Ch 1 - What is Economics?
Economics: the study of the choices that people make in overcoming the problems that arise because resources are limited, while needs and wants are unlimited.
- Scarcity: in a state of being in short supply
Opportunity cost: whenever a choice is made by an economic agent concerning the use of its resources, something is given up or sacrificed.
- The next best alternative when an economic decision is made, a “trade-off”
- If there is no scarcity if a good, and everyone can have as much as they want, it is called a free good
Example:
- Air is a free good
- Breathable air is an economic good
Economic good: is one that is scarce and whose use involves an opportunity cost
Sustainability: ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level
Microeconomics: the choices consumers and producers make in response to the changes in the dynamic world
a. Examines how producers and firms make decisions to improve efficiency
b. Examines how producers and firms make decisions to improve efficiency
c. considers individual industries to see how producers interact with each other and how government intervention may affect producers
Macroeconomics: focuses on the factors affecting the economy as a whole, such as economic growth and the way well being is being maintained by economic growth.
a. Looks at the way income is distributed in an economy (inflation, deflation, unemployment).
Why does the government intervene in markets and in economies?
In terms of microeconomics:
a. To make sure the products meet a certain standard
b. To encourage sustainability
c. To prevent large firms from abusing their ability to influence markets
In terms of macroeconomics:
a. To encourage businesses to produce more to increase gross national income
b. To encourage businesses to produce more to increase gross national income
c. Reduce levels of unemployment
d. Improve economic well-being of workers
9 central concepts of Economics:
- Scarcity: limited amount of resources in the economy
- Choice: measures opportunity cost, determines the choice of selecting alternative options in regards to scarcity of goods or services.
- Equity: distributing wealth in the economy fairly, unlike equally
- Sustainability: preserving current resources in order to ensure that future generations and economies thrive off of the resources
- Intervention: As in government intervention, when it takes over and gets involved to help economies
- Change: constant state of change in an evolving economy
- Economic well-being: general well being of the economy to ensure that societies can prosper from its resources
- Interdependence: extent to which economies and countries rely on each other
- Efficiency: achieving economic progress using as little resources as possible in order not to drain the economy
- Tip: These central key concepts are to be used in the IA, and are the main focal point of the Economics syllabus, understand them well
Four factors of production:
- Land: includes all the resources provided by nature that are used to produce goods. Also known as “natural capital”
- Labour: includes all the human resources used in producing goods. Also known as “human capital”
- Capital: includes buildings, offices, factories, machines, tools, infrastructure and tech to produce goods and services. Also known as “physical capital”
- Entrepreneurship (management): organising and risk taking factor of production. Entrepreneurship organise land, labour, and capital to produce goods and services
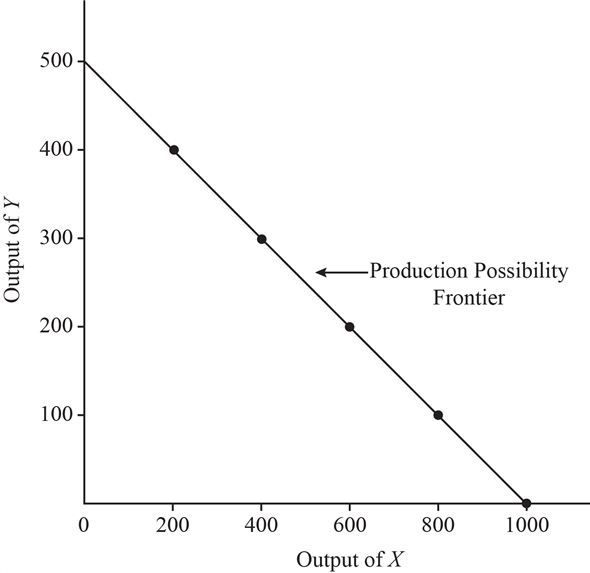
Production possibilities curve (PPC): Is a curve that represents all possible combinations of goods/services in a country using the available resources. Represented by a simple model which conveys two goods or services at any given time
- Opportunity cost
- Choices
- Allocation of resources
Due to scarcity, the economy cannot produce enough agricultural goods due to the lack of resources. All the points beyond the PPC curve are unattainable given the current resources and state of technology
A choice has to be made between the outputs competing for the economy’s resources. A choice have to be made as to which combination of output is to be produced using which resources
Productive efficiency: when the economy is using all of its resources to the fullest extent possible
- Lack of efficiency: waste of resources
- Actual economic growth: any movement which indicates that more output is being produced
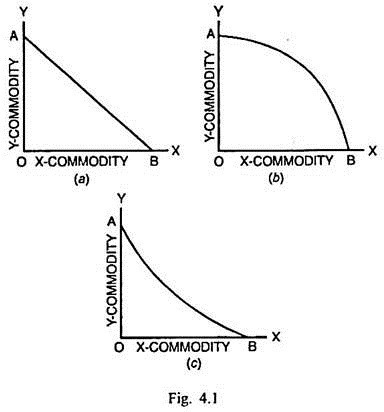
A straight line PPC indicates constant opportunity costs
A concave PPC indicates increasing opportunity costs
\n
 \n
\n Circulation of money in the economy:
\n
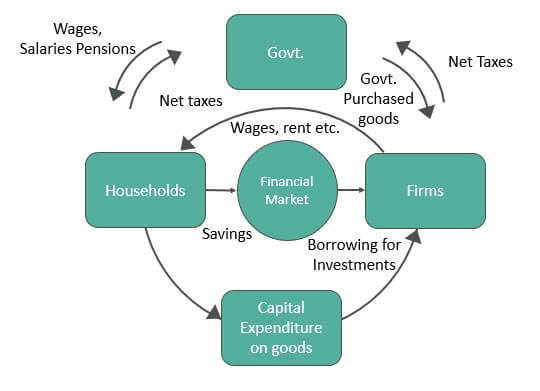
Leakage: any income that leaves the firm sector
The three leakages:
Taxes: some income from firms and households goes to the government sector in the form of taxes
Savings household and firm sector save some of their income in financial institutions (such as: banks, stock markets, pension funds) → these make up the financial sector
Imports: household and firm sectors spend money on foreign goods and services
Gross national income (GNI): amount of money in circular flow
- When GNI is rising, the economy is expanding. When GNI is falling, the economy is in recession.
Planned Economy: decisions as to what to produce, how to produce, and for whom, are made by the government
- Sometimes called a centrally planned economy or command economy
- The government arranges all production, set wages, and set wages
Free market economy: all production is in private hands and demand and supply are left free to set wages and prices in the economy
- Few cases of shortage → efficient work
- Called private enterprise economy or capitalism
- Prices are used to ration goods and services