web development - web components
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
template
Defined by _________ to provide inert HTML: in a DOM page in a standard way
no need to use scri[t to clone the content for later use
shadow
________ DOM:
protected subtrees with their own CSS and DOM
Document Object Model
DOM: ___________ ____________ _________
- including HTML, JS
ES6
“type”: “module”
import * as utils
the latest way to import and export
using javascript version (___+)
if using node.js, need to set ____: ______ in the
package.jsonif i want to import everything, and alias the imported module as
utils, use________ from ….
B
A
event system
web components have 2 forms:
A. single component with attributes and B. multiple components nested
Single component with attributes
<player-card name='Joe' number='21' position='forward'></player-card>Multiple components instead of attributes using the slotted data instead
<player-card>
<player-name>Joe</player-name>
<player-number>21</player-number>
<player-position>Forward</player-number>
</player-card>which favors progressive enhancement? __________
which one is simple to implement? __________
what is the popular way to communicate and coordinate within the multiple components system? _______
export
export
./util.js
for example, i want to export the function add and constant PI in the util.js, and import those at app.js
_____ function add() {...}
_____ const PIimport {add, PI} from "_____"await import("./math.js")
dynamic imports (lazing loading):
when i only need to import at a particular function:
from ./math.js
async function loadMathModule() {
const math = _______;
console.log(math.multiply(3, 4)); // 12
}
loadMathModule();
light
shadow
open
Feature | ____ DOM | _____ DOM |
|---|---|---|
Global Styling | ✅ Yes | ❌ No (Scoped) |
Encapsulation | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
JavaScript Access | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes when set |
Component Isolation | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
shadow
The ________ DOM is a protected sub-tree where implementation details can be hidden, preventing conflicts with other styles or scripts on a webpage.
Light
In contrast, the _____ DOM is part of the public DOM tree and does not provide encapsulation, making it easier to manipulate but potentially vulnerable to conflicts.
style
script
One advantage of using Shadow DOM is that it helps prevent ______ and ____ conflicts by isolating css and js.
slot
The _______ element in a web component allows content to be passed into the Shadow DOM from the Light DOM while still maintaining encapsulation.
variables
parts
foo::part(my-button) <slot name="header"></slot>
<slot name="footer"></slot>CSS _______ and CSS _____ enable developers to style elements inside the Shadow DOM from the external CSS.
suppose web component named foo like this:
<style>
.button {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
<button part="my-button" class="button">Click me</button>how to change the style from external css?
_________{
background-color: red; /* Override Shadow DOM styling */
}now suppose i want to render component liek this
<my-component>
<h1 slot="header">Title Here</h1>
<p slot="footer">Footer content</p>
</my-component>
how do i construct the HTML in shadow DOM:
____________
security
Using Light DOM may introduce robustness or _______ concerns since there is no encapsulation.
attributes
When using the Shadow DOM, developers can use _______ to pass data into the web component.
shadow host
Shadow Tree
Shadow Boundary
Shadow Root
Light DOM
Flattened Tree
_________ : The regular DOM node that the shadow DOM is attached to.
_________: The DOM tree inside the shadow DOM.
________: The place where the shadow DOM ends, and the regular DOM begins.
_____: The root node of the shadow tree.
_________: The DOM that lives outside the shadow DOM.
_________: The DOM which you see in DevTools in your browser.
light
shadow-host
light
root
boundary
shadow tree
shadow
flattened tree
<body>
<h2>This is in the ____ DOM</h2>
<div id="_____-_____">
<p>This is inside the ____ DOM (before Shadow DOM is attached).</p>
</div>
<script>
// Select the Shadow Host
const shadowHost = document.querySelector("#shadow-host");
// Attach a Shadow ____ (Creates a Shadow ______)
const shadowRoot = shadowHost.attachShadow({ mode: "open" });
// Insert Shadow DOM content (____ ___)
shadowRoot.innerHTML = `
<style>
p {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
<p>This is inside the _____ DOM</p>
`;
// Console log to see the structure
console.log("Shadow Host:", shadowHost);
console.log("Shadow Root:", shadowRoot);
console.log("______ ____ (Rendered View): Open DevTools to see the final rendering.");
</script>
</body>super()
this.shadow = this.attachShadow({ mode: 'open' });
this._count = 0;
return [‘count’]
customElements.define('counter-element', CounterElement);
create own wc:
<body>
<!-- Custom element in action -->
<counter-element count="5"></counter-element>
<script>
class CounterElement extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
_________
// Attach a shadow DOM
____________
// Create and style the Shadow DOM content
this.shadow.innerHTML = `
<style>
.counter {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
font-size: 24px;
color: #fff;
background: #007bff;
padding: 10px 20px;
border-radius: 5px;
display: inline-block;
}
button {
margin-left: 10px;
padding: 5px 10px;
font-size: 16px;
}
</style>
<div>
<span class="counter">Count: <span id="count"></span></span>
<button id="increment">Increment</button>
</div>
`;
// Bind methods and references
// create new field incrementButton and countDisplay
this.incrementButton = this.shadow.querySelector('#increment');
this.countDisplay = this.shadow.querySelector('#count');
// create default _count field to store value
_______________
// Event listener for the button
this.incrementButton.addEventListener('click', () => this.increment());
}
// Specify observed attributes count
static get observedAttributes() {
__________
}
// Called when the element is added to the DOM
connectedCallback() {
console.log('CounterElement added to the DOM');
this.updateCount();
}
// Called when an observed attribute changes
attributeChangedCallback(name, oldValue, newValue) {
if (name === 'count') {
this._count = parseInt(newValue, 10) || 0;
this.updateCount();
}
}
// Called when the element is removed from the DOM
disconnectedCallback() {
console.log('CounterElement removed from the DOM');
}
// Increment the count and update the attribute
increment() {
this._count += 1;
this.setAttribute('count', this._count);
}
// Update the displayed count
updateCount() {
this.countDisplay.textContent = this._count;
}
}
// Register the custom element
_______________
</script>
</body>developer experience
user experience
•Once again, we meet two competing issues – DX (____ _____) and UX (_____ _____)
Frameworks may provide a better DX or support for legacy – they win and you should very much know them
UX requires raw speed
Best solution is a framework that provides a thin-ish layer at best and falls away if/when no longer needed (biodegradable deving!
web component
WC stands for ______ ______, a set of web platform APIs that enable the creation of reusable, encapsulated, and framework-agnostic custom HTML elements.
developer-defined HTML elements
custom elements with logic that integrate seamlessly into the DOM and CSS, using standard features immediately.
custom elements
web components
____ _________ are a subset of _____ ___ (wc).
True
Are standard HTML global attributes automatically part of web components?
for example, you can define the class and id of wc, they worked just like other standard components
True
: Does the native event system (addEventListener) work with web components?
light
the normal exposed part of the DOM in a web component is called ___________ DOM
shadow
What is the hidden or protected part of a web component called?
_________ DOM
False
Do you have to use the protected (shadow) DOM when making a web component?
this is recommended for encapsulation
shadow DOM content
What is content enclosed within a web component called
________ ________ ______.
super()
What function is called in the constructor when creating a web component?
__________
this is called to inherit build in functionality of HTML elements
connectedCallback()
What method is fired when a web component is mounted in the page?
__________
connectedCallback()
Where should most of the DOM work be done in a web component?
______________
DOMContentLoaded()
_________ fires once per document:
It runs when the whole HTML document is fully parsed.
It does not account for dynamically added web components.
:not(:defined)
What CSS pseudo-class is used to address styling issues with web components that aren’t rendered?
_________________
disconnectedCallback()
What method is fired when a web component is removed from the page?
____________
static get observedAttributes
attributeChangedCallback
How do you know if attributes are modified in a web component?
first we want to Specify which attributes to observe
_________________() {
return ['data-value', 'title'];
}then, react to attribute changes:
// Step 2: React to attribute changes
__________(name, oldValue, newValue) {
console.log(`Attribute ${name} changed from ${oldValue} to ${newValue}`);
// Add your custom logic here
if (name === 'data-value') {
this.updateValue(newValue);
}
}
adoptedCallback()
called each time the element is moved to a new document.
attributeChangedCallback():
called when attributes are changed, added, removed, or replaced. See Responding to attribute changes for more details about this callback.
False
True or False: The constructor lifecycle method of a Web Component is triggered when the component is removed from the DOM.
observedAttributes
constructor
connectedCallback
disconnectedCallback
adoptedCallback
attributeChangedCallback
define
life cycle of custom element:
// Create a class for the element
class MyCustomElement extends HTMLElement {
static __________= ["color", "size"];
_______() {
// Always call super first in constructor
super();
}
________() {
console.log("Custom element added to page.");
}
_________() {
console.log("Custom element removed from page.");
}
_______() {
console.log("Custom element moved to new page.");
}
_________(name, oldValue, newValue) {
console.log(`Attribute ${name} has changed.`);
}
}
customElements.______("my-custom-element", MyCustomElement);
DOMContentLoaded
connectedCallback
shadow
just like it is best for light shadows to run DOM code in the event ___________, it is also best to run DOM code inside the event __________ for wc.
if we using ______ DOM, we can setup innerHTML in constructor since wc is encapsulated and does not rely on main DOM
if not, we should do it in cc
backward
Web components do not replace frameworks they should just work with them. Anyone hating on them should hate on HTML elements because that is what they are. If a framework relies solely on synthetic components it is more ____ thinking than forward thinking.
<template>
What element is used to store reusable markup inside a web component?
Publish-subscribe
What pattern can be implemented using custom events in web components?
______-______ pattern
false
Do web components replace most web frameworks?
False
True or False: Web Components are fundamentally different from regular HTML elements.
lit
What is a close-to-the-platform library for Web Component creation?
div
Q: Why should developers be cautious about AI-generated markup?
A: AI often reinforces common, mediocre patterns, leading to excessive use of _______ tags.
inefficient
Q: What is a risk of AI favoring statistically common concepts in web development?
A: It can lead to homogenized, uninspired designs and _____ markup.
creativity
Q: What is one strategy to adapt to AI’s influence on web development?
A: Focus on refining AI-generated output and emphasizing _____ in design.
56
user experience / UX
Mobile now accounts for ___% of all website traffic, but mobile commerce lags behind due to terrible ___.
19
2
On average, mobile sites take ___ seconds to load over a 3G network, but users expect pages to load within ___ seconds.
Reliable
fast
engaging
Progressive Web Applications aim to be ___, ___, and ___.
progressive web applications
what is PWA: _____________________
an app that's built using web platform technologies, but that provides a user experience like that of a platform-specific app.
Like a website, a PWA can run on multiple platforms and devices from a single codebase. Like a platform-specific app, it can be installed on the device, can operate while offline and in the background, and can integrate with the device and with other installed apps.
Service Workers
proxy
requests
offline
Installed
manifest
Prefetches
Background
PWA
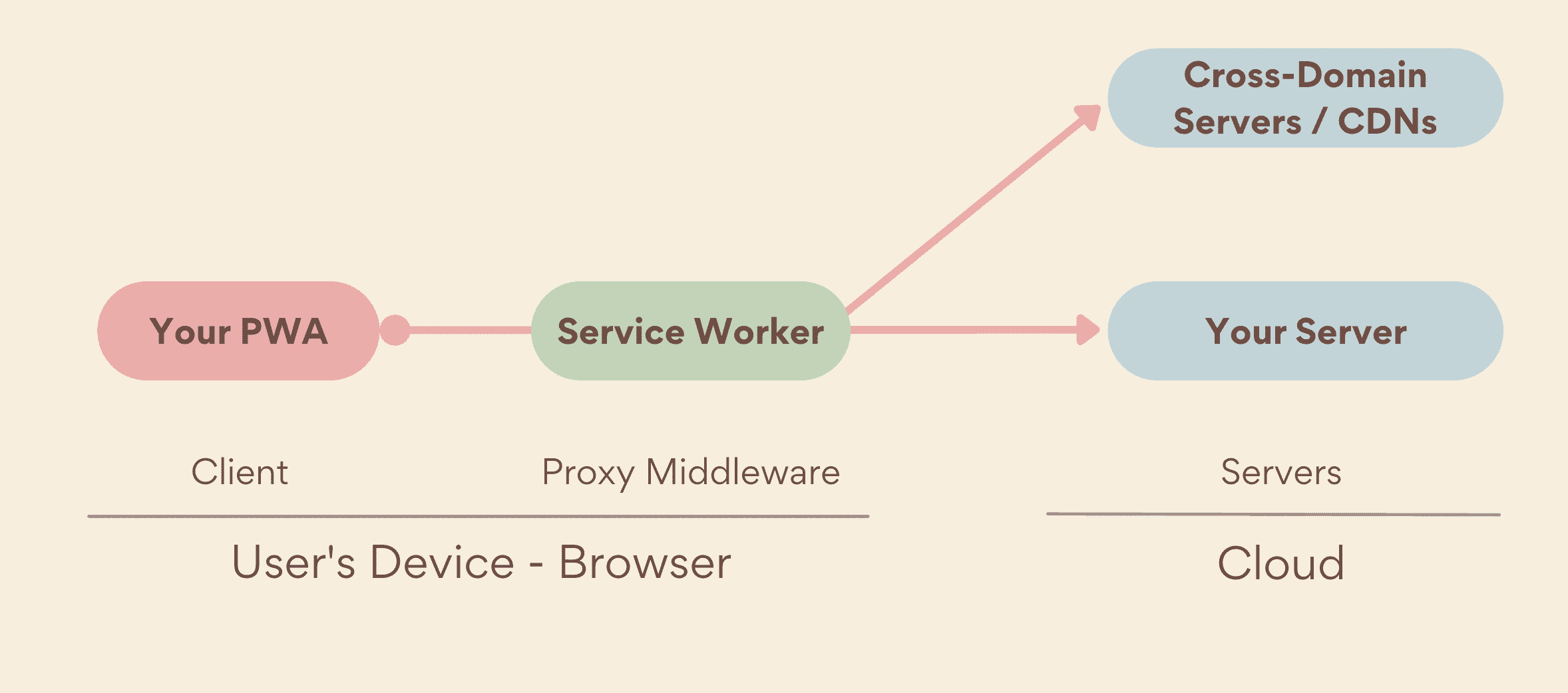
___ are central to PWAs as they allow for offline access and caching.
act as ___ servers that sit between web applications, the browser, and the network (when available)
Controls Network ____:
Service Workers can intercept and modify network requests, acting as a proxy between the browser and the server. This allows them to determine whether to serve cached data or fetch resources from the network, improving efficiency.
Supports _____ Access:
By caching resources (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.), Service Workers ensure that users can interact with the app even when offline. For example, you can still read saved articles in a news app while disconnected from the internet.
Enables "_____" Feel:
With a Service Worker and a _____ file, PWAs can behave like native apps. Users can "install" PWAs, and they’ll run in standalone windows, enhancing the app-like experience.
______ and Improves Performance:
Service Workers can pre-cache assets, reducing load times for frequently accessed content. This makes the application faster and more responsive.
Runs in the ______:
Unlike Web Workers, which are tied to active web pages, Service Workers can run beyond the lifecycle of the page. This means they can handle tasks like syncing data or delivering push notifications even when the webpage is closed.
Integral to ____:
Service Workers are a cornerstone of PWAs because they enable offline capability, better performance, and push notifications. Together with features like the manifest file, they bridge the gap between web and native apps.
Manifest
A ___ file centralizes metadata for PWAs, such as icons and themes.
3
Users abandon sites that take more than ___ seconds to load.
Reach
availability
Progressive Web Apps attempt to balance the richness of a native application with the r___ and a___ of a web application.
PWA
Ajax
service workers are to _______ as XMLHttpRequest to ____
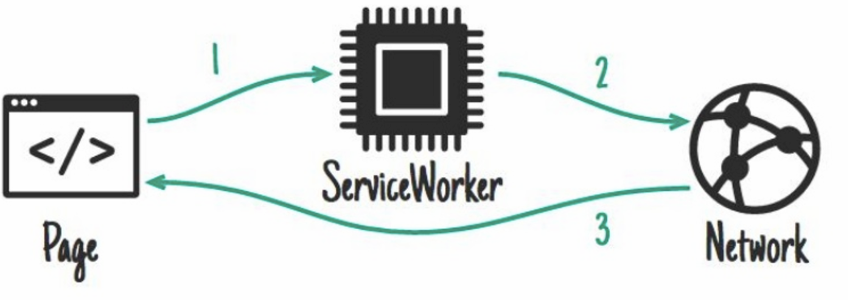
network only
what kind of service worker pattern is this _______________
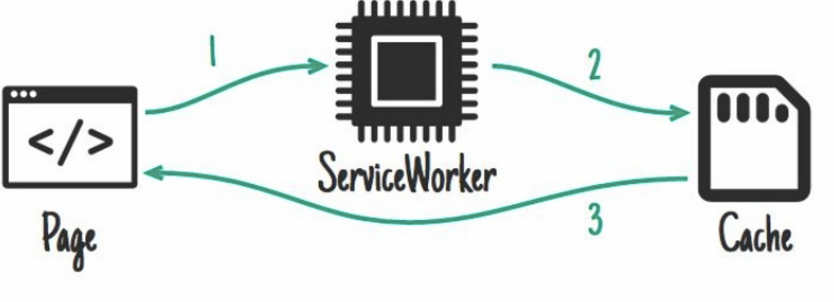
cache only
what kind of service worker pattern is this _______________
cache then network
what kind of service worker pattern is this _______________
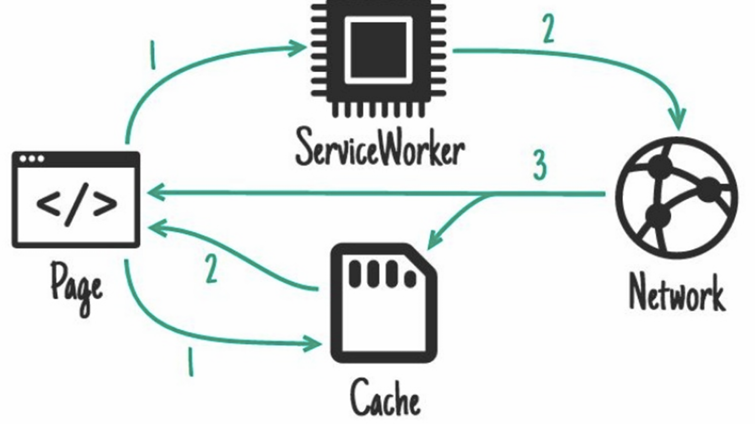
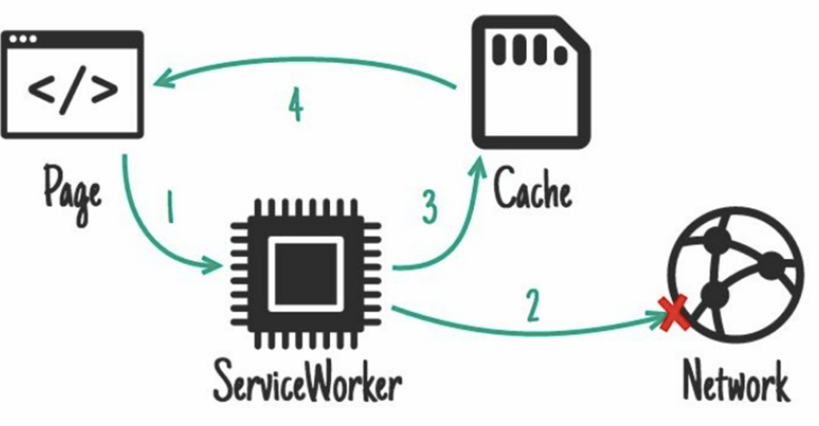
cache, falling back to network
what kind of service worker pattern is this _______________
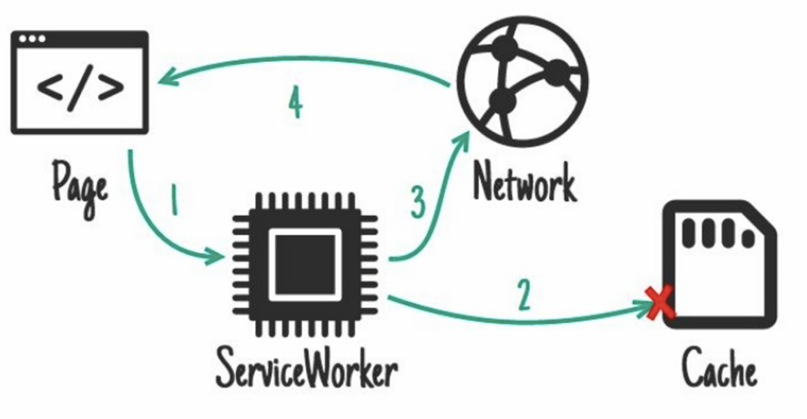
network, falling back to cache
what kind of service worker pattern is this _______________
proxy
What is the main purpose of a Service Worker in a web application?
Answer: A Service Worker acts as a _______ between the client and the server, allowing interception and control of network requests, often caching responses for offline use.
requests
The Service Worker API allows developers to intercept network __________ and control them, often serving cached responses.
localhost effect
A major challenge of web development compared to local development is the _____________ _______, where local environments are stable, but real-world networks are not.
offline
One benefit of Service Workers is enabling __________ browsing, where users can access some content even when the network is unavailable.
false
true/false: service workers can modify browser DOM directly
B
What is the primary motivation for using a Service Worker?
A) Speeding up the initial page load
B) Reducing dependency on a stable network
C) Replacing a traditional server
D) Enhancing JavaScript performance
self.addEventListener("fetch", (event) => {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request).then((response) => {
return response || fetch(event.request);
})
);
});
Write a Service Worker Fetch Event Handler:
Question: Write a Service Worker fetch event handler that serves cached files first and fetches from the network if not available.
navigator.serviceWorker?.register(/service-worker.js)suppose your service worker is defined at /service-worker.js, register it
self.addEventListener("install", (event) => {
event.waitUntil(
caches.open(CACHE).then((cache) => {
return cache.addAll(ASSETS);
})
);
});
Write a Service Worker Fetch Event Handler:
Question: Write a Service Worker install event handler, that cache files
ASSETtoCACHE
{
"name": "MyApp",
"short_name": "App",
"start_url": "/home",
"display": "standalone"
}
what is the manifest of a PWA named MyApp, or App, and start url at /home`
white
what is the final color after everything is loaded and element is defined
<custom-message>This is a custom message</custom-message>
custom-message:not(:defined) {
color: gray;
}
custom-message:defined {
color: blue;
}
custom-message{
color: white;
}
gray
what is the final color after everything is loaded and element is undefined
<custom-message>This is a custom message</custom-message>
custom-message:not(:defined) {
color: gray;
}
custom-message:defined {
color: blue;
}
custom-message{
color: white;
}