E1 EM Review (quizlet)
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
What type of transport should be used for lifesaving maneuvers, BLS, & ALS
Ground transport
What type of transport should be used for critically ill patients or difficult terrain
Air transport
EMS picks up a choking 5 y/o female who is unable to breathe, where should they take her? (Regional or pediatric hospital)
Regional first, EMS might not be equipped for critically ill pts
Stabilize first at ER, then transfer
Pts in cardiac or respiratory arrest go where?
CLOSEST facility
What prohibits ERs from refusing to treat pts
EMTALA
Also prohibits inappropriate transfer of pts
Paramedics operating under a medical director is an example of what type of communication
Indirect
EMS giving vitals to the ER physician is an example of what type of communication
Direct
What should be used to preserve the spinal cord
C spine collar and back boards
What are the decontamination zones
Hot: patients without decontamination / area of spill
Warm: where decontamination and stabilization occurs
Cold: area where fully decontaminated pts go
What class of bioterroism would smallpox, anthrax, and botulism be in?
Class A: highest risk
Class C is lowest risk (B in the middle)
What are chemical agents such as sarin and mustard gas an example of?
Biologically produced toxins
What are contagious agents such as viruses and example of
Infectious agents
Plz know the reversal of opioids and benzos by now
Opioids: naloxone
Benzos: flumazenil
Foot, wrist, and digital blocks are examples of what type of block?
Peripheral nerve block
What should you document before administering a nerve block?
Neuro-vascular status
Your pt has severe pain when you insert the lidocaine, how should you proceed?
Withdraw and reposition
Severe pain = nerve contact
What areas should you not inject epinephrine
Nose, toes, fingers, and hose
What type of block is recommended for fracture reduction, large lacs or FB removal?
IV regional block (Biers block)
Infusion of lido+epi distal to inflated pneumatic tourniquet
Contraindications to biers block
PVD / Raynauds
Sickle Cell
Cardiac conduction probs
HTN
Cellulitis
Kids <5
Alt: Hematoma block
Opioid receptors
Delta, kappa, mu
How would you evaluate pain
Self report measurement : control pain to PATIENTs desires
*do NOT rely on non-self report measurement
4 clinical goals of sepsis
1. Blood cx BEFORE abx
2. Lactate < 90 mins
3. IV abx < 60 mins
4. 30 ml/kg of IVFs <180 mins
Treatment of choice for cardiogenic shock
PCI / CABG
Alt: thrombolytics
MCC: MI
PCI should be done within how long of presentation
90 mins
Management of anaphylaxis
Maintain airway
H1 & H2 blockers
Steroids
Epi
Your pt is in anaphylactic shock and is currently taking propranolol and Metformin, how should you adjust treatment?
Give glucagon b/c BBs can be resistance to epi
Management of neurogenic shock
Atropine and and fluids
d/t hypotension and bradycardia
AUB terminology review :)
Menorrhagia: heavy flow
Metrorrhagia: btwn cycles
Menometrorrhagia: irregular heavy cycles
Amenorrhea: no bleeding >6 mos
Post-menopausal: 6 mo-1 yr after cycles
What is considered of loss of pregnancy <20 wks
Spontaneous abortion
What is the MC abortion
Threatened abortion: 1st trimester bleeding w/o dilation
What is considered vaginal bleeding WITH cervical dilation
Inevitable abortion
dilation = lost pregnancy
Incomplete vs complete abortion
Complete has passage of ALL fetal tissue <20 wks
What is considered a fetal death <20 wks without any passage of fetal tissue x 4 wks
Missed abortion
What is the long term effects of PID and how do you treat?
Can cause tubular factor infertility
Tx: Cefoxitin / ceftriaxone + doxy
Add metronidazole for outpatient
GS diagnostic testing of PID
Laparoscopy
How do you r/o ovarian torsion
Pelvic / transvag US WITH DOPPLER
MC site of ectopic pregnancy
Ampulla (fallopian tube)
What should you think if a pt has abnrormally high bHCG
Gestation trophoblastic disease
1st line treatment of N/V during pregnancy
IVFs
How do you differentiate btwn abruptly placenta and placenta previa
Placenta previa is painLESS red bleeding
What should you do before delivering the body of a baby after the head is out
Suction nose and mouth to avoid aspiration
MCC of mitral stenosis
Rheumatic heart disease
Most pts develop a fib
Mid diastolic rumbling murmur with opening snap is indicative of
Mitral stenosis
Mid systolic click is indicative of
MVP
Not gonna ask specific murmurs but know key words (opening snap / click / systolic v diastolic
:)
Systolic: AS, MR
Diastolic: AR, MS
Rupture of the chordate tendinaea, papillary muscles or valve leaflets is known as
Mitral incompetence
Definitive diagnosis of valvular disorders
TEE
Classic triad of aortic stenosis
SAD : Syncope, angina, dyspnea
Harsh systolic ejection murmur (diamond)
MCC of aortic regurgitation (incompetence)
Infective endocarditis
What should you order if you suspect an MI
FIRST >> EKG within 10 mins
2. Troponin
3. CXR / echo
How does acute coronary syndrome present and what are sx caused by
-Chest/epigastric pain radiating to neck / jaw / ear / arm
-SOB / weakness
Sx d/t ischemia
Treatment of an MI
MONA - morphine, oxygen, nitroglycerin and aspirin 325mg
PCI within 90 mins
What type of CP is episodic lasting 5-15 mins that is worsened with exertion and relieved by rest
Stable angina
What are the 3 distinct forms of unstable angina
- new onset exertional angina
- inc frequency / duration
- angina at rest
What type of CP occurs at rest, is triggered by smoking, and is d/t coronary vasospasms
Variant (Prinzmetal)
Note: have ST elevations like an MI
Pt presents to the ED with dyspnea, orthopnea, PND, with tachycardia and peripheral edema / JVP, what should you order
CHF —>
Order BNP / CXR / Echo
Pt presents with sharp precordial pain that is better when she bends forward. You appreciate a friction rub on PE. What should you initial test be?
Pericarditis —>
Initial: Echo
EKG will show diffuse ST elevation and PR depression
Severe ripping pain is indicative of
Aortic dissection
Pain in abdomen, chest, or back
When is an aortic aneurysm considered emergent
Any symptomatic aneurysm (>5.5 cm needs sx)
Asx <5 cm : monitor carefully
Pt c/o of coughing up blood and notes that it is difficult to breathe and chest hurts. What's your work up?
pulmonary embolism:
- CTA is GS
- CXR (westermark, Hampton hump)
- D Dimer
- r/o DVT with Doppler
Virchows triad
Venous stasis
Venous injury
Hypercoagulable state
Indicative of DVT
Know wells score !!!
PE likely >4 pts
How do you diagnose a DVT
D dimer and Doppler US
Venogram is GS but US is MC
What is becks triad and what is it indicative of
JVD
Hypotension
Muffled heart sounds
Associate with cardiac tamponade
Test of choice for cardiac tamponade
Echo
EKG will show electrical alternanas
Tx with pericardiocentesis
What is almost always present in restrictive cardiomyopathy
S3
Also see: Kussmauls, JVD, ascites, edema
HOCM vs Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
KNOW IT
HOCM: syncope, sudden death in athletes, LVH
Restrictive: right sided CHF sx
Paradoxical pulse, Kussmauls sign, with a pericardial "knock" accompanying SOB is indicative of
Restrictive pericarditis
Kussmaul's sign (inc JVD w/ respiration) think....
RESTRICTIVE cardiomyopathy or pericarditis
(Look @ other sx to ddx)
What are the anterior leads
V3/4
What are the septal leads
V1/2
What are the lateral leads
V5/6, I, & aVL
What are the inferior leads
II, III, & aVF
EKG: flip and dont look at the answer lol
Posterior STEMI
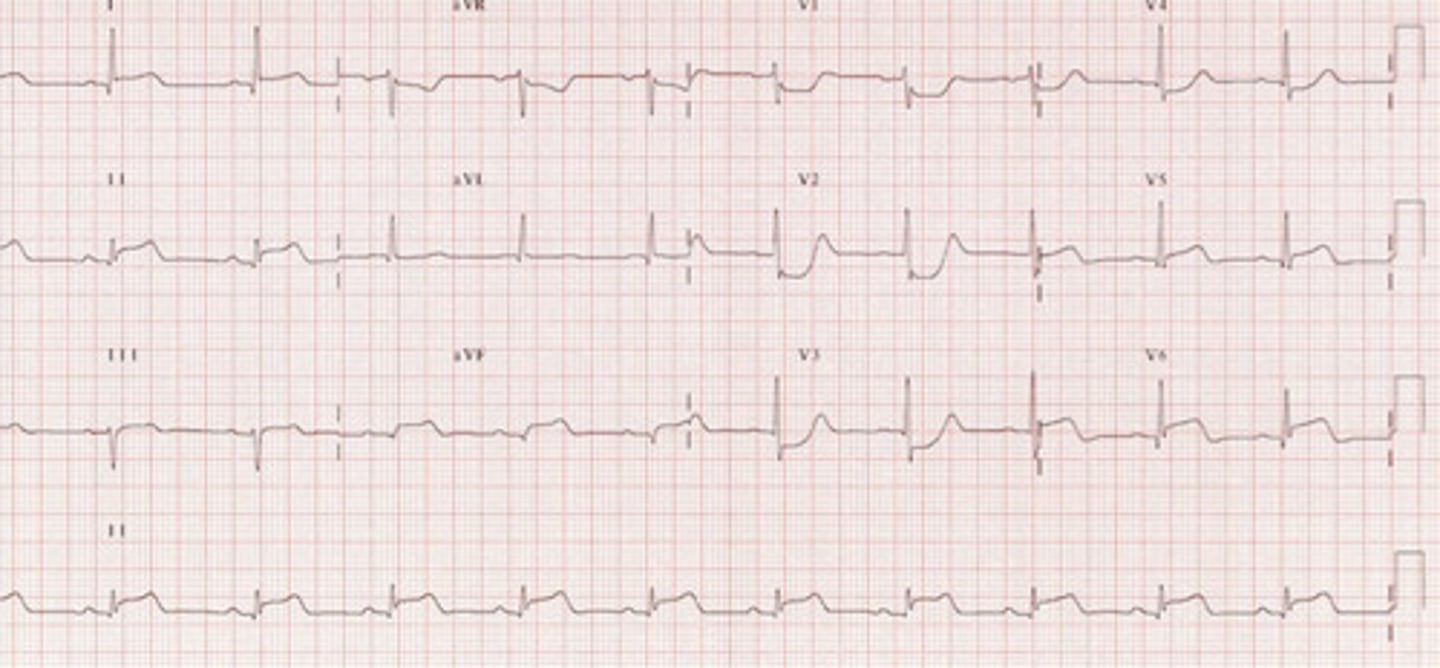
EKG: flip and dont look at the answer lol
Anterior-septal STEMI
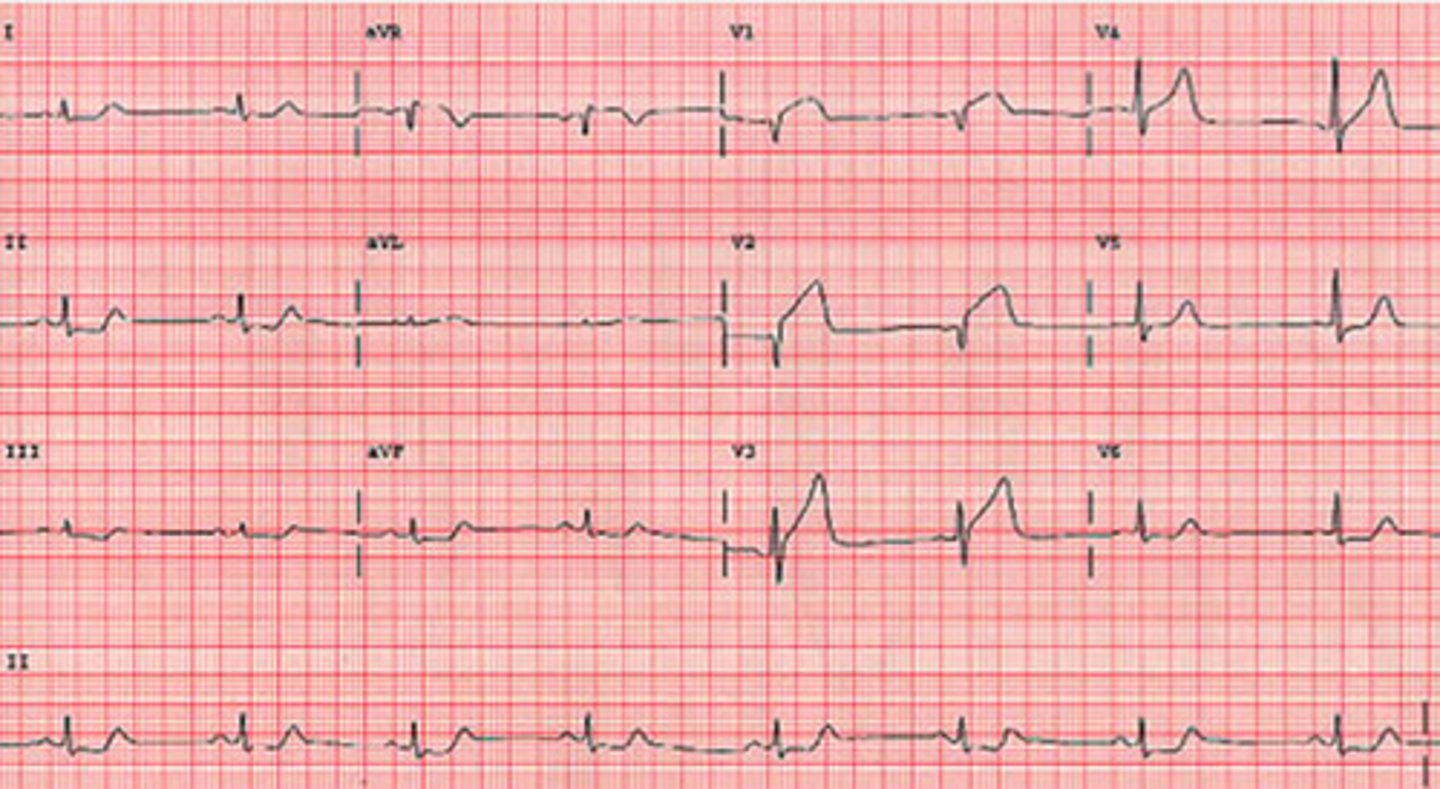
EKG: flip and dont look at the answer lol
Inferior STEMI
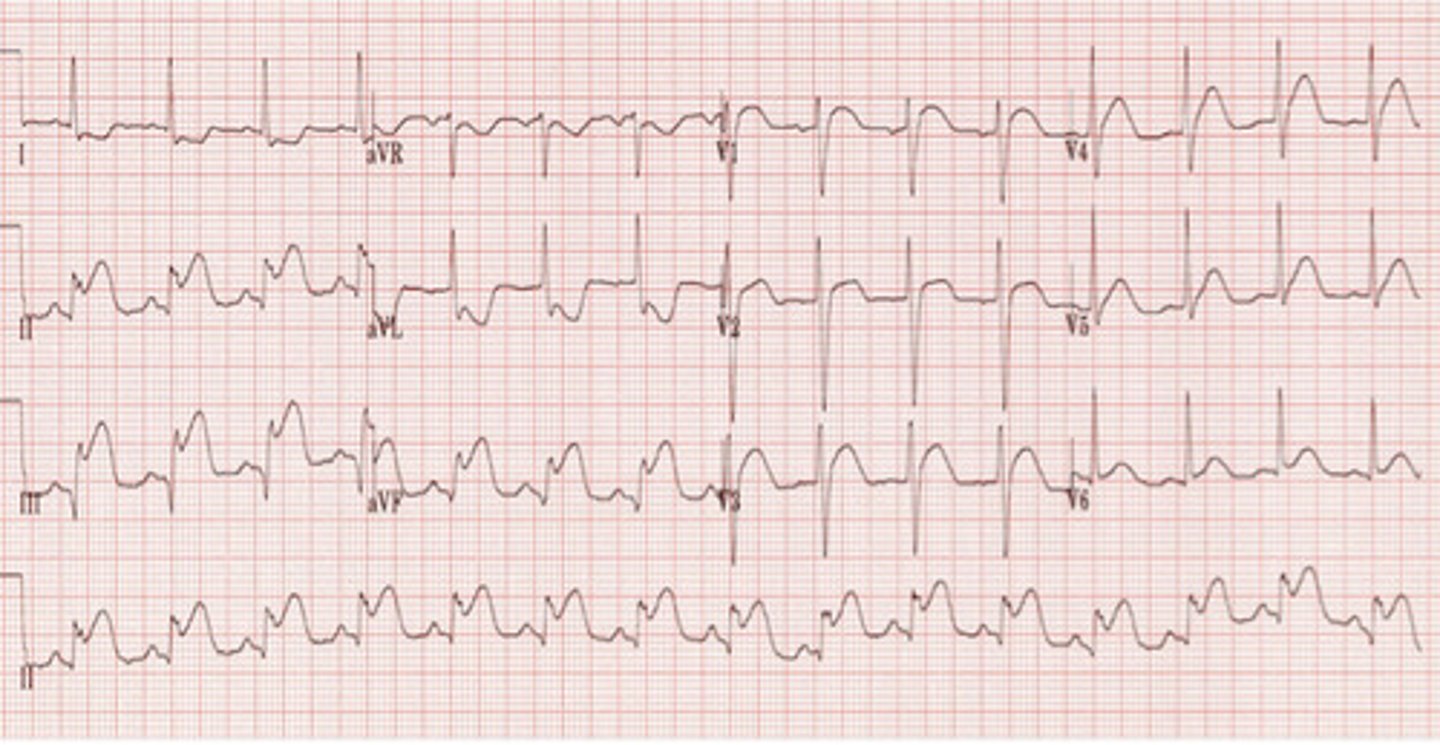
EKG: flip and dont look at the answer lol
Inferior-lateral STEMI
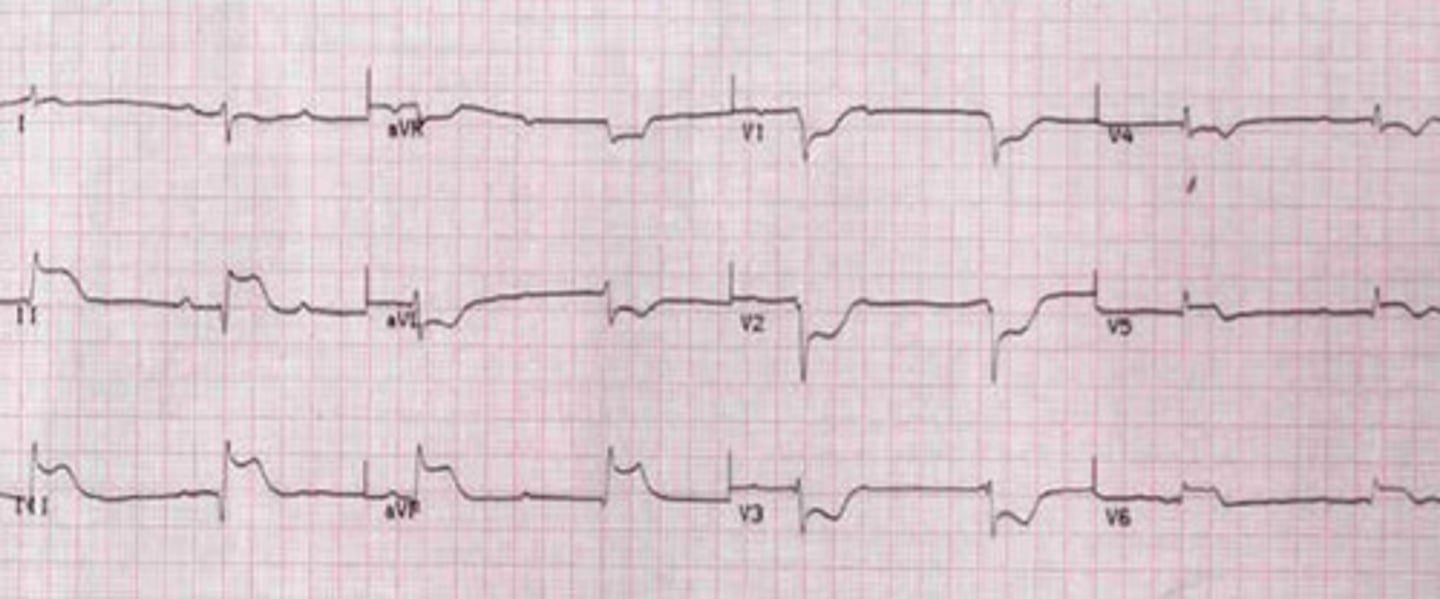
EKG: flip and dont look at the answer lol
V fib
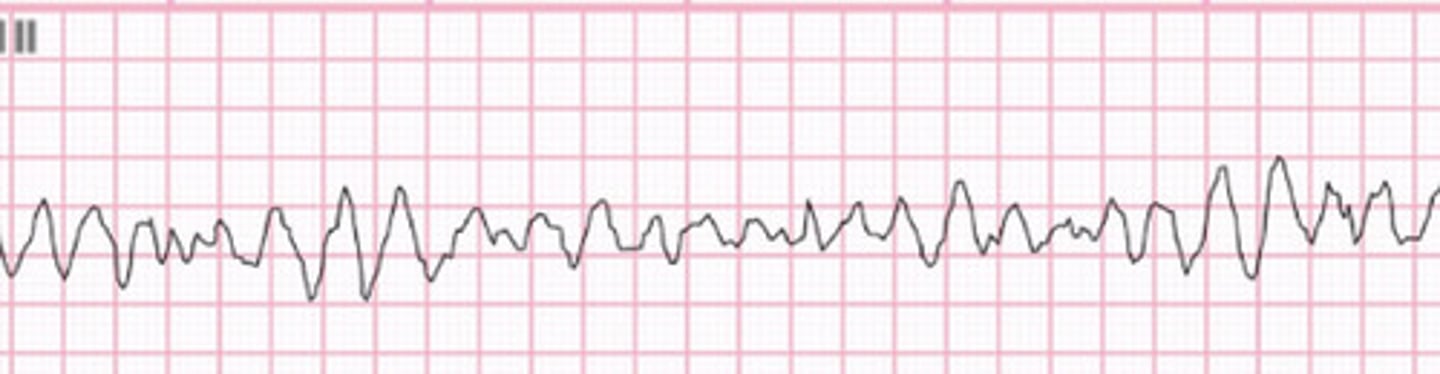
EKG: flip and dont look at the answer lol
A flutter
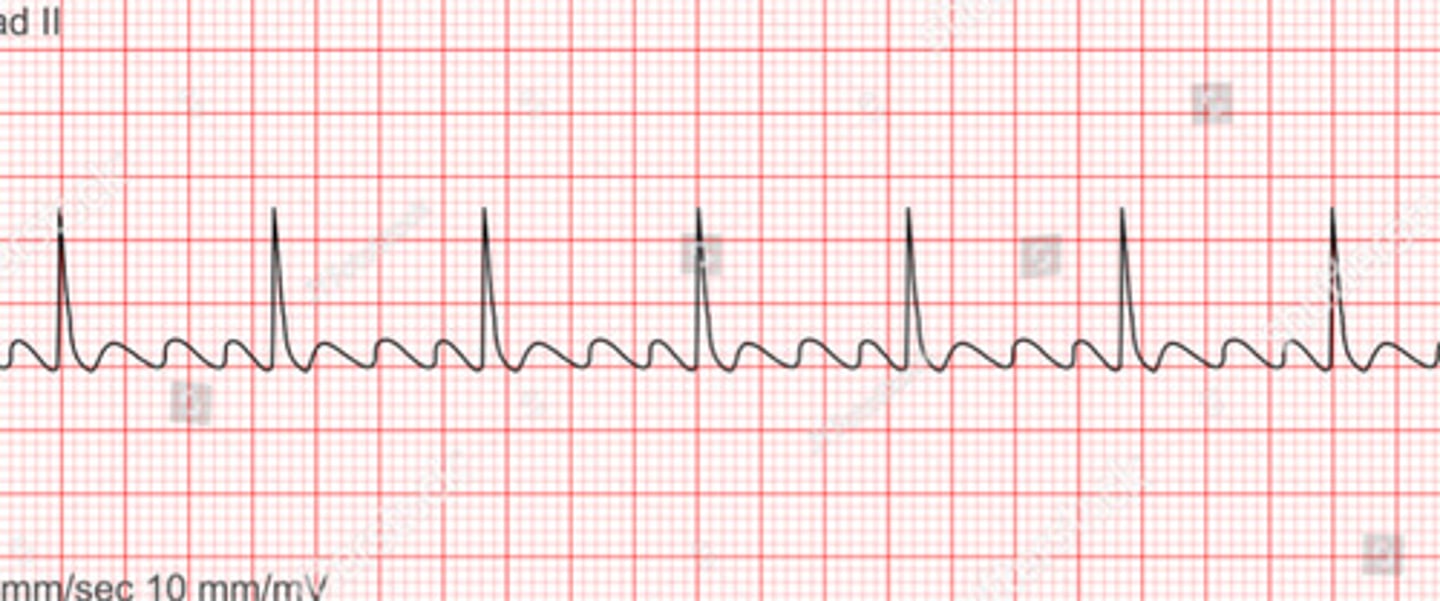
EKG: flip and dont look at the answer lol
A fib
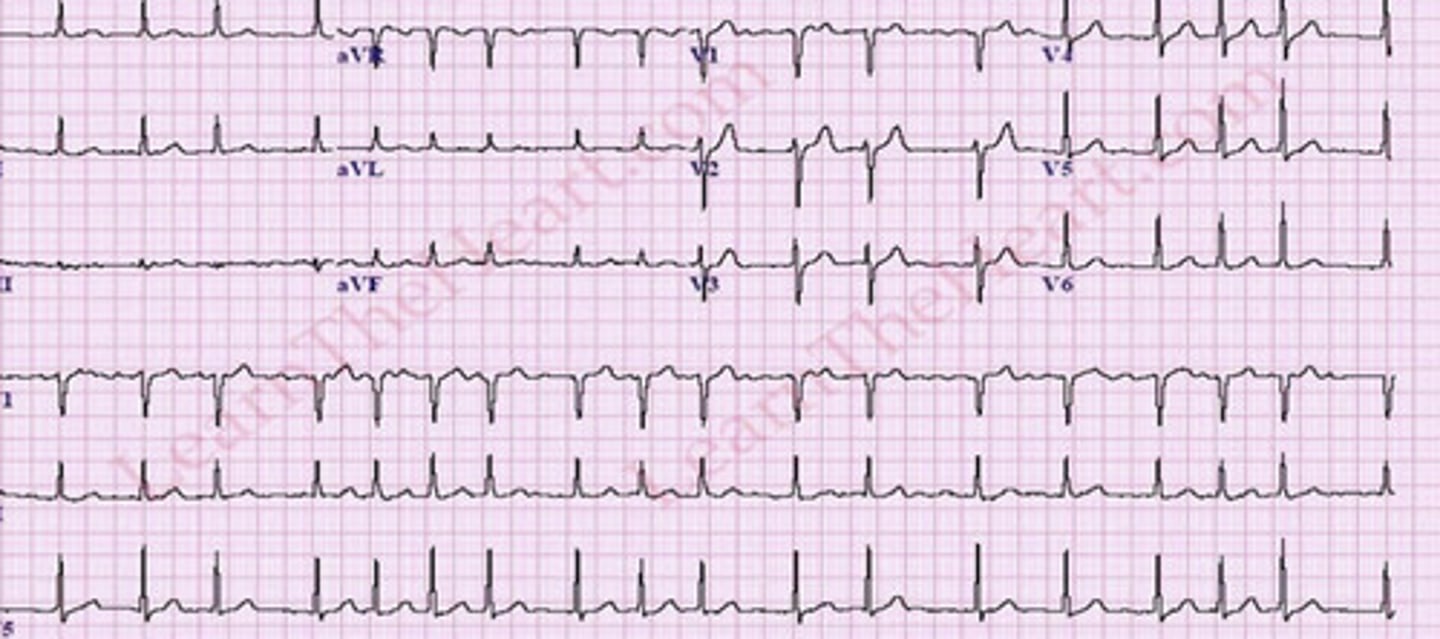
EKG: flip and dont look at the answer lol
Anterior STEMI
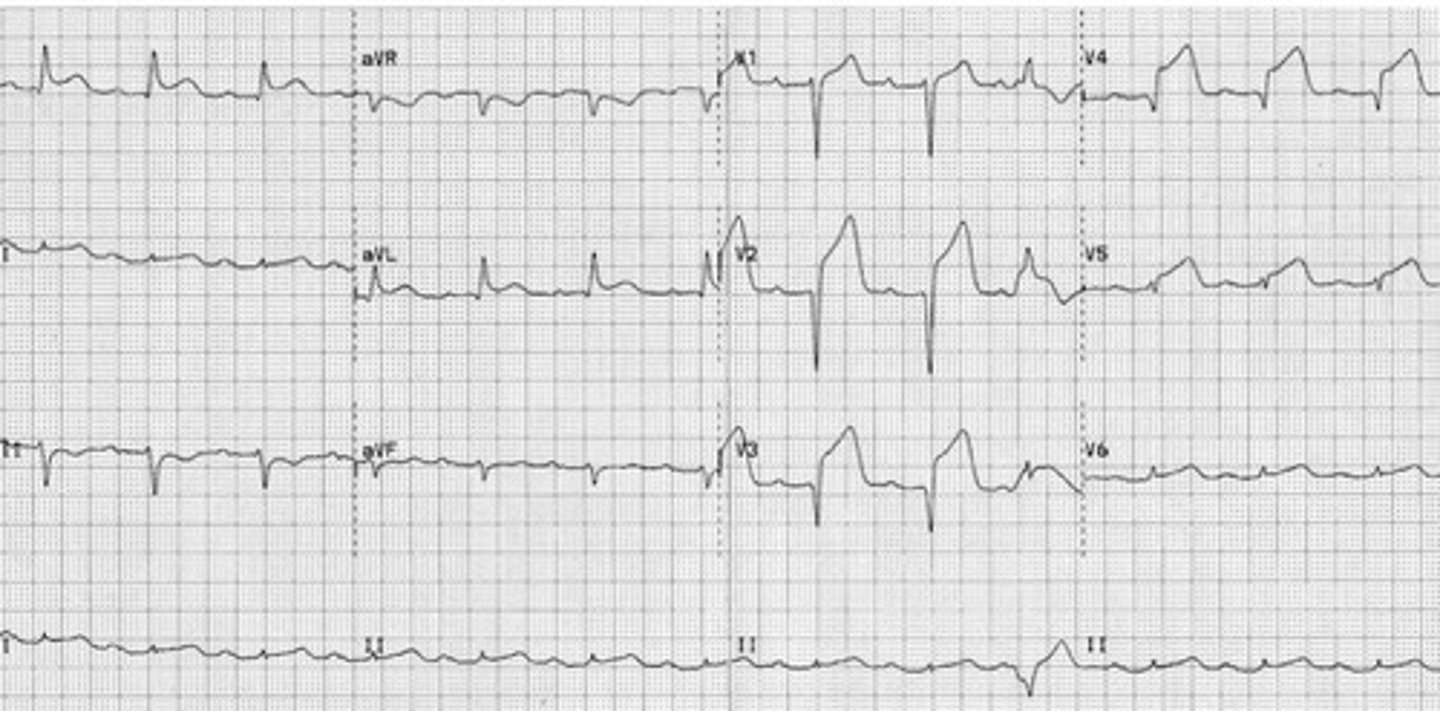
There's gonna be EKGs :(
It's gonna be a STEMI so know your lead locations
Management of HTN
BP lowered to 160/110 over 2-6 hrs
Dec MAP no more than 20% in first hr
Immediate tx only of exam reveals EOD
Preferred test and treatment for kidney stones
Dx: CT
Tx: IVFs, 4mg Zofran, 30mg Toradol
Pt is c/o of back pain that radiates to her groin. You do a CT and see a 3 mm stone, how should you proceed
Pt will likely be able to pass
>8 is unlikely
Ig 4-8 is really difficult ??
How do you treat paraphismosis
URO EMERGENCY
Compression of glans for several minutes, puncture wounds for drainage: 10 & 2 location
How to reduce testicular torsion
EMERGENCY
Manual Detorsion: twist outward and laterally
KNOW THIS
Treatment of prostatitis
Ciprofloxacin
Alt: bactrim
UTI treatment
Bactrim, FQ, macrobid
Phenazopyridine for analgesia
Pt presents with painful and frequent urination, you do a UA and suspect a UTI. What will it show?
+ LE
+ nitrates
+ WBCs
ALWAYS culture
Types of pneumothorax
Iatrogenic: secondary to procedure
Primary spontaneous: healthy pts, no trauma
Secondary spontaneous: known lung dx
GS diagnostic testing for pneumothorax
Upright PA CXR
Management of small vs large pneumothorax's
Small: monitor
Large: catheter aspiration
How should you manage a tension pneumothorax
Immediate needle decompression
2nd intercostal space, mid clavicular line
Mediastinal shift and tracheal deviation on CXR is indicative of
Tension pneumothorax
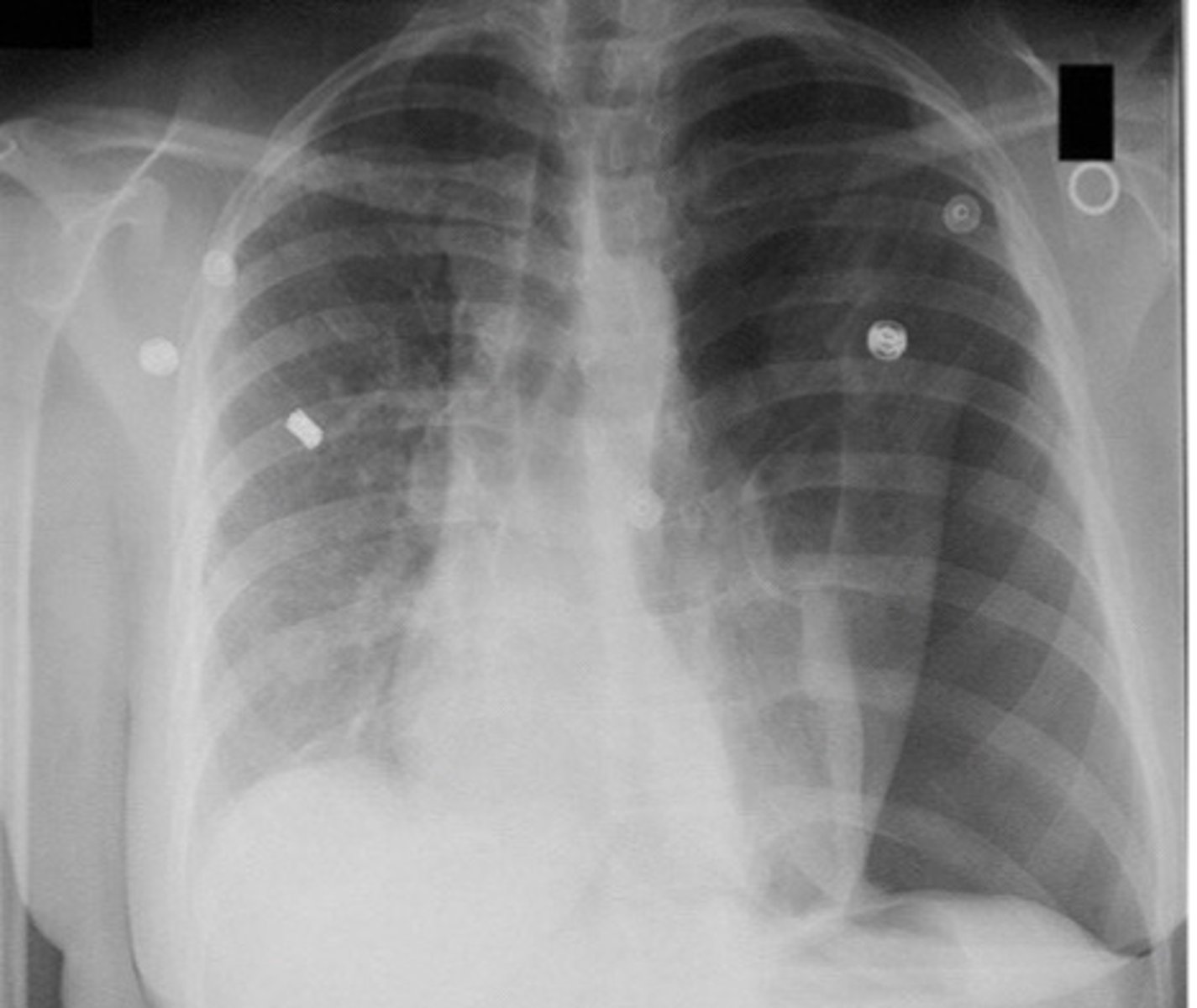
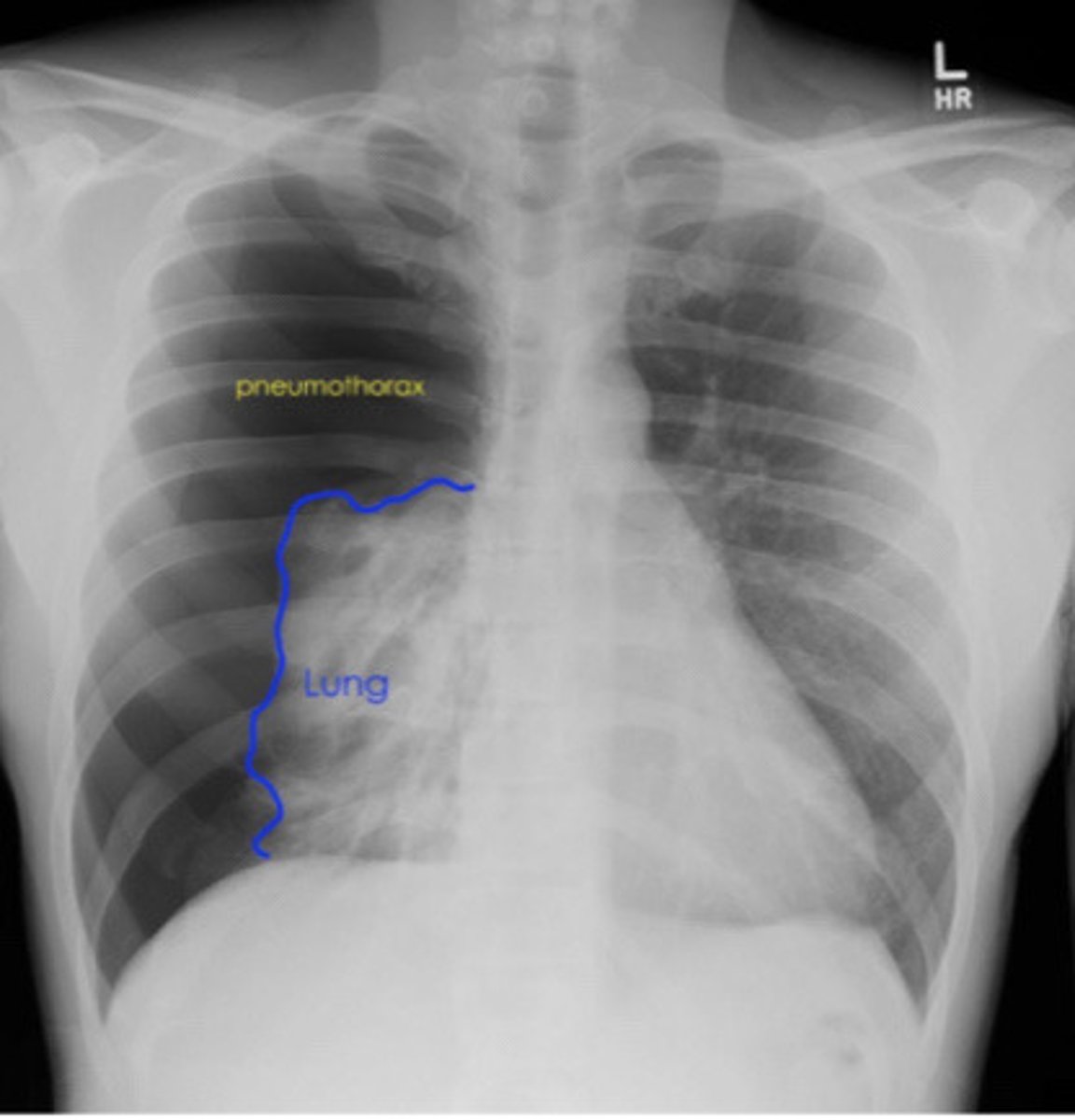
Visualization of visceral pleural line on CXR is indicative of
Pneumothorax
Pneumomediastinum on CXR (just a pic)
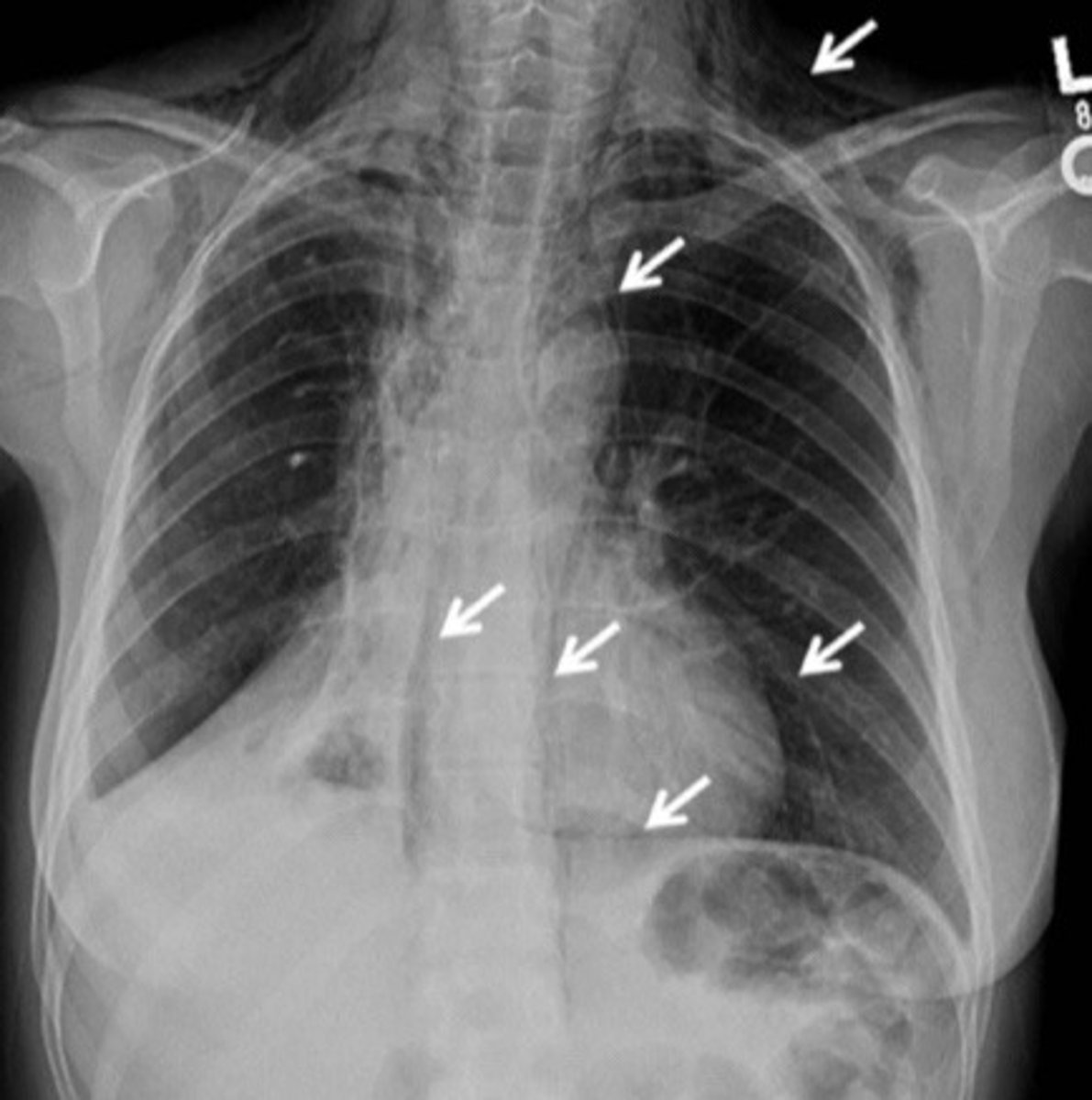
Hammans sign and subcutaneous emphysema is indicative of
Pneumomediastinum
CXR shows bronchial thickening/cuffing without consolidations or infiltrates.....what is the cause of the disease?
Acute Bronchitis —> MCC is VIRAL
What will XR findings show in retropharyngeal abscess
6 at 2, 22 at 6
6 mm at C2
22 mm at C6