Characteristics of Living Organisms (1.1-1.5)
All living organisms undergo:
- %%M%%ovement: when an organism or part of it changes its place/position
- %%R%%espiration: Biochemical reaction in cells that breakdown nutrient molecules for (energy) metabolism
- %%S%%ensitivity: Detection of a stimulus and ability to respond
- %%G%%rowth: Permanent increase in cell size, number or complexity
- %%R%%eproduction: Creation of offspring of the same species as the parents
- %%E%%xcretion: Removal of toxic materials, waste products from metabolic processes or substances in excess
- %%N%%utrition: Intake of substances required for growth and to provide energy
%%MRS GREN%% will help you remember!
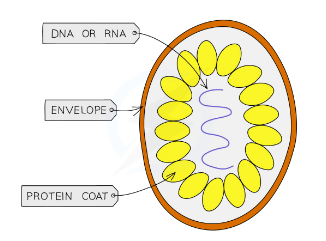
Viruses are NOT considered living organisims because they do not complete these processes
- Viruses are non-cellular and consist of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat
- They reach target cell and inject this genetic material into the cell, which will then replicate to reproduce the virus harming the target cell
Classification systems
==Classification is used to group species==
- Species==:== group of organisms that can be bred to reproduce fertile offspring
- Organisms are divided based on MORPHOLOGY and ANATOMY
- Morphology: Study of external characteristics
- Anatomy: Study of internal characteristics
==DNA sequencing studies give a more accurate comparison==
DNA of each species is mapped and compared; species with similar ancestors will have closer DNA base seqences
Binomial Nomenclature: a system of nomenclature in which each species of animal or plant receives a name of two terms
- Second part is the SPECIES and is all in lowercase letters
- First part of the name is the GENUS and will always start with an uppercase letter
The order of classification of organsims is: ==K==ingdom, ==P==hylum, ==C==lass, ==O==rder, ==F==amily, ==G==enus, ==S==pecies
==KING PHILIP CAME OVER FOR GRAN’S SPAGHETTI== ;)
The Five Kingoms:
- Animal
- Plant
- Fungus
- Prokaryote
- Protoctista
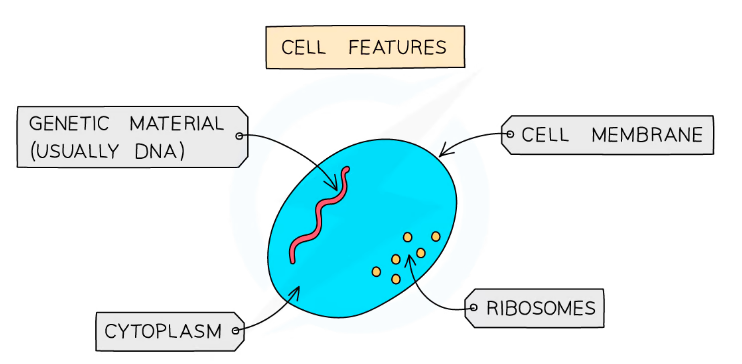
Cell Structures
- Cells of all living organisms contain:
Cytomplasm
Cell membrane
DNA as genetic material
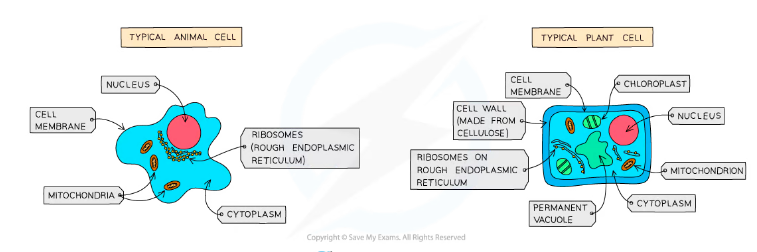
Kingdom: Plants
- %%Autotrophs%%: Living organisms that synthesize organic molecules from simple inorganic substances (through photosynthesis)
- %%Photosynthesis:%% Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
- 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Classifying Plants
- Algae: No leaves, roots or stem and contains chlorophyl
- It is photosynthetic; using the energy of the sun to change carbon dioxide and water into food and oxygen.
- Ferns: Do not produce flowers
- No true roots, stems or leaves but have ‘fronds’ instead
- Reproduces through spores
- Mosses: No vascularisation (xylem/phloem)
- No true leaves but have phyllids instead, no roots or stems (anchored by rhizoid)
- Reproduces by spores and sporangia
- Gymnosperms: Has vascularisation
- Has (true) leaves, roots and stems
- Reproduces through cones
- %%Angiosperms:%% Has vascularisation
- Has (true) leaves, roots and stems
- Reproduces through flowers
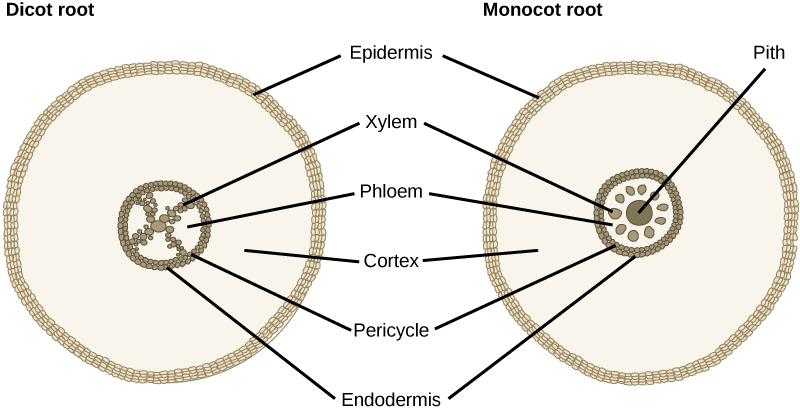
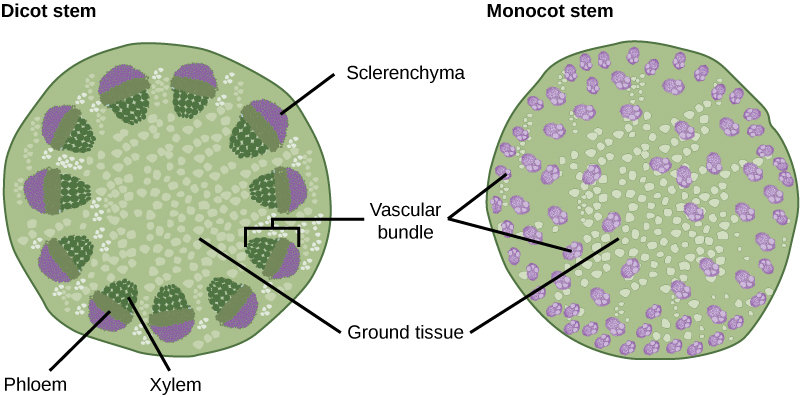
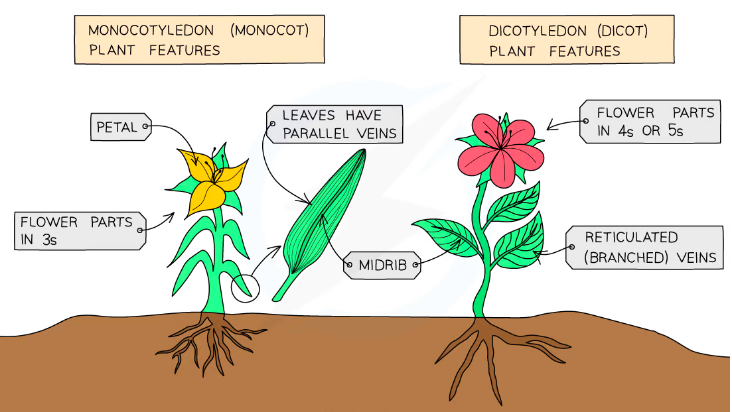
- Angiosperms can be further divided into monocots and dicots
| Monocots | Dicots |
|---|---|
| One cotyledon (seed leaf) | Two Cotyledons (seed leafs) |
| Parallel Veins on leaves | Network of veins on leaves |
| Scattered vascular bundles | Ring of Vascular bundles |
| Flower petals in multiples of 3 | Flowers in multiples of 4/5 |
Least developed →Most developed
Algae → Mosses → Ferns → Gymnosperms → Angiosperms
Kigdom: Fungi
- Either unicellular (eg. yeat) or multicellular (eg. dandruff, mushroom or mould)
- Structure of fungi:
- Grow as thread like filaments called hypha which intertwine to make up the mycelium
- Cell wall is made of chitin (or cellulose)
- Reproduce asexually by producing spores which can be dispersed by water, wind or other organisms OR can be shot out by sporangia
- Feed on dead decaying organic matter; saprophytic
Kingdom: Animals
- All animals are ^^heterotrophs:^^ ^^feed on organic molecules^^
- The animal kingdom is divided into VERTEBRATES ( have a backbone) & INVERTEBRATES (no backbone)
Invertebrates
Arthropods
^^Common features of arthropods^^
- Segmented body
- Hard exostkeleton
- Many pairs of jointed legs
Arthropods are divided into : Crustacea , Insects, Arachnids, Myriapods
Crustacea:
- Many Body segments
- Stalked compound eyes
- 2 pairs of antennae as sense organs
Insects
- Divided into 3: head, abdomen, and thorax
- 1 Pair of antennae as sense organ
- Pair of compound eyes; wider vision
- 3 Pairs of jointed legs
Arachnids
- 2 body segments: Clepathorax and abdomen
- No antennae; Pair of pincers to hold food
- 4 Pairs of legs
- No compound eyes
Myriapods
- Centipedes are carnivorous- 1 pair of legs per segment
- Millipedes are herbivorous- 2 pairs of legs per segment

Nematodes
- No body segements
- Moves by wrigglign but lives in one place
- Parasitic; organism that lives on or in a host organism and gets its food from or at the expense of its host
- Soft bodied
Annelids
- Long segmented body covered in mucus
- Chaete (bristles) on each segment for movement
- Hard, waterproof body covering
- Herbivorous
Molluscs
- Have a shell that protects soft body
- Eyes on tentacles
- Mouth part to scrape vegetation
- Foot muscle with slimy covering for movement
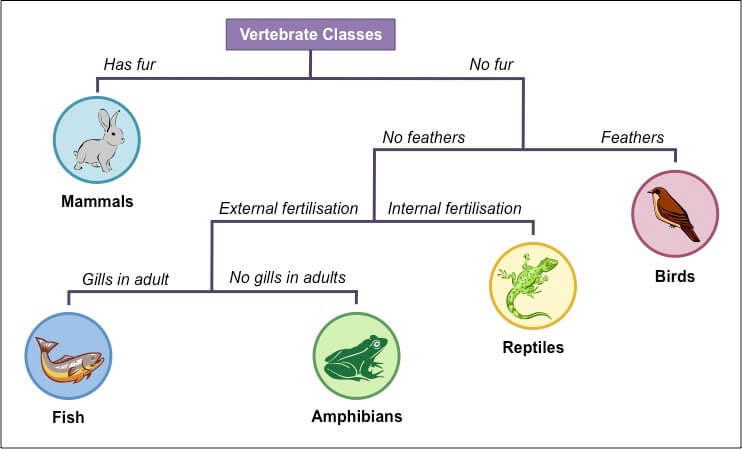
Vertebrates
Fish (Pisces)
- All are aquatic
- Cold blooded
- Scales for protection
- Lateral Line as sense organ and used for balance
- Movement through fins
- Breathing through gills; covered by operculum
- Skeleton is bone or cartillage
- External fertilisation; Female lays eggs in water, male sheds sperm over eggs to form zygote that develops into a young fish
- Stream lined to facilitate easier swimming
Amphibians
- Smooth, Slimy, Naked skin
- Cold blooded
- Moves using legs/limbs with their hind legs end in webbed feet for swimming under water
- External fertilisation
- Can live in both land and water
- Breathe through skin, mouth and lungs
Reptiles
First true land living vertebrates
Cold blooded
Covered with dry scales for protection
Breathe through lungs
Internal fertilization; lay eggs

Birds/Aves
- Warm blooded
- Bodies covered by feathers
- To trap warm air and provide protection
- Quill feathers for wings and plume for the rest of the body
- Scales on legs which are tipped with claws
- Jaws modified into toothless beaks
- Forelegs modified into wings
- Hollow bones to decrease body weight and facilitate flying
- Internal fertilisation; reproduce through laying eggs
- Breathe through lungs; Have extra air sacs to store oxygen
Mammals
Warm blooded
Body covered by hair/fur
Presence of external ear (pinna) to collect sound waves
Females have mammary glands to secrete milk to feed their offspring
Internal fertilization; give birth to live offspring

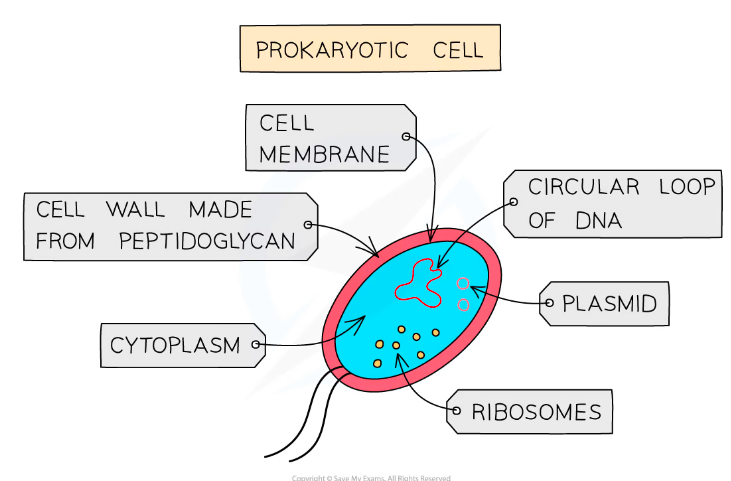
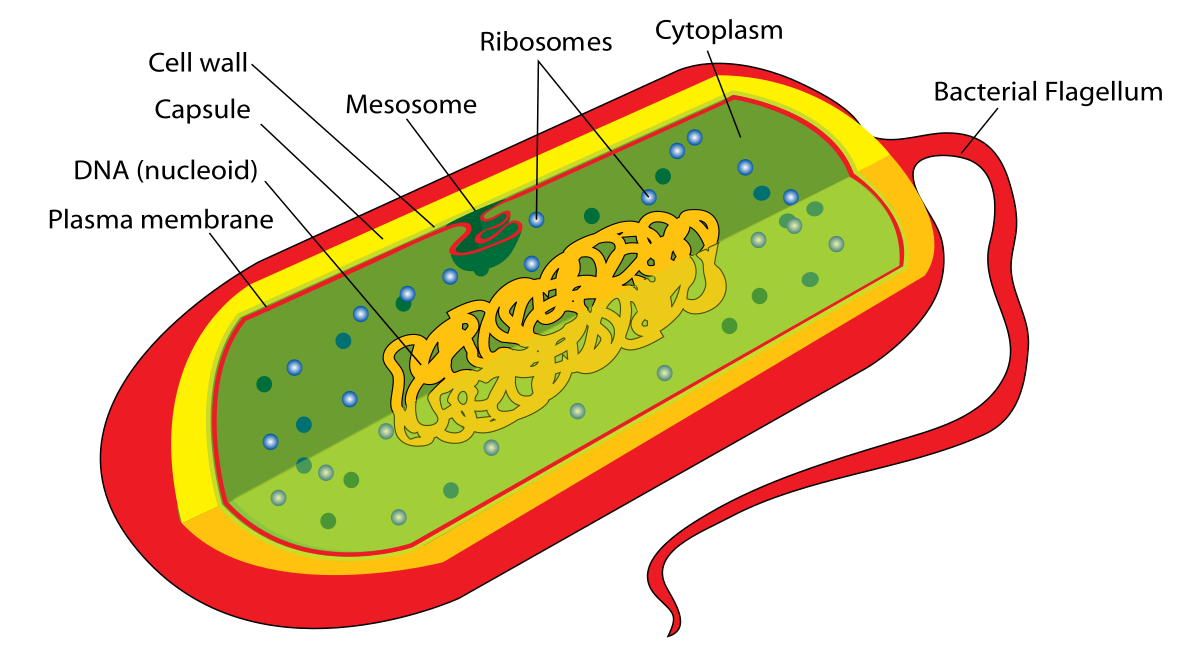
Kingdom: Prokaryote
Microscopic and unicellular
Some have flagella for movement
No nucleus BUT have circular DNA strands instead
Plasmids and extra chromosomal DNA
Composed of: Outer cell wall made of murien, a cell membrane and cytoplasm
Reproduces asexually by binary fission
Dichotomous keys
@@Used to identify species based on a series of questions about their features@@
A user is presented with @@2 questions at a time (hence the name DIchotomous)@@ and is supposed to chose one that correlates with the species
This leads to a pair of other questions
In order to successfully navigate a key, you need to pick a single organism to start with and @@follow the statements from the beginning@@ until you find the name
You then pick another organism and start at the beginning of the key again, repeating until all organisms are named