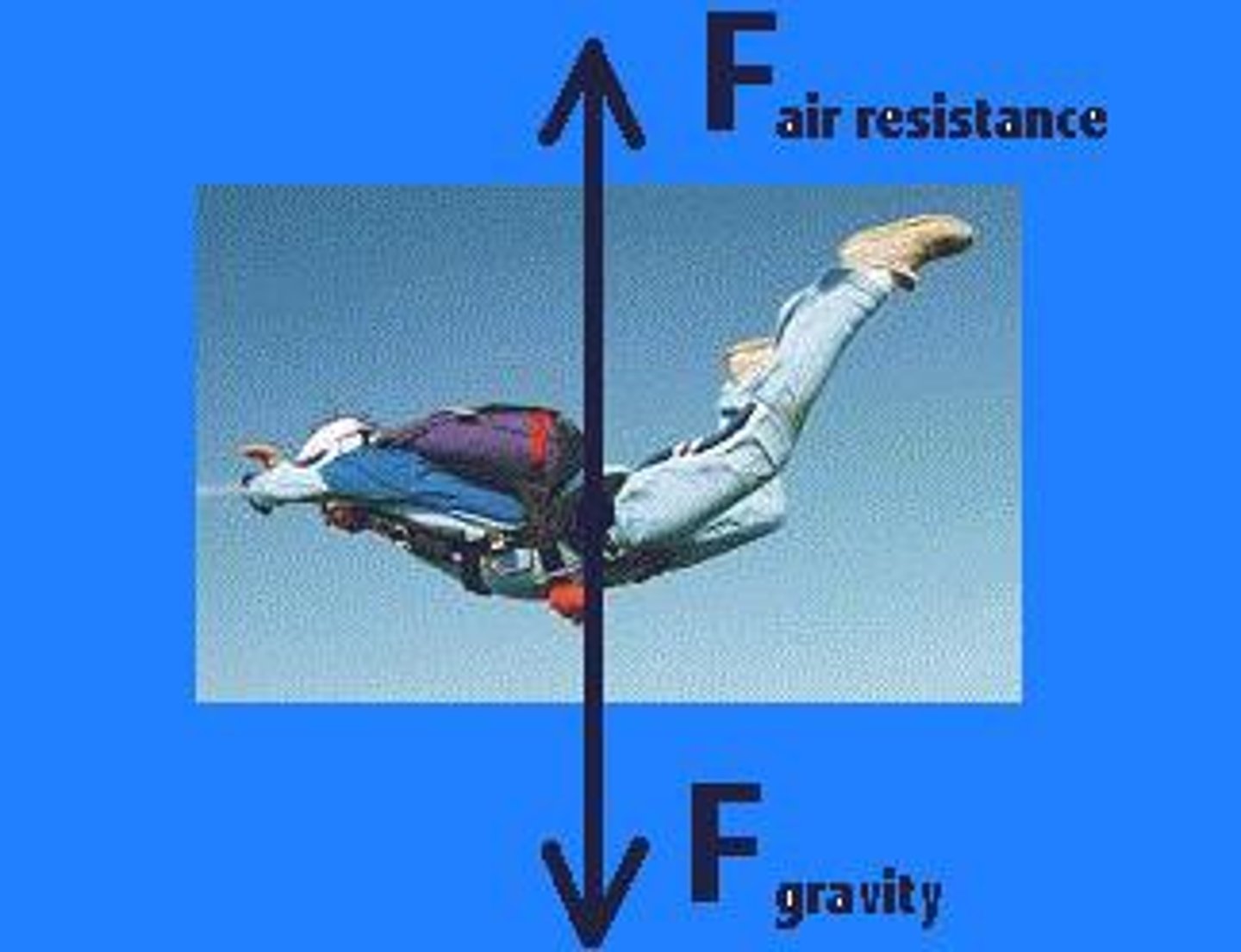
terminal velocity
the maximum falling speed of an object which can be affected by factors like gravity and drag force
weight
the force due to gravity-Equal to the product of the object's mass and the acceleration of gravity (w = mg). At the surface of Earth, the acceleration of gravity is 9.80 m / s² which is the constant used in the equation for g.
