A&P II - Chapter 22
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
D) Assists in the synthesis of vasodilators
Which of the following is not a function of the respiratory system?
A) Control of pH
B) Promotes the flow of lymph and venous blood
C) Helps regulate blood pressure
D) Assists in the synthesis of vasodilators
E) Aids in defecation
D) Regulation of pH
Which of the following is directly related to respiratory production of carbon dioxide?
A) Regulation of blood pressure
B) The synthesis of vasodilators
C) Aids in defecation
D) Regulation of pH
E) Regulation of body temperature
C) larynx
The upper respiratory tract extends from the nose through the __________.
A) trachea
B) pharynx
C) larynx
D) alveoli
E) lungs
B) nasal fossae
The nose is divided into right and left halves called the __________.
A) nasal cavities
B) nasal fossae
C) nasal septa
D) nasal vestibules
E) nasal apertures
A) Vestibular and vocal
Which two ligaments extend from the thyroid cartilage to the arytenoid cartilages?
A) Vestibular and vocal
B) Laryngeal and corniculate
C) Corniculate and cricoid
D) Cricoid and arytenoid
E) Thyrohyoid and cricoids
D) Dust cells
What are the most numerous cells in the lungs?
A) Mucosal cells
B) Type I alveolar cells
C) Type II alveolar cells
D) Dust cells
E) Vibrissal cells
B) pulmonary artery
Each alveolus is surrounded by a web of blood capillaries supplied by the __________.
A) aorta
B) pulmonary artery
C) pulmonary vein
D) inferior vena cava
E) superior vena cava
E) Laryngopharynx
Which of the following does not contain ciliated cells?
A) Nasal cavity
B) Trachea
C) Primary bronchus
D) Terminal bronchiole
E) Laryngopharynx
A) Their shape
What is the basic distinction between an alveolar duct and an alveolar atrium?
A) Their shape
B) Their size
C) Their function
D) Their epithelial type
E) The presence or absence of cilia
D) Left main bronchus
Which bronchus is about 5 cm long and slightly narrower and less vertical than the one on the opposite side?
A) Left segmental bronchus
B) Right segmental bronchus
C) Right lobar bronchus
D) Left main bronchus
E) Right main bronchus
D) cardiac notch
The heart indents into the __________ of the left lung.
A) oblique fissure
B) hilum
C) apex
D) cardiac notch
E) base
D) lobes
The lungs have a total of five __________.
A) segmental bronchi
B) choanae
C) laryngeal cartilages
D) lobes
E) tracheal cartilages
B) epiglottis
Crude sounds are formed into intelligible speech by all of the following except the __________.
A) pharynx
B) epiglottis
C) oral cavity
D) tongue
E) lips
C) Thyroid cartilage
Which of the following cartilages is largest?
A) Corniculate cartilage
B) Epiglottic cartilage
C) Thyroid cartilage
D) Cricoid cartilage
E) Arytenoid cartilage
C) Dalton's
Which law states the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of its individual gases?
A) Boyle's
B) Valsalva's
C) Dalton's
D) Charles's
E) Henry's
C) Bronchiole diameter
In a healthy person, which of the following will have the greatest influence on resistance to pulmonary airflow?
A) Atmospheric pressure
B) Respiratory rate
C) Bronchiole diameter
D) Quantity of surfactant
E) Contraction of the diaphragm
B) Pulmonary compliance
Which of the following is the term for the lungs' resistance to expansion?
A) Pulmonary ventilation
B) Pulmonary compliance
C) Pulmonary stenosis
D) Pulmonary surfactant
E) Pulmonary impedance
B) inspiratory reserve volume
The amount of air in excess of tidal volume that can be inhaled with maximum effort is the __________.
A) vital capacity
B) inspiratory reserve volume
C) expiratory reserve volume
D) residual volume
E) inspiratory capacity
D) Expiratory reserve volume + tidal volume + inspiratory reserve volume
How is the vital capacity calculated?
A) Inspiratory reserve volume + expiratory volume
B) Inspiratory reserve volume + tidal volume
C) Expiratory reserve volume + tidal volume
D) Expiratory reserve volume + tidal volume + inspiratory reserve volume
E) Respiratory reserve volume + tidal volume
E) Kussmaul respiration
Deep, rapid breathing often seen in terminal diabetes mellitus is known as what?
A) Tachypnea
B) Dyspnea
C) Orthopnea
D) Hyperpnea
E) Kussmaul respiration
C) carbonate
Carbon dioxide is transported by all the following means except __________.
A) carbaminohemoglobin
B) carbonic acid
C) carbonate
D) bicarbonate ions
E) dissolved gas
B) There is a venous reserve of oxygen in Tom's blood
Tom is in respiratory arrest due to an electrical shock. Why does a good samaritan have up to 4 to 5 minutes to begin CPR and save Tom's life?
A) There is reserve oxygen in Tom's lungs
B) There is a venous reserve of oxygen in Tom's blood
C) The ambient PO2 can support life that long
D) The Haldane effect lasts up to 5 minutes
E) Tom's hypoxic drive will keep him alive for up to 5 minutes
E) Anticipation of the needs of exercising muscle
During exercise, which of the following directly increases respiratory rate?
A) Increased H+ level in the blood
B) The Bohr effect
C) Reduced blood pH
D) Reduced oxyhemoglobin
E) Anticipation of the needs of exercising muscle
A) An increase in membrane thickness
Which of the following would slow down gas exchange between the blood and alveolar air?
A) An increase in membrane thickness
B) An increase in alveolar surface area
C) An increase in respiratory rate
D) A decrease in membrane thickness
E) A decrease in nitrogen solubility
D) hydrogen
The addition of CH3OCH3 to the blood generates __________ ions in the RBCs, which in turn stimulates RBCs to unload more oxygen.
A) sodium
B) potassium
C) nitrogen
D) hydrogen
E) chloride
E) Erythrocyte count
Which of the following has no effect on oxyhemoglobin dissociation?
A) Epinephrine
B) Fever
C) Thyroid hormone
D) Low pH
E) Erythrocyte count
C) Nitrogen
In the air we breathe, which gas is found in the highest concentration?
A) Oxygen
B) Water vapor
C) Nitrogen
D) Carbon dioxide
E) Hydrogen
E) 4
Each hemoglobin molecule can transport up to __________ oxygen molecules.
A) 6
B) 0
C) 0
D) 3
E) 4
B) 95; 40; 7.4
Normally, the systemic arterial blood has a PO2 of __________ mm Hg, a PCO2 of __________ mm Hg, and a pH of __________.
A) 40; 95; 7.4
B) 95; 40; 7.4
C) 7.4; 40; 95
D) 95; 7.4; 40
E) 40; 7.4; 95
C) Carbon anhydrase
Which of the following enzymes in an RBC breaks H2CO3 down to water and carbon dioxide?
A) Hemoglobinase
B) Carboxyhemoglobinase
C) Carbon anhydrase
D) Bisphosphoglycerase
E) Carbaminoreductase
C) 20% to 25%
In one passage through a bed of systemic blood capillaries, the blood gives up about what percentage of its oxygen?
A) 5% to 10%
B) 10% to 15%
C) 20% to 25%
D) 30% to 40%
E) 70% to 85%
B) Hypoxia
Which of the following is the term for a deficiency of oxygen or the inability to utilize oxygen in a tissue?
A) Apoxia
B) Hypoxia
C) Anoxia
D) Cyanosis
E) Eupnea
B) Ischemic hypoxia
Congestive heart failure results in which of the following?
A) Hypoxemic hypoxia
B) Ischemic hypoxia
C) Anemic hypoxia
D) Histotoxic hypoxia
E) Idiopathic hypoxia
D) Chronic bronchitis
Which of the following is a lung disease marked by a reduced number of cilia, reduced motility of the remaining cilia, goblet cell hypertrophy and hypersecretion, and thick sputum?
A) Asthma
B) Oat-cell carcinoma
C) Atelectasis
D) Chronic bronchitis
E) Emphysema
A) Sickle-cell anemia
Which of the following would lead to anemic hypoxia?
A) Sickle-cell anemia
B) Emphysema
C) Squamous-cell carcinoma
D) Asthma
E) Atelectasis
C) Emphysema
Which of the following is a lung disease marked by abnormally few but large alveoli?
A) Cor pulmonale
B) Pulmonary hemosiderosis
C) Emphysema
D) Atelectasis
E) Collapsed lung
D) Tuberculosis
In which condition are the lungs infected with Mycobacterium and produce fibrous nodules around the bacteria, leading to progressive pulmonary fibrosis?
A) Pneumonia
B) Dyspnea
C) Pneumothorax
D) Tuberculosis
E) Rhinitis
C) Adenocarcinoma
Which malignancy originates in the lamina propria of the bronchi?
A) Squamous-cell carcinoma
B) Oat-cell carcinoma
C) Adenocarcinoma
D) Pulmonary edema
E) Cor pulmonale
E) Ondine's curse
Automatic respiratory functions can be disabled by traumatic brain injury and result in which condition?
A) A Bohr effect
B) Adult respiratory distress syndrome
C) A pneumothorax
D) Atelectasis
E) Ondine's curse
D) Acute rhinitis
Which of these is most likely to result from contact between contaminated fingers and the nasal mucosa?
A) Apnea
B) Adult respiratory distress syndrome
C) Acute bronchitis
D) Acute rhinitis
E) Asthma
B) Oxygen toxicity
Scuba divers breathe a nitrogen-oxygen mixture rather than pure compressed oxygen in order to avoid what condition?
A) The bends
B) Oxygen toxicity
C) Rapture of the deep
D) Caisson disease
E) Hypoxemic hypoxia
A) decompression sickness
Nitrogen bubbles can form in the blood and other tissues when a scuba diver ascends too rapidly, producing a syndrome called __________.
A) decompression sickness
B) hyperbaric disease
C) cerebral embolism
D) pulmonary barotrauma
E) pulmonary edema
D) medulla oblongata
The vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves carry afferent signals from peripheral chemoreceptors to a chemosensitive area in the __________.
A) pontine respiratory group
B) dorsal respiratory group
C) ventral respiratory group
D) medulla oblongata
E) pons
E) goblet cells
Mucus plays an important role in cleansing inhaled air. It is produced by __________ of the respiratory tract.
A) squamous alveolar cells
B) great alveolar cells
C) the pleurae
D) ciliated cells
E) goblet cells
C) bicarbonate ions
The blood transports more CH3OCH3 in the form of __________ than in any other form.
A) carbaminohemoglobin
B) carboxyhemoglobin
C) bicarbonate ions
D) dissolved CH3OCH3 gas
E) bisphosphocarbonate
A) To aid in defecation and urination
Among its other purposes, how is the Valsalva maneuver used?
A) To aid in defecation and urination
B) As part of the procedure for giving CPR to a person in respiratory arrest
C) To ventilate the lungs during eupnea
D) To expel more than the usual tidal volume from the lungs
E) To clear carbon monoxide from the body and replace it with oxygen
C) Erythrocytes low in BPG do not unload O2 very well
Blood banks dispose of blood that has low levels of bisphosphoglycerate. What would be the probable reason for doing so?
A) A low BPG level causes acidosis of blood
B) Erythrocytes low in BPG do not unload CH3OCH3 very well
C) Erythrocytes low in BPG do not unload O2 very well
D) Erythrocytes low in BPG do not load O2 very well
E) A decline in BPG level is accompanied by a decline in hemoglobin level
C) 4,200
Your breathing rate is 12 breaths/minute; your tidal volume is 500 mL; your vital capacity is 4700 mL; and your dead air space is 150 mL. Your alveolar ventilation rate is __________ mL/min.
A) 2,400
B) 3,600
C) 4,200
D) 5,600
E) 6,400
D) 4,700
Your breathing rate is 14 breaths/minute; spirometric measurements reveal your tidal volume is 500 mL; your inspiratory reserve volume is 3000 mL; and your expiratory reserve volume is 1,200 mL. Your vital capacity is __________ mL.
A) 2,400
B) 3,000
C) 3,800
D) 4,700
E) 5,800
False
T/F: The maximum amount of air the lungs can contain is known as inspiratory capacity.
False
T/F: Respiratory arrest is an irreversible condition.
True
T/F: The pleurae and pleural fluid help prevent the spread of pulmonary infection to the pericardium.
False
T/F: Breathing is controlled solely by the medulla oblongata and pons.
False
T/F: The rate of oxygen diffusion is affected by the pressure gradient of carbon dioxide.
True
T/F: Gas transport is the process of carrying gases from the alveoli to the systemic tissues and vice versa.
False
T/F: According to the Bohr effect, a low level of oxyhemoglobin enables the blood to transport more CH3OCH3.
True
T/F: Erythrocytes do not carry out aerobic respiration; thus, they do not consume any of the oxygen they are transporting.
False
T/F: Hemoglobin releases the same amount of oxygen to all the tissues regardless of variations in their metabolic rate.
B) spinal integration centers
Output from higher brain centers can bypass both the DRG and VRG and go directly to __________, which controls the accessory muscles of respiration.
A) the diaphragm
B) spinal integration centers
C) the cerebral cortex
D) the vagus nerve
E) the cerebellum
A) DRG
Which of the following issues output to the VRG to adjust the respiratory rhythm?
A) DRG
B) PRG
C) NRG
D) SRG
E) QRG
C) VRG
Which center bears the primary responsibility for generating the respiratory rhythm, but is influenced by several other centers?
A) PRG
B) DRG
C) VRG
D) SRG
E) TRG
D) Central chemoreceptors
The pH of the cerebrospinal fluid is monitored by which of these brainstem centers?
A) PRG
B) Hypothalamic osmoreceptors
C) Medullary baroreceptors
D) Central chemoreceptors
E) Hypothalamic thermoreceptors
B) PRG
Emotional states are integrated by the ___________, which generates an output that creates such respiratory variations as laughing and crying.
A) VRG
B) PRG
C) DRG
D) SRG
E) TRG
A) Nares → Vestibule → Nasal Cavity → Nasopharynx → Oropharynx → Laryngopharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Primary Bronchus → Secondary Bronchus → Tertiary Bronchus → Bronchiole → Terminal Bronchiole → Respiratory Bronchiole → Alveolar Duct → Alveolar Sac → Alveolus
If one inspires through their nose, which of the following answers has the correct order of structures the air would move through?
A) Nares → Vestibule → Nasal Cavity → Nasopharynx → Oropharynx → Laryngopharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Primary Bronchus → Secondary Bronchus → Tertiary Bronchus → Bronchiole → Terminal Bronchiole → Respiratory Bronchiole → Alveolar Duct → Alveolar Sac → Alveolus
B) Nares → Nasal Cavity → Vestibule → Nasopharynx → Oropharynx → Laryngopharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Primary Bronchus → Secondary Bronchus → Tertiary Bronchus → Bronchiole → Terminal Bronchiole → Respiratory Bronchiole → Alveolar Duct → Alveolar Sac → Alveolus
C) Nares → Vestibule → Nasal Cavity → Nasopharynx → Oropharynx → Laryngopharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Bronchiole → Respiratory Bronchiole → Terminal Bronchiole → Primary Bronchus → Secondary Bronchus → Tertiary Bronchus → Alveolar Duct → Alveolar Sac → Alveolus
D) Nares → Nasal Cavity → Vestibule → Nasopharynx → Oropharynx → Laryngopharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Primary Bronchus → Secondary Bronchus → Tertiary Bronchus → Bronchiole → Respiratory Bronchiole → Terminal Bronchiole → Alveolar Duct → Alveolar Sac → Alveolus
E) Nares → Nasal Sinuses → Laryngopharynx → Nasopharynx → Trachea → Larynx → Primary Bronchus → Secondary Bronchus → Tertiary Bronchus → Bronchiole → Terminal Bronchiole → Respiratory Bronchiole → Alveolar Sac → Alveolar Duct → Alveolus
C) Anatomical dead space
Upon inspiration, what is the name of the air in the conducting zone that is not available for gas exchange?
A) Alveolar dead space
B) Tracheal dead space
C) Anatomical dead space
D) Conducting dead space
E) Metabolic dead space
B) After swerving to narrowly avoid an accident while driving
The anatomical dead space is greatest in which of the following situations?
A) After eating a large meal
B) After swerving to narrowly avoid an accident while driving
C) After waking up from a long nap
D) After watching TV for an hour
E) While sleeping
C) 0.3 mmHg
Air consists of about 78.6% nitrogen, 20.9% oxygen, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and 0.5% water. At sea level, (760 mmHg) what is the PCO2?
A) 597 mmHg
B) 159 mmHg
C) 0.3 mmHg
D) 3.7 mmHg
E) 37 mmHg
D) Dalton's
Which law states that the total atmospheric pressure is a sum of the contributions of the individual gases?
A) Henry's
B) Charles's
C) Boyle's
D) Dalton's
E) Newton's
D) Alveolar air has a higher water vapor content than inspired air
How is alveolar air different than inspired air?
A) Alveolar air has a higher PN2 than inspired air
B) Alveolar air has a lower PCO2 than inspired air
C) Alveolar air has a higher PO2 than inspired air
D) Alveolar air has a higher water vapor content than inspired air
E) Alveolar air is always colder than inspired air
B) ↓ PO2, ↑ PCO2, ↑ temperature, ↑ BPG
Which of the following sets of conditions would shift the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the right?
A) ↑ PO2, ↓ PCO2, ↑ temperature, ↑ BPG
B) ↓ PO2, ↑ PCO2, ↑ temperature, ↑ BPG
C) ↓ PO2, ↑ PCO2, ↓ temperature, ↑ BPG
D) ↑ PO2, ↓ PCO2, ↑ temperature, ↓ BPG
E) ↑ PO2, ↓ PCO2, ↓ temperature, ↓ BPG
A) Shift it right
Conditions around metabolically active tissues do what to the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
A) Shift it right
B) Shift it left
C) Decrease the slope
D) Increase the slope
E) They do not affect it
B) Hypoventilation due to alkalosis
Hypocapnia will lead to which of the following conditions?
A) Hypoventilation due to acidosis
B) Hypoventilation due to alkalosis
C) Hyperventilation due to acidosis
D) Hyperventilation due to alkalosis
E) Hypocapnia does not affect ventilation rate
D) Small-cell carcinoma
What is the least common but most dangerous form of lung cancer?
A) Mesothelioma
B) Adenocarcinoma
C) Squamous cell carcinoma
D) Small-cell carcinoma
E) Basal cell carcinoma
False
T/F: After the terminal bronchi air enters the alveoli next.
False
T/F: The serratus anterior is active in eupnea.
True
T/F: The expansion of the lungs during inspiration generates a pressure gradient causing air to flow into the lungs. This is an example of Boyle's law.
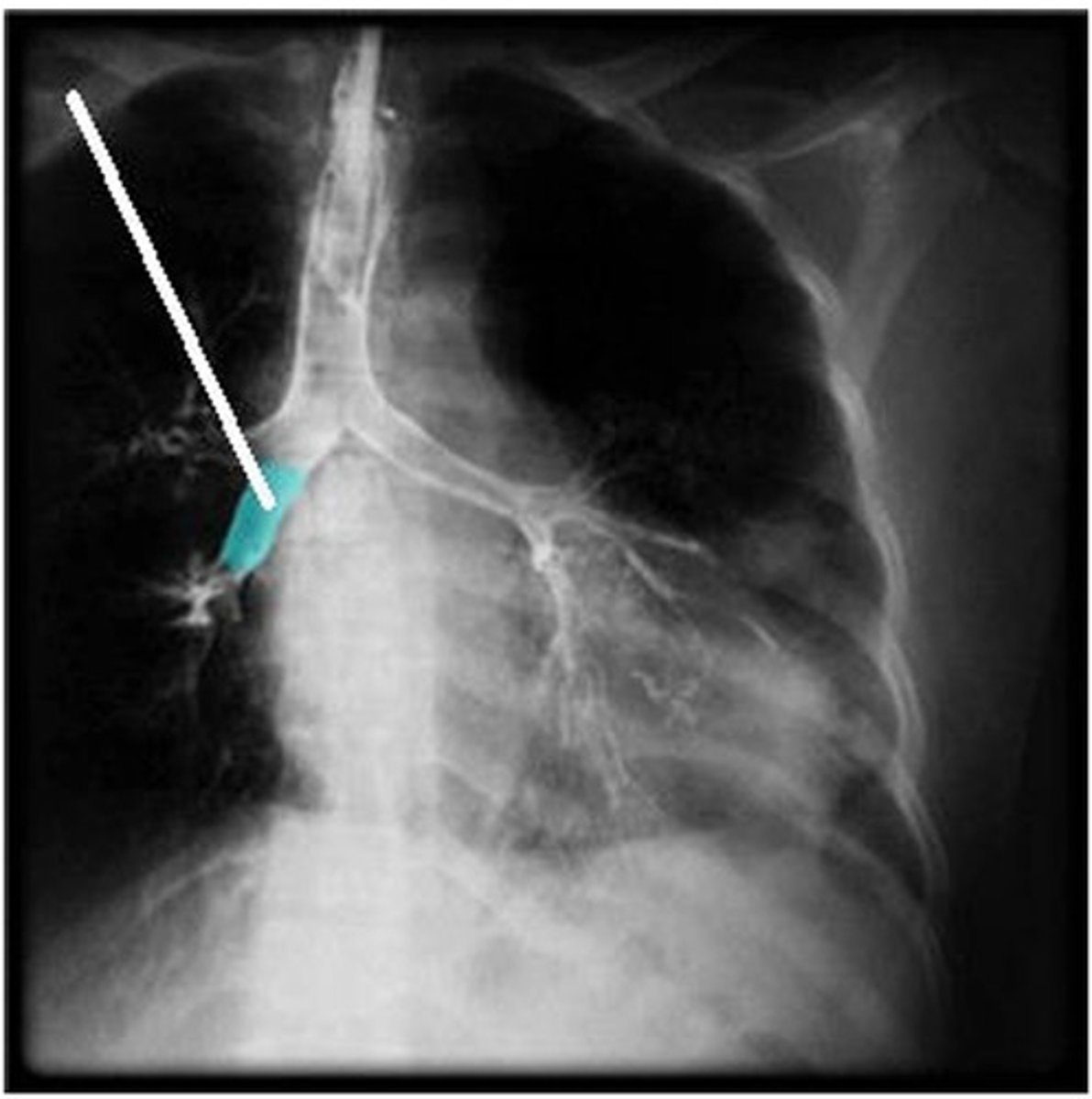
D) intermediate bronchus
Which structure is highlighted (reference leader line)?
A) left lobar bronchus
B) left segmental bronchus
C) right segmental bronchus
D) intermediate bronchus
E) right lobar bronchus
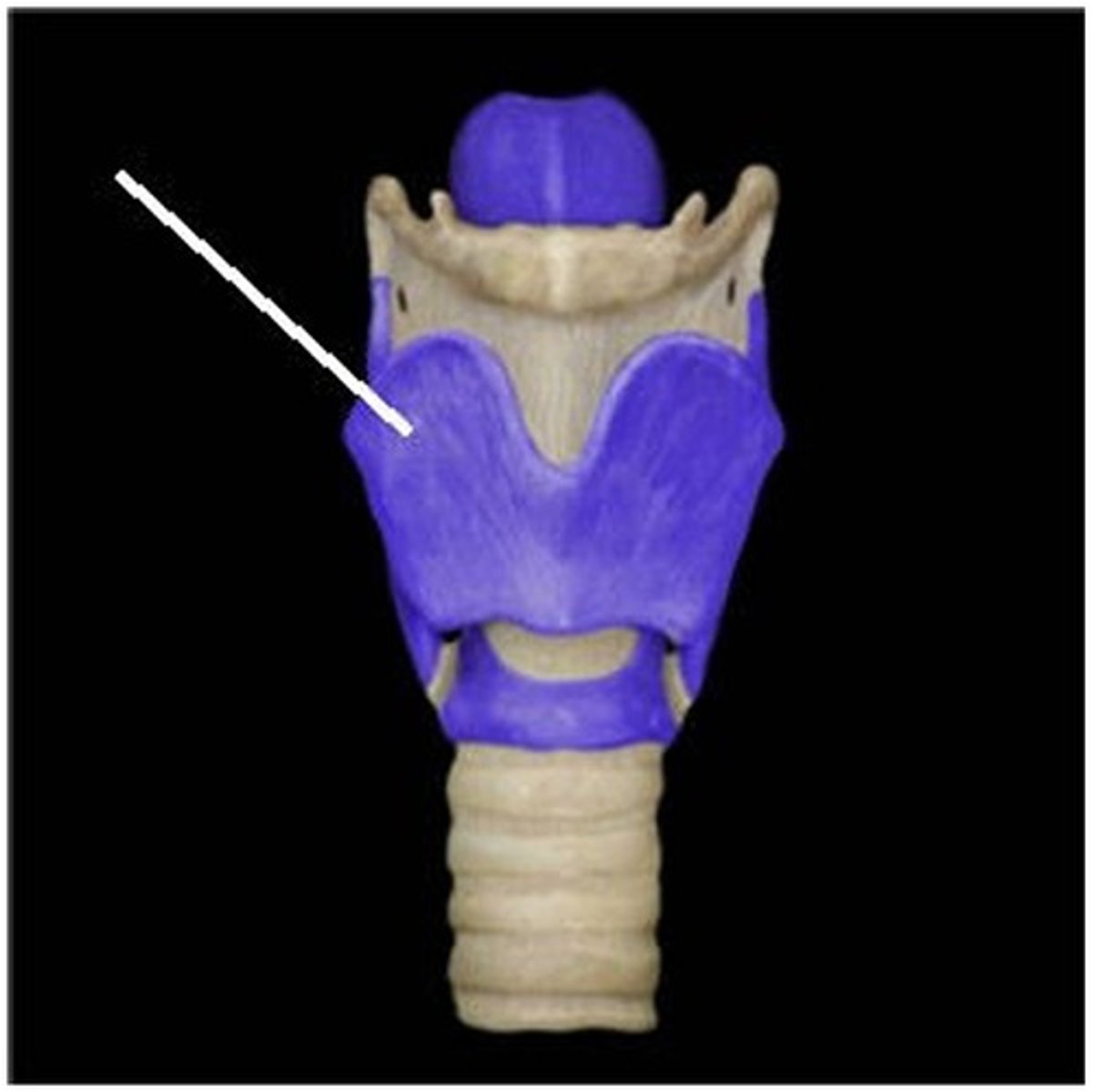
A) laryngeal cartilages
Which structure is highlighted (reference leader line)?
A) laryngeal cartilages
B) hyoid bone
C) thyrohyoid ligament
D) tracheal cartilages
E) cricothyroid ligament
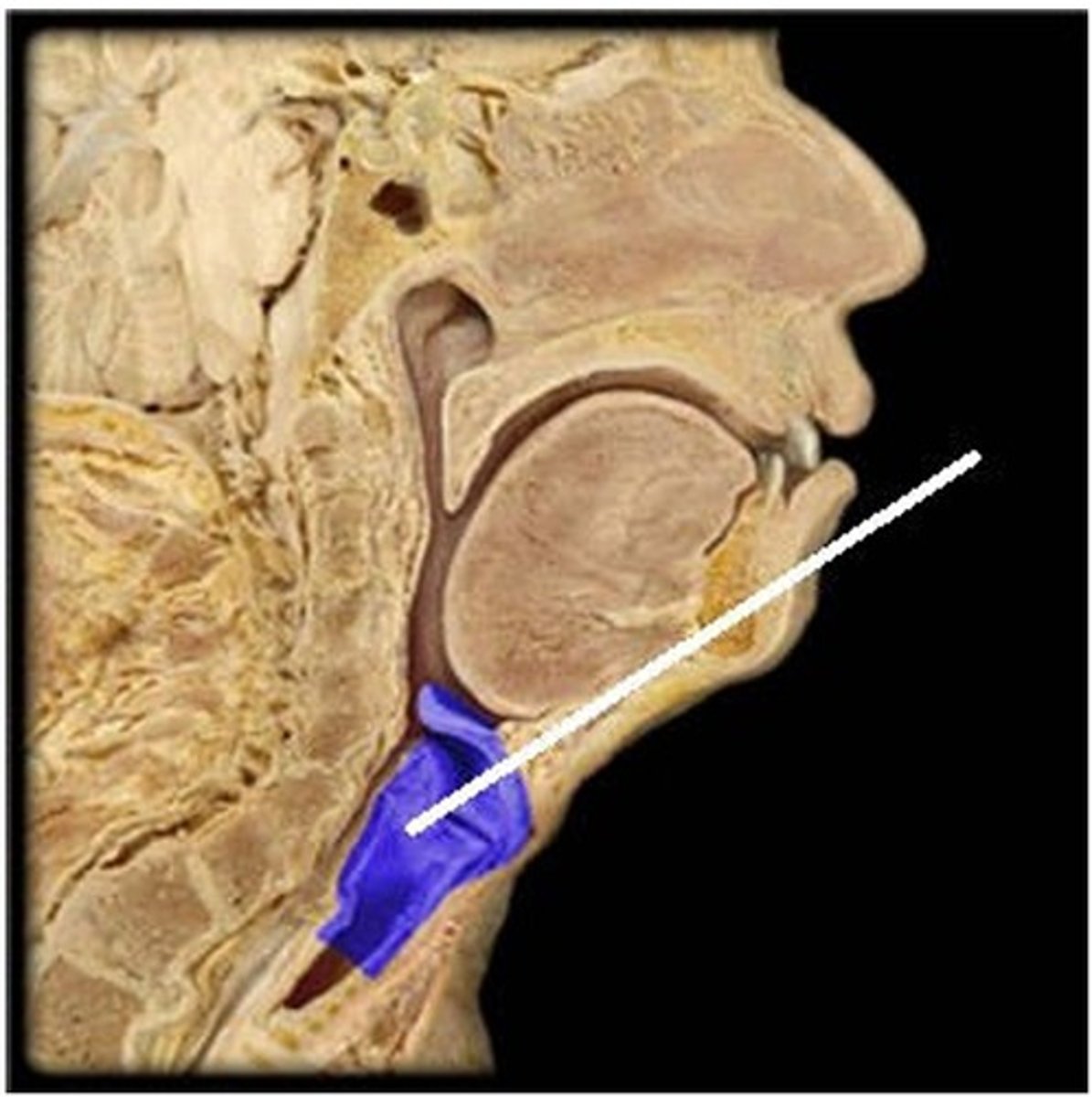
E) larynx
Which structure is highlighted (reference leader line)?
A) primary bronchus
B) nasal concha
C) esophagus
D) pharynx
E) larynx
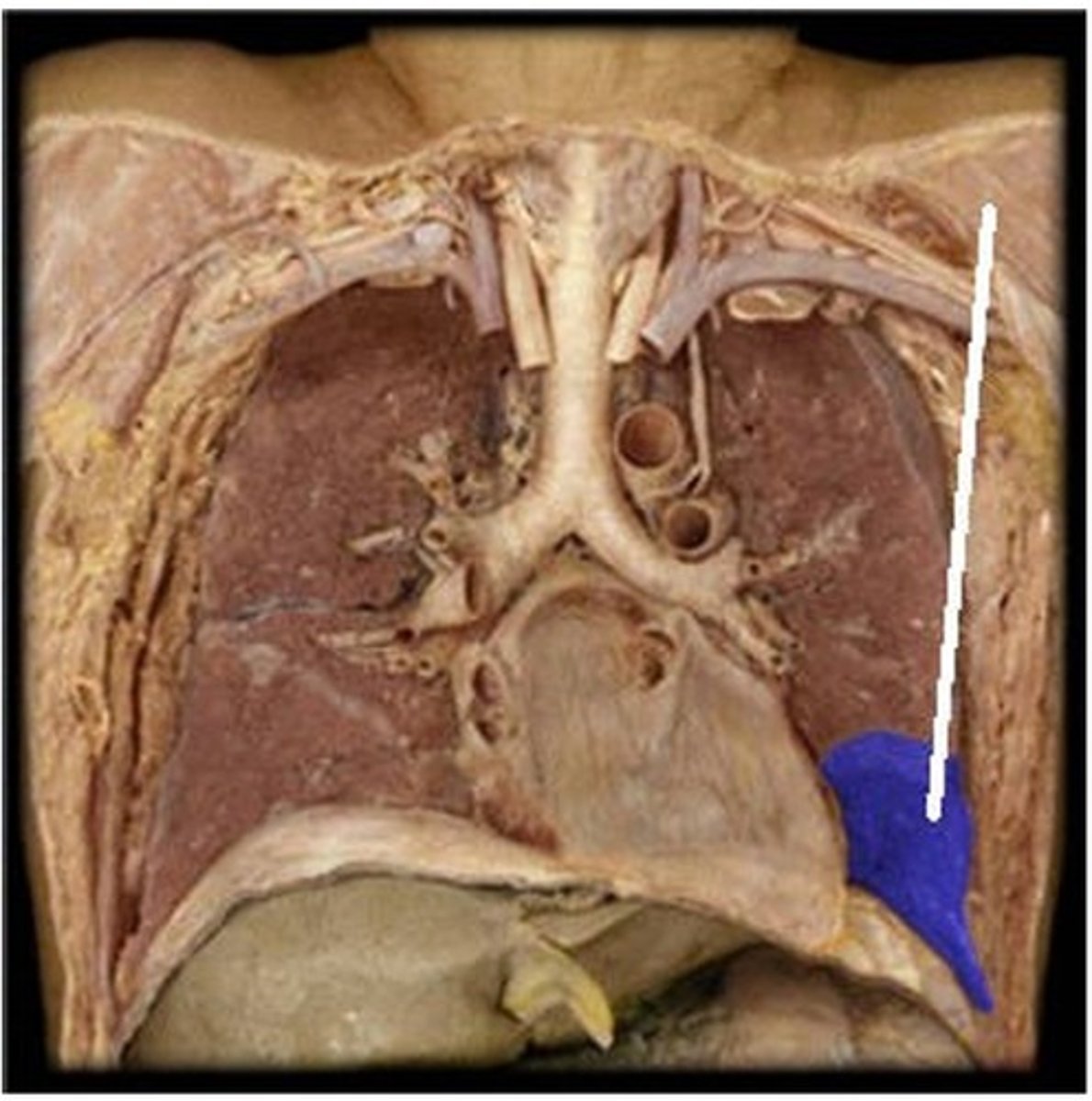
E) lower lobe of left lung
Which structure is highlighted (reference leader line)?
A) upper lobe of left lung
B) lower lobe of right lung
C) upper lobe of right lung
D) middle lobe of right lung
E) lower lobe of left lung
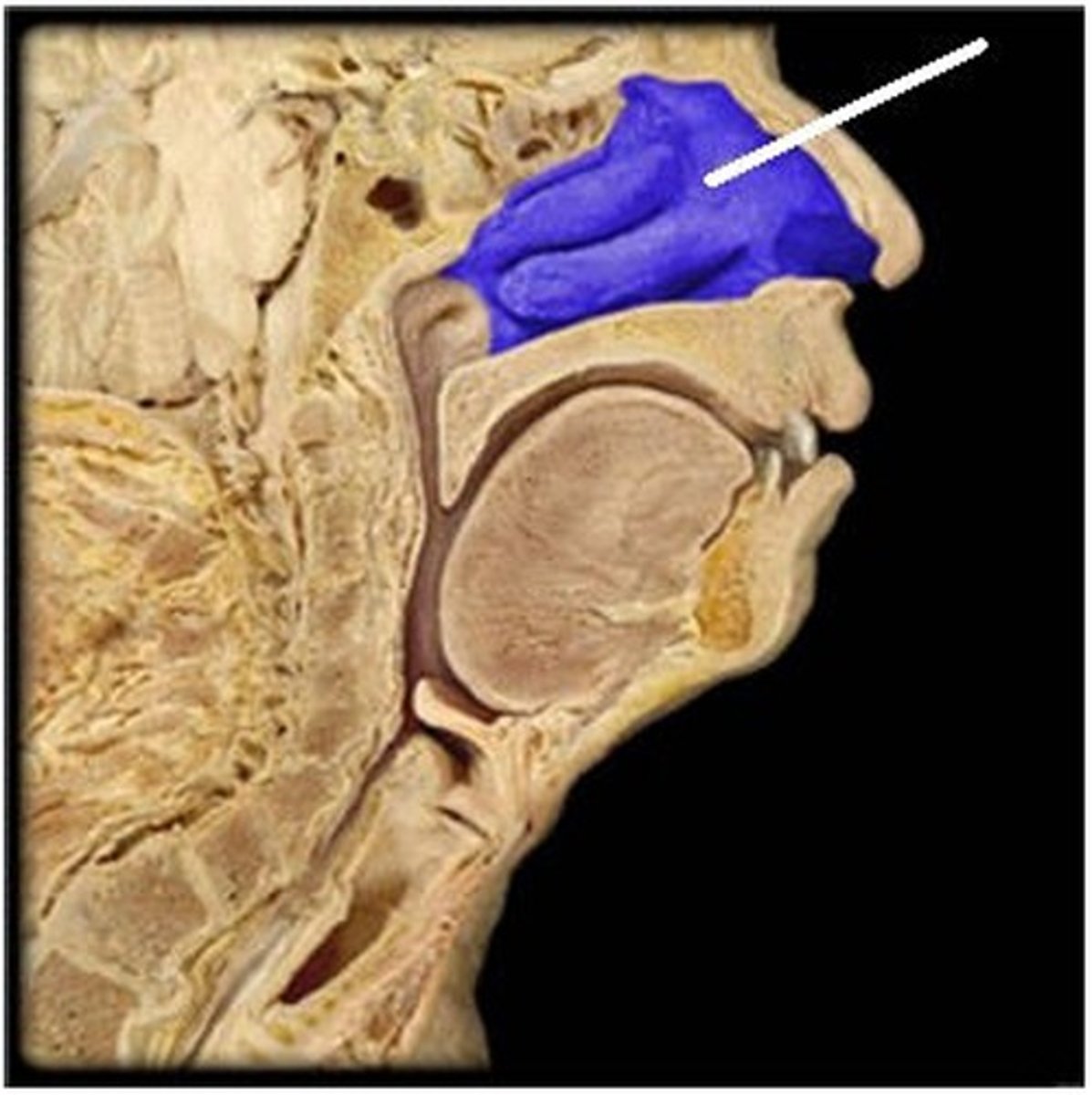
E) nasal cavity
Which structure is highlighted (reference leader line)?
A) soft palate
B) oropharynx
C) uvula
D) hard palate
E) nasal cavity
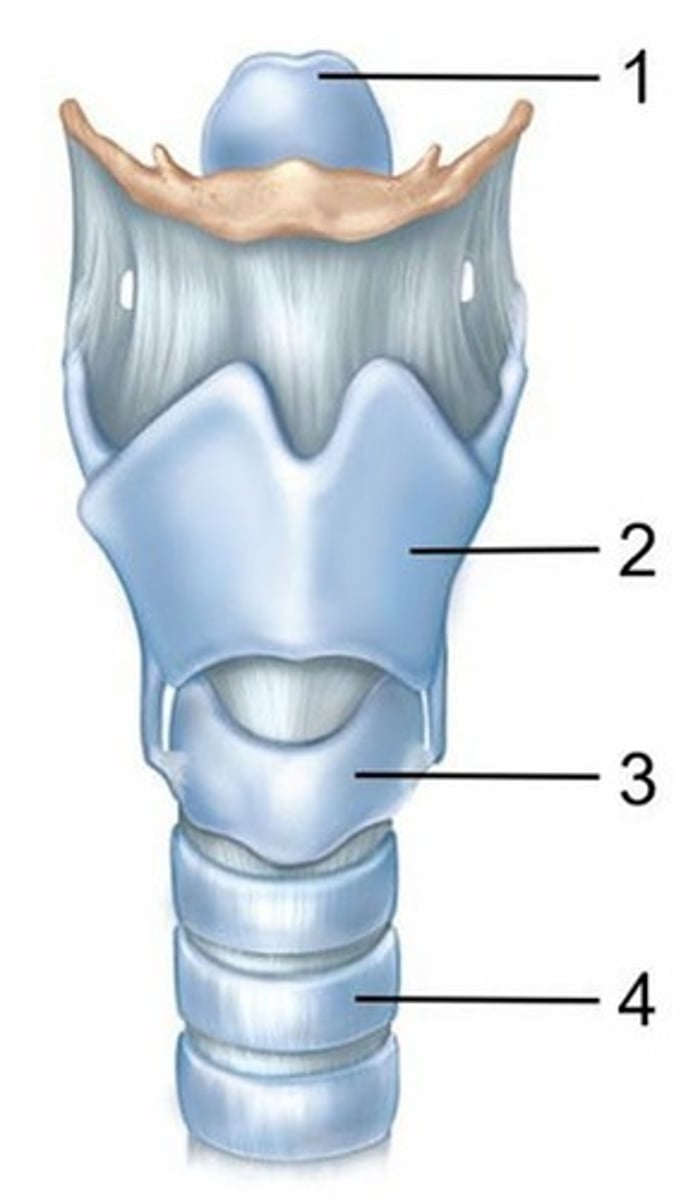
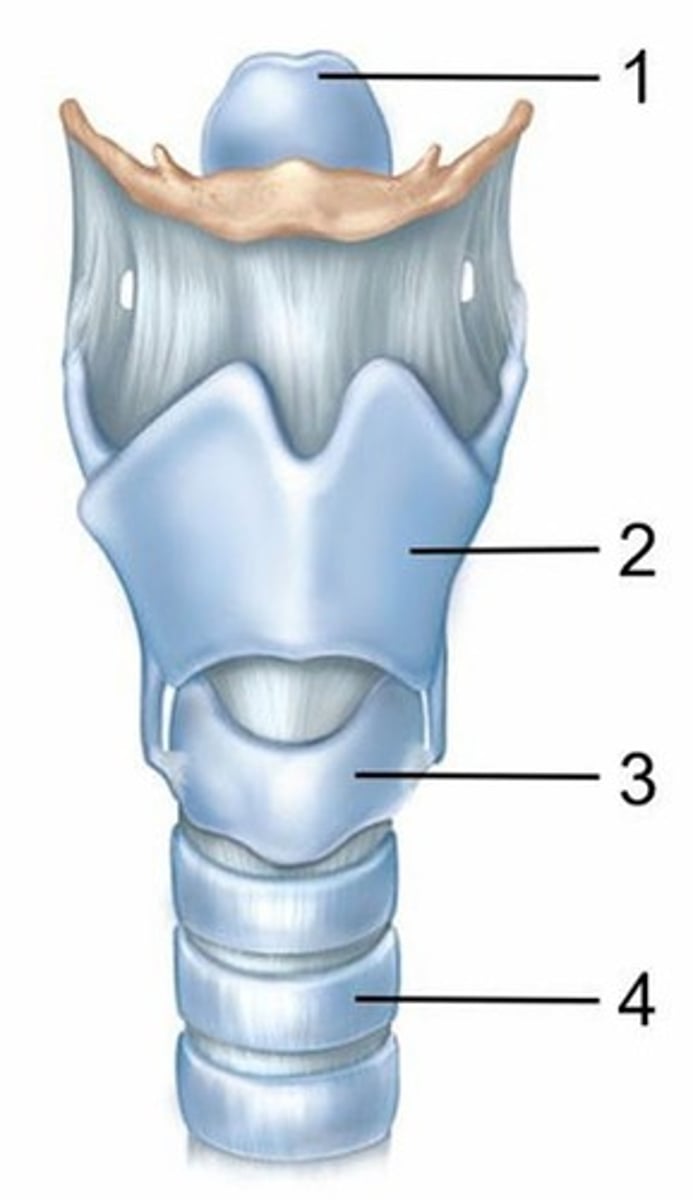
A) Epiglottic cartilage
Name the cartilage labeled 1.
A) Epiglottic cartilage
B) Thyroid cartilage
C) Cricoid cartilage
D) Tracheal cartilage
E) Arytenoid cartilage
B) Thyroid cartilage
Name the cartilage labeled 2.
A) Epiglottic cartilage
B) Thyroid cartilage
C) Cricoid cartilage
D) Tracheal cartilage
E) Arytenoid cartilage
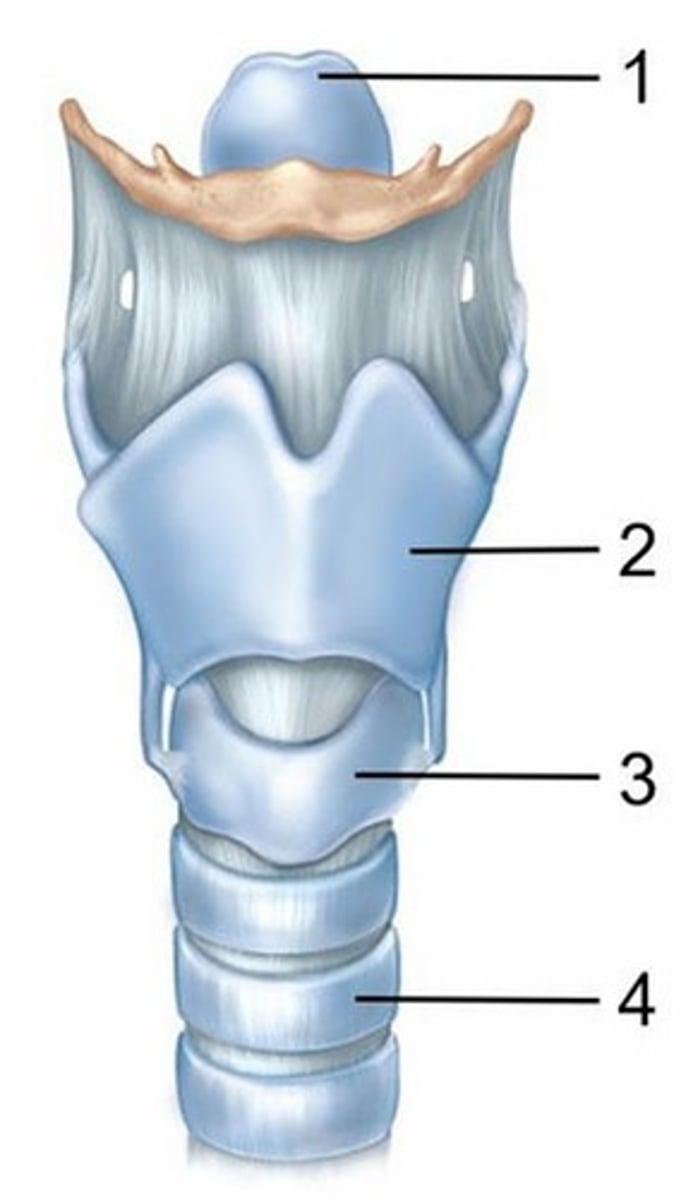
C) Cricoid cartilage
Name the cartilage labeled 3.
A) Epiglottic cartilage
B) Thyroid cartilage
C) Cricoid cartilage
D) Tracheal cartilage
E) Arytenoid cartilage
A) Thyroid cartilage
Which structure is labeled 1?
A) Thyroid cartilage
B) Cricoid cartilage
C) Larynx
D) Trachea
E) Arytenoid cartilage
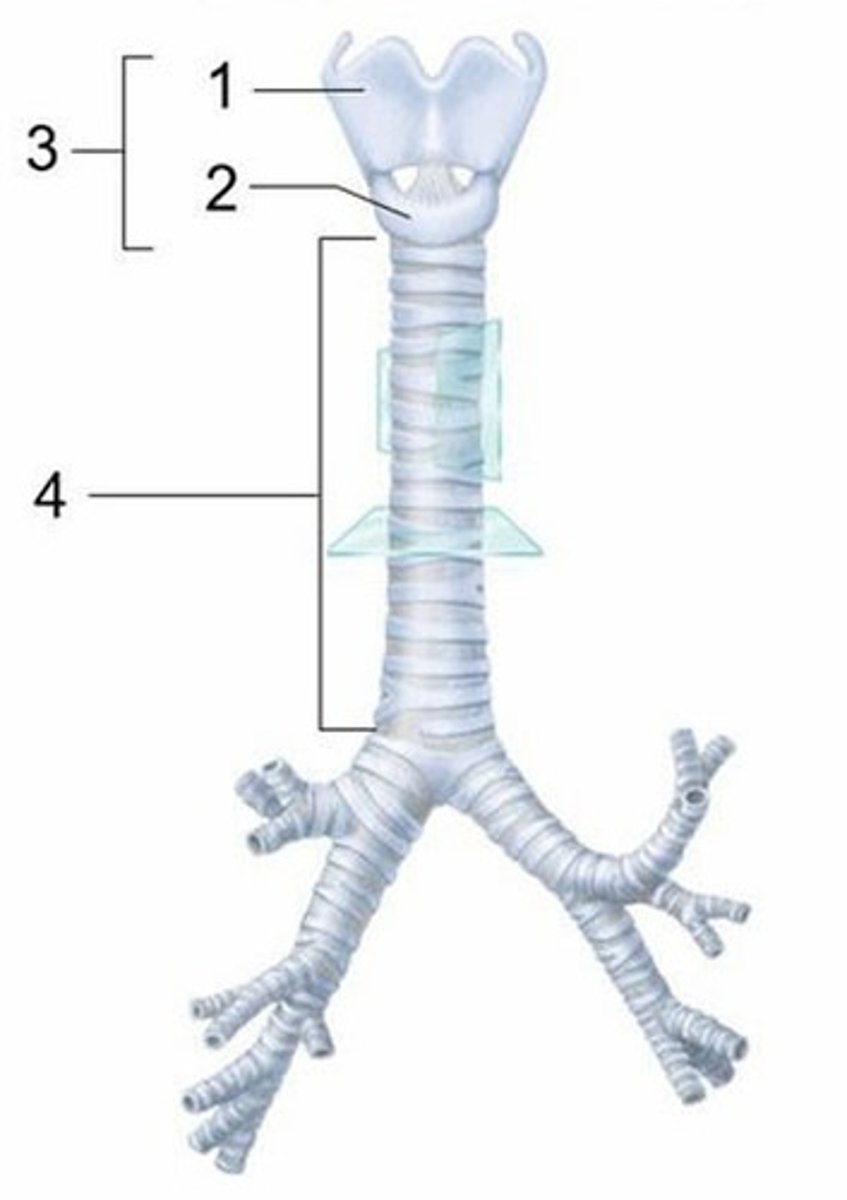
B) Cricoid cartilage
Which structure is labeled 2?
A) Thyroid cartilage
B) Cricoid cartilage
C) Larynx
D) Trachea
E) Arytenoid cartilage
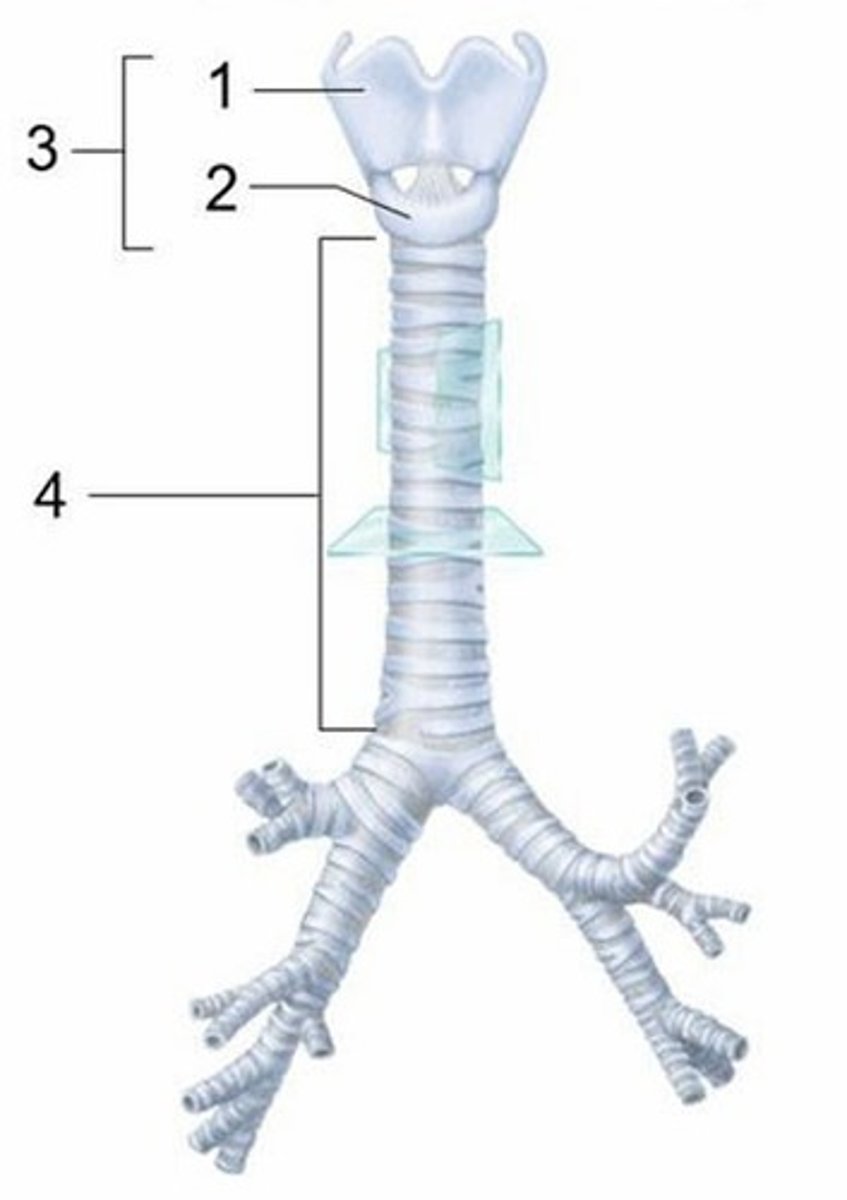
C) Larynx
Which structure is labeled 3?
A) Thyroid cartilage
B) Cricoid cartilage
C) Larynx
D) Trachea
E) Arytenoid cartilage
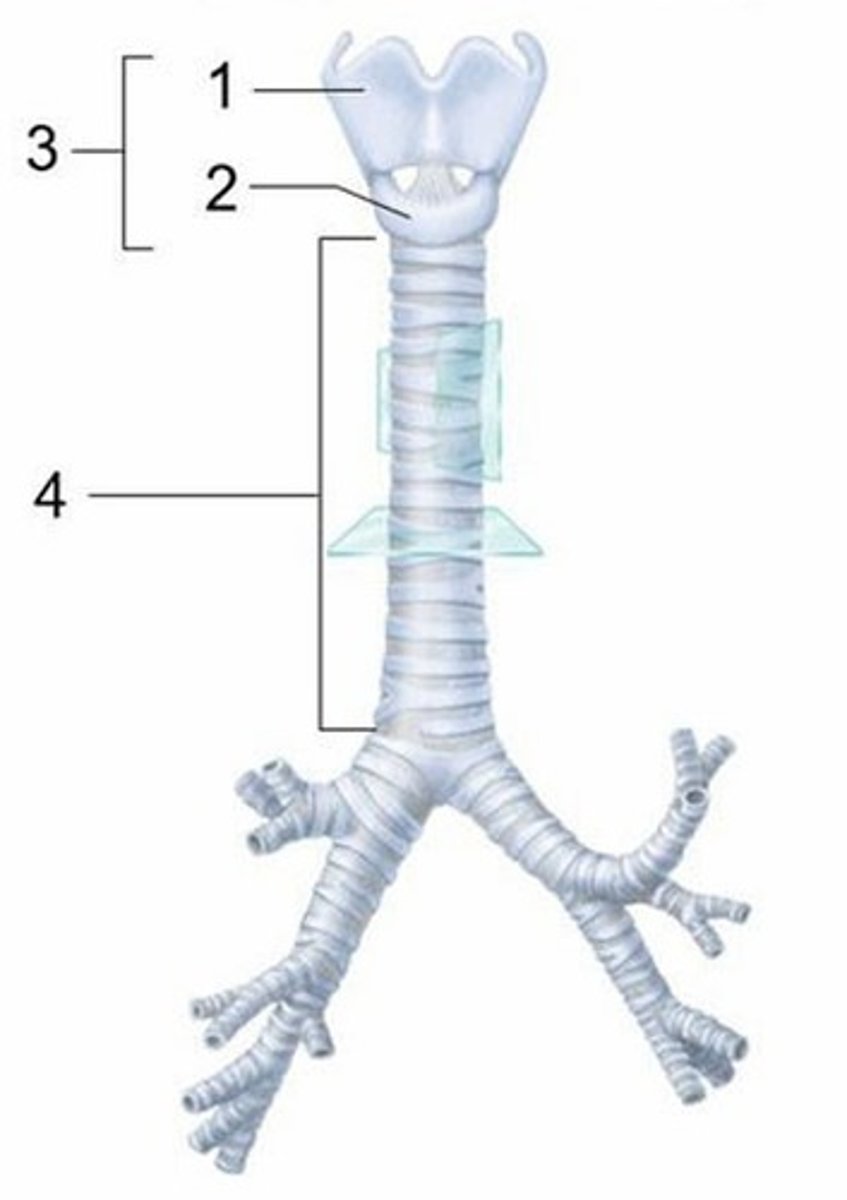
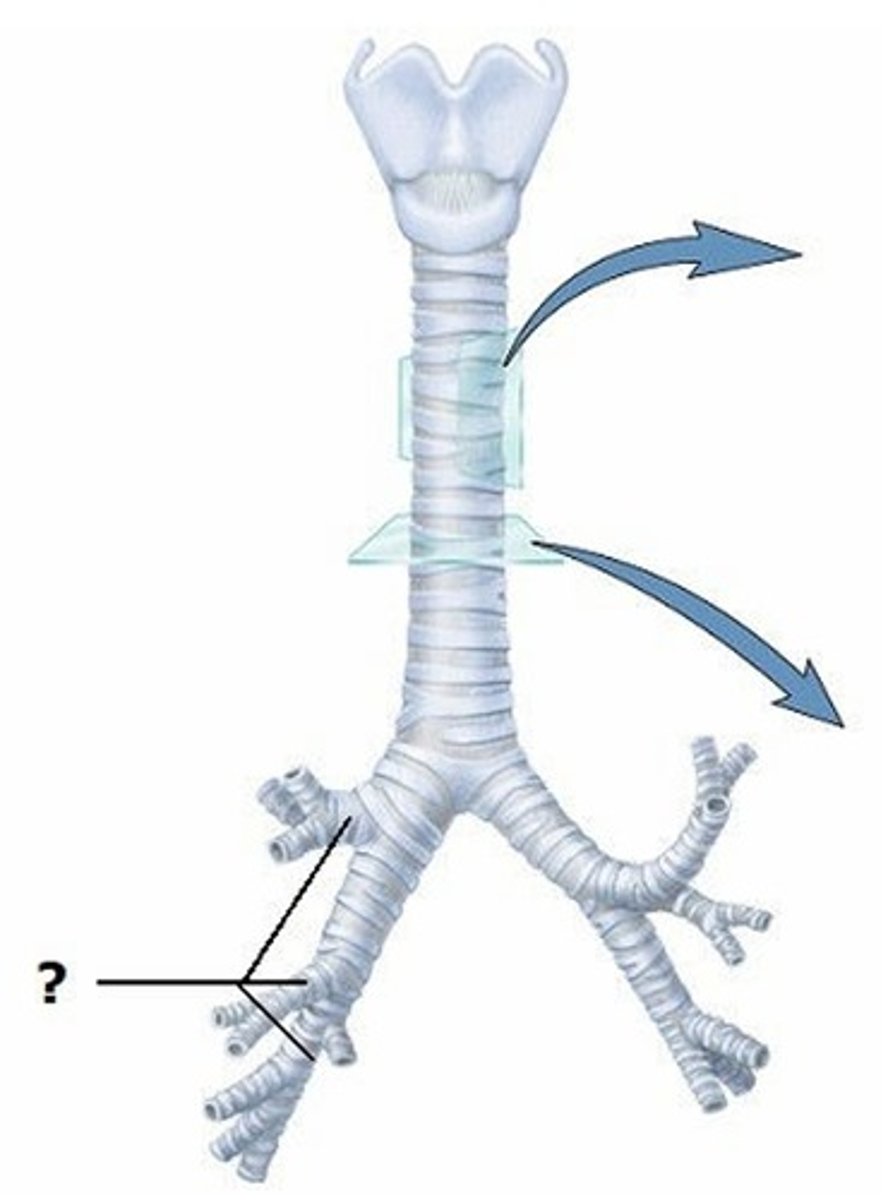
C) Lobar bronchi
What is indicated in this figure?
A) Trachea
B) Main bronchi
C) Lobar bronchi
D) Segmental bronchi
E) Respiratory bronchioles
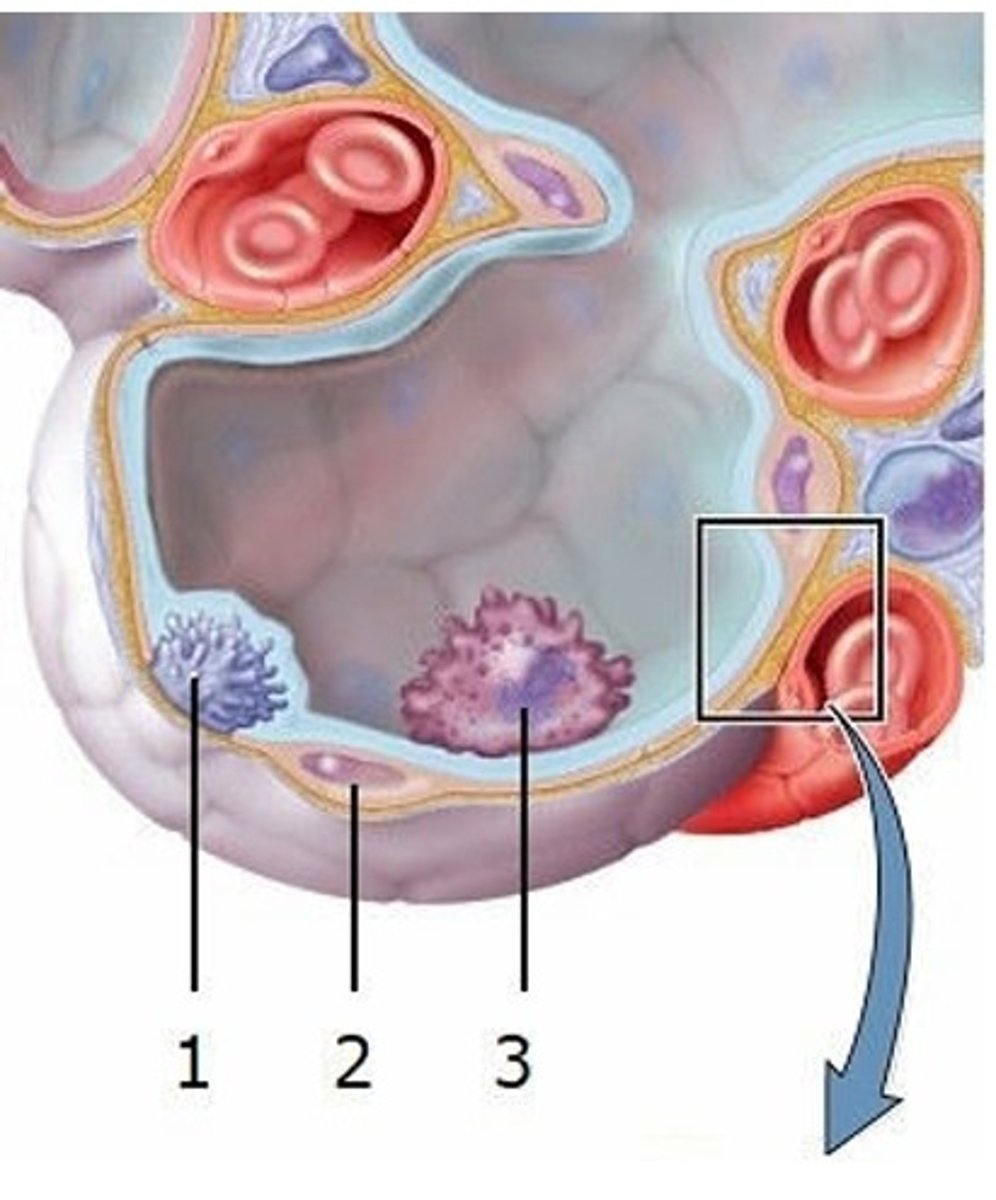
A) They secrete of pulmonary surfactant
What is the function of the cell labeled 1?
A) They secrete of pulmonary surfactant
B) They form part of the respiratory membrane
C) They phagocytose dust particles
D) They carry oxygen and carbon dioxide
E) They secrete enzymes necessary for the production of bicarbonate
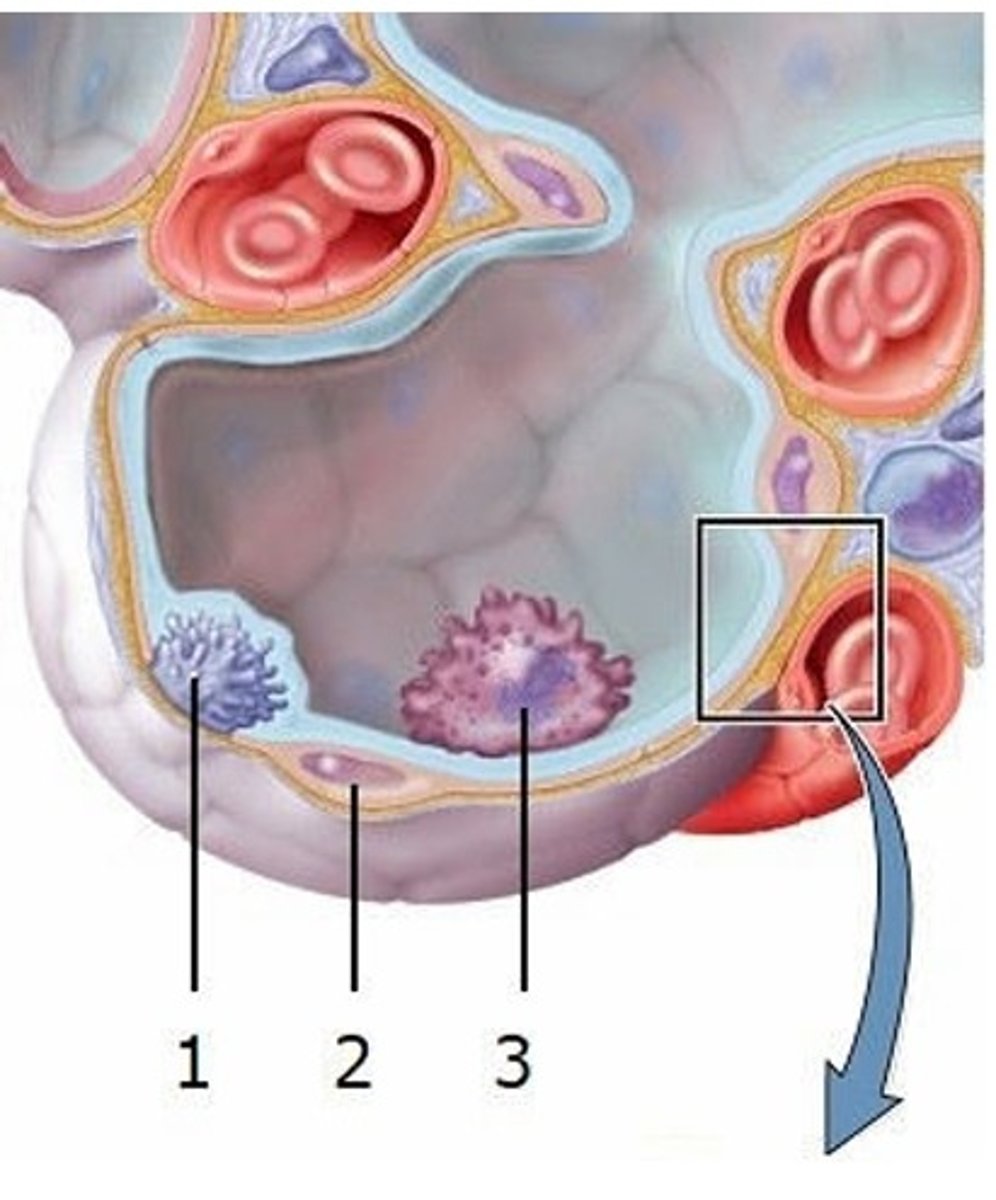
A) Great alveolar cell
What type of cell is labeled 1?
A) Great alveolar cell
B) Alveolar macrophage
C) Squamous alveolar cell
D) Lymphocyte
E) Erythrocyte
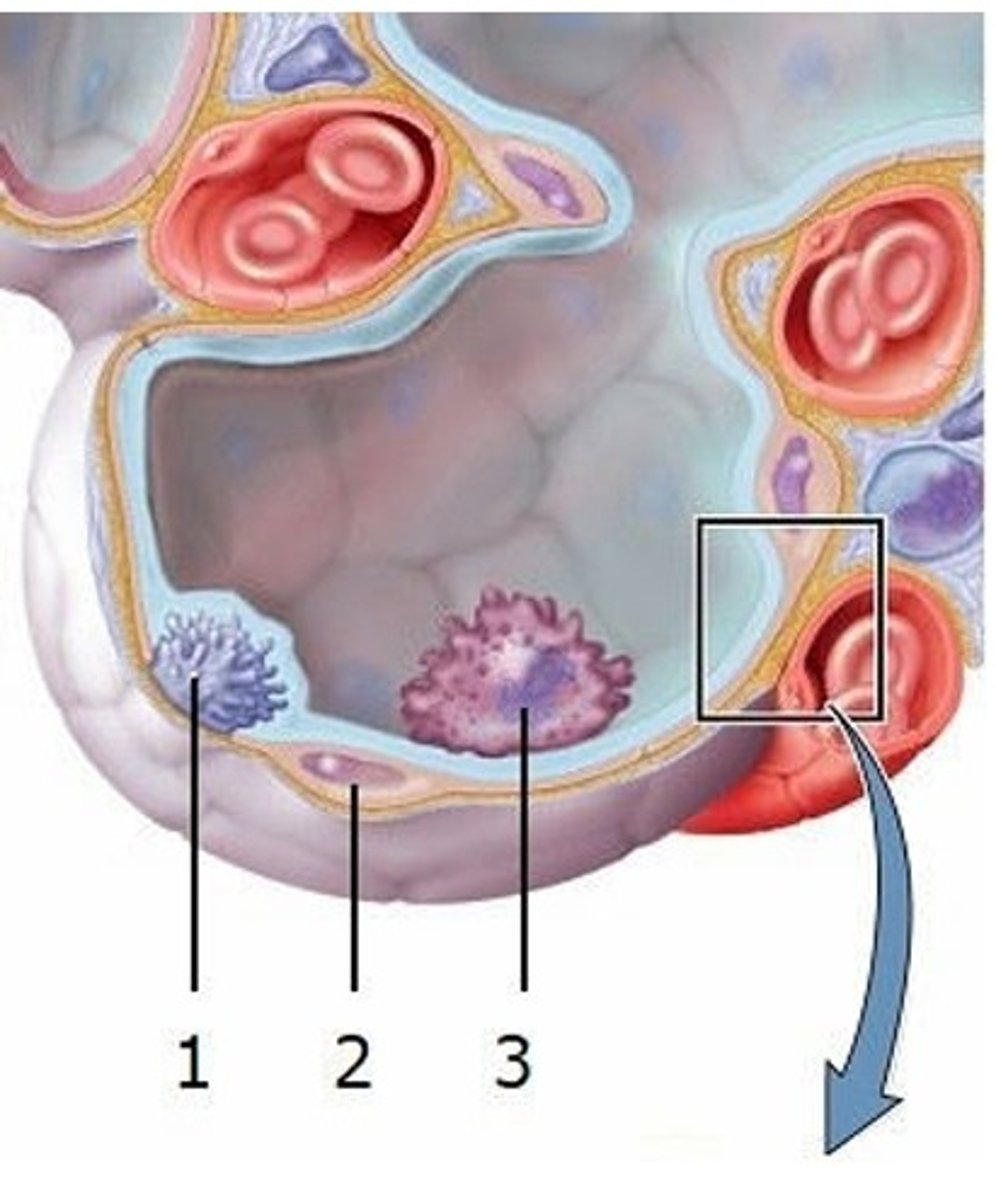
B) Alveolar macrophage
What type of cell is labeled 3?
A) Great alveolar cell
B) Alveolar macrophage
C) Squamous alveolar cell
D) Lymphocyte
E) Erythrocyte
A) Sternocleidomastoid
This diagram shows some of the muscles that are active during inhalation. Which muscle is labeled 1?
A) Sternocleidomastoid
B) Scalenes
C) External intercostals
D) Internal intercostals
E) Diaphragm
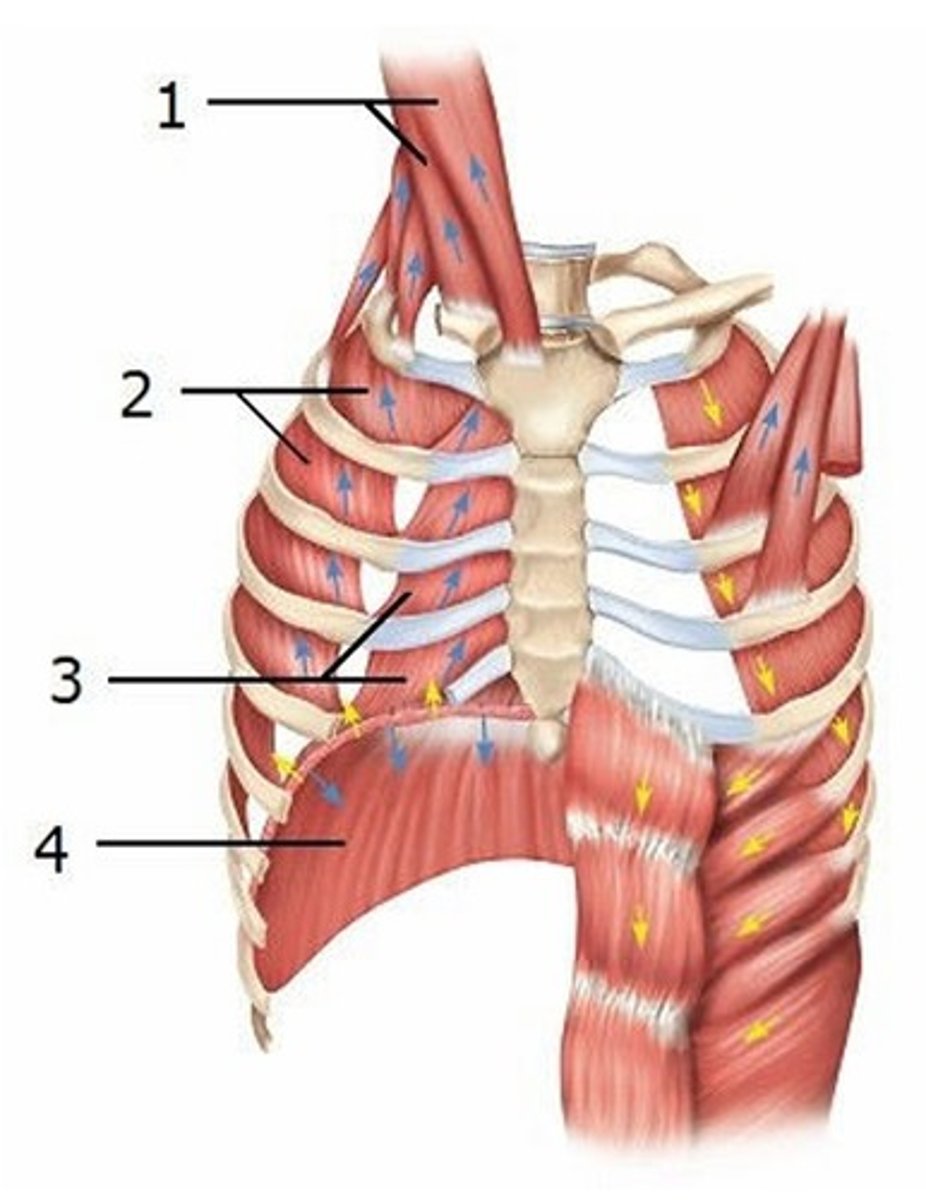
D) Internal intercostals
This diagram shows some of the muscles that are active during inhalation. Which muscle is labeled 3?
A) Sternocleidomastoid
B) Scalenes
C) External intercostals
D) Internal intercostals
E) Diaphragm
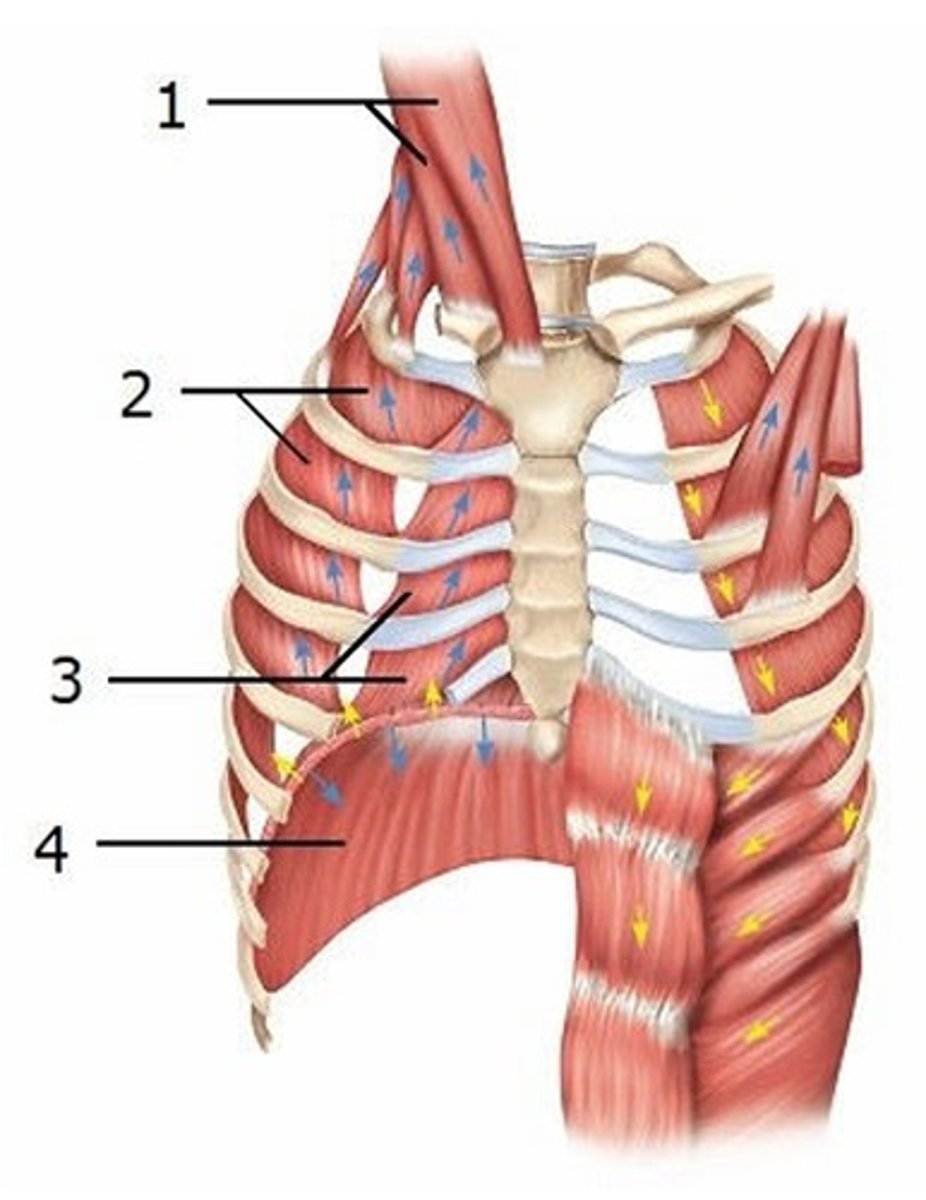
A) 2 and 4
Which two of the muscles labeled on this diagram are the principal respiratory muscles of inspiration? (The other two act as synergists and are considered accessory.)
A) 2 and 4
B) 1 and 4
C) 3 and 4
D) 2 and 3
E) 1 and 3
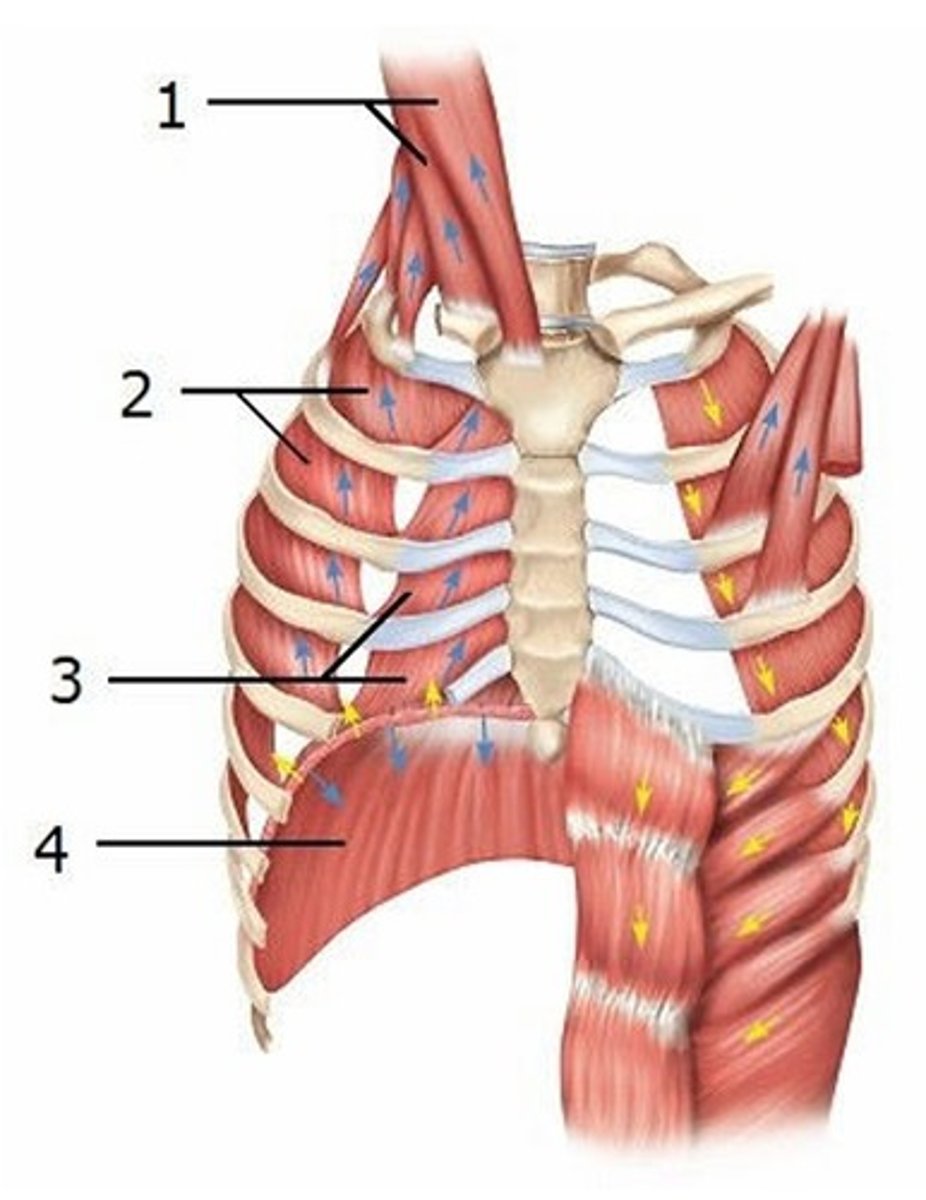
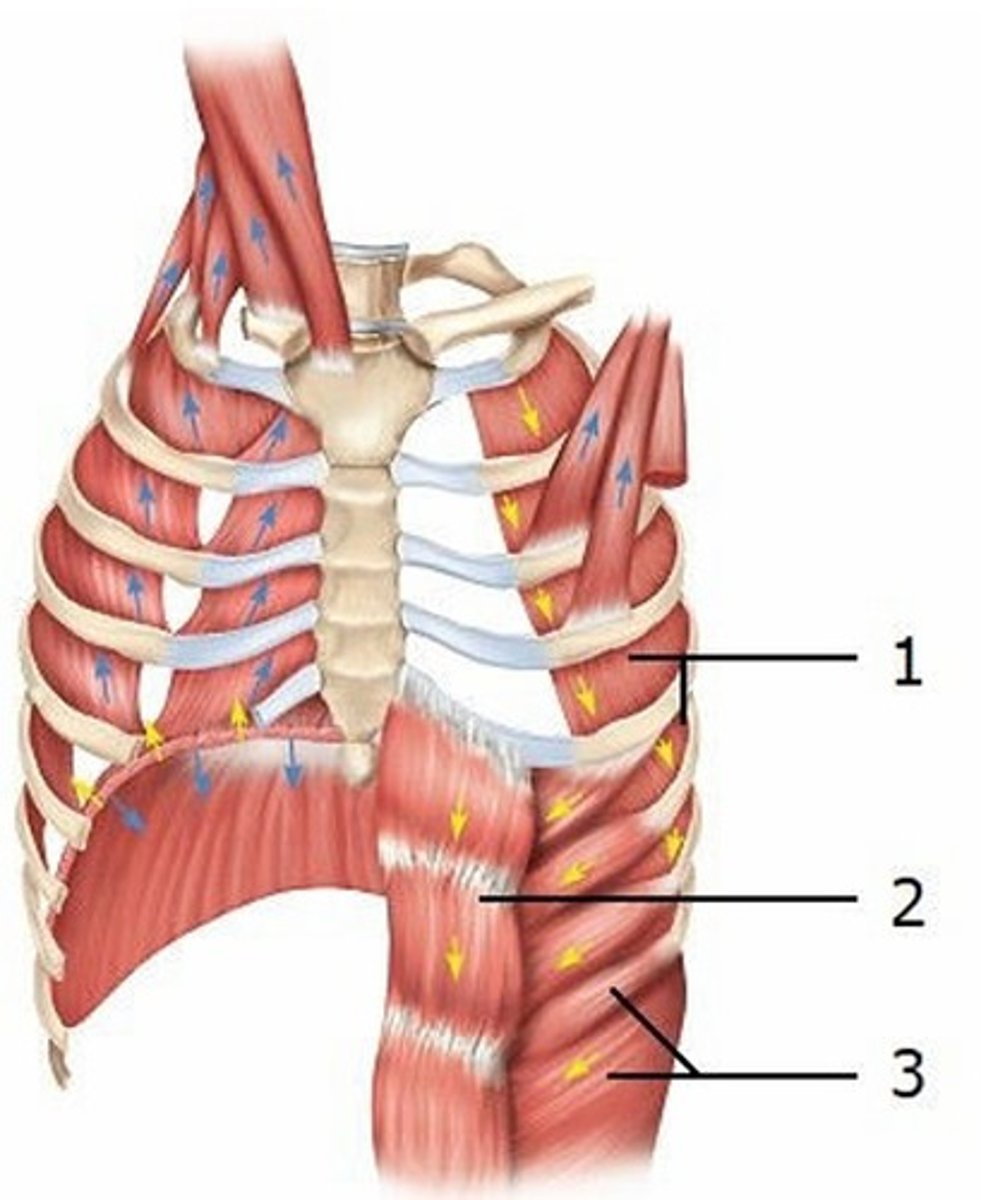
A) Internal intercostals, interosseous part
This diagram shows some of the muscles that are active during exhalation. Which muscle is labeled 1?
A) Internal intercostals, interosseous part
B) Internal intercostals, intercartilaginous part
C) External intercostals
D) Internal abdominal oblique
E) External abdominal oblique
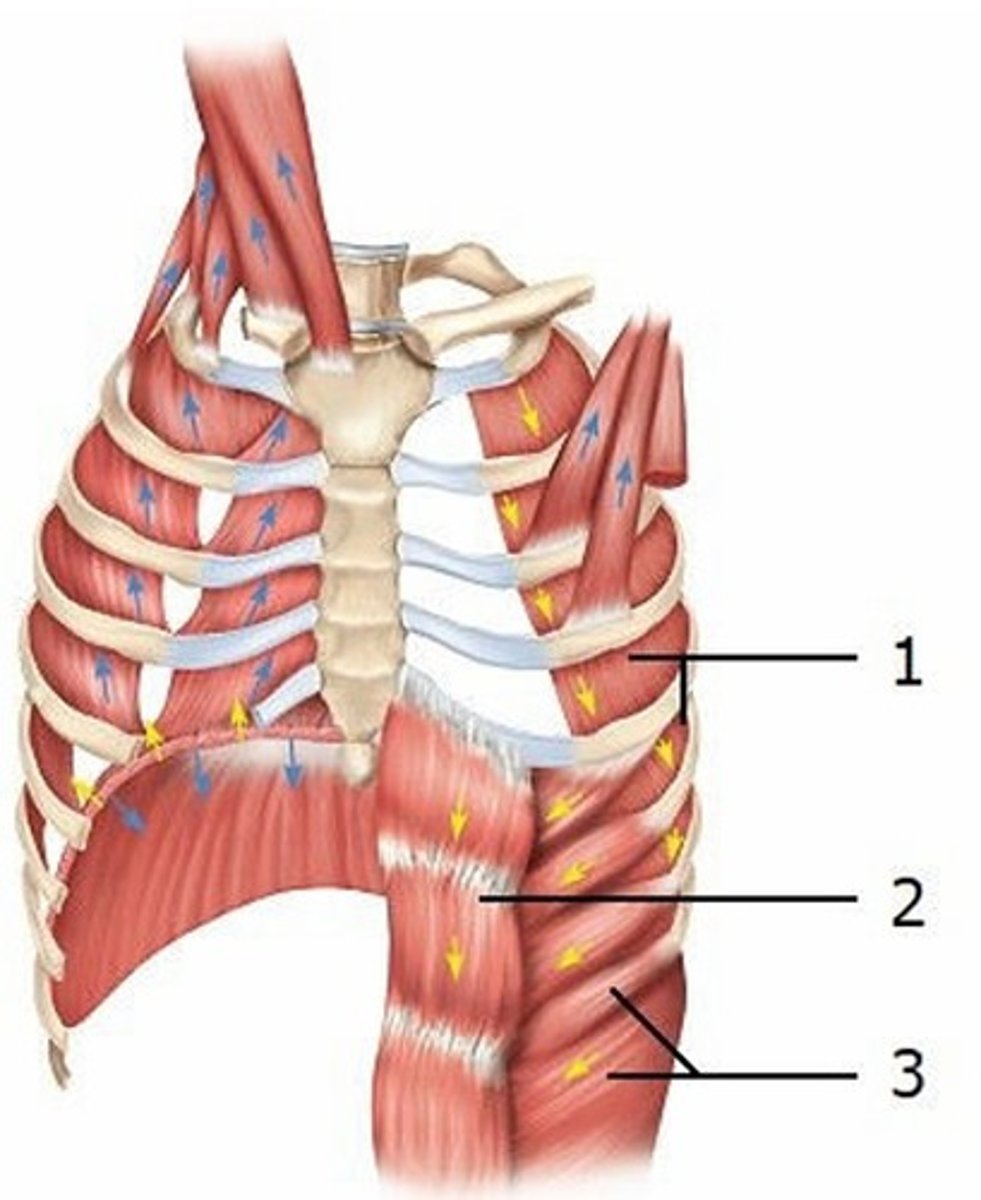
E) External abdominal oblique
This diagram shows some of the muscles that are active during exhalation. Which muscle is labeled 3?
A) Internal intercostals, interosseous part
B) Internal intercostals, intercartilaginous part
C) External intercostals
D) Internal abdominal oblique
E) External abdominal oblique
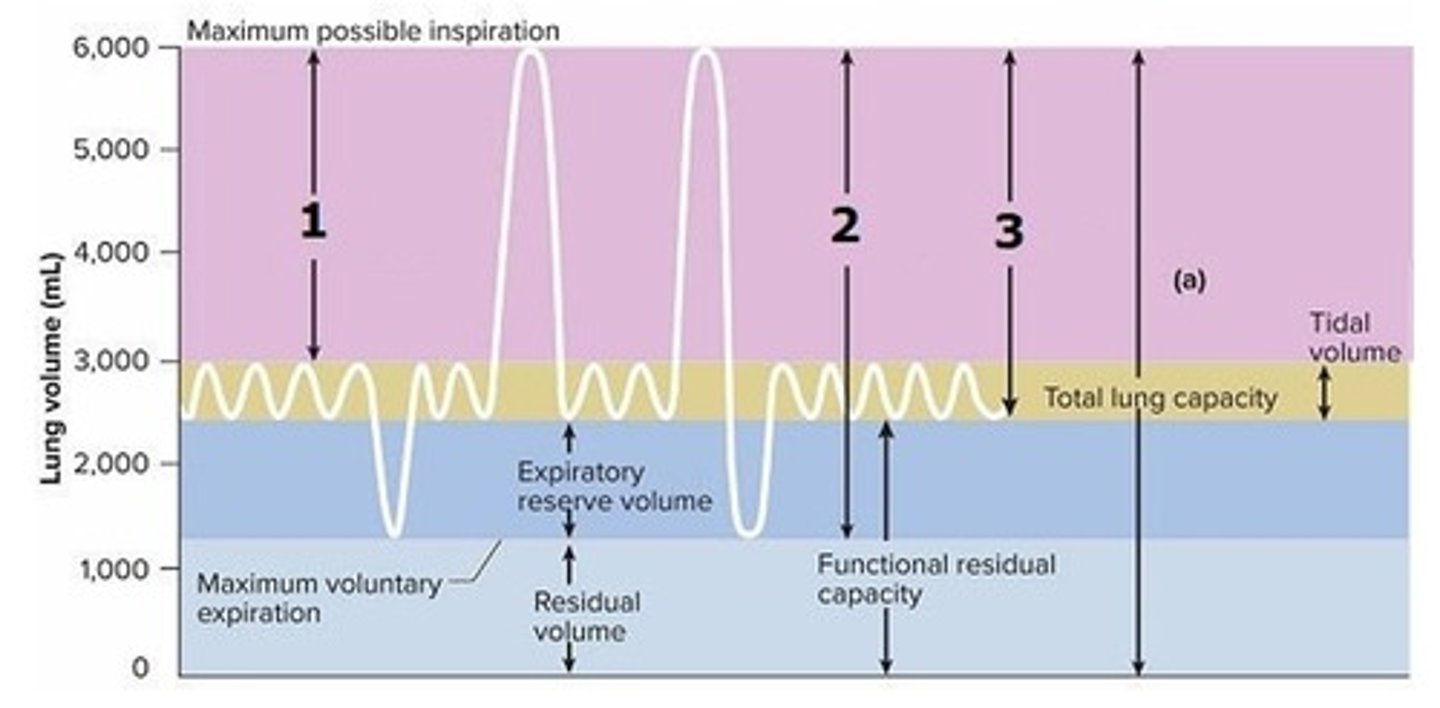
A) Inspiratory reserve volume
Name the respiratory volume labeled 1 on this graph.
A) Inspiratory reserve volume
B) Maximum inspiratory volume
C) Forced inspiratory volume
D) Functional inspiratory volume
E) Inspiratory ventilation volume
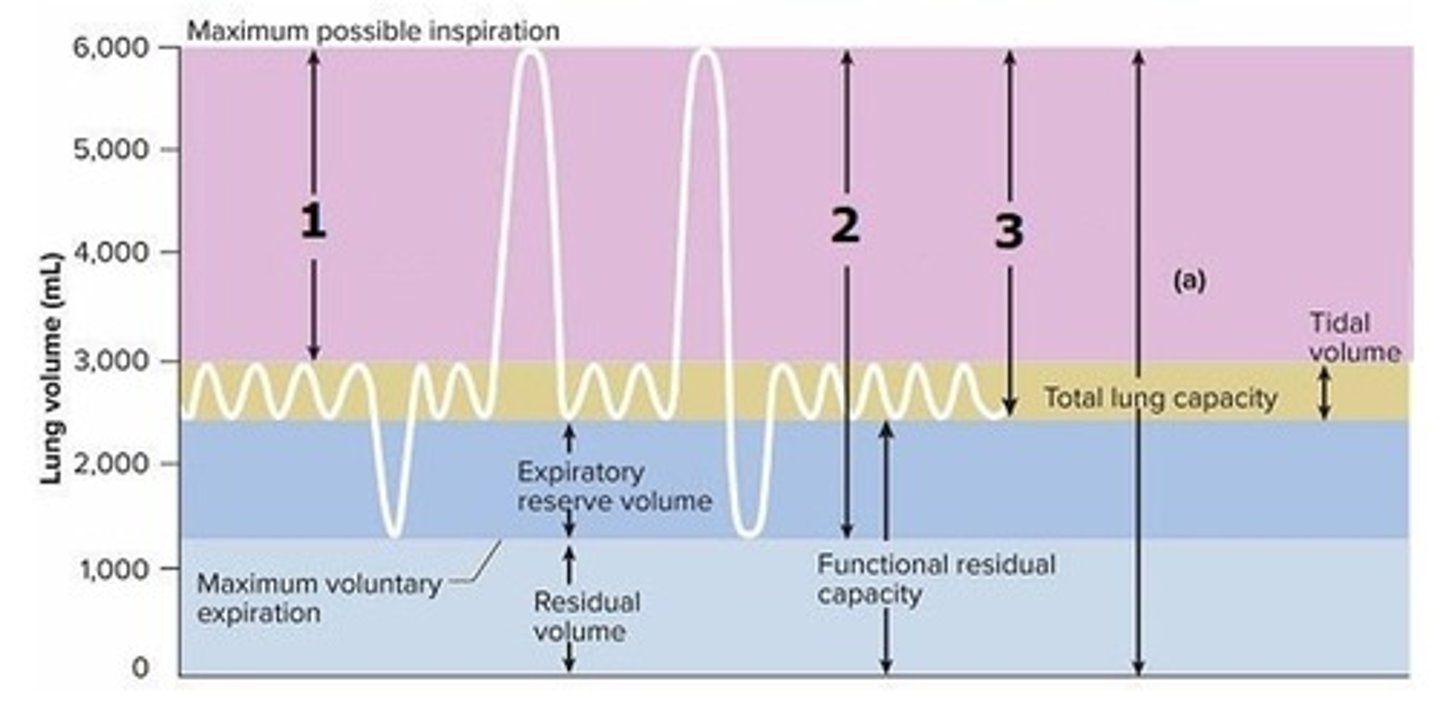
A) Vital capacity
What is labeled 2 on this graph?
A) Vital capacity
B) Inspiratory capacity
C) Forced inspiratory volume
D) Maximum voluntary ventilation
E) Minute respiratory volume
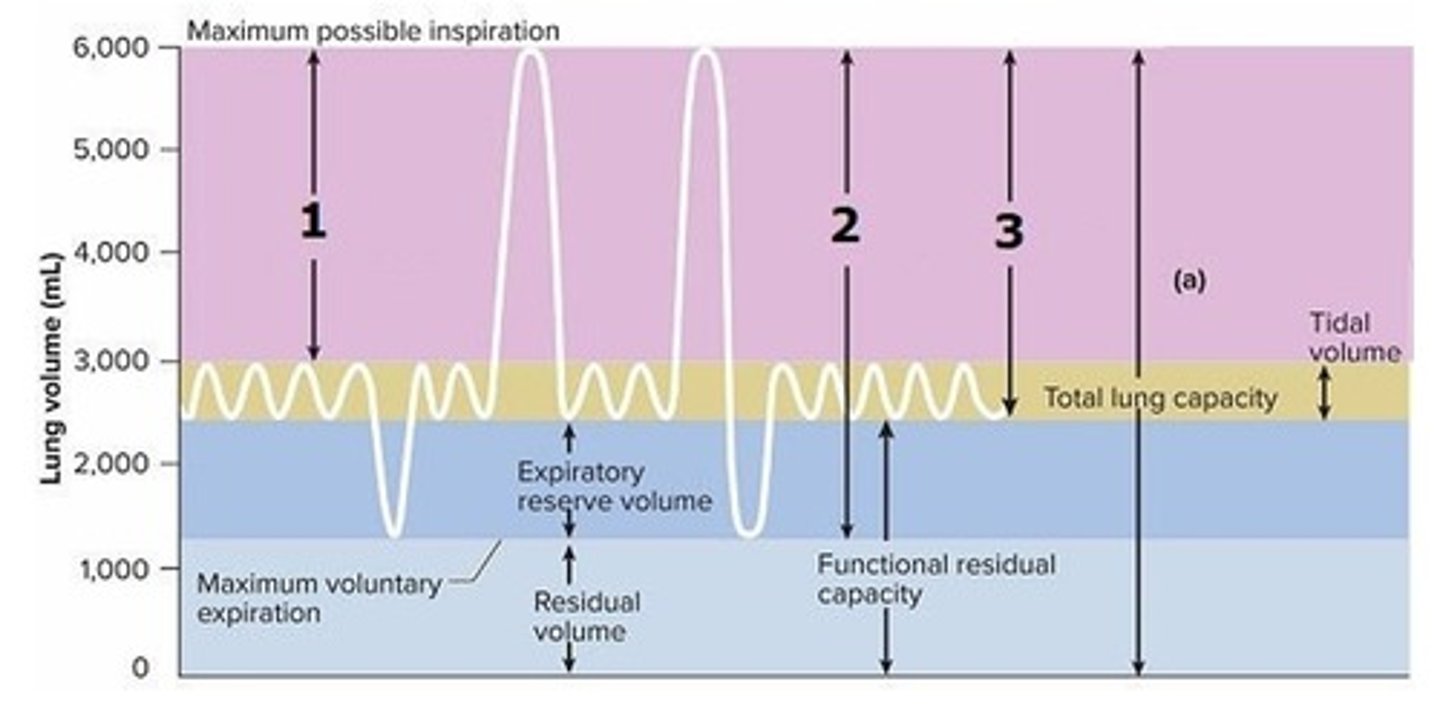
B) Inspiratory capacity
What is labeled 3 on this graph?
A) Vital capacity
B) Inspiratory capacity
C) Forced inspiratory volume
D) Maximum voluntary ventilation
E) Minute respiratory volume
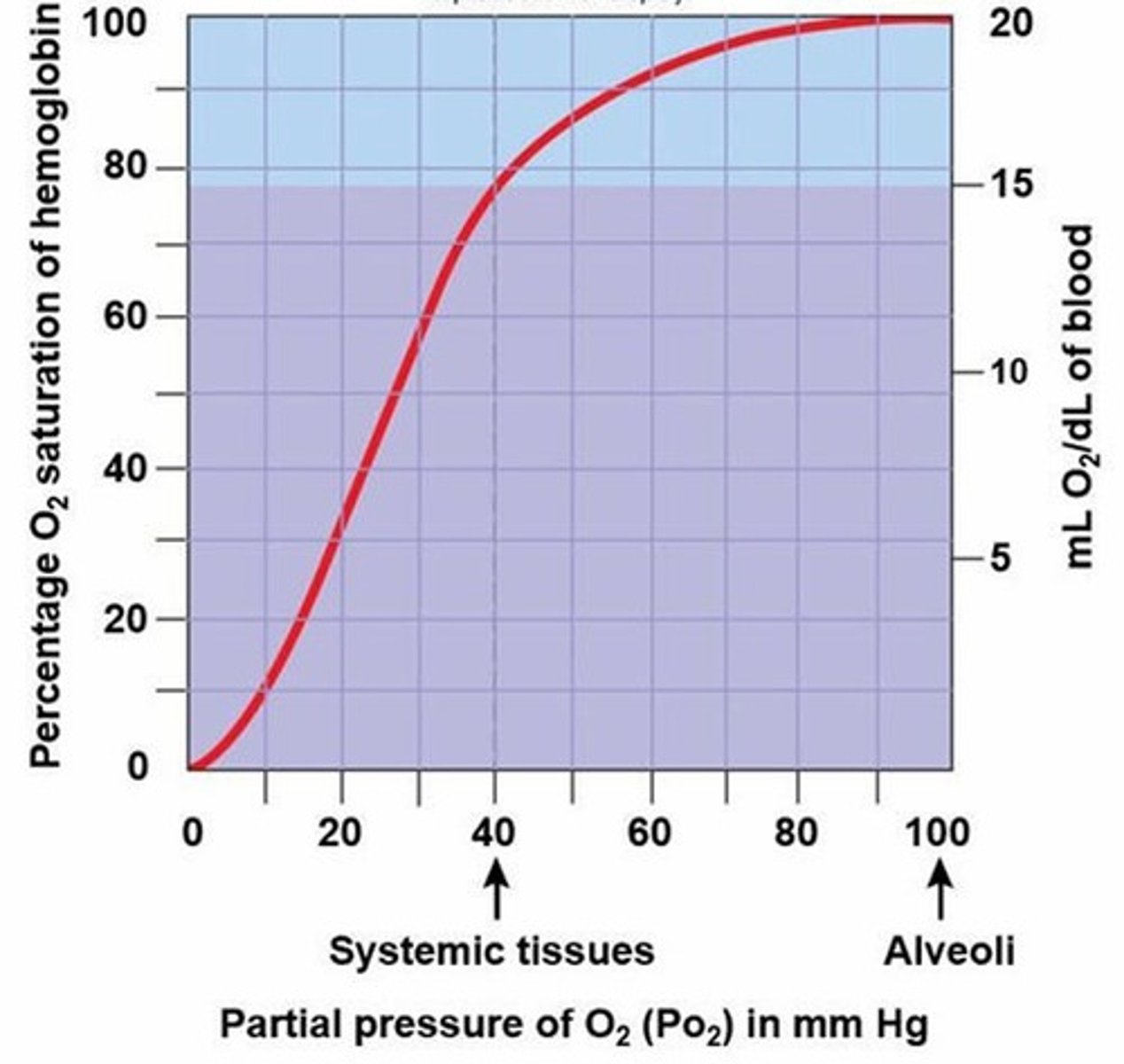
A) 22%
According to the graph above, hemoglobin delivers about __________ of its oxygen load to the systemic tissues.
A) 22%
B) 78%
C) 1.5%
D) 56%
E) 98.5%