THE MACROECONOMICS AP CARDS (MEAP) evil basic economics (evil)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Economics
study of how societies and individuals choose to allocate resources
Scarcity
Limited resources to satisfy unlimited want
Economic resources
Factors of production: land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship that individuals and businesses use in production of goods and services
Models
Graphical and mathematical tools used to better understand processes
Cereros paribus
“all else equal.”
Agent
Entity that makes decisions; could be individual, business, or government.
Incentives
Rewards or punishments associated with a possible action; agents make decisions based on incentives.
Rational decision making
Use of all available information to choose an action that allows one to be the most well off as possible, agents are “rational” if true; economic models assume that agents are rational.
Positive analysis
Analytical thinking about objective facts and cause-and-effect relationships that are testable. E.g., how much of a good will be sold when a price changes.
Normative analysis
Subjective thinking about what one should value or a course of action that should be taken. E.g., importance of environmental factors and the approach to managing them
Microeconomics
Study of the interactions of buyers and sellers in the markets for particular goods and services.
Macroeconomics
Study of aggregates and the overall commercial output and health of nations. Analysis of factors i.e. unemployment, inflation, economic growth, and interest rates.
Economic aggregates
Frequently used as measures of the economic performance of an economy. Summarizes all markets in an economy (i.e., unemployment rate, inflation rate, and national output) rather than individual markets.
Capital
Already-produced goods that are used in production of other goods or services. E.g., an automated manufacturer, not loans.
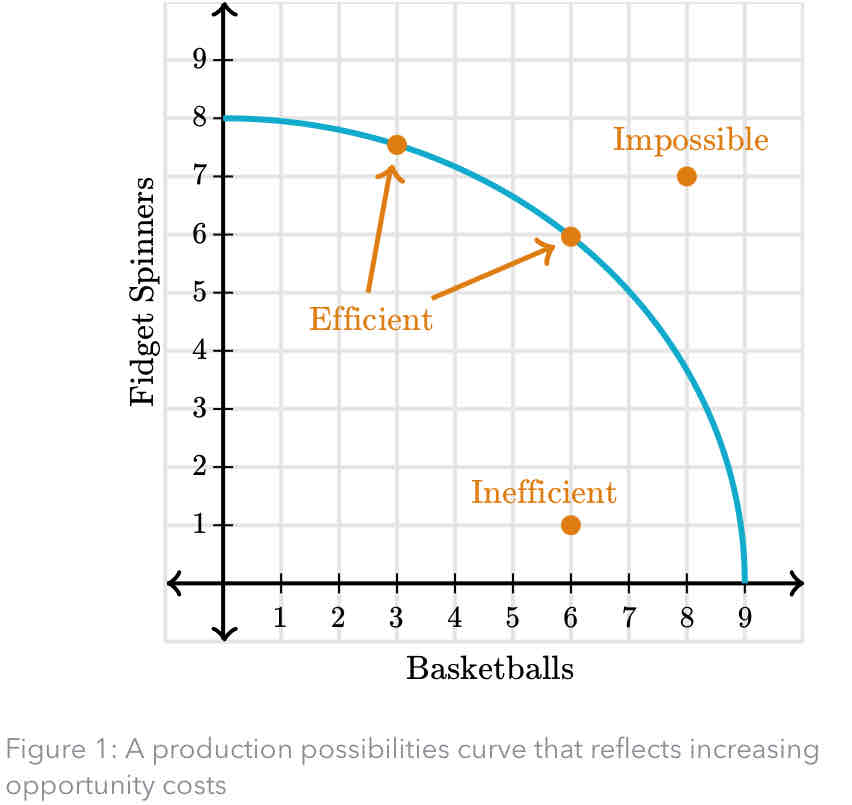
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
Graphical model that represents all of the different combinations of two goods that can be produced; also captures the scarcity of resources and opportunity costs.
Opportunity cost
The value of the next best alternative to any decision. E.g., hour of sobbing because of ap vs hour of studying for ap.
Efficiency
The full employment of resources in production. PPC will always record efficient combinations of output.
Inefficient use of resources
Underemployment of any of the economic resources. Inefficient combinations of production are represented using a PPC as points on the interior of the PPC.
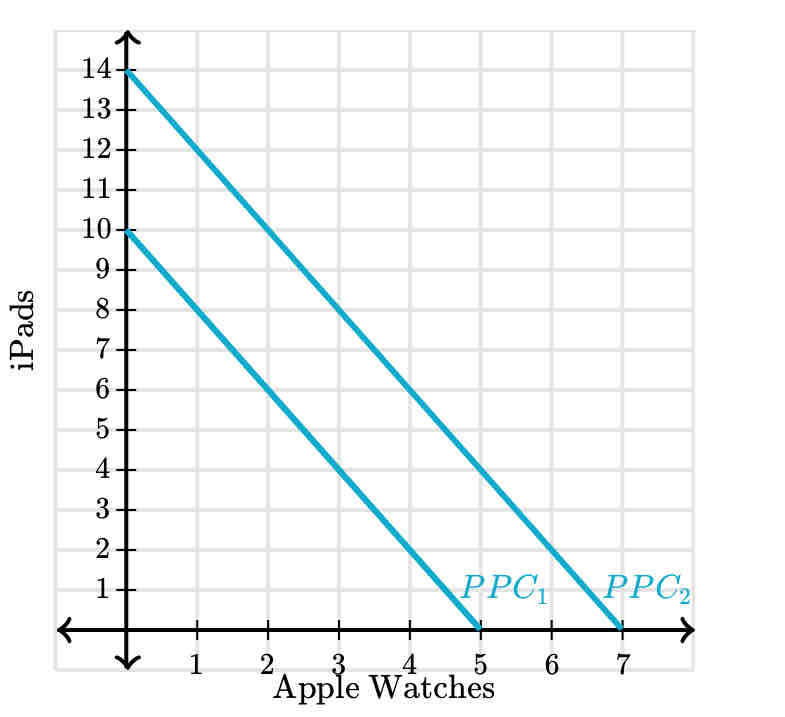
Growth
An increase in an economy’s ability to produce goods and services over time. In the PPC model, it’s Illustrated by a shift out of the PPC.
Contraction
A decrease in output that occurs due to the inefficient use of resources. In the PPC model, it’s represented by moving to a point that is further away from, and on the interior of, the PPC.
Constant opportunity costs
When the opportunity cost of a good remains constant as output of the good increases. Represented as a PPC that is a straight line.
Increasing opportunity costs
When the opportunity cost of a good increases as the output of the good increases. Represented in the graph as a PPC that is bowed out from the origin.
increasing opportunity costs in PPC graph
increasing economic growth in PPC graph
PPC key equation for opportunity costs
Opportunity cost of each unit of good X = (y1-y2)/(x1-x2) units of good Y. Also known as the average rate of change.
Productivity
The ability to combine economic resources. An increase in productivity causes economic growth even if economic resources have not change, which would be represented by a shift out of the PPC. Also called technology.
Absolute advantage
The ability to produce more of a good than another entity, given the same resources.
Comparative advantage
The ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another entity.
Specialization
When an agent allocates most or all of its resources towards the production of a particular good or service
Trade
The exchange of goods, services, or resources between one economic agent and another
International trade
The exchange of goods, services or resources between one economic agent and another
Gains from trade
The ability of two agents to increase their consumption possibilities by specializing in the good in which they have comparative advantage and trading for a good in which they do not have comparative advantage.
Terms of trade
The price of one good in terms of the other that two countries agree to trade at; beneficial terms of trade allows a country to import a good at a lower opportunity cost than the cost for them to produce the good domestically, thus the country gains from trade.