HEALTHCARE 11 2023 EXAM REVIEW
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/146
Last updated 6:23 AM on 1/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
1
New cards
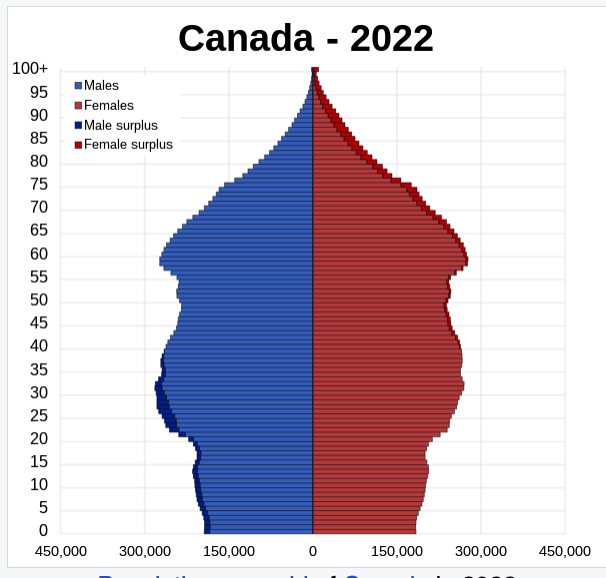
Look at the population graph on google classroom. What is important to know about this graph? What implications does this have on health care?
* the growing population signifies the healthcare system is successful
\
* as the population rises and the people in it age, the healthcare expenses rise and hospitals become more busy
\
* as the population rises and the people in it age, the healthcare expenses rise and hospitals become more busy
2
New cards
What are the 3 trends in health care?
technology, patient centered care and wellness
3
New cards
How are these trends changing health care? What is the ultimate goal of health care?
* Reduce the number of medical
* Increases patient safety
* Reduce issues that lead to burnout
* Increases patient safety
* Reduce issues that lead to burnout
4
New cards
What is gene therapy? How has this medicine been successful so far?
when genetic material (DNA) is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in an organism
* some researchers believe that with genome editing we will have the ability to edit our cells in our immune systems to improve them against cancer cells
* potentially preventing cancer
* some researchers believe that with genome editing we will have the ability to edit our cells in our immune systems to improve them against cancer cells
* potentially preventing cancer
5
New cards
What does it mean by patient centred care? How have ideas of hierarchies changed from the past?
1. focuses more on the patient's problem than on his or her diagnosis. Patients have trusted, personal relationships with their doctors in patient-focused care models (multidisciplinary team)
\
2. clinical care is becoming more complex and specialized, forcing medical staff to specialize in focused areas
6
New cards
What does regenerative medicine mean? Where are we today with this trend? How long has it taken to get here?
* can take up to 20 years of development time
* can create organs such as a 3D print gallbladder by taking cells from a healthy donor
* can create organs such as a 3D print gallbladder by taking cells from a healthy donor
7
New cards
Define wellness. Who can achieve wellness?
an active, lifelong process of becoming aware of your choices and making decisions that will help you to live a more balanced and fulfilling life. Many factors can influence your health and well-being.
\
* also 7 dimensions of wellness
* ANYONE CAN ACHIEVE WELLNESS
\
* also 7 dimensions of wellness
* ANYONE CAN ACHIEVE WELLNESS
8
New cards
What are the 7 different interacting dimensions of wellness ?
* occupational
* emotional
* spiritual
* environmental
* physical
* social
* intellectual
* emotional
* spiritual
* environmental
* physical
* social
* intellectual
9
New cards
Define holistic health care. What kinds of professionals would you see in a holistic health care setting?
* Holistic health care is an approach to health care that treats the "whole" person, not simply symptoms and disease.
* Various aspects of a patient's lifestyle and health issues are examined, and a course of treatment is designed to help them reach their optimum level of wellness.
* professions ie. social worker
* Various aspects of a patient's lifestyle and health issues are examined, and a course of treatment is designed to help them reach their optimum level of wellness.
* professions ie. social worker
10
New cards
What was the overall message of the movie ‘Patch Adams?’
Healthcare providers should do their best to provide compassionate, professional care to our fellow human beings through holistic care
11
New cards
What are the job prospects for future health care workers?
Teamwork is KEY!
1. working together can reduce the number of medical errors and increases patient safety
2. collaboration also reduce issues that lead to burnout
3. breaks down the traditional hierarchy of healthcare professionals. everyone has their speciality and unique skill set
* clinical care is becoming more complex and specialized, forcing medical staff to specialize in focused areas
1. working together can reduce the number of medical errors and increases patient safety
2. collaboration also reduce issues that lead to burnout
3. breaks down the traditional hierarchy of healthcare professionals. everyone has their speciality and unique skill set
* clinical care is becoming more complex and specialized, forcing medical staff to specialize in focused areas
12
New cards
What does the term ‘social determinants of health’ mean?
The non-medical factors that influence health outcomes
* They are conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age, which shape the conditions of daily life
* They are conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age, which shape the conditions of daily life
13
New cards
What are examples of social determinants of health?
* Housing, Education, Money, Language, food, women, LGBTQ+, etc
14
New cards
How important are the social determinants of health? What does the research show?
* Research shows that the social determinants can be more important than health care or lifestyle choices in influencing health. SDH accounts for between 30-55% of health outcomes.
* Inequities in health are socially determined, preventing poorer population from moving up in society and making the most of their potential.
* Inequities in health are socially determined, preventing poorer population from moving up in society and making the most of their potential.
15
New cards
Define socioeconomic status
The social standing or class of an individual or group. It is often measured as a combination of education, income, and occupation
16
New cards
Does health equal wealth? Explain
Wealth equals health
* Lower income countries with the lack of access of healthcare
* However mentally in terms of health wealth does not equal health
* Lower income countries with the lack of access of healthcare
* However mentally in terms of health wealth does not equal health
17
New cards
What is the difference between equitable and equal?
* Equity → recognizes that each person has different circumstances and meets the equal outcome for each individual or group
\
* Equality → individual or group of people is given the same resources or opportunities
\
* Equality → individual or group of people is given the same resources or opportunities
18
New cards
What is the RHPA? What does it have to do with standards of practice, scope of practice, and regulatory colleges?
* This act regulates 26 professions to protect the public
* They deal with complaints
* They deal with complaints
19
New cards
What is a regulatory college? What is their role? Who do they protect?
responsible for making sure employees are trained and certified. They determine the jobs ‘scope of practice’
20
New cards
What is confidentiality? What are the exceptions?
* Confidentiality: keeping all information about a patient, including patient records, private. Essential for maintaining a patient’s trust
* It is against the law to “breach” confidentiality.
\
EXCEPTIONS:
* Disclosure is required to prevent clear and imminent danger to the client or others.
* Legal requirements demand that confidential material be revealed
* It is against the law to “breach” confidentiality.
\
EXCEPTIONS:
* Disclosure is required to prevent clear and imminent danger to the client or others.
* Legal requirements demand that confidential material be revealed
21
New cards
what information should you not talk to anyone but the client about
DO NOT DISCUSS CLIENT INFORMATION WITH:
* One client about another client
* Relatives and friends of the client
* Representatives of news media
* Fellow workers, except when in conference or reporting
* Your own relatives and friends
* One client about another client
* Relatives and friends of the client
* Representatives of news media
* Fellow workers, except when in conference or reporting
* Your own relatives and friends
22
New cards
What does it mean to be ethical? Give an example
Ethics is a code of rules set up to govern behaviour.
* To be ethical, you should always take into consideration the feelings and needs of all concerned.You must also show respect to individuals and their rights. (ie. taking responsibility or accountability)
* To be ethical, you should always take into consideration the feelings and needs of all concerned.You must also show respect to individuals and their rights. (ie. taking responsibility or accountability)
23
New cards
What is the age of consent to medical care in Canada? Is there one?
NO SPECIFIC AGE OF CONSENT FOR TREATMENT
24
New cards
What are the two treatment approaches?
conventional and cam
25
New cards
what is conventional treatment?
Conventional: practiced by healthcare professionals who hold an M.D. (Medical Doctor)
\
* Conventional medicine may also be called allopathic, western, mainstream, standard medical care, athodox, or regular medicine
\
* Conventional medicine may also be called allopathic, western, mainstream, standard medical care, athodox, or regular medicine
26
New cards
give examples of conventional treatment
* medication
* physiotherapy
* surgery
* physical therapy
* psychological counseling
* dentistry
* stitches
* speech therapy
* casts
* physiotherapy
* surgery
* physical therapy
* psychological counseling
* dentistry
* stitches
* speech therapy
* casts
27
New cards
what is Complementary/Alternative Medicine (CAM)
these practices generally are not considered part of standard medical approaches standard treatments to go through long and careful research processes to prove they are safe and effective, but less is known about most types of complementary and alternative medicine
28
New cards
what are examples of CAM treatment
* pet therapy
* acupuncture
* yoga
* reiki
* cupping
* naturopathy
* massage therapy
* herbal medication
* chiropractic care
* art therapy
* acupuncture
* yoga
* reiki
* cupping
* naturopathy
* massage therapy
* herbal medication
* chiropractic care
* art therapy
29
New cards
List 5 treatments that you would find in a __holistic__ health care center (remember – you must treat mind, body and spirit with the combination of treatments)
1. aromatherapy
2. music therapy
3. pet therapy
4. yoga/meditation
5. reiki
30
New cards
Why is the holistic approach of health care better than the traditional approach?
It provides support that looks at the whole person, not just their mental health needs.
The support should also consider their physical, emotional, social and spiritual wellbeing
The support should also consider their physical, emotional, social and spiritual wellbeing
31
New cards
Explain how the two different types of practitioners view each other now and in the past
doctors and CAM practitioners competed with each other mainly due to very few standards and regulations around who could call themselves doctors
* doctors often thought that CAM practitioners were “shysters” or “quacks”
* Cam practitioners thought that mainstream doctors rely too much on potentially dangerous drugs and surgery, and being so over specialized in particular areas that they failed to treat the patient as a whole
* doctors often thought that CAM practitioners were “shysters” or “quacks”
* Cam practitioners thought that mainstream doctors rely too much on potentially dangerous drugs and surgery, and being so over specialized in particular areas that they failed to treat the patient as a whole
32
New cards
What is the process for care planning?
1. take history
2. do physical examination
3. use diagnostic tests
4. make a diagnostic
5. give treatments
6. monitor
7. evaluate
33
New cards
what is take history?
What is the complaint? What happened?
* find out background information that might be relevant
* ie. family history, diet, exercise, previous illnesses, school/work life, major stresses (ex. ex divorces, job loss), relationships, substance use
* find out background information that might be relevant
* ie. family history, diet, exercise, previous illnesses, school/work life, major stresses (ex. ex divorces, job loss), relationships, substance use
34
New cards
what is physical examination ?
look for clues to the problem: use 4 senses
* smell (foul odour could indicate infection/bad hygiene)
* look: observe for obvious signs (redness, bruising, bleeding, inappropriate body language, something the observer sees)
* listen: (auscultate -> heart rate, vowel sounds, breathing)
* feel: (palpate -> lumps, broken bones, joint dislocation)
\
* symptoms: things the patient experiences
* vital signs: blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, temperature, oxygen levels
* smell (foul odour could indicate infection/bad hygiene)
* look: observe for obvious signs (redness, bruising, bleeding, inappropriate body language, something the observer sees)
* listen: (auscultate -> heart rate, vowel sounds, breathing)
* feel: (palpate -> lumps, broken bones, joint dislocation)
\
* symptoms: things the patient experiences
* vital signs: blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, temperature, oxygen levels
35
New cards
what is use diagnostic tests?
* biopsy: helps diagnose a medical condition
* colonoscopy: tube inserted through anus to view inside of large bowel
* CT Scan: combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body
* MRI scan: an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic forces, radiofrequency (RF) waves and a computer to make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of the organs, bones and tissues inside your body
* colonoscopy: tube inserted through anus to view inside of large bowel
* CT Scan: combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body
* MRI scan: an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic forces, radiofrequency (RF) waves and a computer to make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of the organs, bones and tissues inside your body
36
New cards
what does it mean to make a diagnosis?
Naming/Determining the illness (if possible)
* identification of the nature of an illness or other problem by examination of the symptoms
* ie. asthma, flu, broken bone, depression
* identification of the nature of an illness or other problem by examination of the symptoms
* ie. asthma, flu, broken bone, depression
37
New cards
what does it mean to give treatments?
Conventional and CAM treatments (if possible)
* offer appropriate treatments based on diagnosis; do not offer too many
* cost, time consuming, certain treatments can interact with each other (you want to know which one actually worked)
* offer appropriate treatments based on diagnosis; do not offer too many
* cost, time consuming, certain treatments can interact with each other (you want to know which one actually worked)
38
New cards
what does it mean to monitor ?
(take vital signs, retest diagnostic tests)
\
Evaluate the effect of treatment. Did the treatment work? If not, was my diagnosis correct? You may need to reconsider the plan
\
Evaluate the effect of treatment. Did the treatment work? If not, was my diagnosis correct? You may need to reconsider the plan
39
New cards
What is a diagnosis based on?
* process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury based on the signs and symptoms a patient is having and the patient's health history and physical exam
40
New cards
What is the difference between Monitor and Evaluation?
* monitor: process of gathering information of the patient (ie. monitoring/tracking process, collecting data, vital signs and retest diagnosis tests)
* evaluate: process of assessing the effectiveness
* evaluate: process of assessing the effectiveness
41
New cards
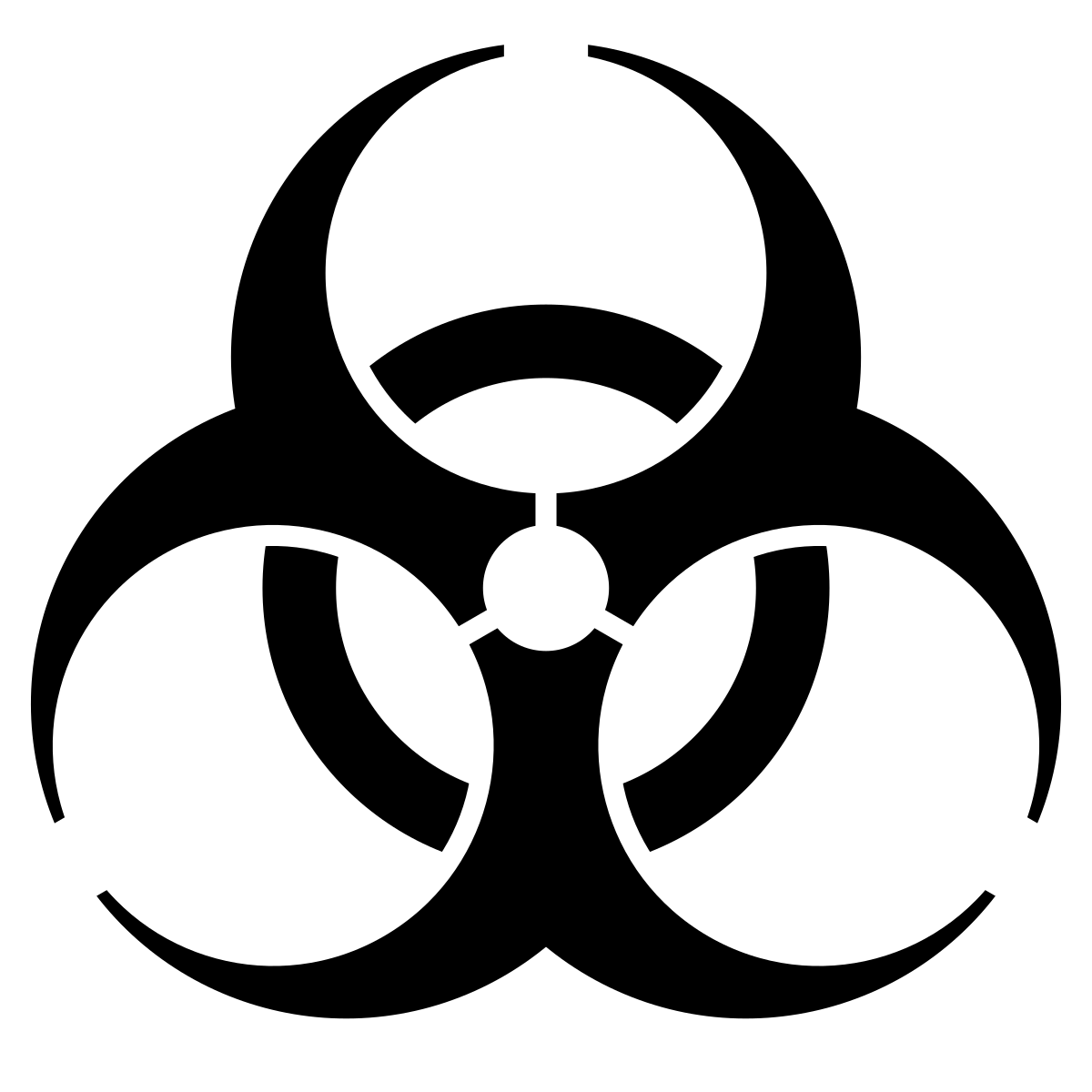

What is WHIMS? Why is it important? How is it changing? What symbol is commonly used in health care? Give some examples of where you’d see it.
"Right to Know" about the hazardous materials you are working with; **workplace hazardous materials information system**
* Most commonly used symbol in health care is BIOHAZARDOUS: infectious materials
* Where you will see it: needle disposal box
* Most commonly used symbol in health care is BIOHAZARDOUS: infectious materials
* Where you will see it: needle disposal box
42
New cards
What are blood borne pathogens? What specific diseases are considered blood borne?
blood borne pathogens are microorganisms that cause diseases in the human blood
* examples: hpv, hiv, hepatitis
* examples: hpv, hiv, hepatitis
43
New cards
What are some safety precautions to prevent a sharps injury?
1. slow down and act in the calmest manner possible; no rush
2. using the scoop method to recap a needle
44
New cards
What can grow on wet surfaces?
fungi, bacteria, mold
45
New cards
What are the 3 types of modes of transmission of pathogens? Give some ways that the chain of infection can be broken
3 types: direct contact, droplet particles, airborne particles
* chain of infection can be broken by washing your hands, wearing ppe, getting vaccinated
* chain of infection can be broken by washing your hands, wearing ppe, getting vaccinated
46
New cards
What types of infection are there and how are they caused?
* nosocomial is when an infection is caused by a person in a healthcare facility
* opportunistic is when an infection is caused due to the person having a weak immune system (ie. AIDS or Cancer)
* opportunistic is when an infection is caused due to the person having a weak immune system (ie. AIDS or Cancer)
47
New cards
Define standard precautions and state when they are used. Give a few examples.
a practice that all healthcare workers must follow and do at all times assuming that everyone could be infectious
* examples: hand hygiene, PPE, safe injection practice
* examples: hand hygiene, PPE, safe injection practice
48
New cards
what are transmission-based precautions
when there are special precautions used due to a known infectious illness and standard precautions are not enough
49
New cards
what is antiseptic?
* liquid used to “clean” the skin
50
New cards
what is disinfectant?
* a method to eliminate MOST pathogens from equipment (ie. lysol wipe)
51
New cards
What are potential consequences of not using proper infection control practices
* losing your licenses (ie. doctor license)
* losing business/customers
* getting sued/fined
* losing business/customers
* getting sued/fined
52
New cards
Define sterile field and why it is used. Explain how you know an instrument has been effectively sterilized.
a sterile field is required to prevent microorganisms present
* an instrument has been effectively sterlied when the autoclave sterilization tape has black stripes
* an instrument has been effectively sterlied when the autoclave sterilization tape has black stripes
53
New cards
what is ppe?
personal protective equipment
54
New cards
what is the correct donning order?
hand hygiene, gown, hat, mask, eye protection, gloves
55
New cards
what is the correct doffing order?
gloves, gown, hand hygiene, eye protection, mask, hat, hand hygiene
56
New cards
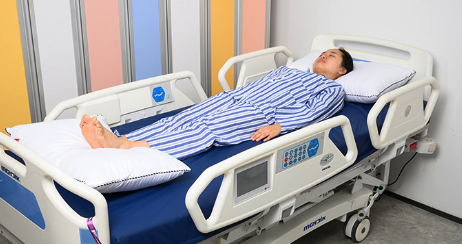
what is this position? what is it used for?
1. supine
2. commonly used for general examination or physical assessment
57
New cards
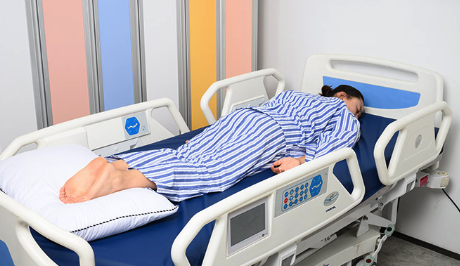
what is this position? what is it used for?
1. prone
2. used in medical settings to help patients with certain conditions and symptoms get relief
58
New cards
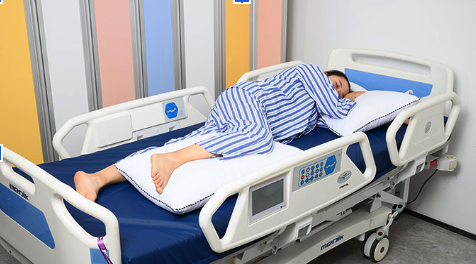
what is this position? what is it used for?
1. lateral
2. helps relieve pressure on the coccyx. Support pillows are needed to correctly position the patient in a lateral position
59
New cards
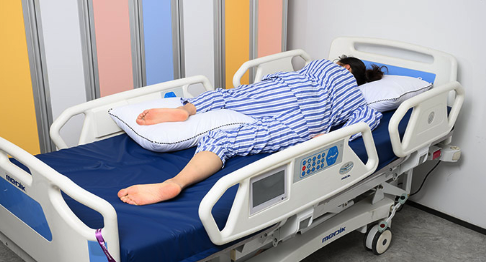
what is this position? what is it used for?
1. sims
2. used for rectal examination, treatments, enemas, and examining women for vaginal wall prolapse
60
New cards

what is this position? what is it used for?
1. semi fowler
2. used when the patient faces difficulty breathing or is undergoing breathing treatments
61
New cards

what is this position? what is it used for?
1. high fowlers
2. prescribed to elderly patients as it is scientifically proven to aid in the digestion process and help the patient overcome breathing problems
62
New cards
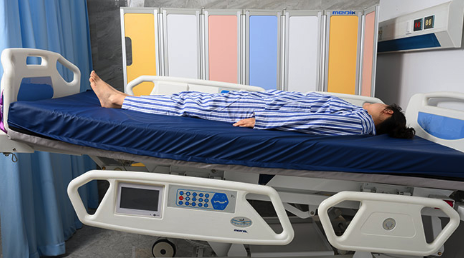
what is this position? what is it used for?
1. trendelenburg
2. used in situations such as hypotension and medical emergencies. It helps promote a venous return to major organs such as the head and heart
63
New cards

what is this position? what is it used for?
1. reverse trendelenburg
2. often used for patients with gastrointestinal problems as it helps minimize esophageal reflux
64
New cards
what are the 8 basic rules of body mechanics?
1. Broad base of support (ie. standing feet apart than together)
2. Bend from the hips and knees (don’t pick things up with your back)
3. Use strong muscles (ie. thighs and arm)
4. Carry objects close to body (ie. easier to carry)
5. Avoid twisting (ie. step and reach)
6. Avoid bending for long periods of time (ie. washing dishes, stocking shelves, gardening)
7. Get help! (ie. asking for help, machines)
8. Use your weight to push a wheelchair
65
New cards
What are the rules about using a wheelchair safely?
* using brakes
* using your weight to push a wheelchair
* not leaning forward; may cause to tip over
* using your weight to push a wheelchair
* not leaning forward; may cause to tip over
66
New cards
What does ‘working height’ mean? What is the first thing you should do before performing any type of transfer on a patient?
* working height means where there is a risk of falling as you are either above or below ground
* washing hands and making sure the patient is positioned correctly to ensure no injuries
* washing hands and making sure the patient is positioned correctly to ensure no injuries
67
New cards
What can result from poor body mechanics?
back problems
68
New cards
what is the function of the digestive system?
breaks down food and nutrients into smaller parts in order for your body to absorb and use it for energy, growth, and cell repair
69
New cards
the digestive system pathway starting with the mouth. (List the parts in order)
1. mouth
2. esophagus
3. stomach
4. small intestine
5. large intestine
6. “accessory organs” → liver, gallbladder and pancreas
70
New cards
What does the epiglottis do when you swallow?
When you swallow, the epiglottis will fold backwards and cover the entrance of the larynx/pharynx so that food and liquid will not enter the windpipe and into the lungs.
71
New cards
Where does “digestion” (absorption of nutrients) occur?
small intestine absorbs most of the nutrients in your food, and your circulatory system passes them on to other parts of your body to store or use
72
New cards
Where does the water get absorbed from your digested food into the capillaries?
The walls of the small intestine absorb water and the digested nutrients into your bloodstream
73
New cards
What makes your food move one direction through the long tube (digestive system)
Waves of muscle contractions called peristalsis
74
New cards
What are some Sx of Crohn’s and Colitis?
* fatigue
* abdominal pain/cramping
* diarrhea
* reduced appetite
* abdominal pain/cramping
* diarrhea
* reduced appetite
75
New cards
Explain the procedure of a colonoscopy and endoscopy
* colonoscopy: the examination done with a scope of the large intestine
\
* endoscopy: the examination done with a scope of the digestive tract
\
* endoscopy: the examination done with a scope of the digestive tract
76
New cards
what is the difference between anatomy and physiology?
* Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism or its parts. ex. the parts that make up a mouse ex. the parts that make up a mouse heart
\
* Physiology: The study of how an organism works or its parts. ex. how the mouse's body operates ex. how the mouse's heart operates
\
* Physiology: The study of how an organism works or its parts. ex. how the mouse's body operates ex. how the mouse's heart operates
77
New cards
How are organisms organized? Atoms, molecules etc
* Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism
78
New cards
what are cells?
basic building blocks of life
79
New cards
explain homeostasis and give examples
* Homeostasis: ability/tendency to maintain internal stability in an organism to compensate for environmental changes.
* Examples include: sweating, shivering, baroreceptors signaling your kidneys to eliminate water when consuming large amounts of liquids, eyes dilating/constricting
* Examples include: sweating, shivering, baroreceptors signaling your kidneys to eliminate water when consuming large amounts of liquids, eyes dilating/constricting
80
New cards
what is the function of the skeletal system?
to protect organs, provide blood, allow movement, provide shape, as well as hold vital organs in place
81
New cards
how many bones are in an adult skeletion?
206
82
New cards
why do babies have more bones?
Babies are born with more cartilage than bones and as the baby grows, the bones fuse together into one bone
83
New cards
Describe the structure of a bone.
The structure of the bone is periosteum (outer layer), compact bone, spongy bone, and then bone marrow
84
New cards
define ligament
Strong, elastic bands of tissue that hold bones together in the joints
85
New cards
define tendon
Connective tissue that connects the muscle to bone
86
New cards
define cartilage
Type of connective tissue that’s found all throughout the body and helps protect and cushion our bones against impact
87
New cards
what is the function of the cardiovascular system?
provides oxygen and nutrients to every cell in the body as well as removing waste such as carbon dioxide
88
New cards
Identify the major veins and arteries on your body
* The major veins include the pulmonary veins, the vena cavas
\
* The major arteries include the coronary artery, and aorta
\
* The major arteries include the coronary artery, and aorta
89
New cards
Trace the route of a blood cell through your circulatory system
1. Oxygen poor blood from the body collects in the vena cava
2. Oxygen poor blood moves from the vena cava and into the right atrium
3. Blood moves from the right atrium and into the right ventricle
4. Blood leaves the right ventricle and flows into the pulmonary artery
5. Oxygen poor blood enters the lungs and becomes oxygenated (Gas exchange occurs)
6. Oxygen rich blood leaves the lungs and enters the pulmonary veins on the way back to the heart
7. Oxygen rich blood enters the left atrium
8. Blood moves from the left atrium and into the left ventricle
9. Oxygen rich blood enters the aorta
10. Oxygen rich blood is then distributed throughout the body
90
New cards
what is the function of the respiratory system?
helps us breathe. It moves fresh air into the body while removing waste gases such as carbon dioxide
91
New cards
label parts of the circulatory system
* Nasal cavity
* Cilia
* Pharynx
* Trachea
* Lung
* Bronchus
* Bronchioles
* Alveoli
* Cilia
* Pharynx
* Trachea
* Lung
* Bronchus
* Bronchioles
* Alveoli
92
New cards
Review the respiratory system pathway starting with the nasal cavity. (List the parts in order)
1. Nasa cavity2
2. Pharynx
3. Trachea
4. Lung
5. Bronchus
6. Bronchioles
7. Alveoli
93
New cards
What is cilia and how does it help you?
tiny hairs that help move microbes/dust, and mucus upwards and out of the throat
94
New cards
what is the function of the nervous system?
transmits signals from the brain to the rest of the body
95
New cards
what is a neuron?
information messengers and use electrical impulses and chemical signals to transmit information
96
New cards
what is a reflex? how does it work?
A reflex is an involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus. A reflex is an automatic response from the body to protect itself from harm
97
New cards
What is the difference between a motor and a sensory neuron?
Motor neurons send internal signals that control the movement of muscles in the body and sensory nerves bring external signals to perceive senses such as touch, pain, etc
98
New cards
define CNS
Central Nervous System
* made up of the brain and spinal cord
* made up of the brain and spinal cord
99
New cards
define PNS
Peripheral nervous system
* made up of the nerves, cranial nerves and spinal nerves
* made up of the nerves, cranial nerves and spinal nerves
100
New cards
How can you assess for brain damage? Explain normal and abnormal findings.
* CT Scan, spinal tap/lumbar puncture, Pupil Reflex test, and Glasgow coma scale.
* Clear CSF: Normal
* Bloody CSF: Bleeding in the brain
* Cloudy CSF: Puss, meningitis
* Right pupil constricts/left pupil stays dilated: Right side is damaged
* Right pupil stays dilated: Left pupil constricts: Left side is damaged
* If both sides stay dilated both sides of the brain are damaged
* Clear CSF: Normal
* Bloody CSF: Bleeding in the brain
* Cloudy CSF: Puss, meningitis
* Right pupil constricts/left pupil stays dilated: Right side is damaged
* Right pupil stays dilated: Left pupil constricts: Left side is damaged
* If both sides stay dilated both sides of the brain are damaged