Signal Transduction: IP3, DAG and PKC Overview
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Signal Transduction
Process of transmitting signals within cells.
Second Messenger
Intracellular molecules activating target proteins.
Effector Enzyme
Enzyme generating second messengers.
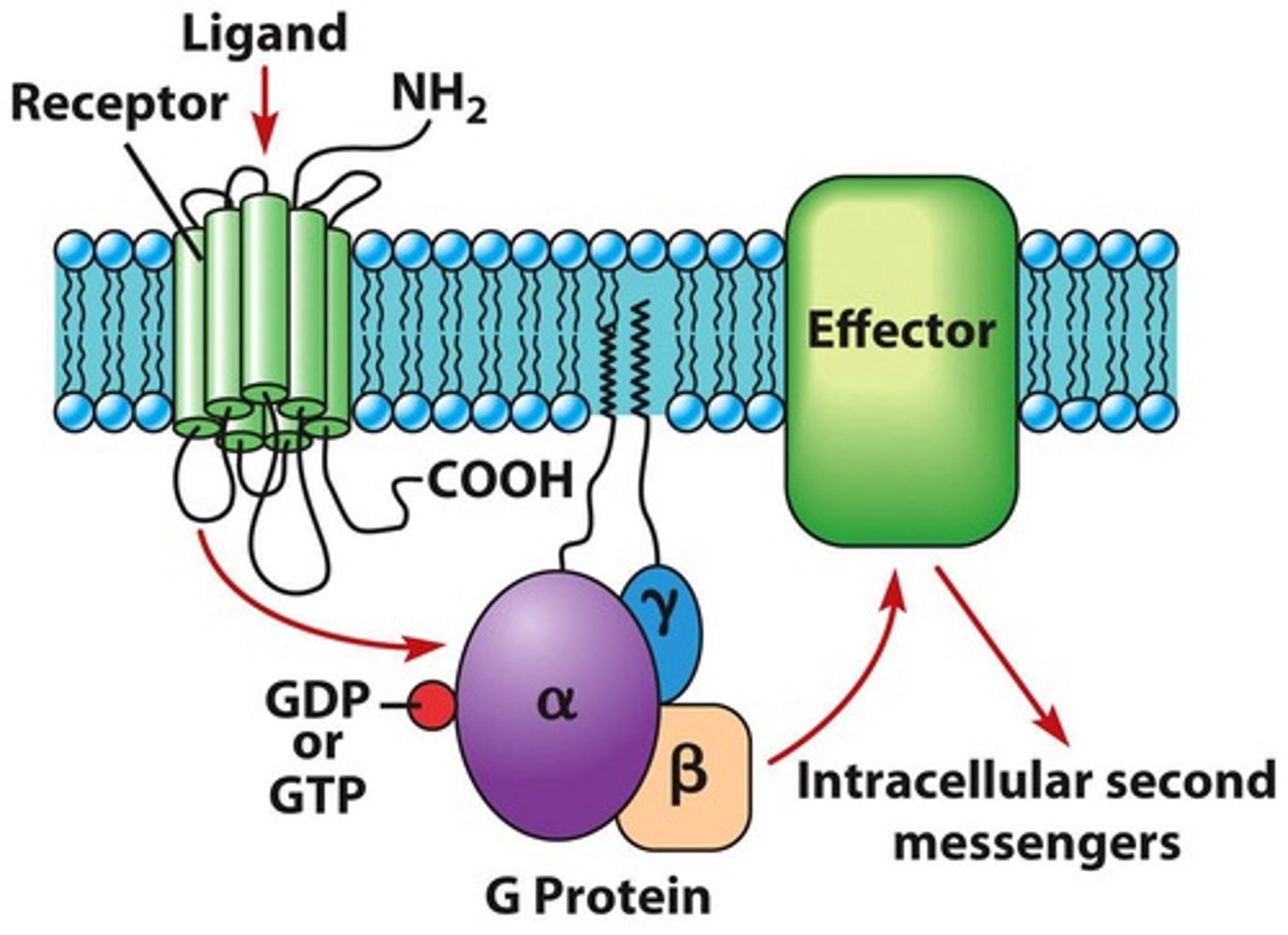
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Membrane proteins activating intracellular signaling.
Adenylyl Cyclase
Enzyme converting ATP to cAMP.
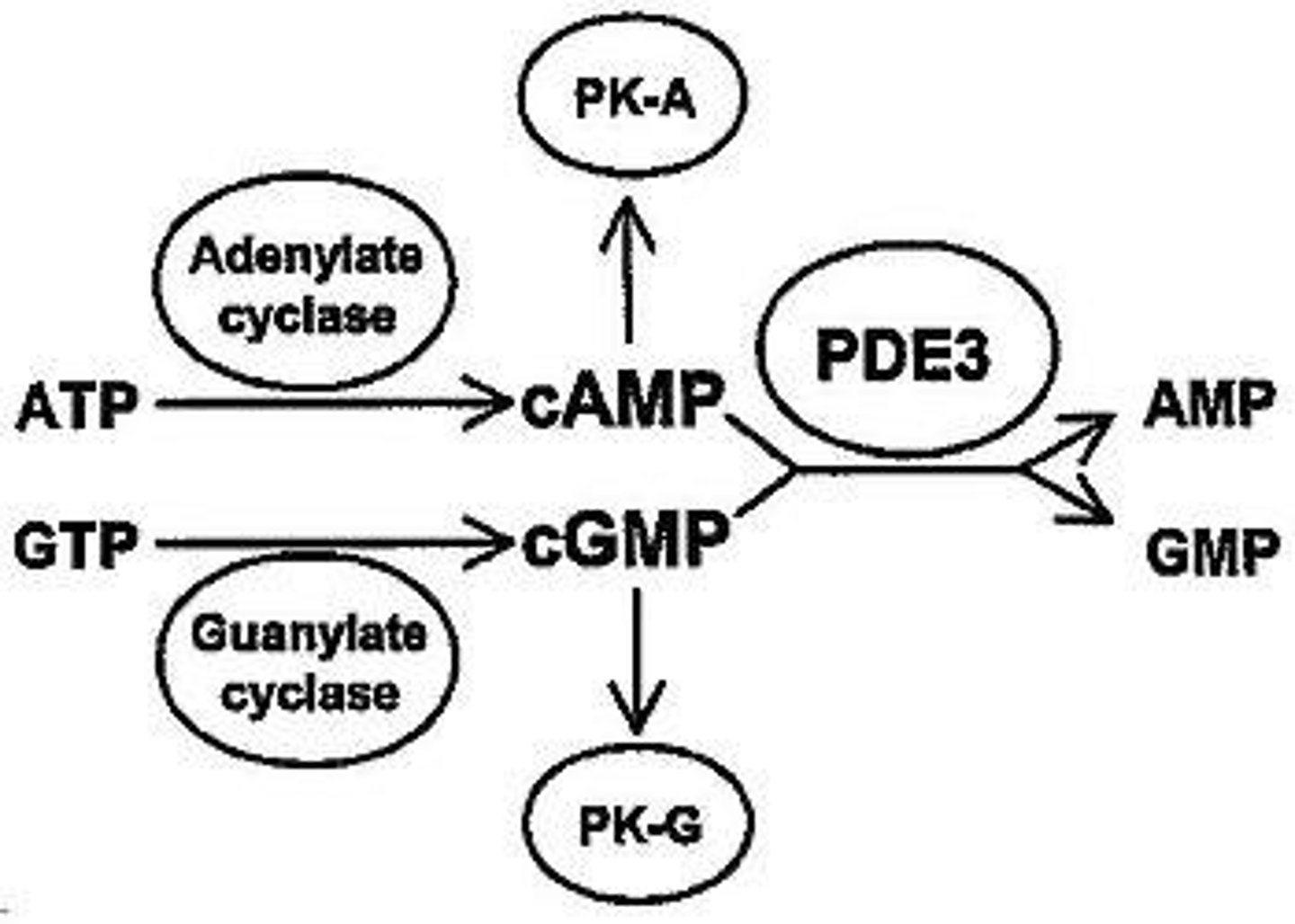
cAMP
Cyclic AMP, a key second messenger.
Phospholipase C
Enzyme producing IP3 and DAG from phospholipids.
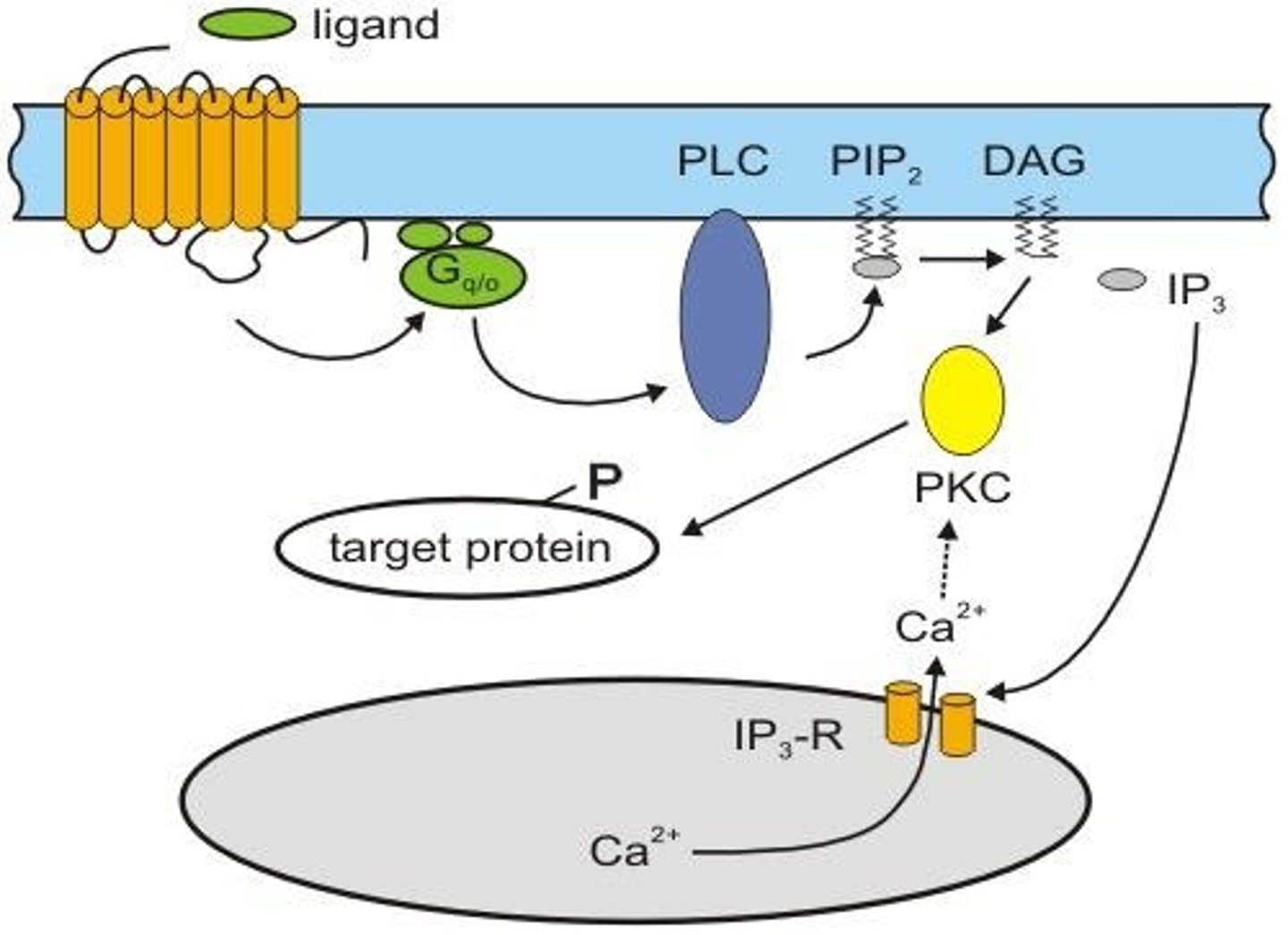
IP3
Inositol trisphosphate, mobilizes calcium from ER.
DAG
Diacylglycerol, activates Protein Kinase C.
Protein Kinase C
Enzyme activated by DAG for signaling.
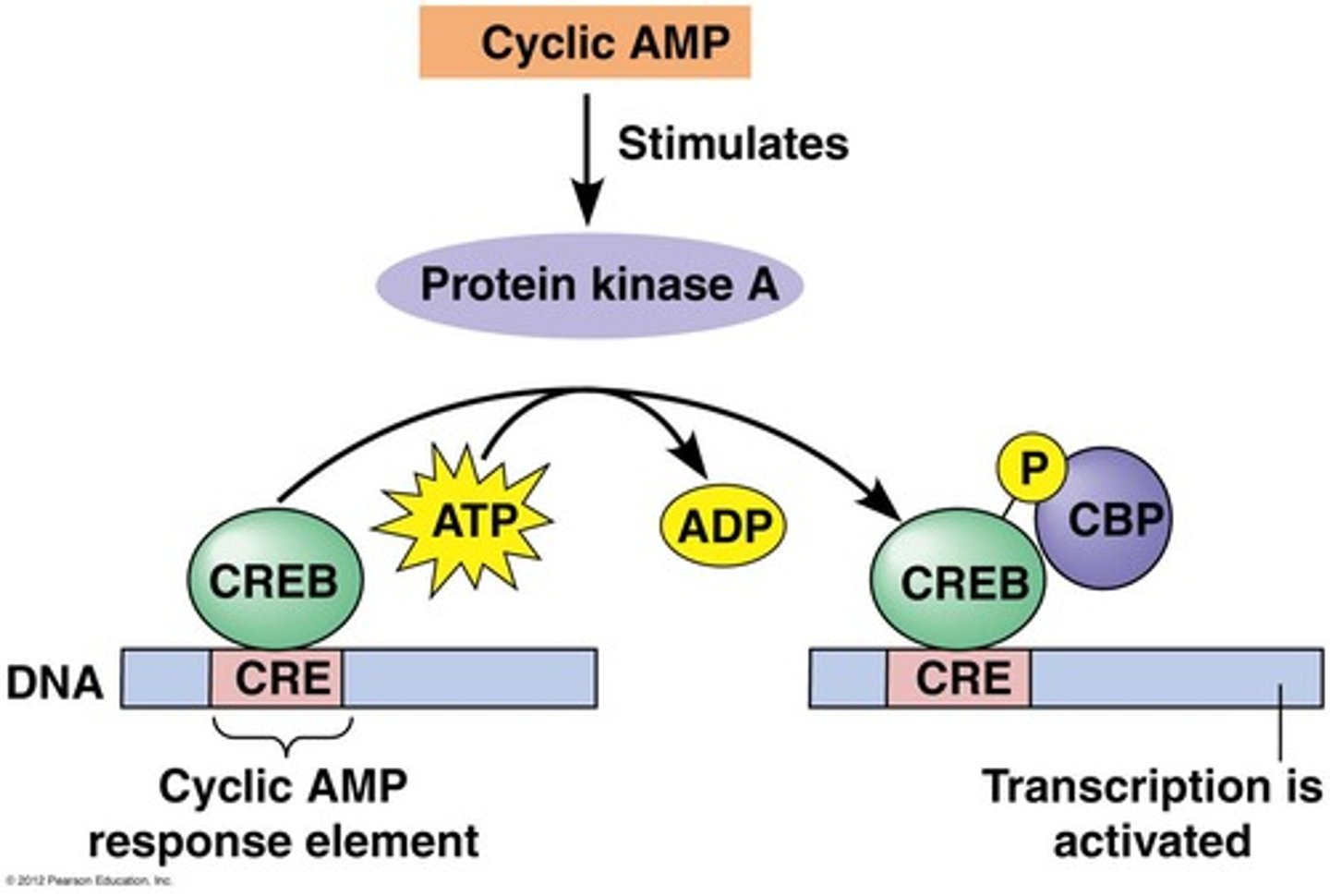
CREB
Transcription factor activated by cAMP signaling.
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrates.
p-CREB
Phosphorylated CREB, enhances gene transcription.
Glucagon
Hormone increasing blood glucose levels.
Epinephrine
Hormone stimulating fight-or-flight response.
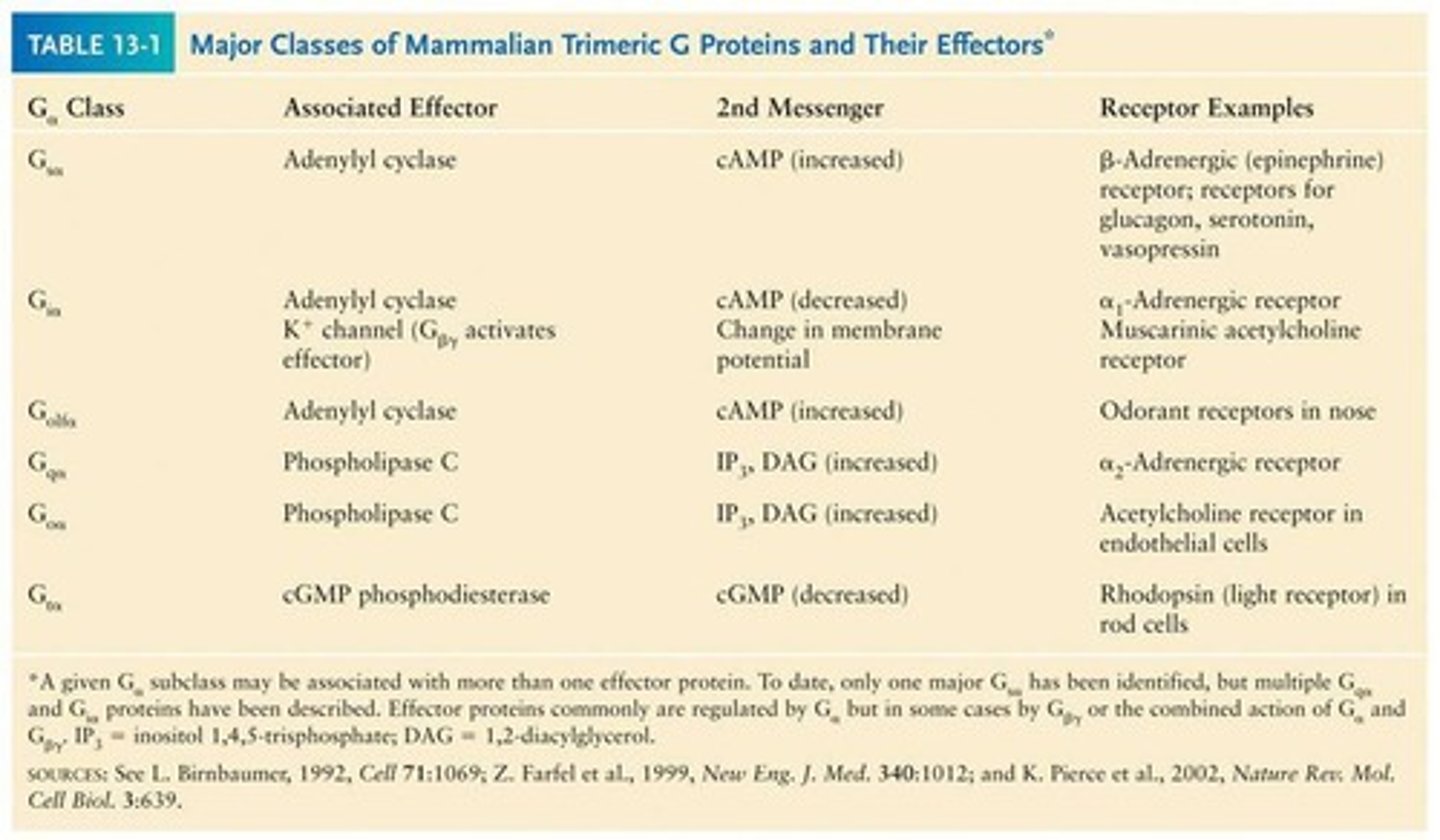
Gs Protein
Stimulates adenylyl cyclase to increase cAMP.
Gi Protein
Inhibits adenylyl cyclase to decrease cAMP.
Gq Protein
Activates PLCβ to produce IP3 and DAG.
G12/13 Proteins
Activate small G proteins, linked to proliferation.
Rhodopsin
Light-sensitive receptor in rod cells.
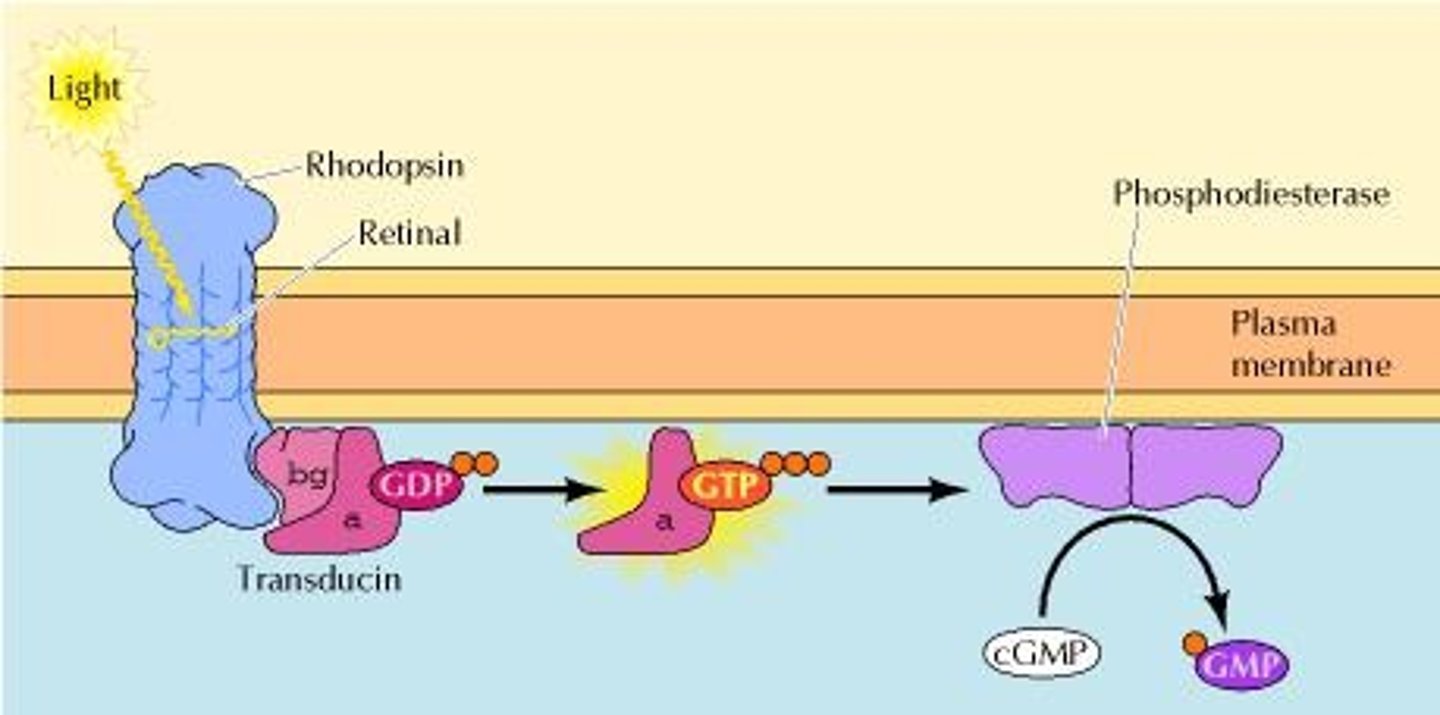
Transducin
G-protein activated by rhodopsin.
cGMP Phosphodiesterase (PDE)
Enzyme that converts cGMP to GMP.
cGMP
Second messenger that regulates ion channels.
Bradyopsia
Slow vision due to RGS9 mutations.
RGS9
Protein that inactivates transducin in light.
Phospholipase C (PLC)
Enzyme that cleaves PIP2 into IP3 and DAG.
Inositol Trisphosphate (IP3)
Second messenger that releases calcium from ER.
Diacylglycerol (DAG)
Second messenger that activates protein kinase C.
Phosphatidylinositol (PI)
Lipid precursor for second messengers IP3 and DAG.
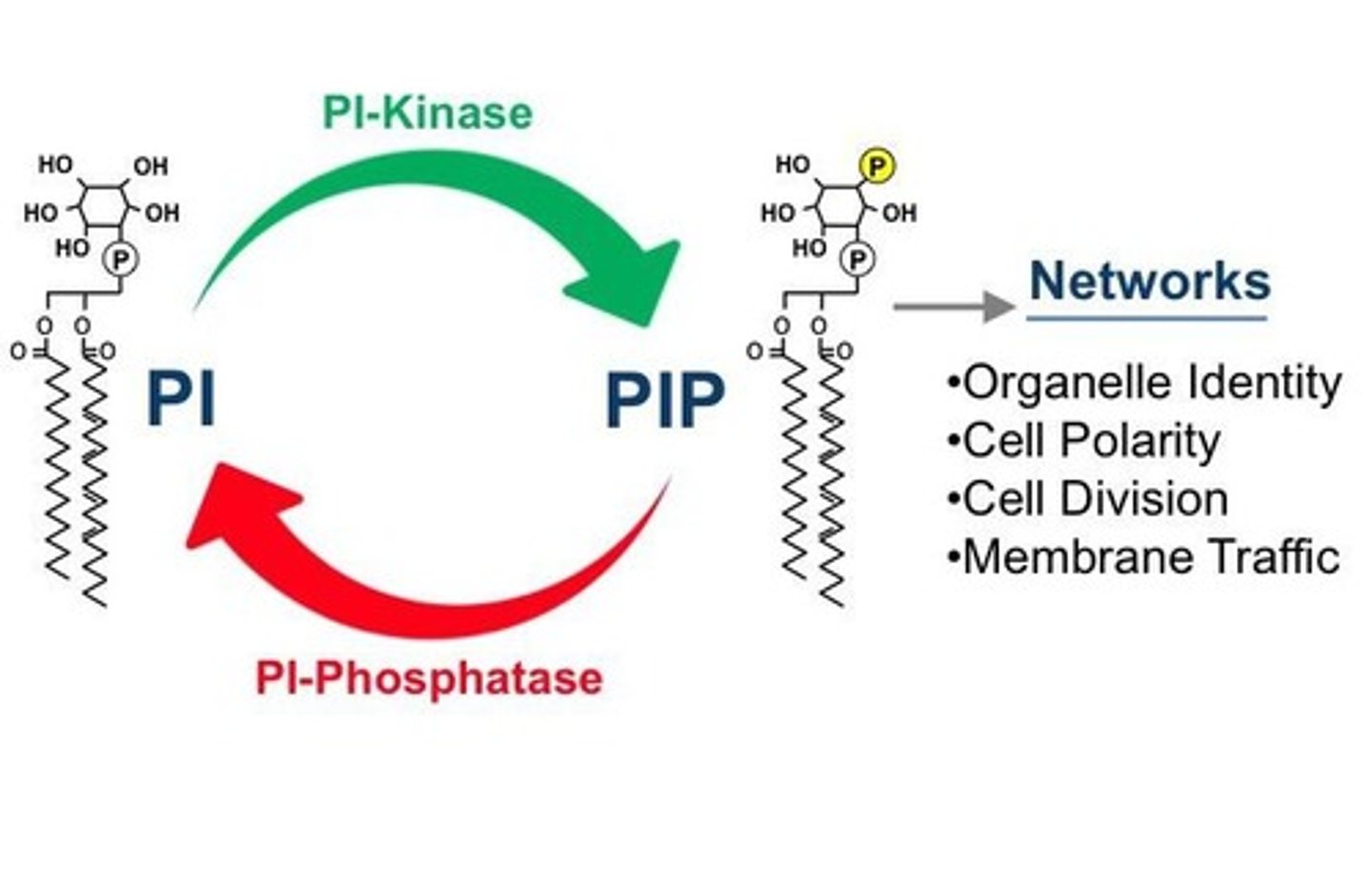
PIP2
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, substrate for PLC.
Gαt
G-protein subunit involved in phototransduction.
Calcium Channels
Ion channels regulated by IP3 signaling.
Protein Kinase C (PKC)
Enzyme activated by DAG and calcium.
G12/13
G-proteins associated with cell proliferation.
Phospholipid Kinases
Enzymes that phosphorylate phospholipids.
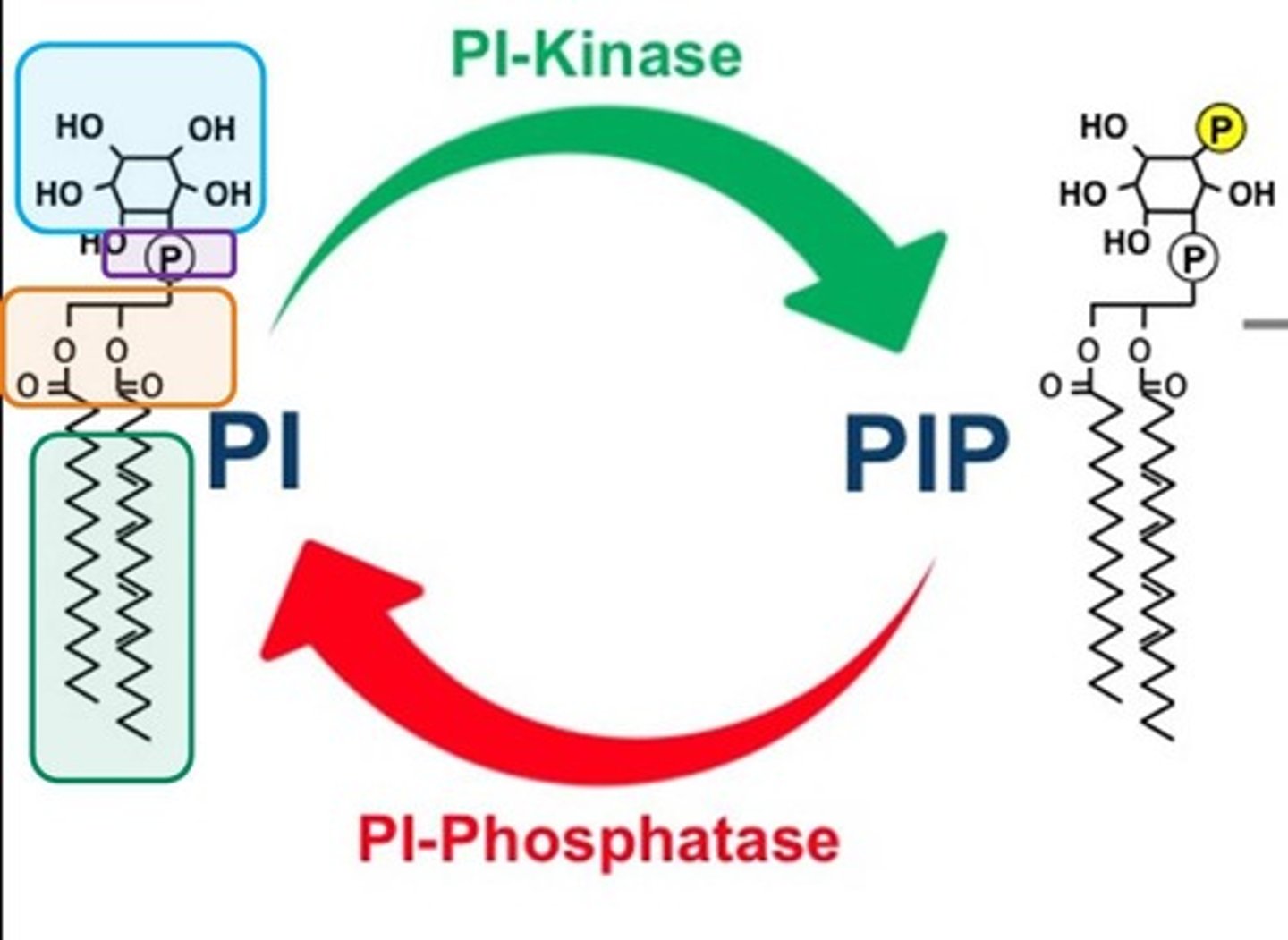
Phospholipid Phosphatases
Enzymes that dephosphorylate phospholipids.
Membrane Hyperpolarization
Increased negativity of membrane potential.
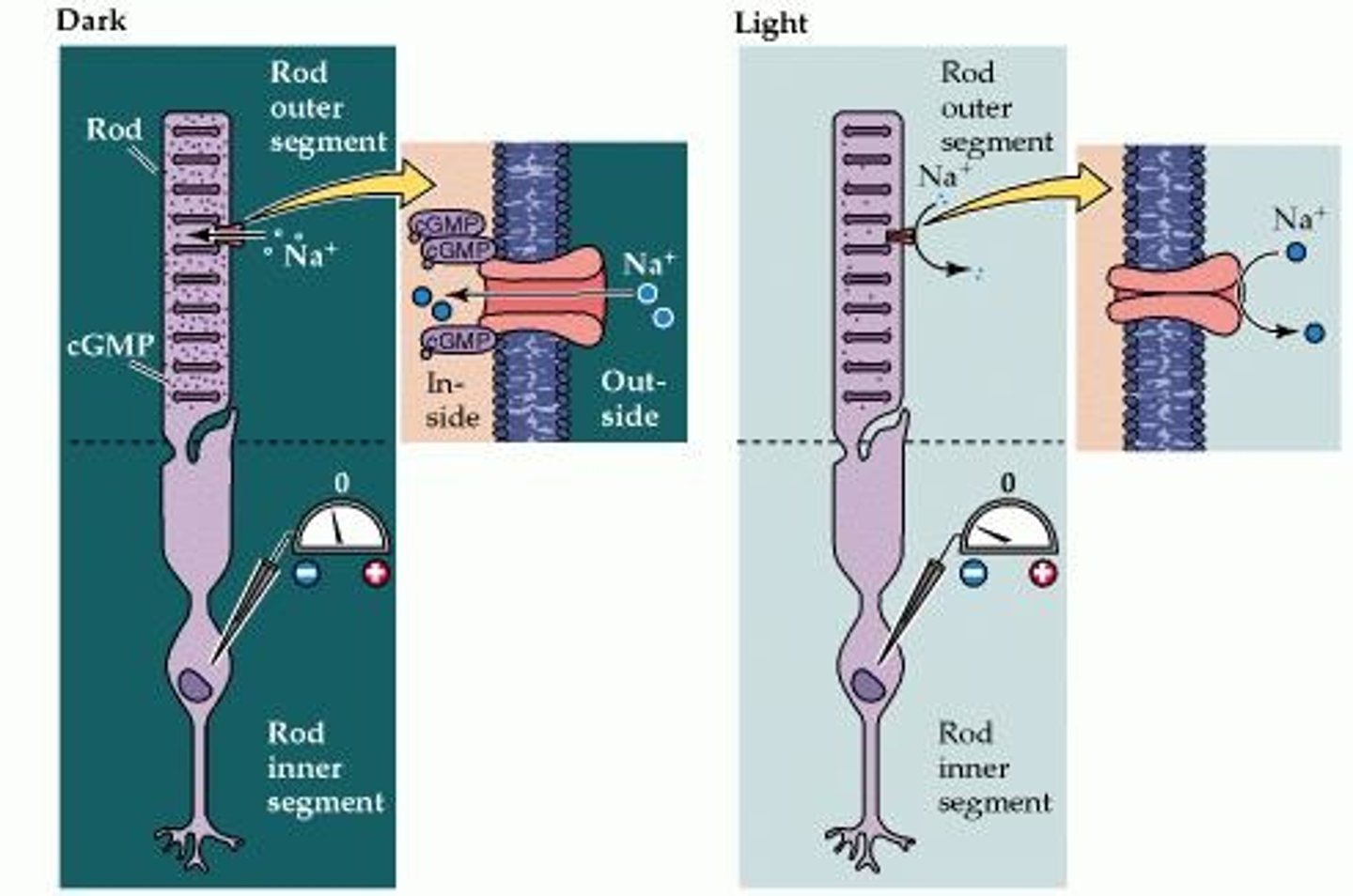
Na+ and Ca2+ Ion Channels
Channels affected by cGMP levels.
Ligands
Molecules that bind to receptors, activating them.
Cellular Growth
Process regulated by PKC signaling.
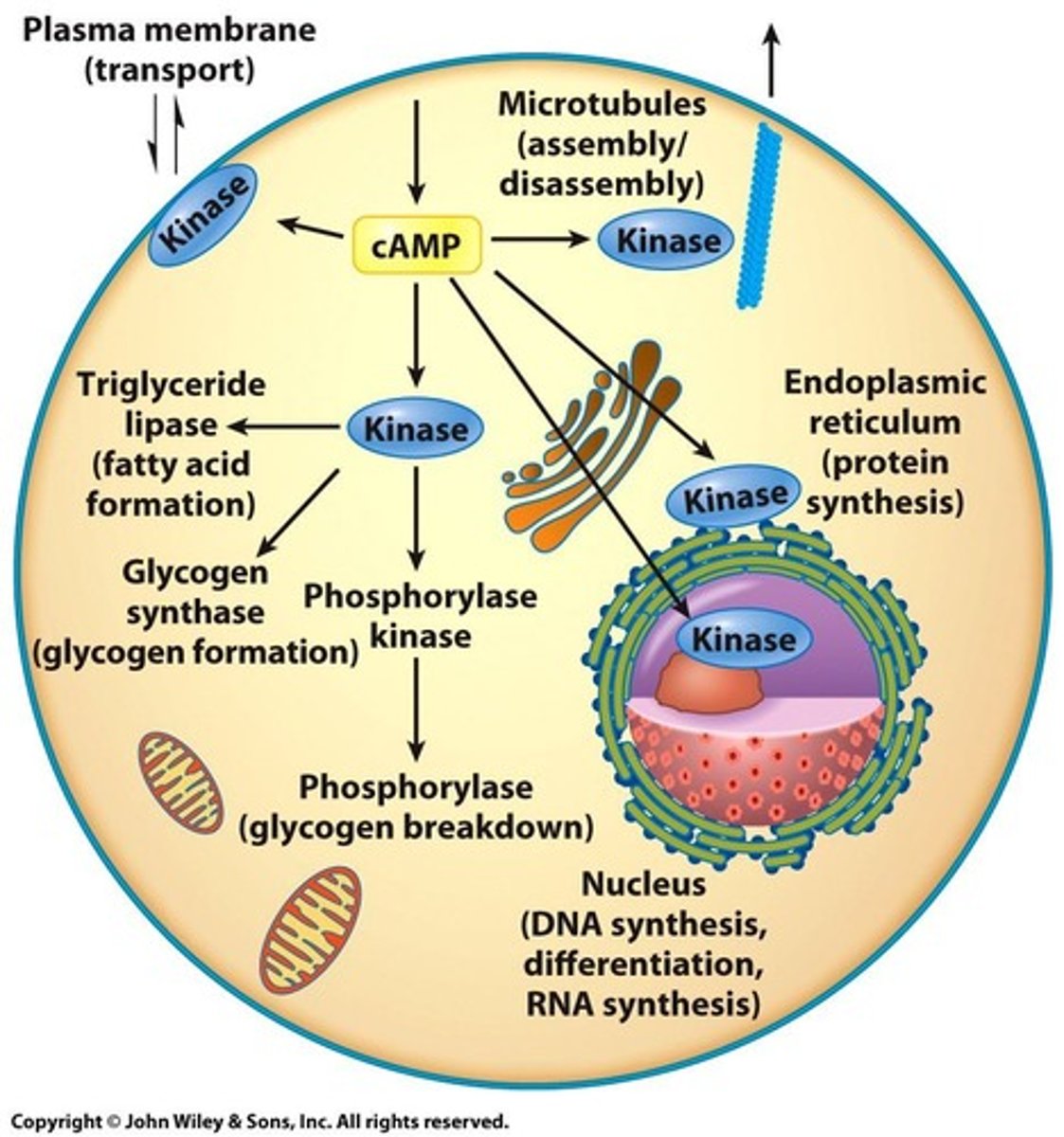
Cell Death
Process influenced by PKC activation.
G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
Receptors that mediate cellular responses to signals.
Protein Kinase A (PKA)
Enzyme activated by cAMP, phosphorylates target proteins.
PKC
Protein kinase activated by DAG and calcium.
Ligand
Molecule binding to a receptor to initiate signaling.
Transcription Activation
Process of increasing gene expression via transcription factors.
Calcium Signaling
Cellular process regulated by calcium ion release.
G Protein
Molecular switch activated by GPCRs.
Small G Proteins
Monomeric G proteins involved in signaling pathways.
Hyperpolarization
Increase in membrane potential making it more negative.
Cell Proliferation
Process of cell growth and division.
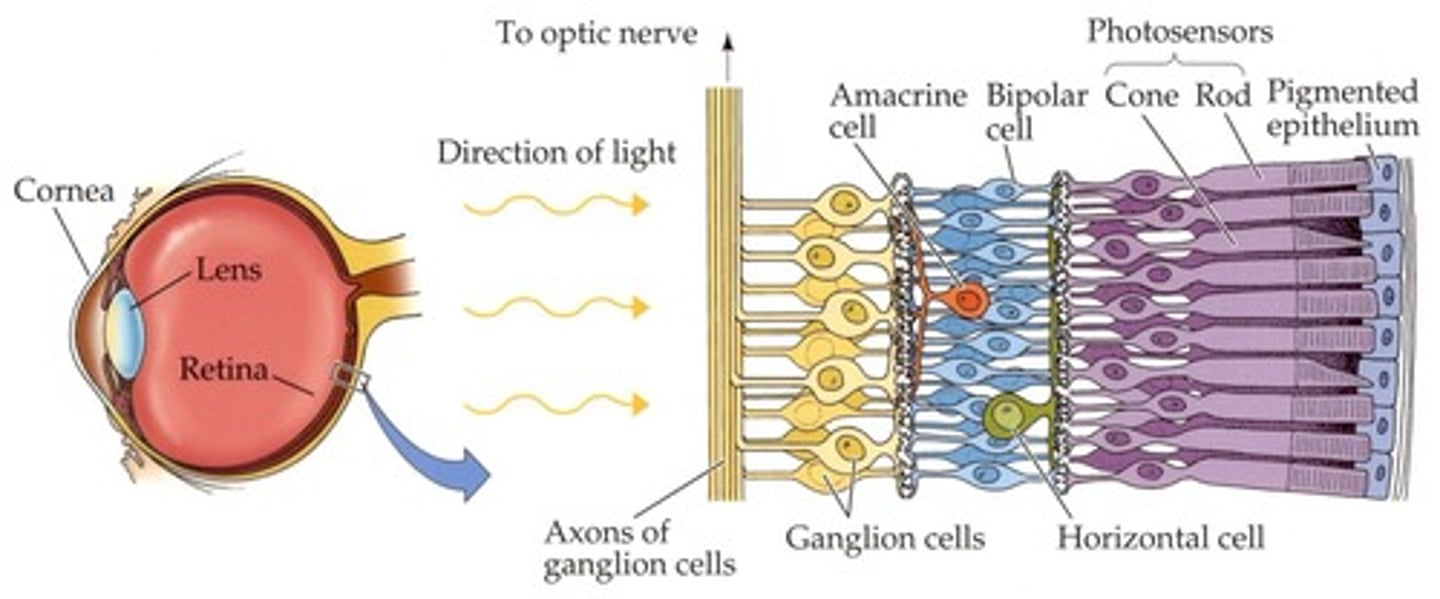
Visual Center
Brain region processing visual information.
PKA
Protein kinase A, phosphorylates CREB to activate transcription.
cGMP Phosphodiesterase
Enzyme that reduces cGMP levels in cells.
Gq
G protein that activates phospholipase C.
Gs
G protein that stimulates adenylyl cyclase.
Gi
G protein that inhibits adenylyl cyclase.
Calcium Release
Triggered by IP3 binding to smooth ER receptors.
Second Messengers
Intracellular molecules that relay signals.
Visual Signal
Membrane hyperpolarization in response to light.
Ca2+ Signalling
Cellular signaling pathway involving calcium ions.
Intracellular Messengers
Molecules that relay signals within cells.
Muscle Contraction
Triggered by an increase in intracellular Ca2+.
Exocytosis
Process of neurotransmitter release at synapses.
Hormone Secretion
Release of hormones like insulin in response to Ca2+.
T Cell Activation
Ca2+ plays a role in activating immune cells.
Cell Adhesion
Ca2+ aids in cell attachment to extracellular matrix.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death influenced by Ca2+ levels.
Cytosolic Ca2+ Concentration
Maintained at approximately 0.1 mM for signaling.
Signal:Noise Ratio
Optimal balance for effective cellular signaling.
Calcium Transport Mechanisms
Active transport and sequestration maintain low Ca2+.
Voltage-Activated Ca2+ Channels
Allow Ca2+ entry based on membrane potential.
Calcium Induced Calcium Release (CICR)
Process where Ca2+ release stimulates further release.
Ryanodine Calcium Channels
Respond to Ca2+ to release more calcium.
IP3 Receptors
Calcium release channels sensitive to IP3.
Polyspermy
Condition where multiple sperm fertilize one egg.
Sperm Binding Receptor
Activates GPCR to initiate calcium release.
Cortical Reaction
Calcium influx prevents polyspermy during fertilization.
Perivitelline Space
Area where cortical vesicle contents are released.
Calcium Granules
Release contents to prevent multiple sperm fertilization.