Bio unit 3.3
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Phtosynthesis
When a cell captures energy in the sunlight and uses it to make food
Factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis
light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature
Where does photosynthesis occur?
chloroplasts in the leaves of a plant
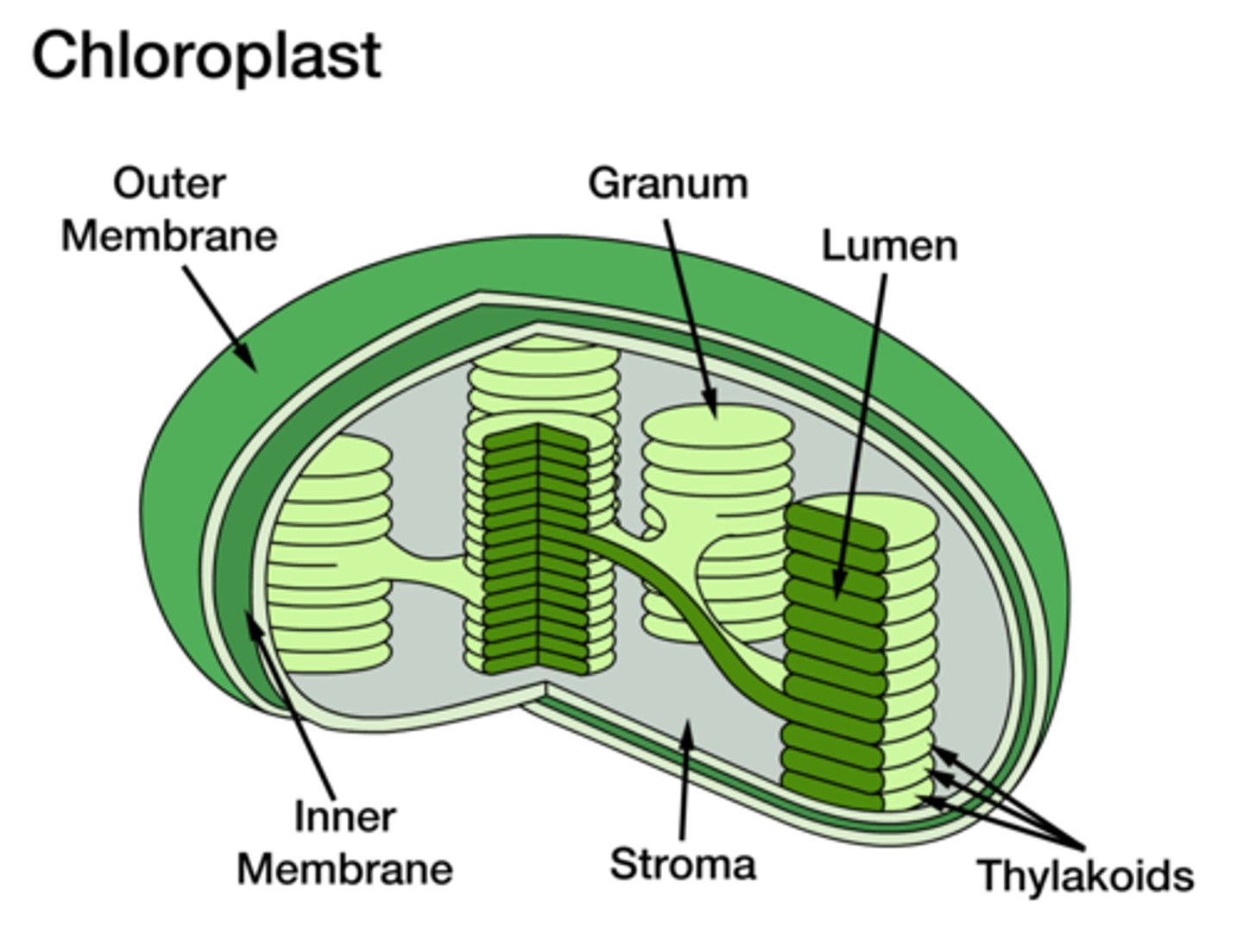
Chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy
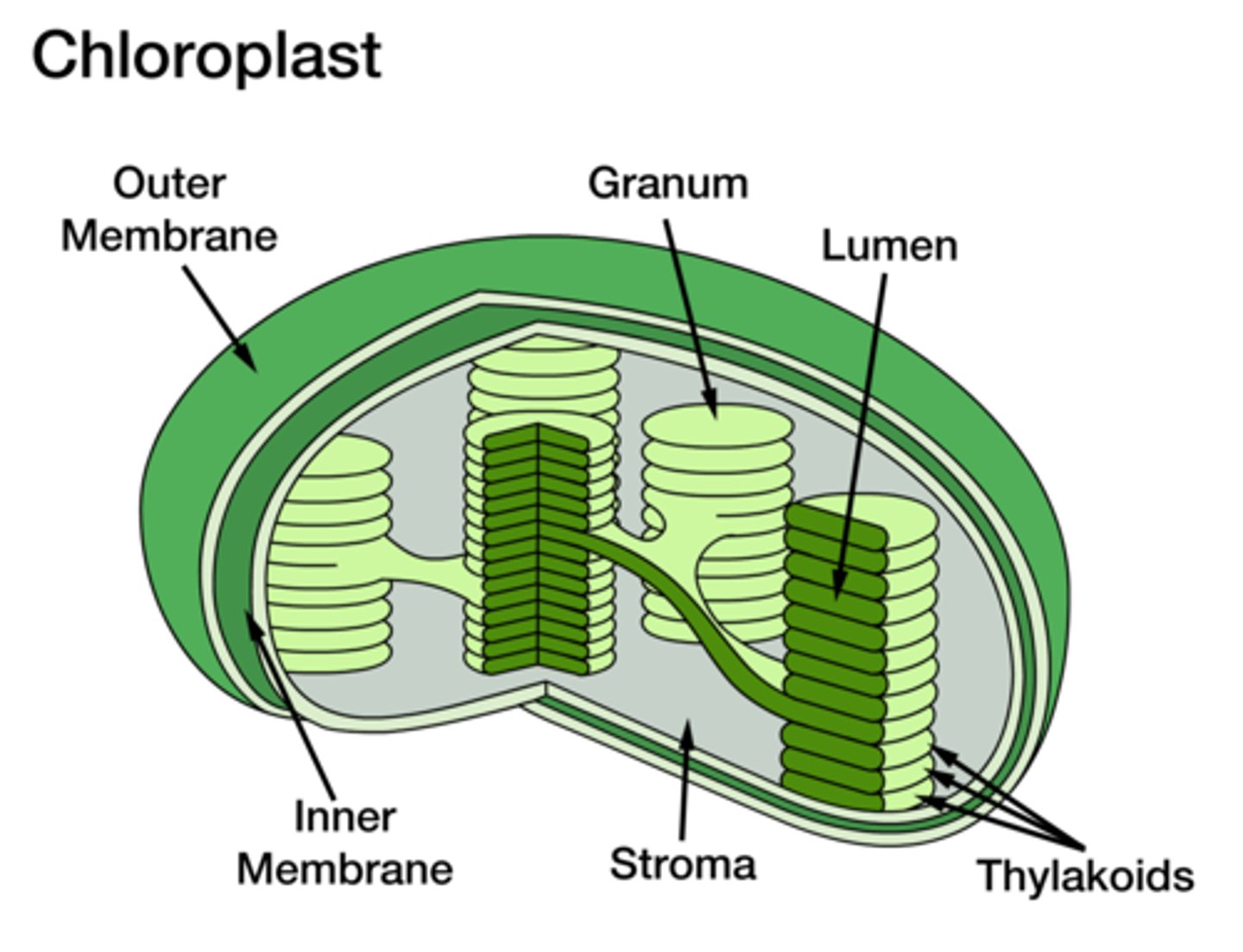
Granum
stack of thylakoids
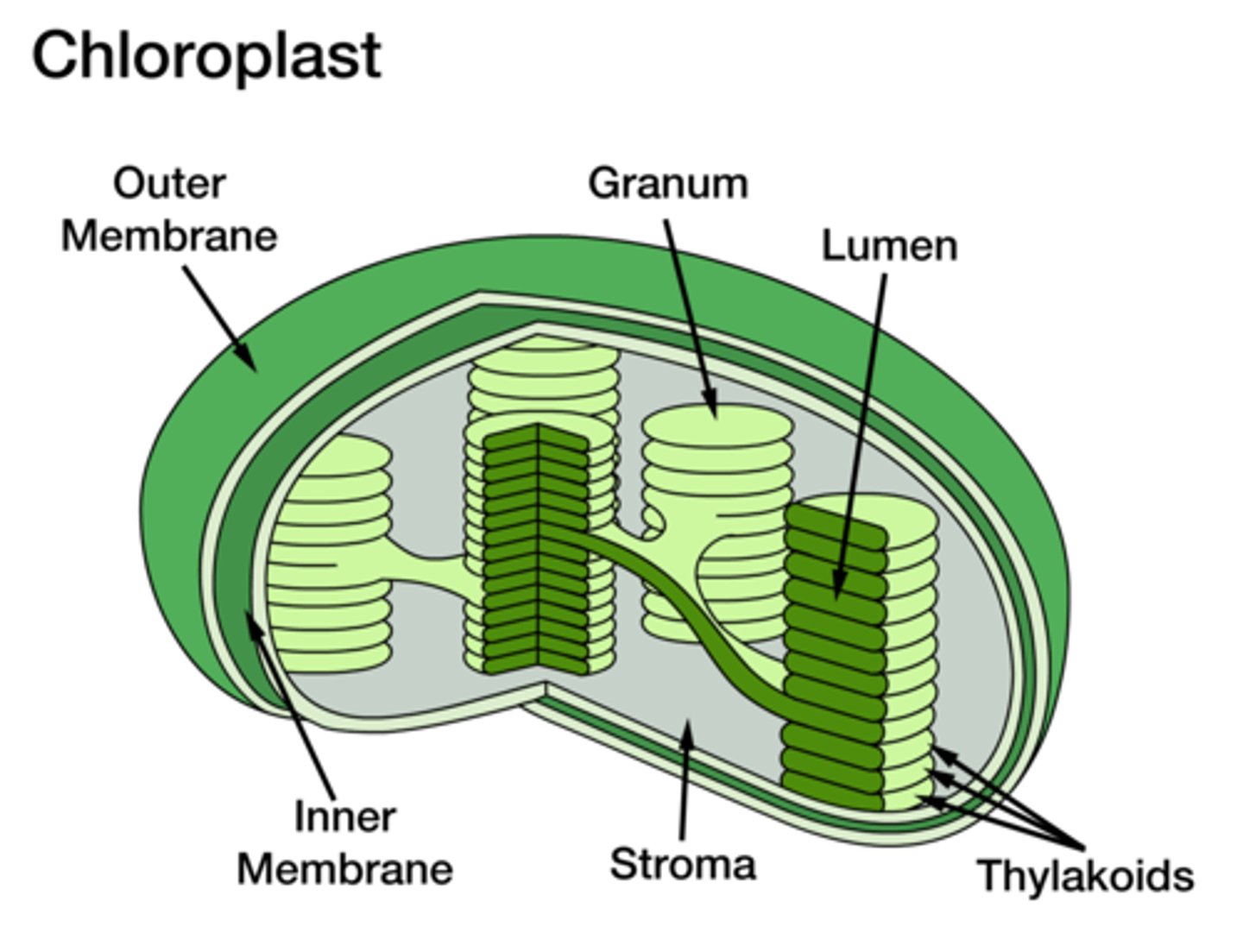
outer membrane of chloroplast
permeable to small organic molecules
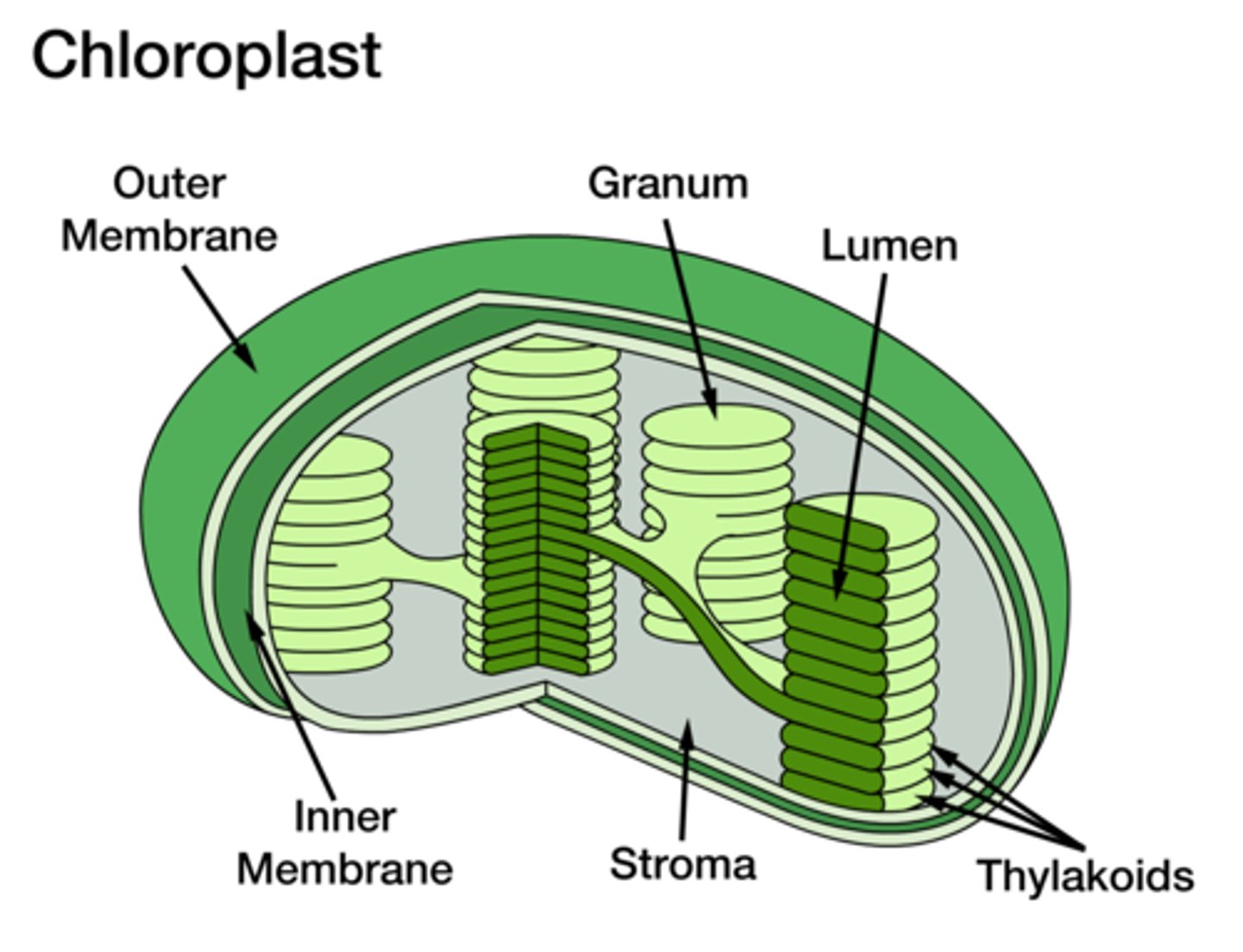
inner membrane of chloroplast
The inner plasma membrane composed of a phospholipid bilayer.
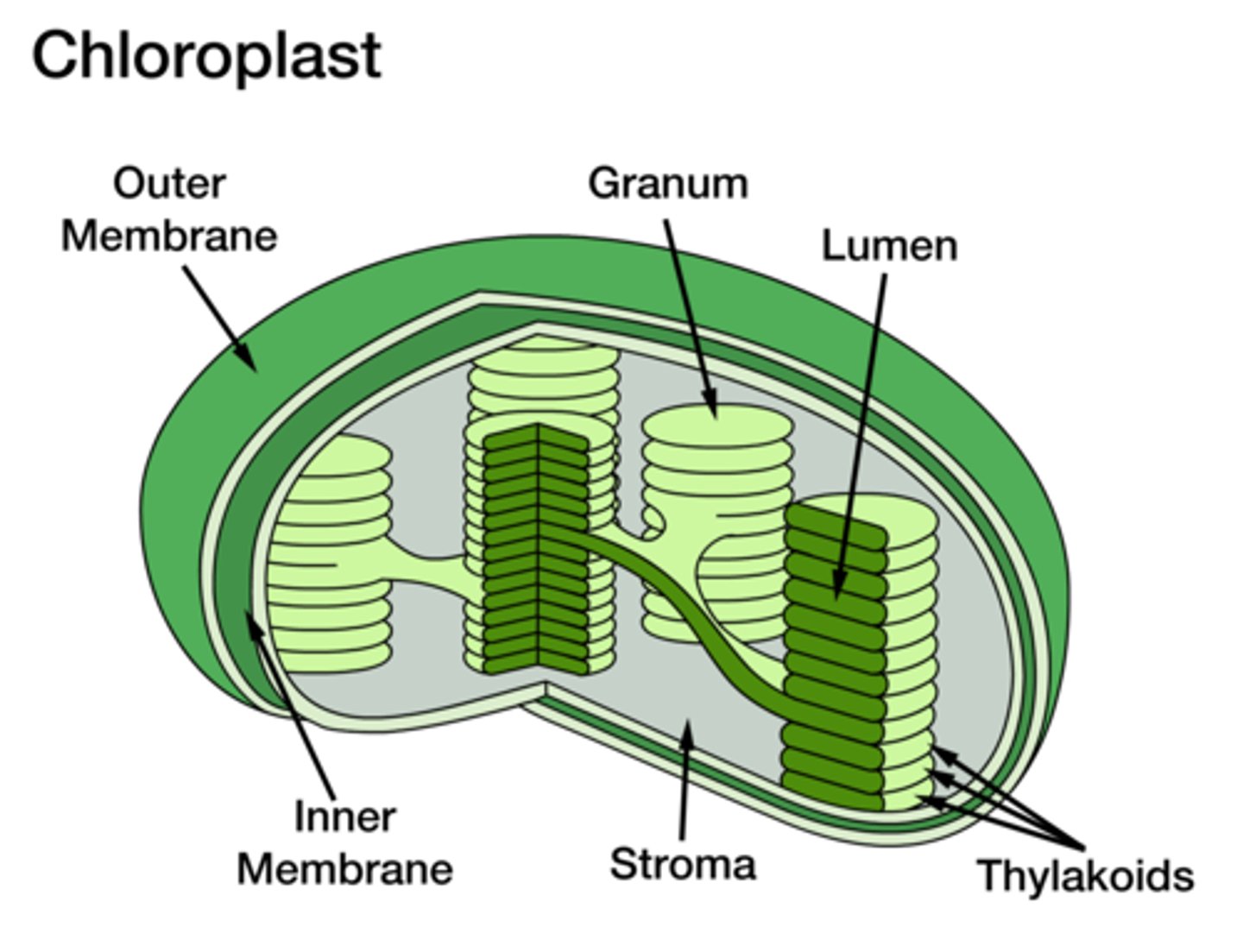
Thylakoids
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy to chemical energy.
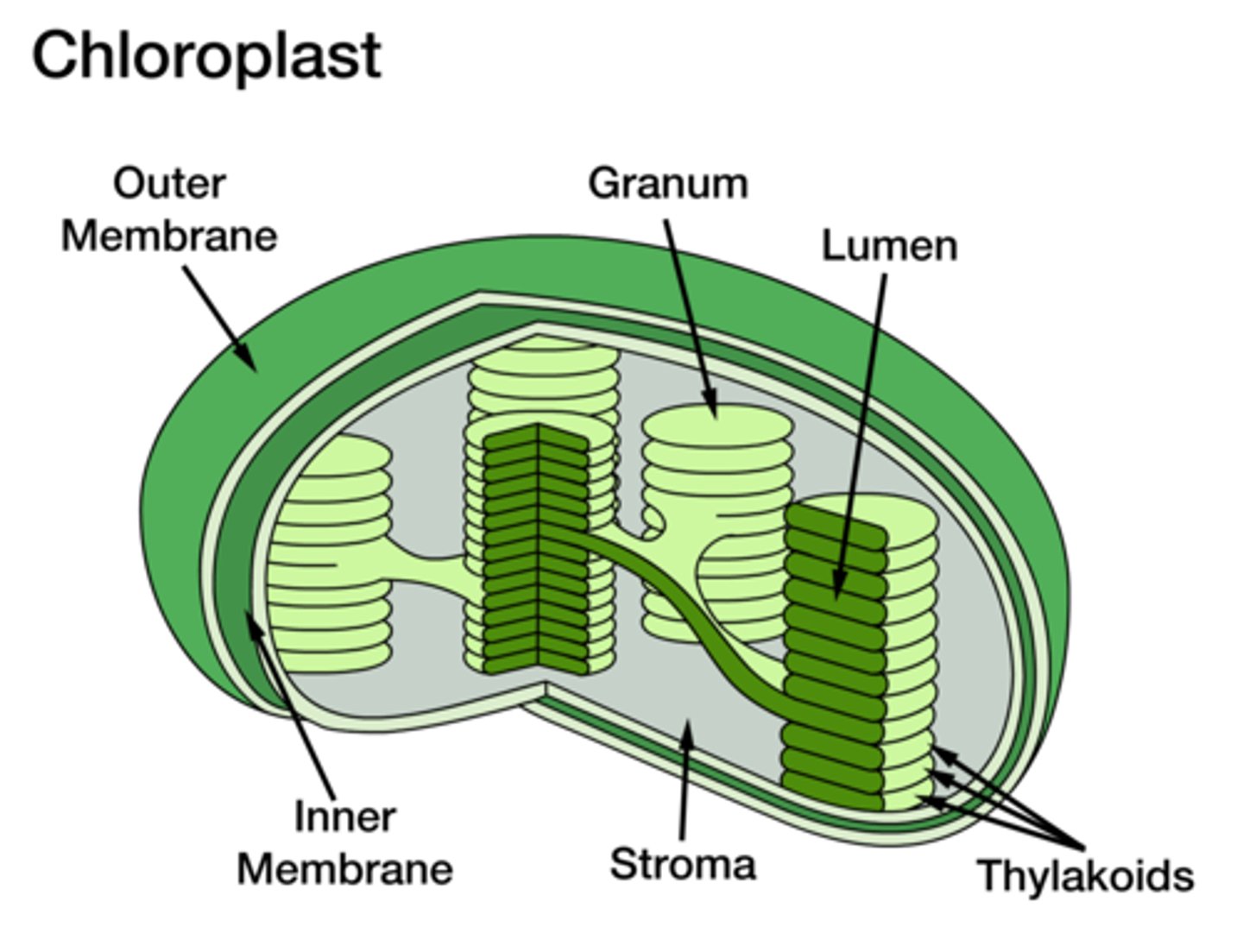
stroma
The fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane; involved in the synthesis of organic molecules from carbon dioxide and water.
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2
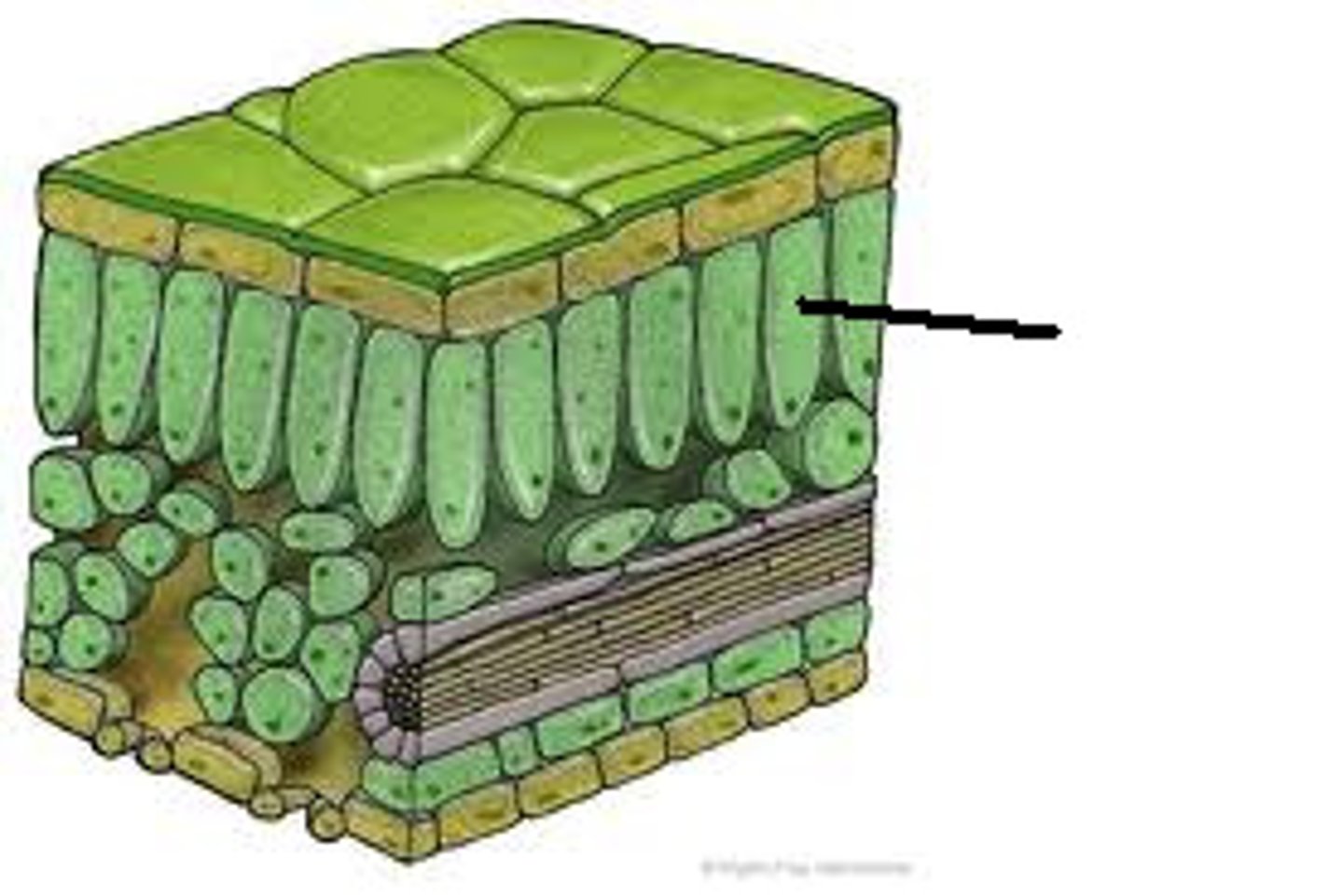
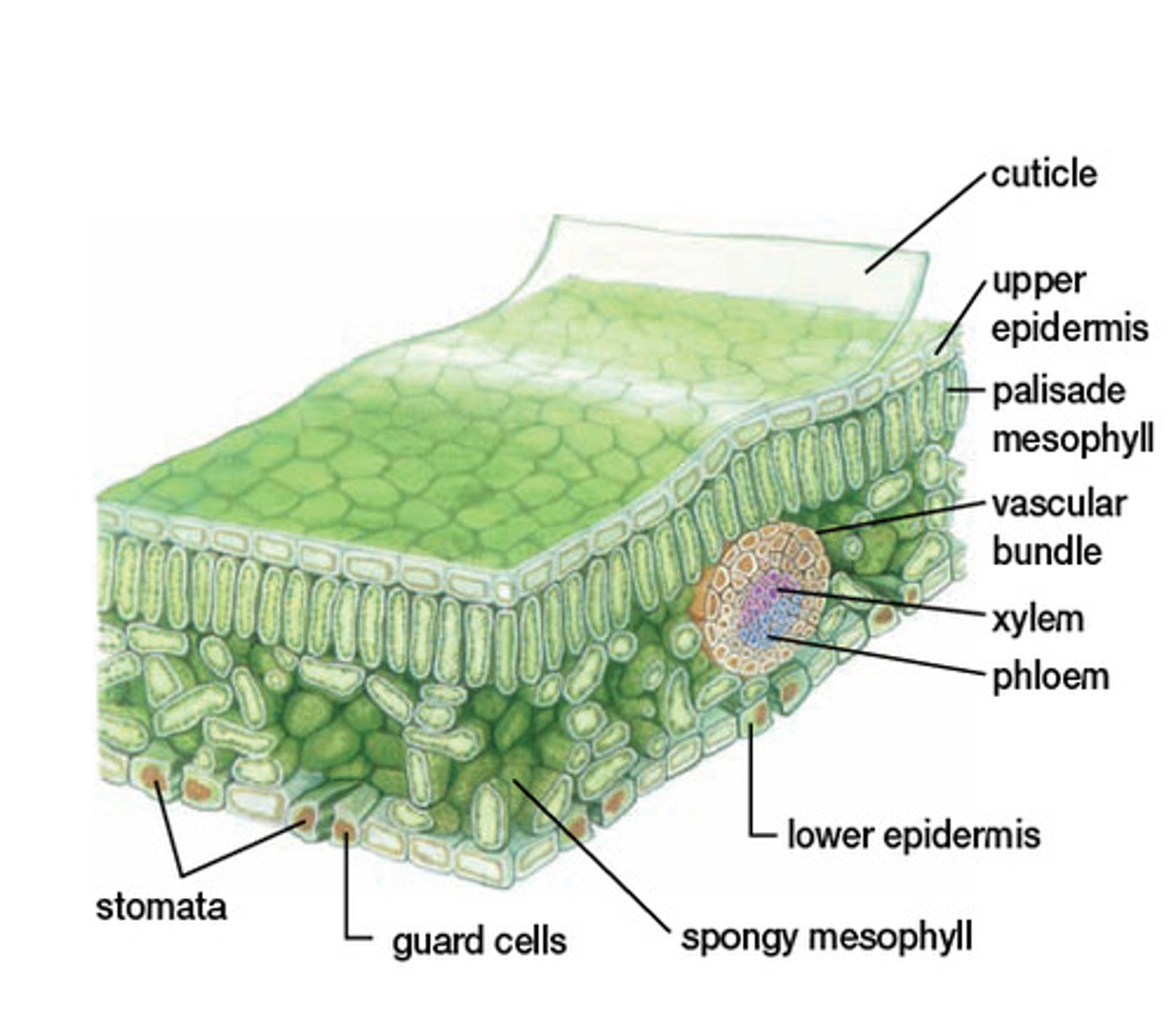
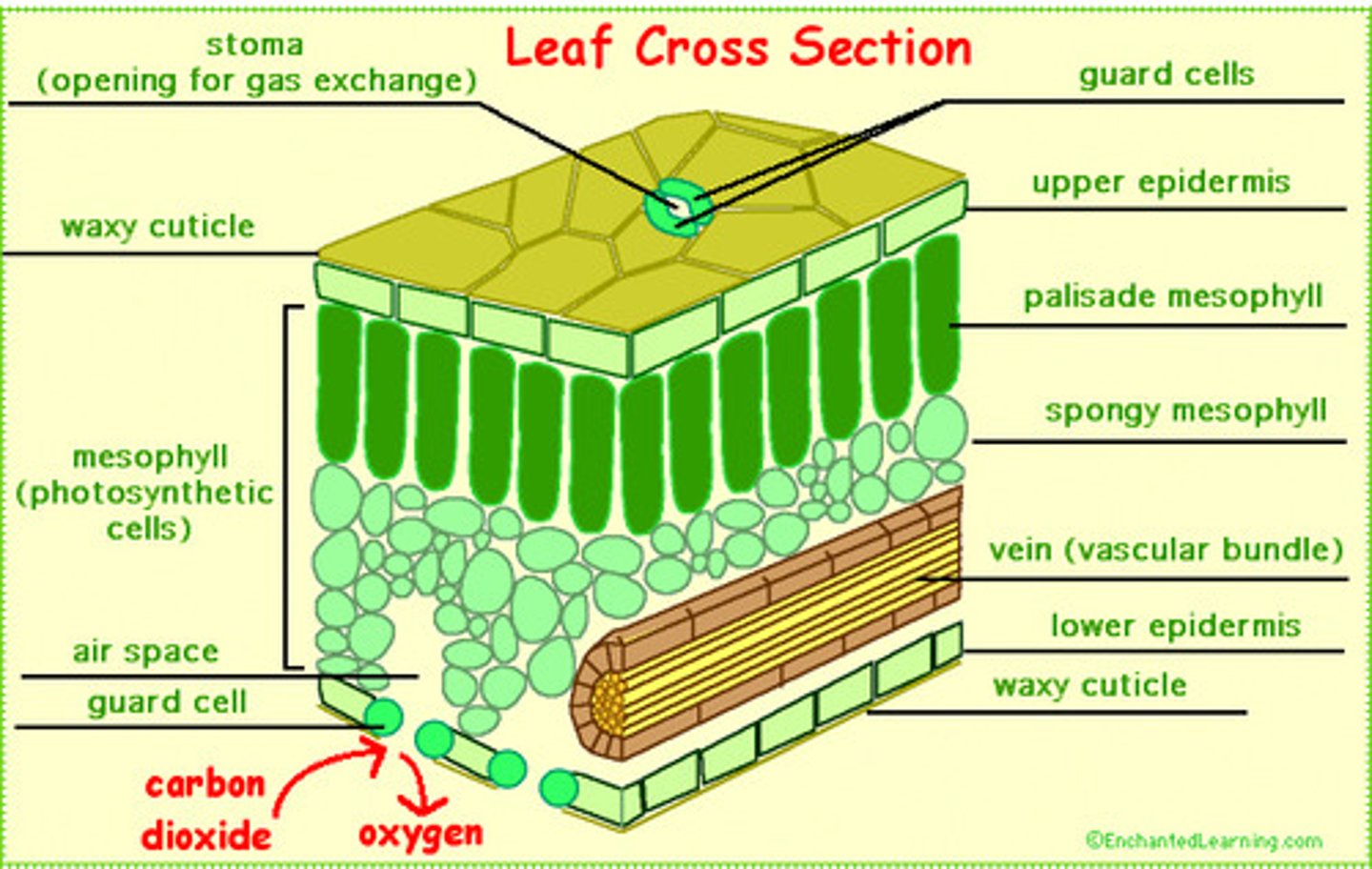
Palisade mesophyll-
This layer of cells
is located near the top of the leaf and
is
characterized by tightly packed
photosynthetic cells.
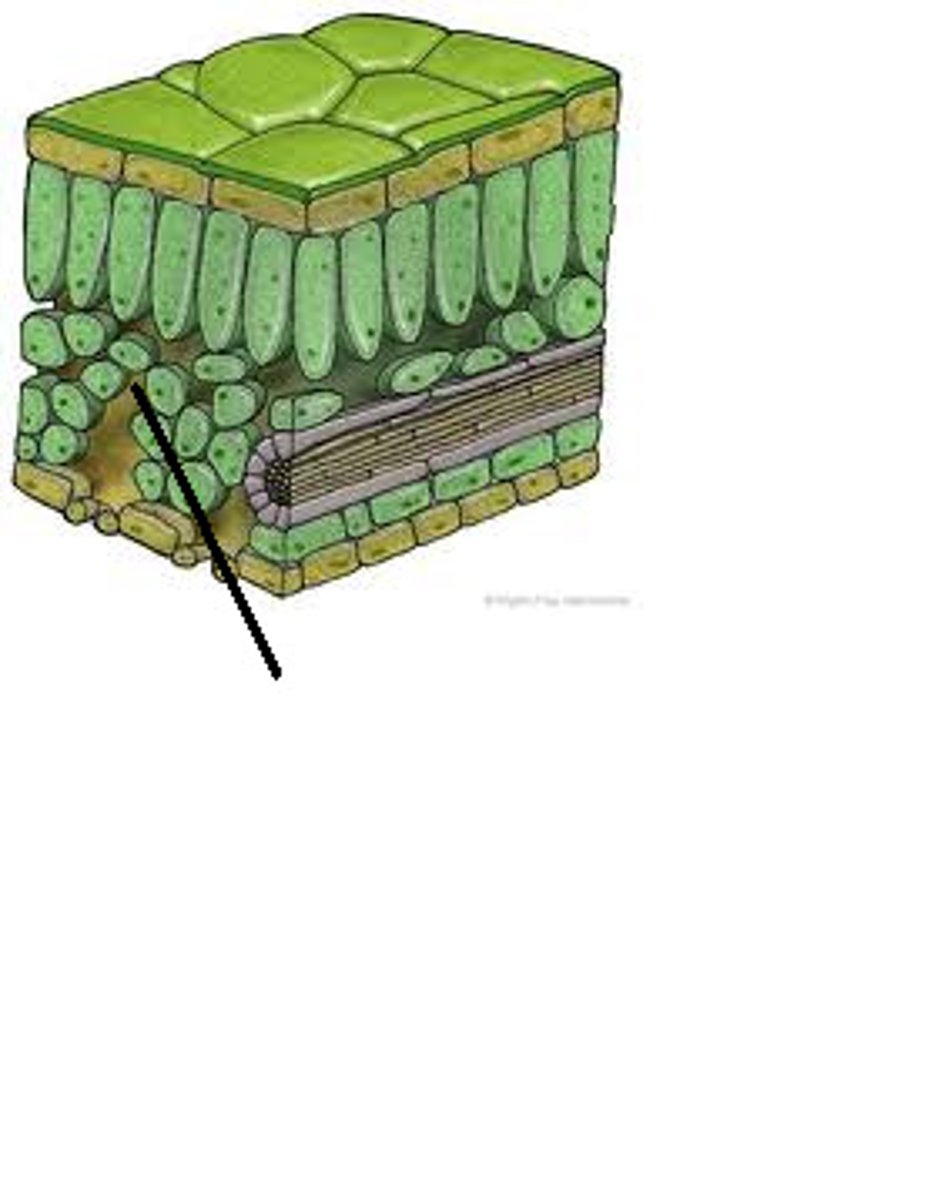
Spongy mesophyll—
This part of the
leaf includes photosynthetic cells full
of
chloroplasts, but it also includes air
space between many of the cells.
Epidermis—
This layer of cells at the very
top and bottom of the leaf has small cells
that are tightly linked together. The
epidermis creates a boundary between
the leaf and its environment.
Stoma (plural: stomata)—
This is a pore or small hole,
usually found in the bottom
of a leaf.
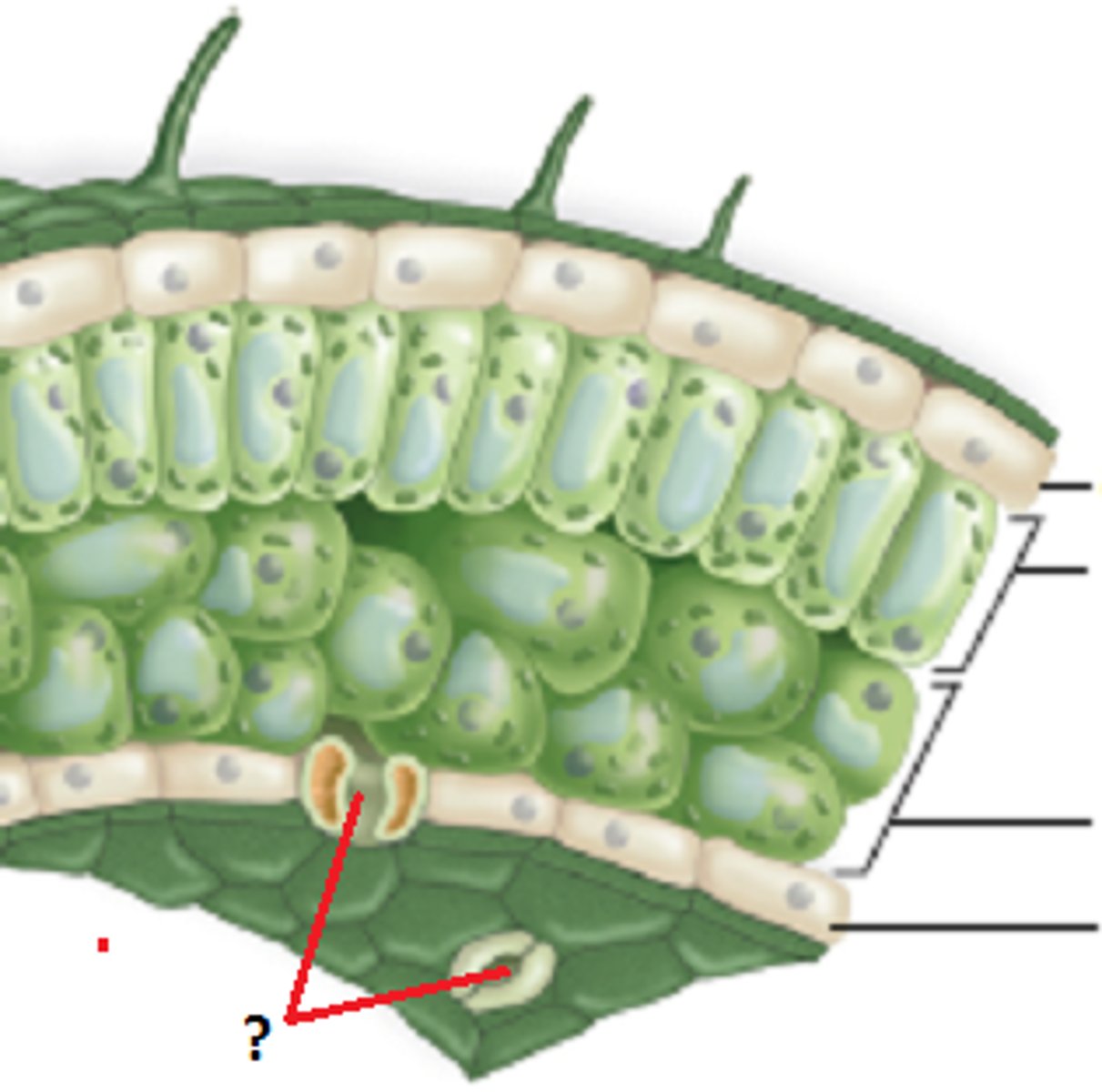
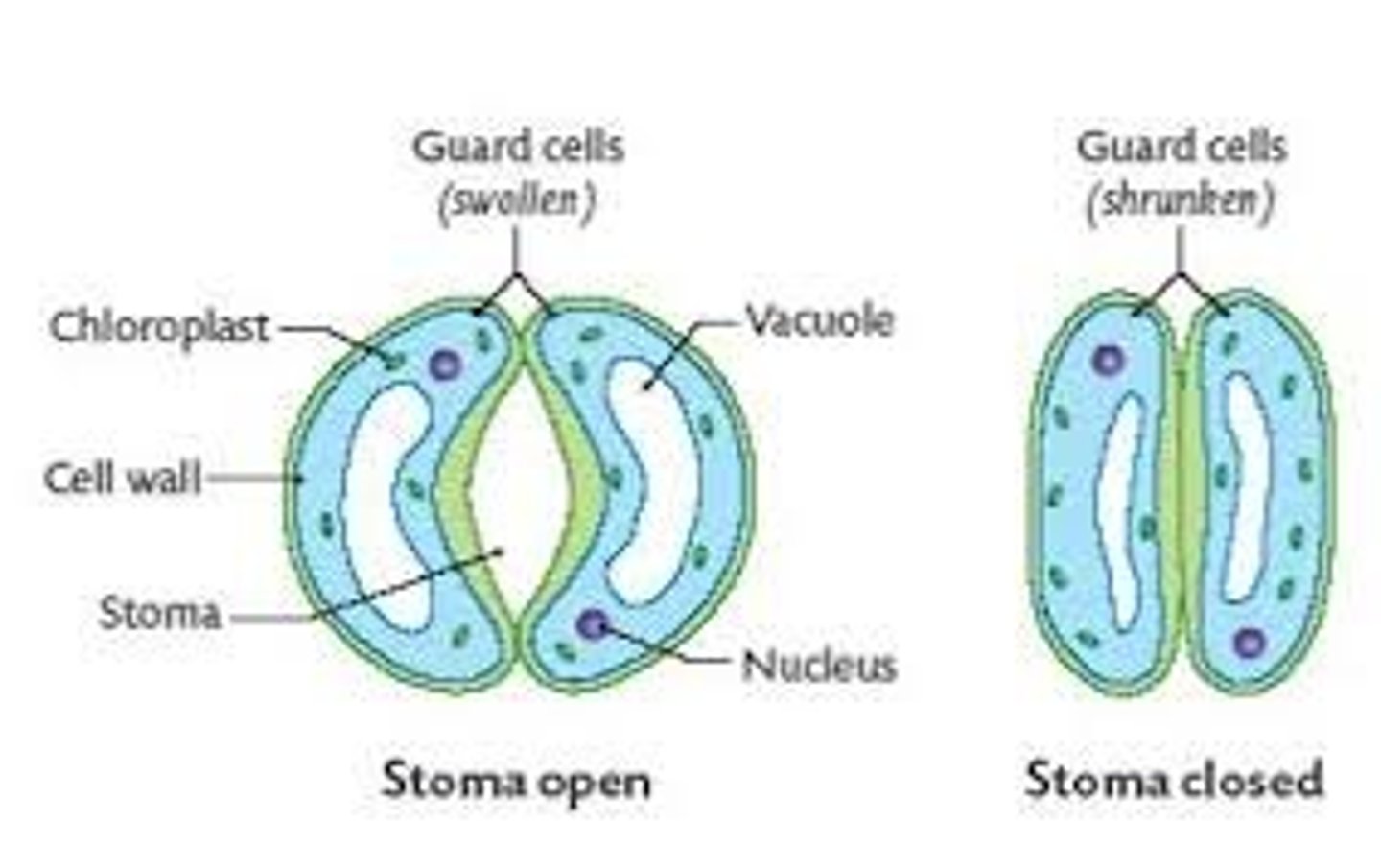
Guard cells—
These are cells found on either side of a
stoma that can control
Whether the stoma is open or
closed.
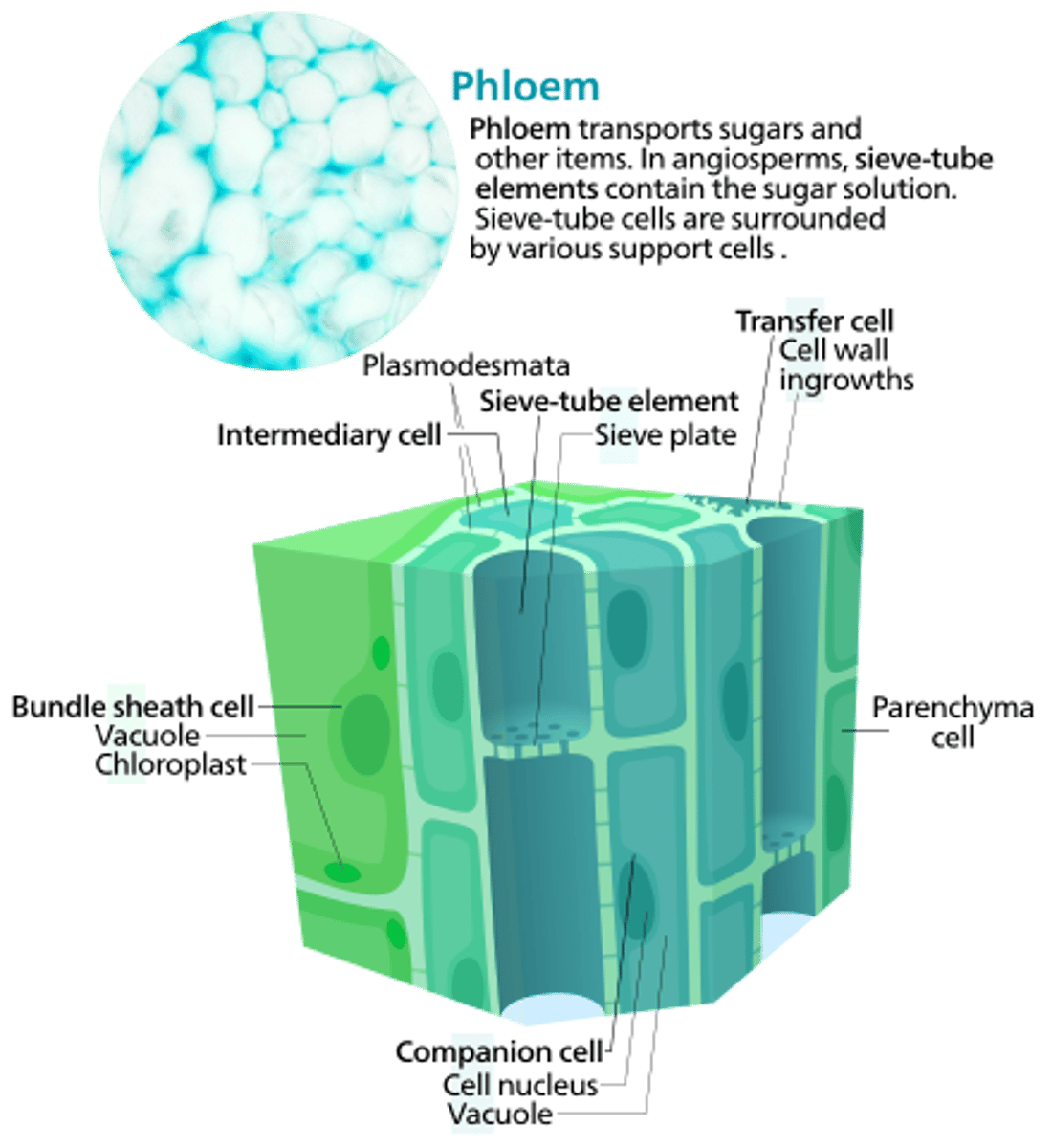
Vascular bundle—
The vascular
bundles of the leaf are
primarily composed of two
types of cells:

Xylem cells-
responsible
for transporting water (and
minerals dissolved in
it) from the roots.
Phloem cells
responsible
for transporting glucose made
in the cells of the
leaf to other locations in the
plant where the glucose is
needed.
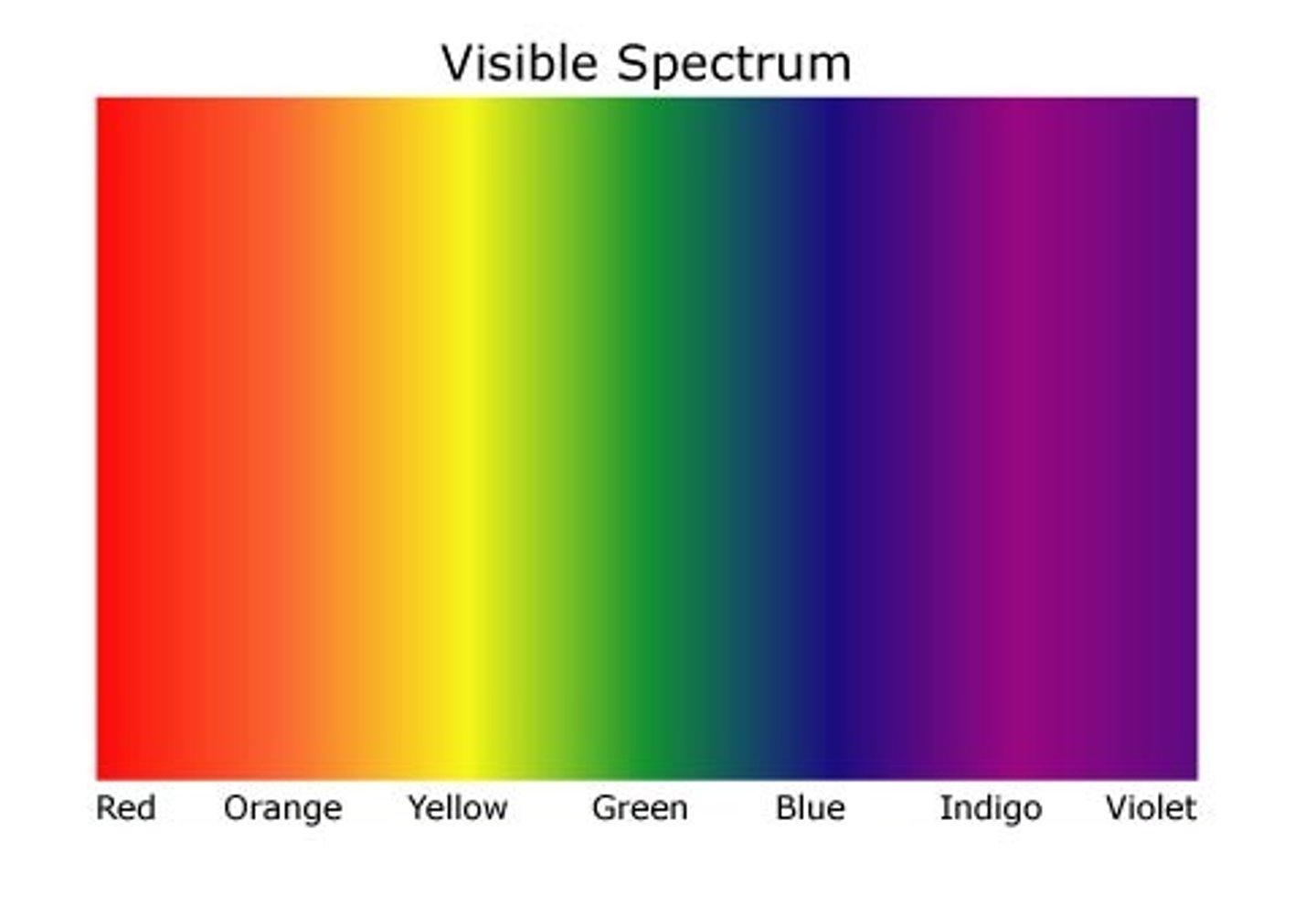
visible spectrum
portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can see
chlorophyll
principal pigment of plants and other photosynthetic organisms (green)

leaf anatomy
Upper epidermis Palisade mesophyll
Spongy mesophyll Vascular bundles
xylem phloem
Lower epidermis
photosynthetic pigments
Chemicals that absorb light energy and use it to carry out photosynthesis. Contained in thylakoid membranes in chloroplast. Examples are chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoids, xanthophylls, and phycobilins.
chlorophyll absorbs
blue and red light
Carotenoids
An accessory pigment, either yellow, orange or red, in the chloroplasts of plants. By absorbing wavelengths of light that chlorophyll cannot, carotenoids broaden the spectrum of colors that can drive photosynthesis.

carotenoids absorb
blue and green light