Biological molecules (2.3-2.4)
All organic molecules contain carbon and hydrogen atoms; Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules can be large and show a wide variety of chain and ring structures
Organisms need organic molecules to:
- Provide energy to drive life processes
- Provide raw materials for the growth and repair of tissues
Main organic molecules used by organisms are:
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Nucleic Acids
Biochemistry: The study of the organic and inorganic molecules that make up living organisms
Metabolism: Sum of all the chemical reactions in an organism
Large organic molecules are made of many simmilar smaller molecules (subunits/isomers)
Subunits can be split apart by Hydrolisis
- Hydrolisis: Reaction that uses water to break apart subunits
- They can be joined together again by condensation
Living organisms can obtain molecules from their environment and rearrange them into shapes that suit their own particular requirements
- Large molecules are made from smaller ones
Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates: Organic compounds containing Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
- Sources: rice, wheat, oats, maize barley
- Carbohydrates are long chains of simple sugars (glucose)
- Simple sugars are also called monosaccharides; made of one sugar molecule
- When 2 glucose molecules join together they form maltose (a disaccharide)
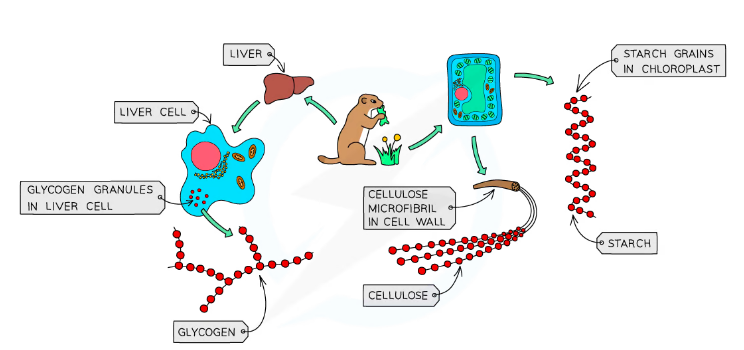
- Many glucose molecules can join together to form starch, cellulose or glycogen (polysaccharides)
Example:
Glucose (monosaccharide) →Glycogen (polysaccharide)
Importance of Carbohydrates
- Good sources of energy
- Plants store excess carbohydrates as starch
- Animlas store excess carbohydrates as glycogen in the liver and muscles
- Eating excess carbohydrates causes obesity
- Defiency of carbohydrates causes ‘Marasmus’
Protein
Proteins: Organic compounds containing Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen (and sometimes sulphur)
- Sources: Milk, eggiwhite, fish, peas, beans and meat
Made up of the basic subunit (monomer) amino acids
- 20 types amino acids are naturally occuring
- 8 are essential (from food) 12 are non-essential (present in your body)
Amino acids are soluble in water; can be transported in organisms
The sequence of amino acids determines the shape of the protein molecule
- Shape determines the function of the protein
- Different sequences of amino acids causes the polypeptide chains to fold in different ways and form differently shaped proteins
Examples
Enzymes have active sites where substrate molecules bind for a reaction to take place
- Since enzymes are substrate specific the shape of the active site has to match the shape of the molecule
- The shape of the active site determines which molecules will bind and react using the enzyme
Antibodies are proteins produced by WBCs which bind to antigens on the surface of antibodies
- The shape of the anitbody has to match the shape of the antigen so it can bind to it and signal for destruction
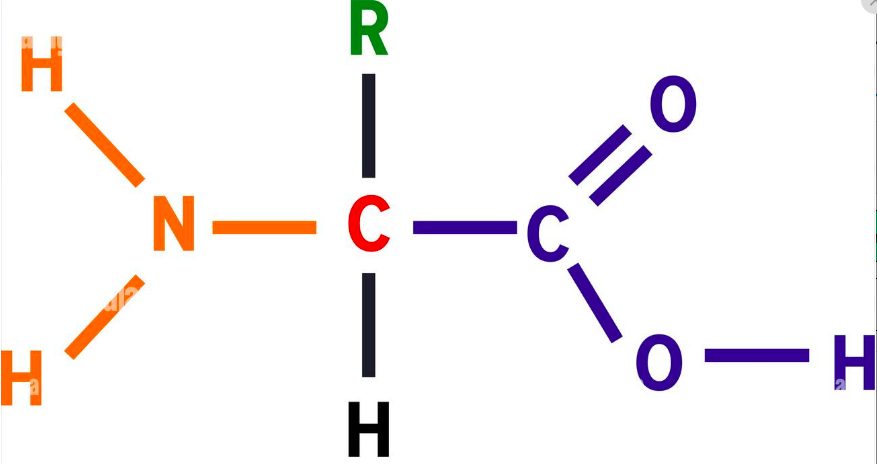
In proteins there are four components attached to a central carbon
Importance of proteins
Proteins are body builders and they are used in tissue growth and tissue repair
They are used to make antibodies, enzymes, hormones, and plasma proteins
Excess proteins are not stored in the body, they are converted into urea in the liver -deamination of amino acids
Lack of protein causes' ‘Kwashiorkor’
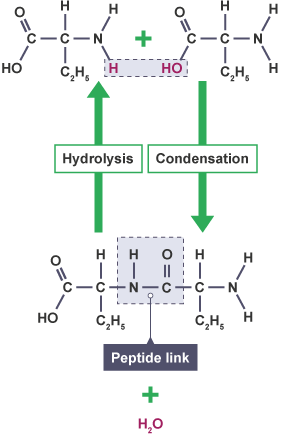
Hydrolisis breaks down proteins into amino acids by adding water
Condensation reactions synthesise protein molecules and water from amino acids
Lipids
Lipids: Organic compounds containing chemical elements Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
- Sources: Cream, ghee, oil, nuts, butter, dairy
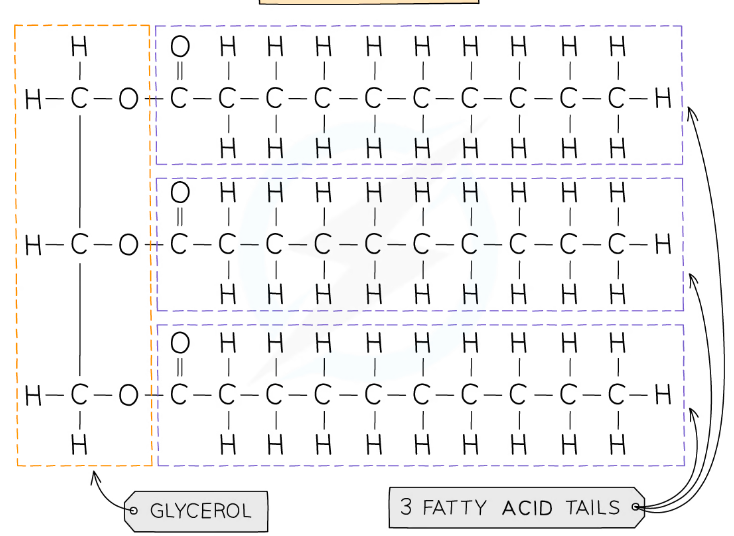
One molecule of lipid is made of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids and is made by condensation
Importance of lipids
- Acts as an energy store
- Provides insulation
- Less dense than water
- Harvesting animals store food in bodies as fat as a source of energy
- (fats- solid, oils- liquid)
Nucleic Acids
- The 2 nucleic acids are DNA and RNA
| DNA | RNA |
|---|---|
| Deoxyribonucleic acid | Ribonucleic acid |
| Double helix | Single stranded |
| A,C,T,G | A,C,G,U |
| Contains genetic material | Shape changes depending on function |
| Situated ONLY within the nuclei | Moves around cell |
DNA contains the instruction for the growth and development of organisims and is made of 2 strands wrapped around eachother forming a double helix
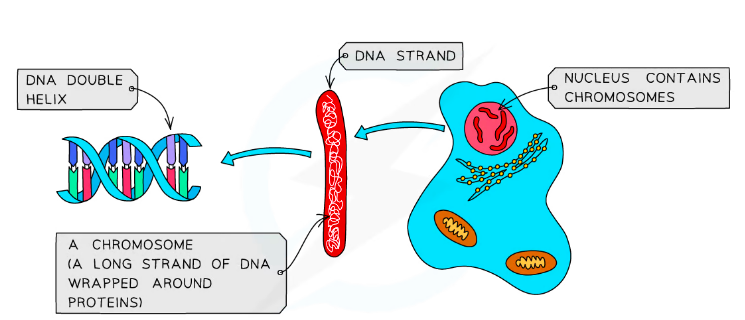
Nucleotides: individual units of DNA
- They all have the same phosphate and sugar ‘backbone’ but have different bases attached
- Adenine, Cytosine, Thymine and Guanine
The bases on each strand form cross links (hydrogen bonds) and form base pairs holding the two strands of DNA in the double helic together
- Adenine always pairs with Thymine (A-T)
- Cytosine always pairs with guanine (C-G)
Apple Tree and Car Garage to remember ;)
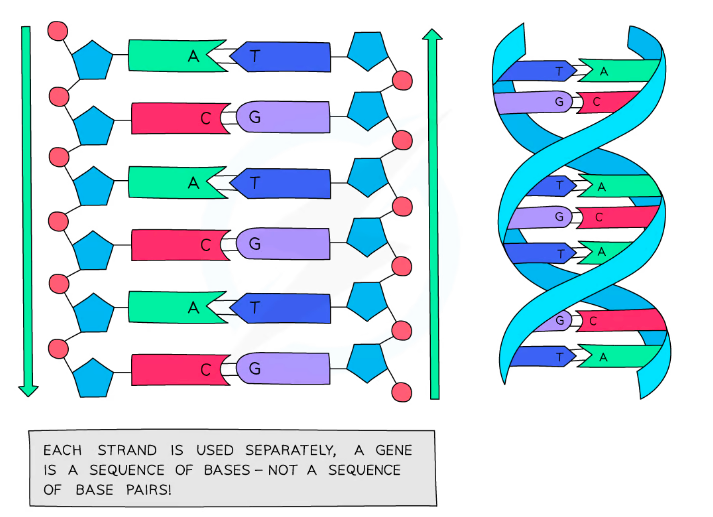
- The sequence of base pairs holds the code for the formation of proteins
Food tests
- Reducing sugars
- Add Benedicts solution into sample in test tube
- Heat at 60-70 C in a water bath for 5 minutes
- Take test tue out
- Positive test; Blue → orange/brick red
- Starch
- Add drops of iodine to sample
- Positive test; Orange/brown → Blue/black
- Protein
- Add drops of Biuret solution to sample
- Positive test; Blue →Purple
- Lipids
- Mix 2cm3 of Ethanol with food sample
- Add equal volume of water
- Positive test; Cloudy emulsion
OR
- Take a sample of oil and add water and shake; forms an emulsion (bubbles)
- Vitamin C
- Add 1cm3 of @@DCPIP@@ solution to test tube
- Add food sample to solution
- Positive test; @@Blue color of the dye will turn colorless @@
Water
- Water is an important solvent; many substances can dissolve in it , making it essential for life on earth
Importance of water
Water allows substances to be easily transported arounf organisms
Digested food molecules in the alimentary canal are moved around the body using water as a solvent
Toxic substances (eg. urea) and substances in excess (eg. salts) are dissolved in water to be removed from the body (as urine)
Water is an important part of the cytoplasm and is involved in ensuring metabolic reaction can take place in cells
\n