Marine invert lecture exam 1- taxa
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
** Minus foraminifera and radiolaria, which are in the general info deck
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
True or False: Though protozoans are single-celled, they are still animals
False, they aren’t really animals
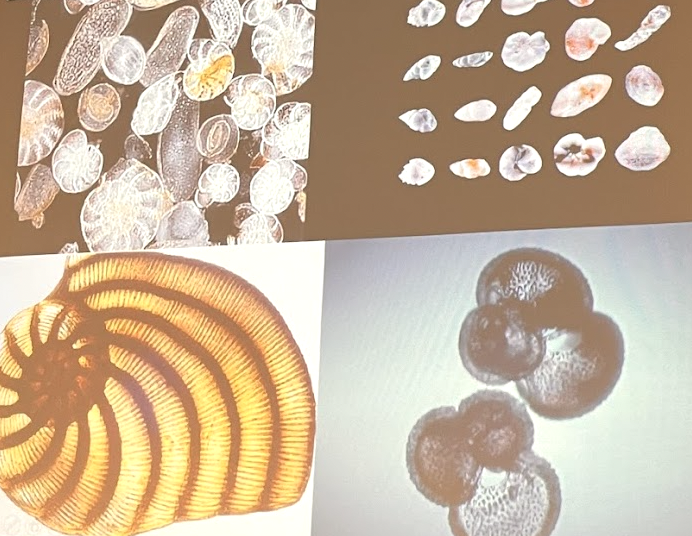

What phyla are these?
Foraminifera, as are these.
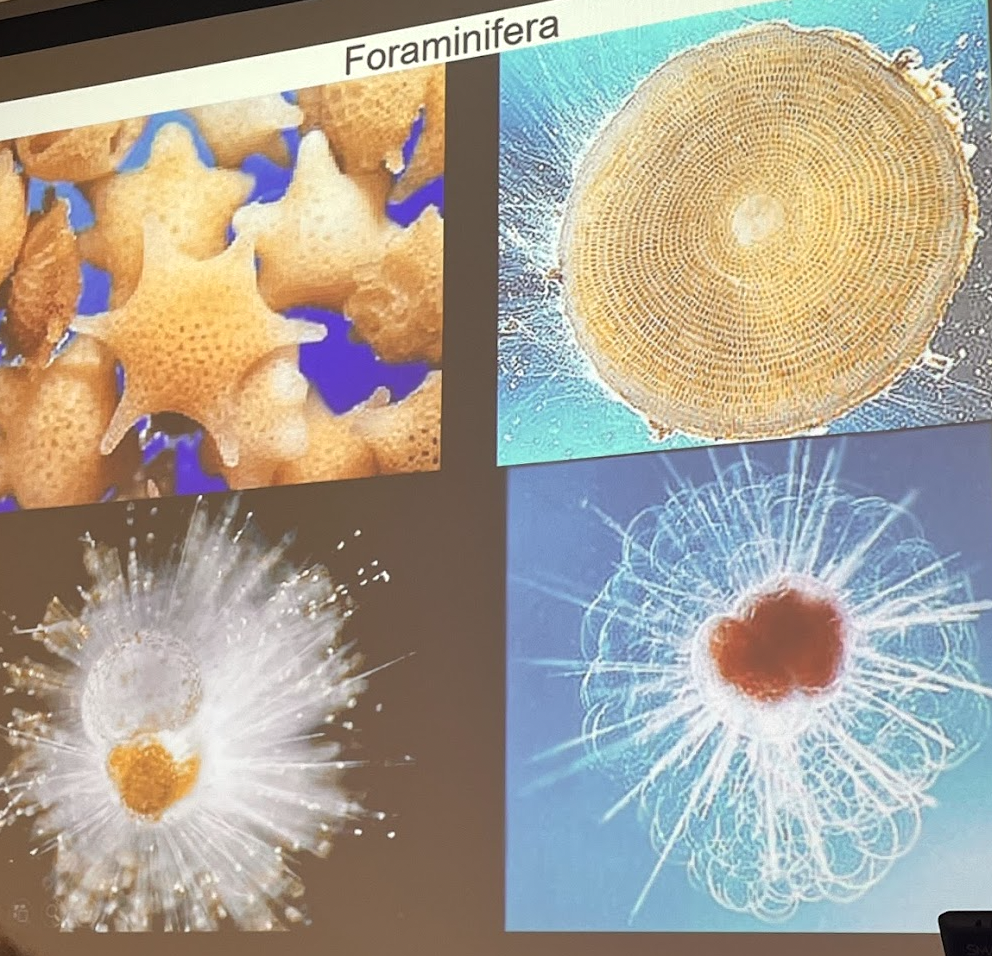

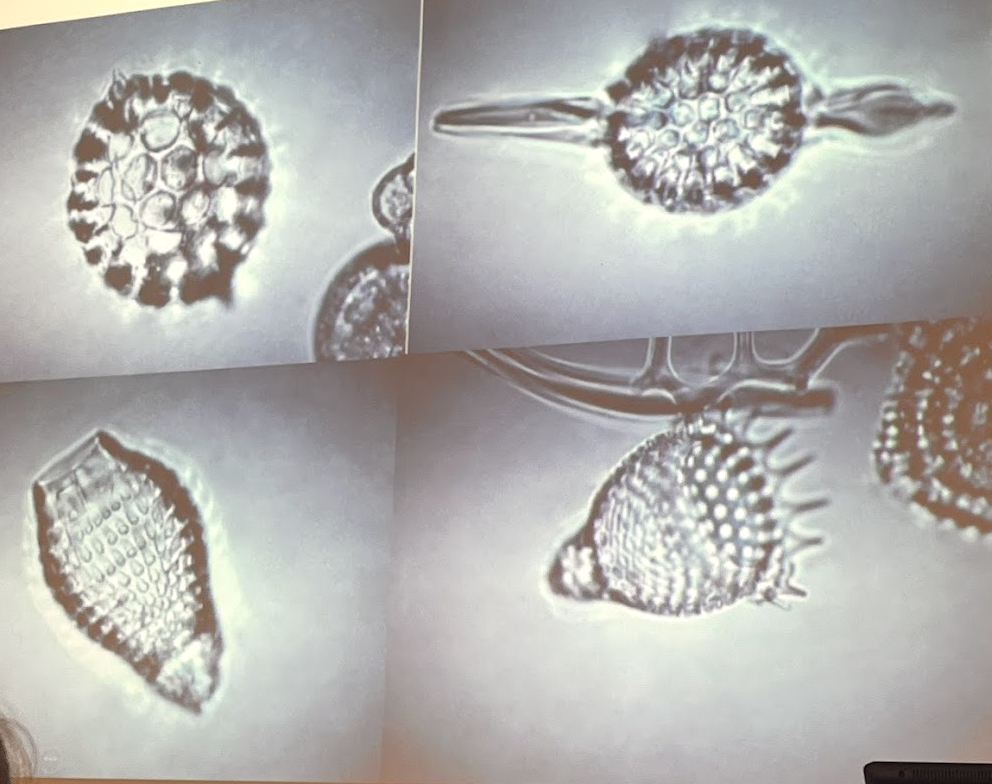
What phylum and class are these organisms in?
Phylum Radiolaria, class Polycystinea
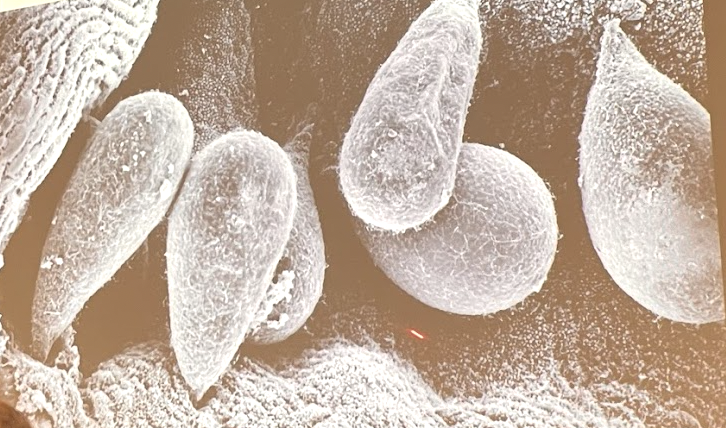
What phylum and subclass are these organisms in? Describe their life cycle.
Phylum Apicomplexa, subclass Gregarinasina
Parasitic and large (0.5-2 mm)
Life cycle:
Feeding stage: trophozoite = main stage, haploid, in gut
Gametocyst stage: oocysts form inside old trophozoite, ONLY diploid stage
Sporozoite: haploid
Parasitic stage (invert hosts)
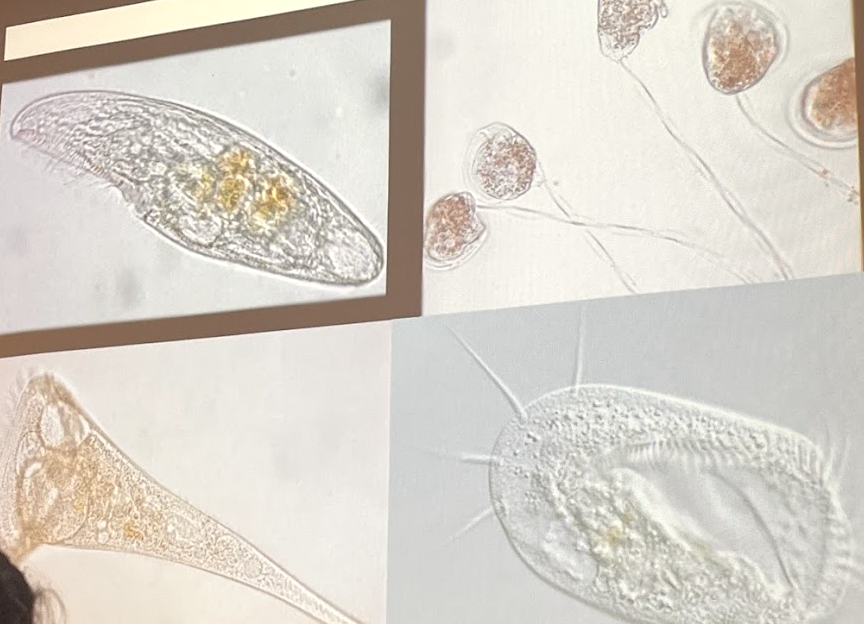
What phylum are these organisms in?
Phylum ciliophora
Approximately how many species are in Phylum Ctenophora?
~200
Describe Ctenophore body tissues:
Partly mesoglea (gelatinous substance made of proteins, carbs, etc.)
Have muscles that contract
Biradial/rotational symmetry
8 ctens/comb rows (plates of cilia glued together)
True or False: Ctenophores are mostly benthic, with one order that is planktonic.
False. The opposite is true.
Describe the ctenophore digestive system:
The ctenophore digestive system contains:
Mouth cavity
Pharynx
Stomach
Anal pores
For some: tentacles with colloblasts (sticky cells) to keep food down
Describe the ctenophore circulatory system:
Ctenophores don’t have a circulatory system
Describe the Ctenophore excretory and respiratory systems
They dispose of lipid waste through diffusion, and also respire through diffusion.
How do ctenophores reproduce?
They are monoecious (hermaphroditic) and make cydippid larvae.
Describe the ctenophore nervous system.
Ctenophores have nerve nets and a statocyst for balance and orientation.
True or False: Ctenophores use bioluminescence as self-defense.
True, they have a defensive flash.
True or False: genetic evidence suggests that Porifera were the first multicellular organisms, not Ctenophora.
False. Ctenophores are most likely the first multicellular organism.
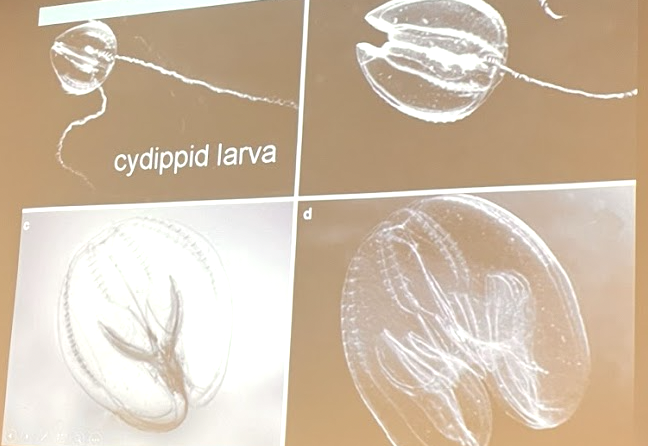
Describe order Cydippida within phylum Ctenophora.
Body shape is round with tentacles longer than body
Tentacles retract into sheaths when not hunting to avoid breakage
Planktonic
Larva looks like adult
What phylum and order is this organism in?
Phylum Ctenophora and Order Lobata.
Tentacles are short, lack a well-developed sheath
Planktonic
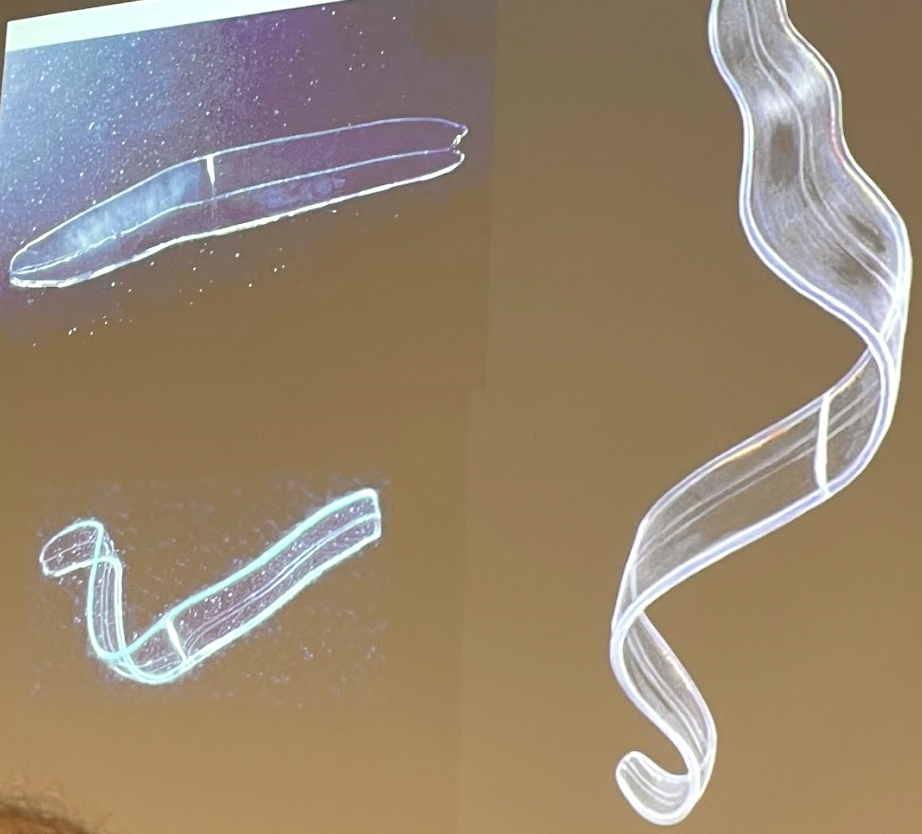

What Phylum and Order is this organism?
Phylum Ctenophora and order Cestida
very short tentacles, some have small sheaths
move with body undulations
Planktonic
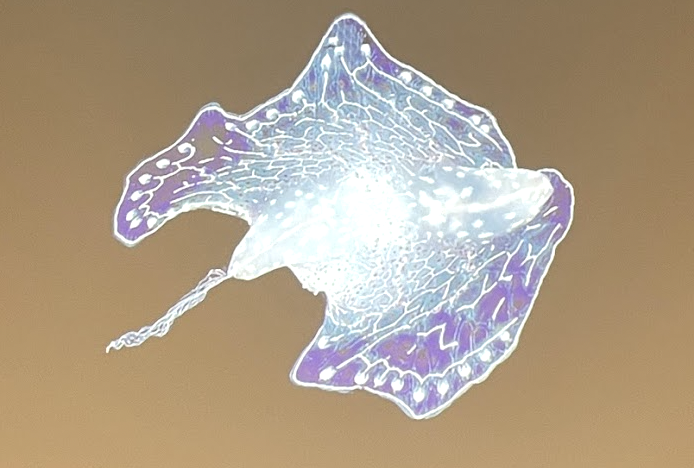
What phylum and order is this animal?
Phylum Ctenophora, Order Platyctenida
Several body shapes in this group
Short tentacles, small sheath
PRIMARILY BENTHIC
What order of ctenophores have no tentacles and are carnivorous to other ctenophores?
Order Beroida
Planktonic
Flat when swimming, mouth open when hunting.
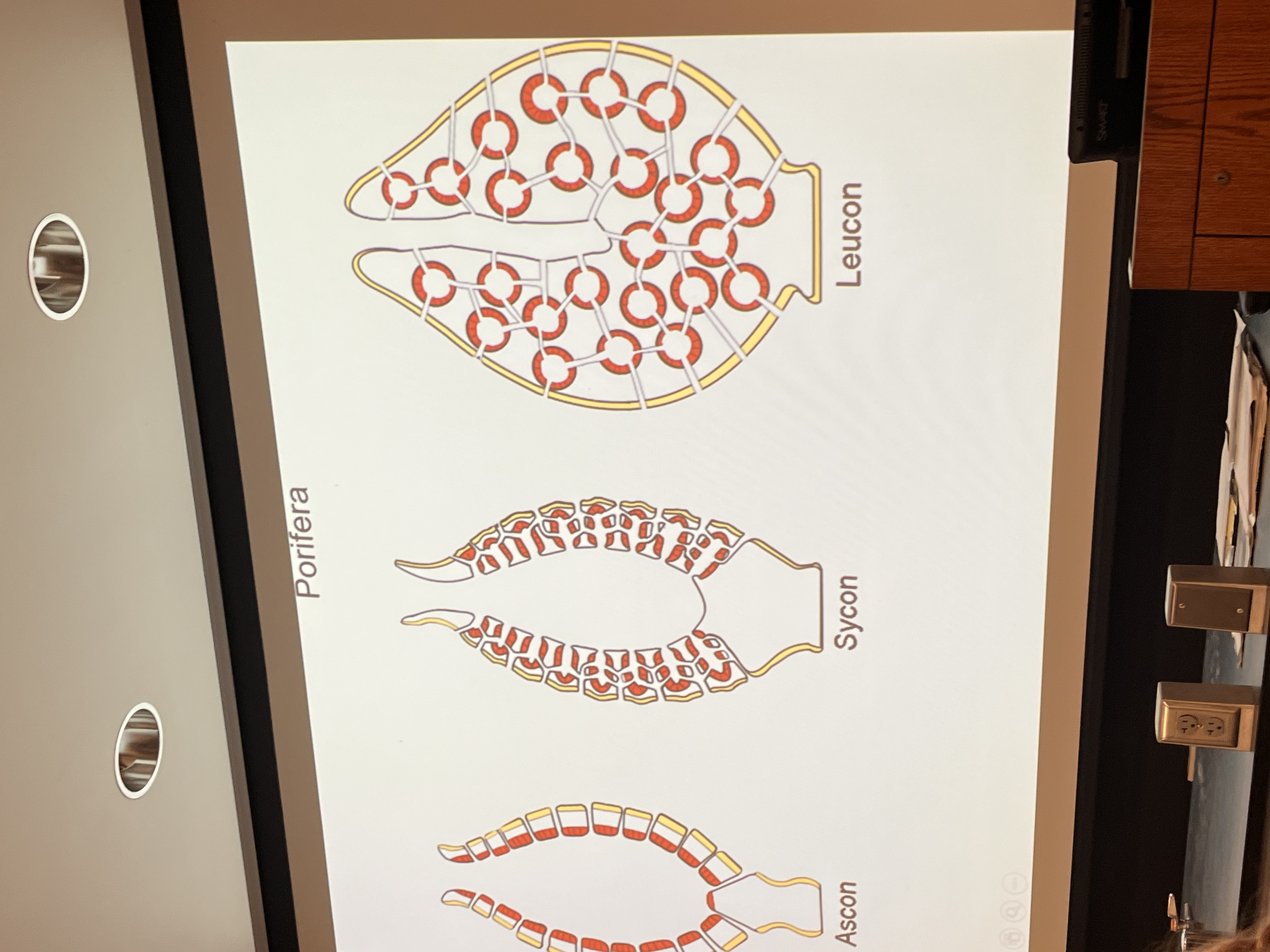
What are the three main proiferan body types?
Ascon
Sycon
Leucon (big sponges)
What habitat do poriferans inhabit?
Benthic, usually hard substrate
A few in mud
What is the poriferan digestion system?
They are micro filter feeders and use choanocyte feeding cells
What are the poriferan circulatory, excretory, and respiratory systems?
Circulatory: none
Excretory: diffusion
Respiratory: diffusion
How do poriferans reproduce?
They are monoecious/hermaphroditic and make larvae.
Larvae types (in class): Amphiblastula and Parenchymella
What is the ecology of poriferans?
eaten by some fish and turtles
biggest role is on the reefs: they can build or destroy reefs
boring sponges destroy
Larger sponges are homes for inverts
How does poriferan regeneration work?
Cells of the same species can recognize each other after being broken apart and come back together
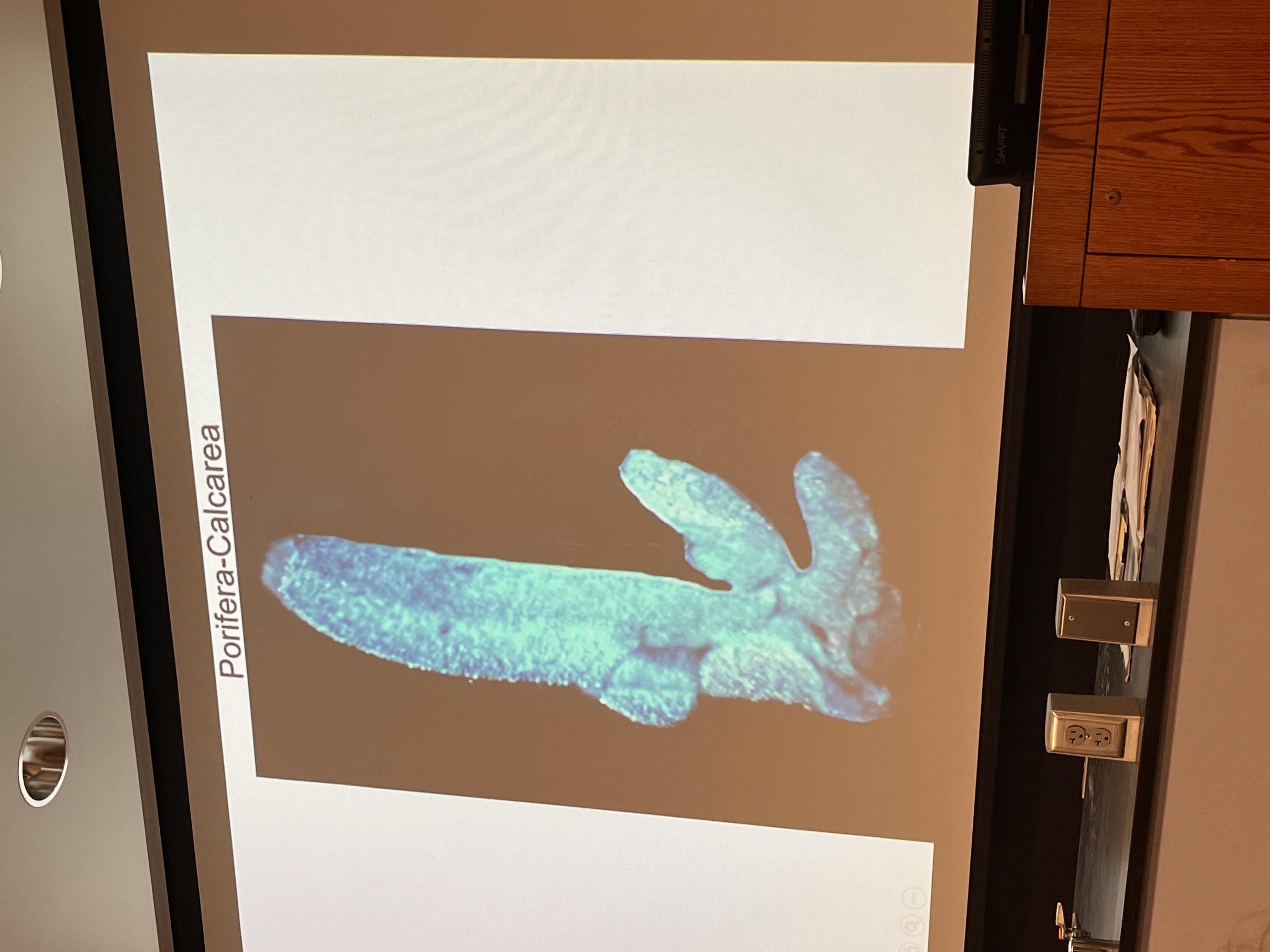
Describe class calcarea (phylum porifera)
Spicules = CaCO3
Spicules either 1, 3 or 4 rays
No spongin
Ascon, sycon, leucon
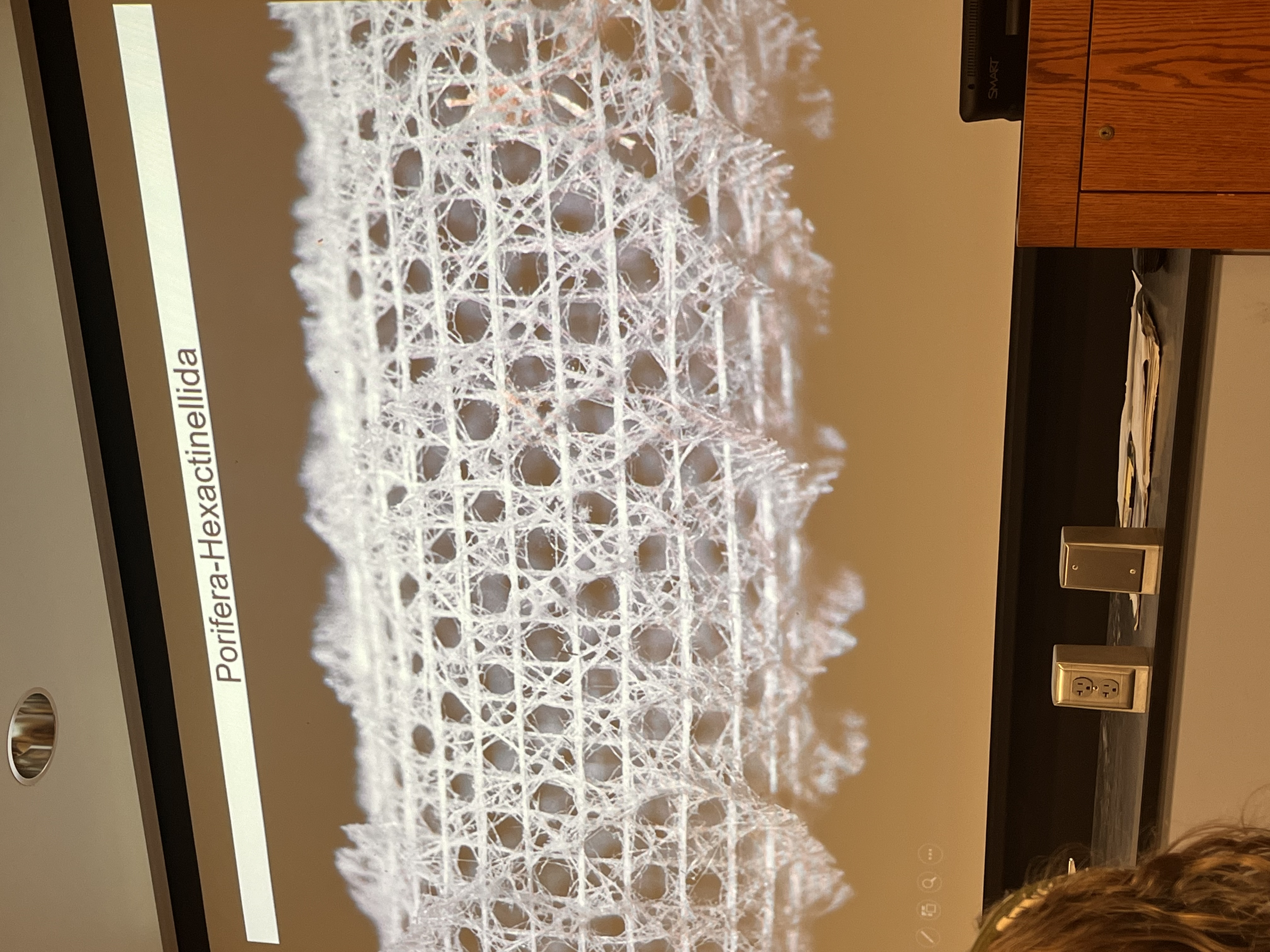

Describe class hexactinellida (phylum porifera)
“glass sponges” made of silica
6 rayed spicules
Mud anchor= fibers at bottom
Spongin absent
Body: sycon-leucon mix, NO PINACODERM
Deep water reef and mud habitats

Describe class homoscleromorpha (phylum porifera)
Spicules=silica
4 rays, no axial filament
Spongin absent
Body: leucon
Ecology: encrusting
Describe class Demospongiae (phylum porifera)
Spicules = silica
Less than 6 rays, WITH axial
some microscleres or megasclerer, some no spicules
Some have spongin
Body: leucon
Some carnivores: spicules snag zooplankton
Sclerosponges have a CaCO3 cover over silica spicules. What phylum and class are they in?
Phylum porifera, class demospongiae
What is the acid test for sponges?
The acid test is used to determine spicule composition. When put in acid, CaCO3 spicules dissolve, but silica don’t
How are sponge pumping rates measured?
By putting dye right by the sponge and watching it be pumped out of the sponge
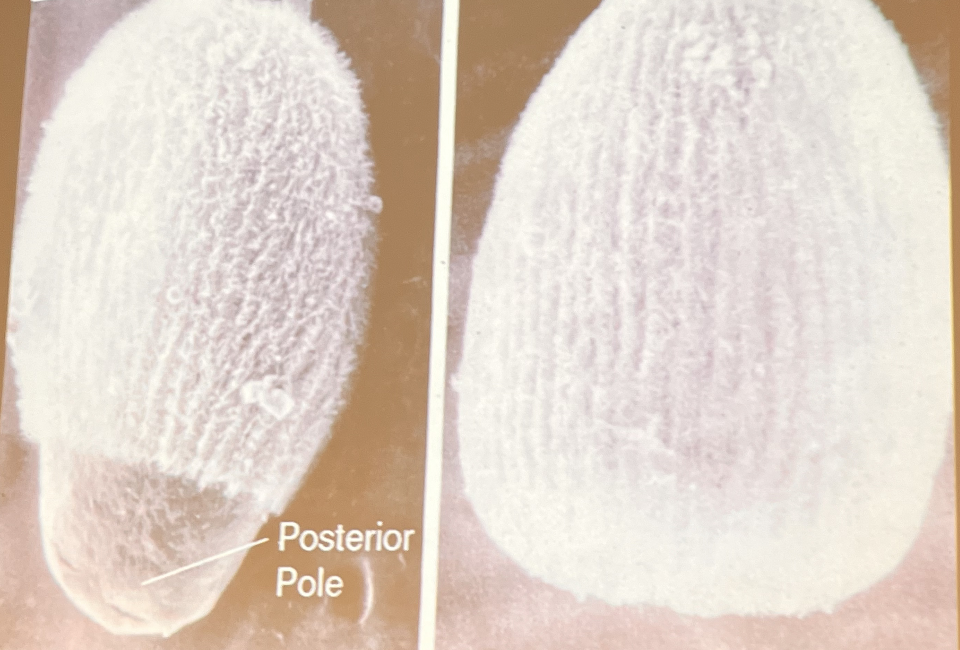
What type of larvae is this?
Parenchymella

What kind of larvae is this?
Amphiblastula
True or false: Ciliophores are primarily freshwater.
True, most of them live in freshwater, and they have two types of nuclei
Some ciliophorans have a lorica. What is a lorica?
A lorica is a hard covering, similar to a shell.
Describe the habitat, feeding, and ecology of ciliophores.
Habitat: Planktonic, benthic, and parasitic
Feeding: Micro omnivores
Ecology: lower part of food web
Describe Phylum Choanoflagellata
Body: Single cell, colony
Flagellum, lorica
Habitat: planktonic and benthic
Lead to metozoan