Python Programming: Software Development, Functions, and Loops
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is the first step in the software development process?
Analyze the Problem: Figure out exactly the problem to be solved.
What does determining specifications involve?
Describing exactly what your program will do, including inputs, outputs, and their relationships.
What is the purpose of creating a design in programming?
To formulate the overall structure of the program and choose or develop an algorithm that meets the specifications.
What does implementing the design mean?
Translating the design into a computer language, specifically Python in this course.
What is the goal of testing and debugging a program?
To try out the program to see if it works and to locate and fix any errors (bugs).
What does maintaining a program involve?
Continuing to develop the program in response to user needs, as most programs evolve over time.
In the Temperature Converter example, what is the input?
The temperature in Celsius.
What is the formula used to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit in the Temperature Converter?
F = 9/5(C) + 32.
What is pseudocode?
Precise English that describes what a program does, step by step, focusing on the algorithm rather than the programming language.
What is an identifier in Python?
A name given to variables, modules, etc., which must begin with a letter or underscore and can include letters, digits, or underscores.
What are reserved words in Python?
Identifiers that are part of Python itself and cannot be used as names for variables, such as 'and', 'for', 'print', etc.
What are expressions in programming?
Fragments of code that produce or calculate new data values, including literals and simple identifiers.
What error occurs when trying to use a variable without a value assigned?
NameError.
What operators can be used to combine simpler expressions?
+, -, , /, *.
What does a print statement do in Python?
It can print any number of expressions, with successive print statements displaying on separate lines.
What is the structure of a simple assignment statement in Python?
What is the output of the following code: print(3 + 4)?
7
How can you print multiple values on the same line in Python?
By using the 'end' parameter in the print function, e.g., print(3, 4, end=' '), which will not add a newline after printing.
What does an assignment statement do in Python?
It assigns a value to a variable, which can be reassigned multiple times.
How does Python handle variable assignment?
Assigning a variable is like putting a 'sticky note' on a value, indicating which variable refers to it.
What is the purpose of an input statement in Python?
To get input from the user and store it into a variable.
Describe the process of an input statement.
The prompt is printed, the program waits for user input, and the entered expression is evaluated and assigned to a variable.
What is simultaneous assignment in Python?
It allows multiple variables to be assigned values at the same time using the syntax
How can you swap the values of two variables in Python?
By using the syntax x, y = y, x.
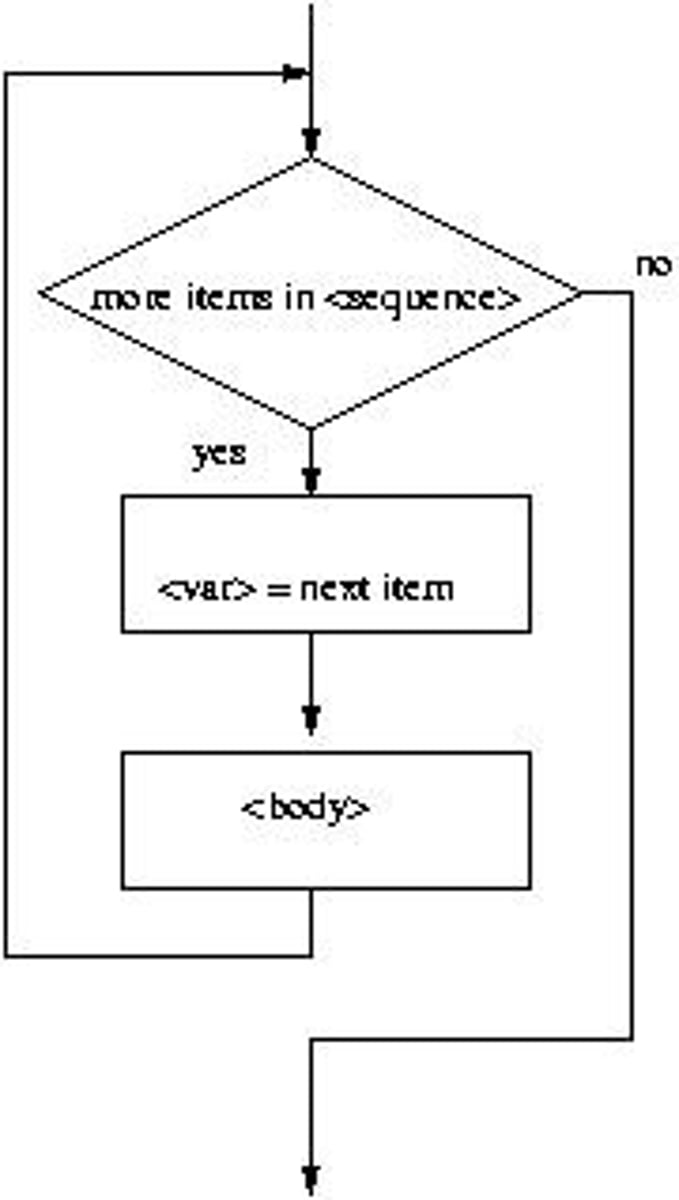
What is a definite loop in Python?
A loop that executes a specific number of times, defined at the start.
What is the role of the loop index in a for loop?
The loop index takes on each successive value in the specified sequence.
What does the range function do in Python?
It generates a sequence of numbers starting from 0 up to, but not including, the specified number.
What are control structures in Python?
They alter the flow of program execution, such as for loops.
What is the future value program designed to calculate?
The value of an investment after 10 years based on the initial principal and interest rate.
What inputs does the future value program require?
The initial amount to invest (principal) and the annual percentage rate (apr).
How is the future value calculated in the program?
By repeating the calculation principal = principal * (1 + apr) for 10 iterations.
What is the output of the future value program?
The value of the investment after 10 years.
What does the eval function do in Python?
It evaluates a string expression and returns the result.
How is user input handled in the future value program?
User input is taken for both principal and apr using eval(input(...)).
What does the print function do in the future value program?
It outputs text or variable values to the console.
What is the purpose of indentation in Python?
It indicates the beginning and end of the body of loops and functions.
What is the significance of the main function in the future value program?
It encapsulates the program logic and is called to execute the program.
What are the two key elements that define a modern computer?
Computers are devices for manipulating information and operate under the control of a changeable program.
What is a computer program?
A detailed, step-by-step set of instructions telling a computer what to do.
What does it mean for programs to be executed?
Programs are carried out by the computer, allowing it to perform tasks based on the instructions provided.
Why is learning to program important?
It helps understand the strengths and limitations of computers, enhances problem-solving skills, and is a fundamental part of computer science.
What is the analogy used to describe computer science?
Computers are to computer science what telescopes are to astronomy.
What is an algorithm?
A step-by-step process for achieving a desired result.
What is the process of analyzing algorithms and problems mathematically called?
Analysis.
What is the role of the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer?
The CPU is the 'brain' of the computer that carries out basic operations on data.
What is the difference between main memory and secondary memory?
Main memory (RAM) is fast but volatile, while secondary memory provides more permanent storage.
What are input and output devices?
Input devices pass information to the computer (e.g., keyboards), while output devices present processed information to the user (e.g., monitors).
What is the Fetch-Execute Cycle?
The process where the first instruction is retrieved from memory, decoded, executed, and then the next instruction is fetched and processed.
What are the two types of programming languages?
High-level languages designed for human understanding and low-level languages that the computer hardware can understand.
What is the difference between compiling and interpreting a program?
Compiling translates the entire program into machine language at once, while interpreting analyzes and executes the source code instruction by instruction.
What is the role of a compiler?
A compiler converts programs written in a high-level language into the machine language of a computer.
What does it mean for a programming language to have syntax and semantics?
Syntax refers to the precise form of structures in the programming language, while semantics refers to their precise meaning.
What is a high-level language example for adding two numbers?
c = a + b.
What happens when a program is compiled?
It can be executed multiple times without needing the source code or compiler.
What is the significance of problem-solving skills in programming?
They help analyze complex systems by reducing them to interactions between simpler systems.
What is the main limitation of natural language in programming?
Natural language has ambiguity and imprecision problems when describing complex algorithms.
What is the purpose of using an interpreter?
An interpreter simulates a computer that understands a high-level language, executing the source code instruction by instruction.
What does it mean for a problem to be unsolvable?
It means that no algorithm can provide a solution to that problem.
What is the role of experimentation in computer science?
It involves implementing a system and studying its behavior when problems are too complex for analysis.
What are interpreted languages?
Languages that can be developed and run interactively, offering more flexibility and portability.
What does the Python prompt (>>>) indicate?
It indicates that Python is ready for the user to input a command.
How do you define a function in Python?
By using the 'def' keyword followed by the function name and parentheses, e.g., 'def hello():'
What is the purpose of indentation in Python function definitions?
It indicates which lines of code are part of the function.
How do you invoke a function in Python?
By typing the function's name followed by parentheses, e.g., 'hello()'.
What are parameters in Python functions?
Changeable parts within parentheses that customize the function's output.
What happens to defined functions when you exit the Python prompt?
They cease to exist until the program is run again.
What is a module file in Python?
A text file containing function definitions, saved as plain text.
What does the 'main()' function do in a Python program?
It tells Python to execute the code defined within the main function.
What is the purpose of comments in Python code?
They are intended for human readers and are ignored by Python.
What is a variable in Python?
A name assigned to a value that can be referred to later in the program.
What does the 'for' loop do in Python?
It repeats a block of code a specified number of times.
What is an assignment statement in Python?
It assigns a computed value to a variable using the '=' operator.
What type of function is illustrated by the chaos.py program?
A logistic function, which models certain unstable electronic circuits.
What does the 'eval(input())' function do in Python?
It evaluates the user input and assigns it to a variable.
What is the output of the chaos.py program based on user input?
It returns 10 seemingly random numbers between 0 and 1 based on the initial input.
What is the significance of the number 3.9 in the chaos.py program?
It is a parameter in the logistic function that influences the chaotic behavior.