Chemistry 11 + 3.2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
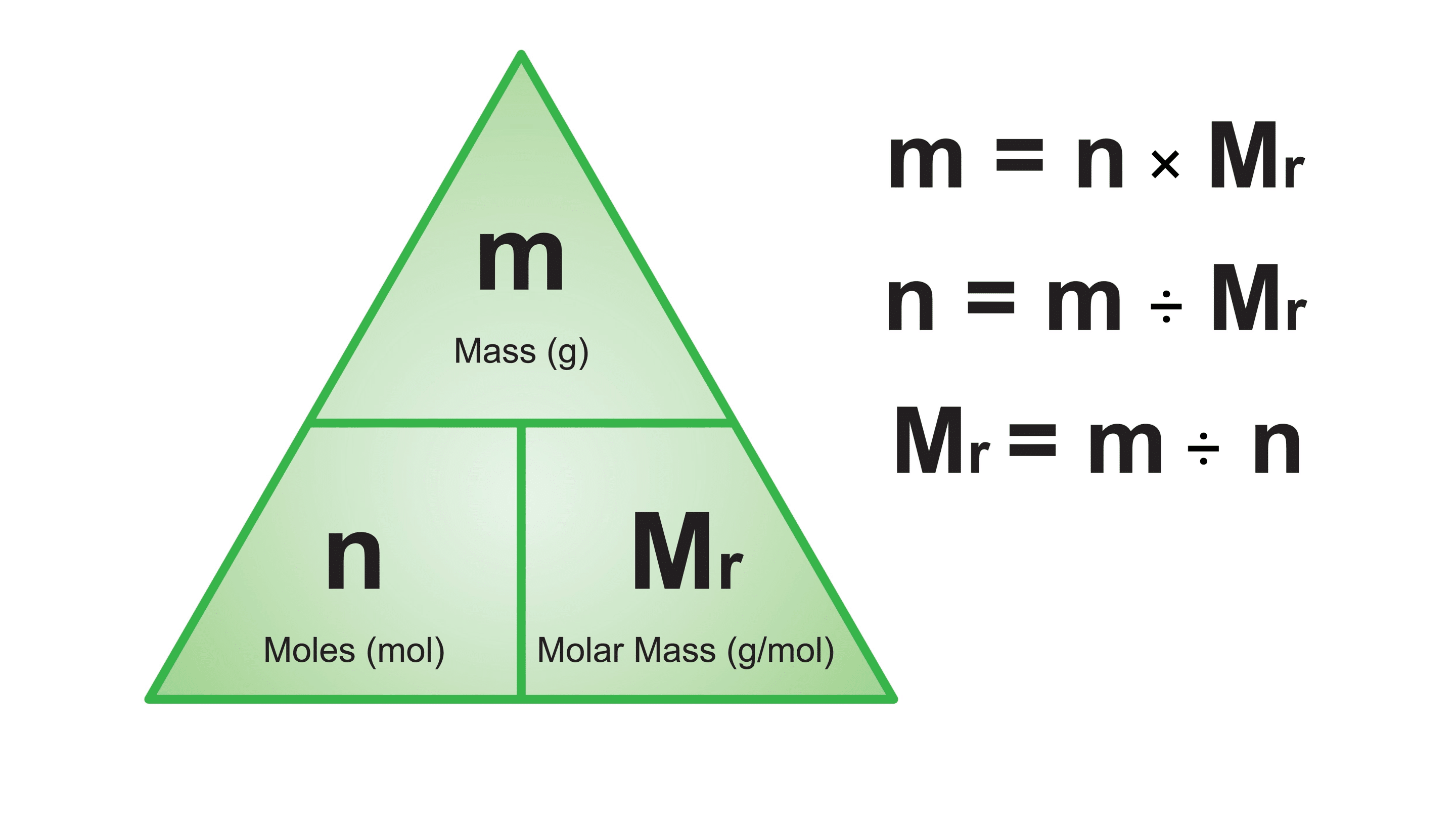
Formulas for mass, molar mass, and moles?
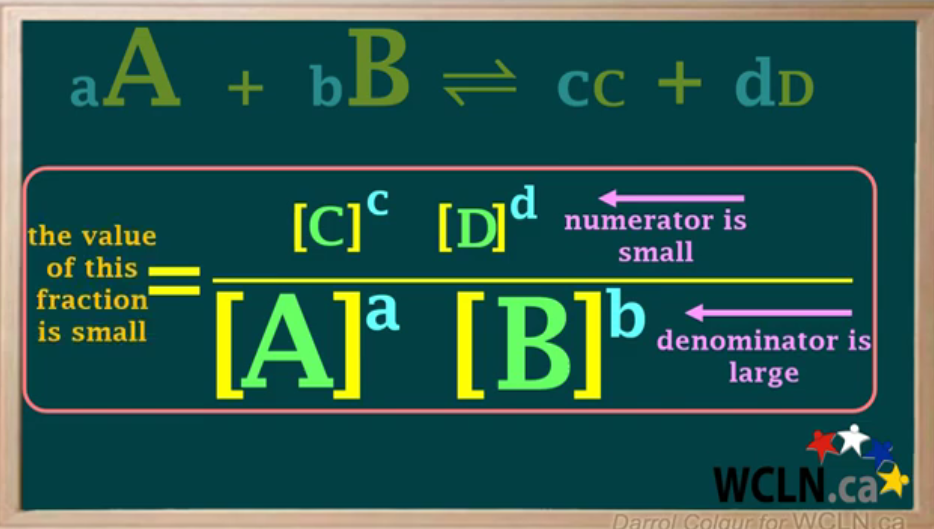
Equilibrium law:
aA + bB + … <—> xX + yY + …
Keq (equilibrium constant) = [X]^x [Y]^y / [A]^a [B]^b
![<p>aA + bB + … <—> xX + yY + …</p><p>Keq (equilibrium constant) = [X]^x [Y]^y / [A]^a [B]^b</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/85f4ffde-a70b-4f8e-b22b-b7a72095d448.png)
What substances’ concentrations cannot change?
Solids and solvent
What is the concentration representing any substance whose concentration cannot be changed?
1
What happens to Keq when temperature changes?
It changes, too.
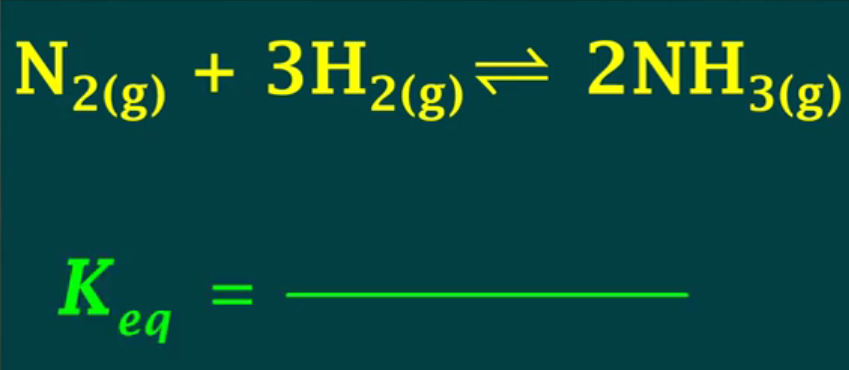
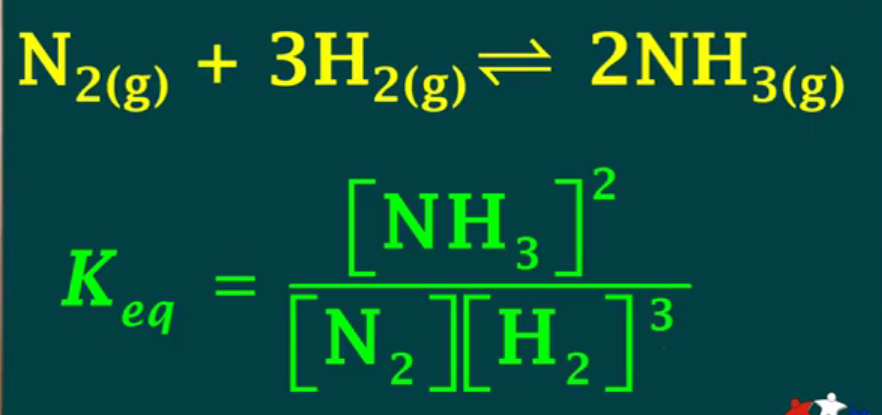
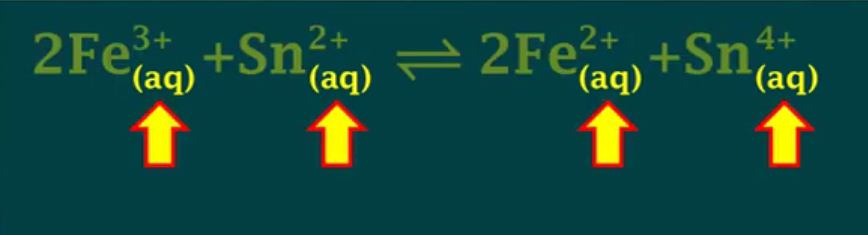
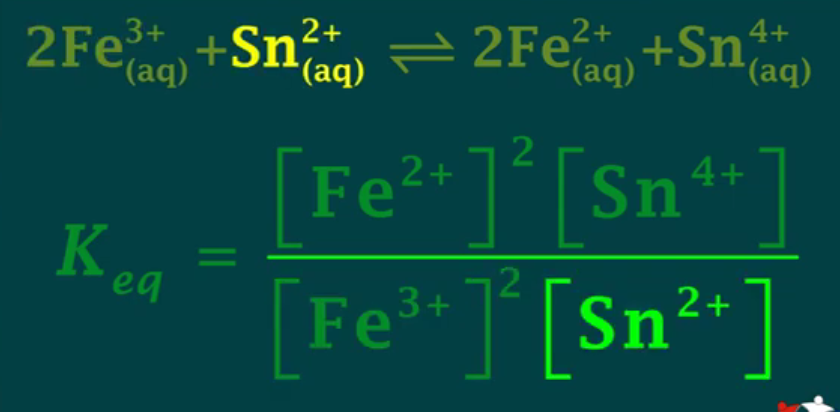
Keq works for:
Concentrations of gase that can be changed.
How to increase concentration?
Constant temperature
Increase pressure
Decrease volume
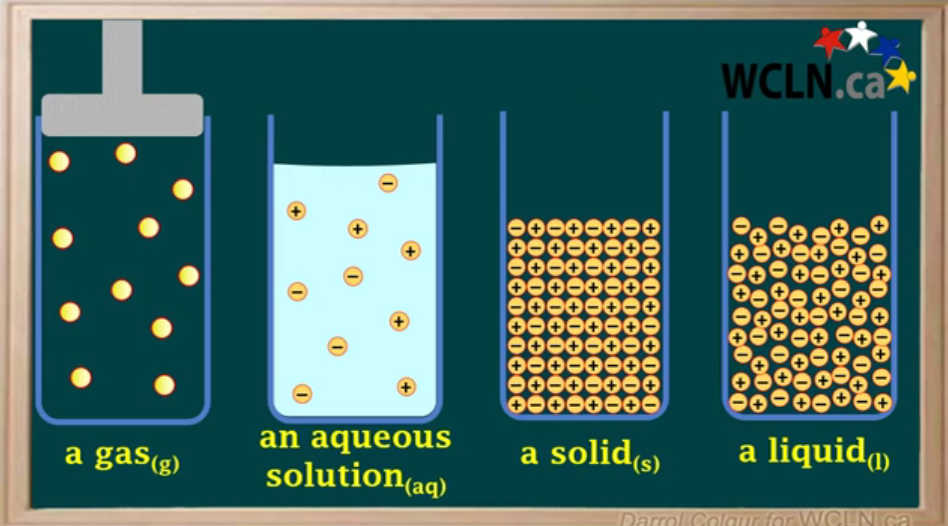
Which of these are used in equilibrium? (Concentrations can change).
Gas
Aqueous
Gas
Aqueous
Solid
Liquid
Used:
Gas: The concentration can be changed (decreasing volume/increasing pressure = concentration increases) (increasing temperature = concentration decreases)
Aqueous: Adding ionic compounds will increase concentration.
Not used:
Solid: Can’t be compressed.
Liquid: Concentration is constant, so compression is neglected.
Find Keq of: CaCO3(s) ←→ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Keq = [CO2(g)]
Find Keq of: 2Au(aq) + 3Cu(s) ←→ 2Au(s) + 3Cu(aq)
Keq = [Cu(aq)]³ / [Au(aq)]²
Find Keq of: CH3CH2OH(aq) ←→ CH3CH2OH(l)
Keq = 1 / [CH3CH2OH(aq)]
How does Keq get larger? Smaller?
Keq gets larger when numerator (product) is higher than denominator (reactants).
Keq gets smaller when numerator (product) is smaller than denominator (reactants).
Keq small —> reactants are higher
Keq large —> products are higher
;)

Keq changes when:
Switch reaction
Change temperature
Change the form of equation
Draw formula when Keq is large.
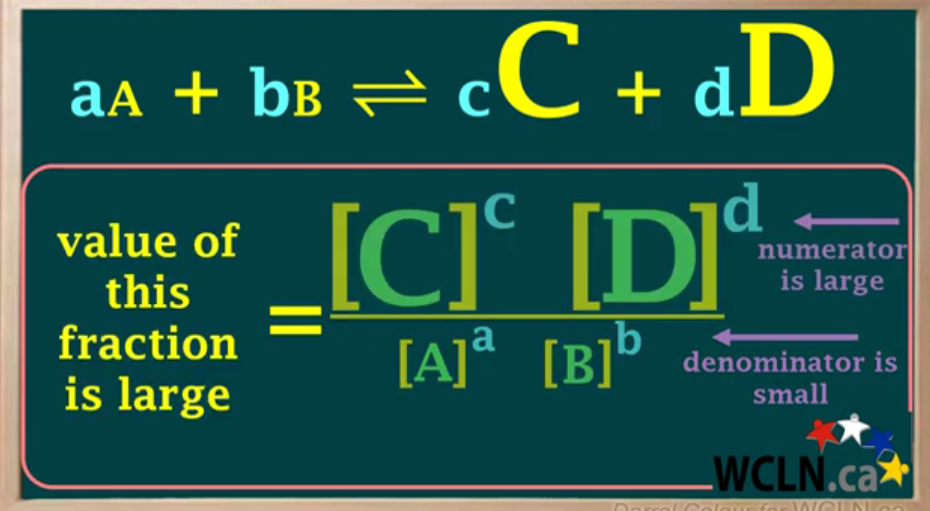
Draw formula when Keq is small.
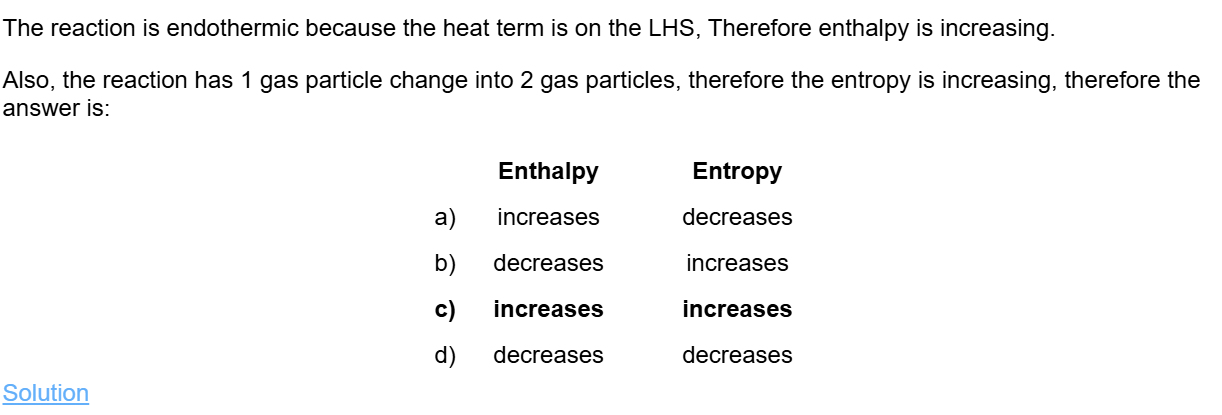
What happens when temperature increases in endothermic reaction?
Equilibrium shifts to the right, which increase products, which increases the Keq.
What happens when temperature decreases in endothermic reaction?
Equilibrium shifts to the left, which increases reactants, which decreases the Keq.
What happens when temperature increases in exothermic reaction?
Equilibrium shifts to the left, which increases reactants, which decreases the Keq.
What happens when temperature decreases in endothermic reaction?
Equilibrium shifts to the right, which increase products, which increases the Keq.
The only factor that changes Keq is TEMPERATURE!
Bora Dogrusuz ladies and gentleman!

What do we do to the Keq when equation is reversed?
Keq is reversed (reciprocal).
What do we do to the Keq when coefficients in equation are doubled?
Keq is squared (exponent 2).
What do we do to the Keq when coefficients in equation are tripled?
Keq is cubed (exponent 3).
What do we do to the Keq when coefficients in equation are halved/multiplied by ½?
Find square root of Keq.
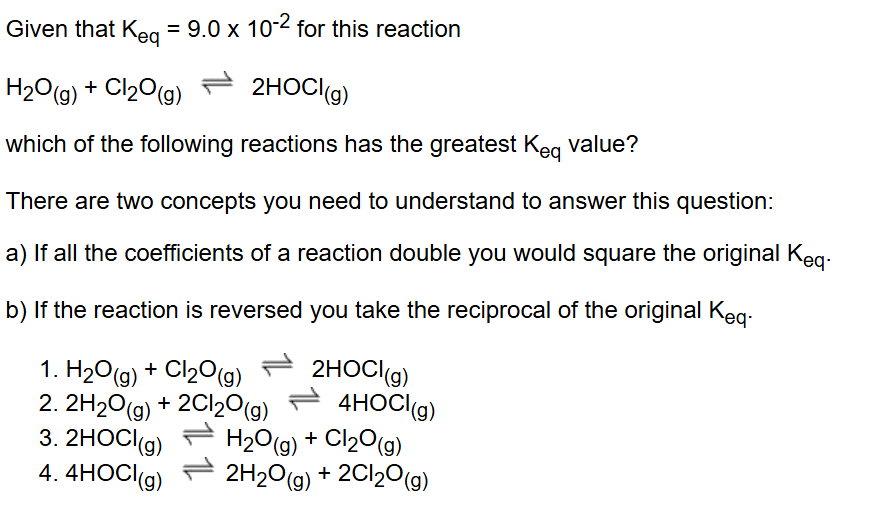
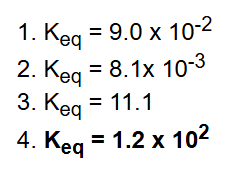
What are the four laws of Thermodynamics?
“Temperature (T) makes sense”
The law of conservation of energy
The principal of entropy (S)
Absolute zero exists
“Temperature (T) makes sense”
Temperature is a measure of average molecular speed.
As temperature increases, the average molecular speed increases.
To really make sense, temperature must be measured in Kelvins.
The law of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change form.
The principal of entropy (S)
Increased entropy can occur in three different ways in a chemical reaction
1.
Entropy is a measure of disorder.
Whenever energy changes form, some of that energy will result in the production of heat which dissipates in the surroundings.
Heat speeds up molecules and increases disorder. As events occur, the entropy of the universe always increases.
2.
If the phase changes from solid to liquid to gas
If a solid dissolves
If the number of particles increases
Absolute zero exists
Particles in a system cannot move more slowly than “full stop”. This condition occurs at –273 °C or 0 K.
Two Natural Tendencies:
Chemical reactions are exothermic. Go toward minimum enthalpy.
Chemical reactions have more disorder. Go toward maximum entropy.
What does S represent? H?
S —> Disorder (entropy)
H —> Heat content (enthalpy)
On which side is minimum enthalpy in endothermic reactions?
Reactants (favored in endothermic)
On which side is minimum enthalpy in exothermic reactions?
Products (favored in exothermic)
Entropy of solid and why.
Low entropy because solid is very ordered.
Entropy of liquid and why.
More entropy than solid because liquid is less ordered.
Entropy of aqueous and why.
More entropy than solid and liquid because aqueous is a mixture.
Entropy of gas and why.
Most entropy because gas is random.
Which side will entropy favor: less gas particles —> more gas particles.
Products (right)
Which side will entropy favor: more gas particles —> less gas particles.
Reactants (left)
What happens when both minimum enthalpy (H) and maximum entropy (S) favor reactants?
No reaction occurs when reactants are mixed.

What happens when both minimum enthalpy (H) and maximum entropy (S) favor products?
Reaction will go to completion when reactants are mixed.
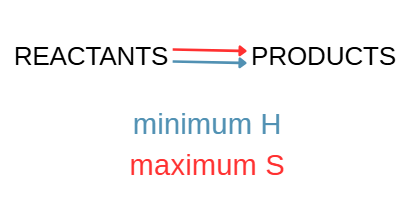
What happens when minimum enthalpy (H) favors reactants and maximum entropy (S) favor products?
Reaction reaches equilibrium when reactants are mixed.

What happens when minimum enthalpy (H) favors products and maximum entropy (S) favor reactants?
Reaction reaches equilibrium when reactants are mixed.

Which of those are spontaneous?
They are all spontaneous except when minimum enthalpy and maximum entropy favor reactants (no reaction).
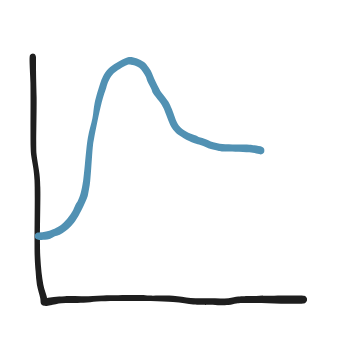
Which side does minimum enthalpy favor?
Which side does maximum entropy favor?
What happens when reactants are mixed?
Is it spontaneous or not?
Reactants (lowest enthalpy)
Products (entropy favors products in endothermic)
Reaction reaches equilibrium
Spontaneous
Which side does minimum enthalpy favor?
Which side does maximum entropy favor?
What happens when reactants are mixed?
Is it spontaneous or not?
Products (lowest enthalpy)
Products
Reaction reaches completion
Spontaneous
What does spontaneous mean?
Needs to lead to product formation.
Entropy > Heat = Favorable
Entropy < Heat = Unfavorable




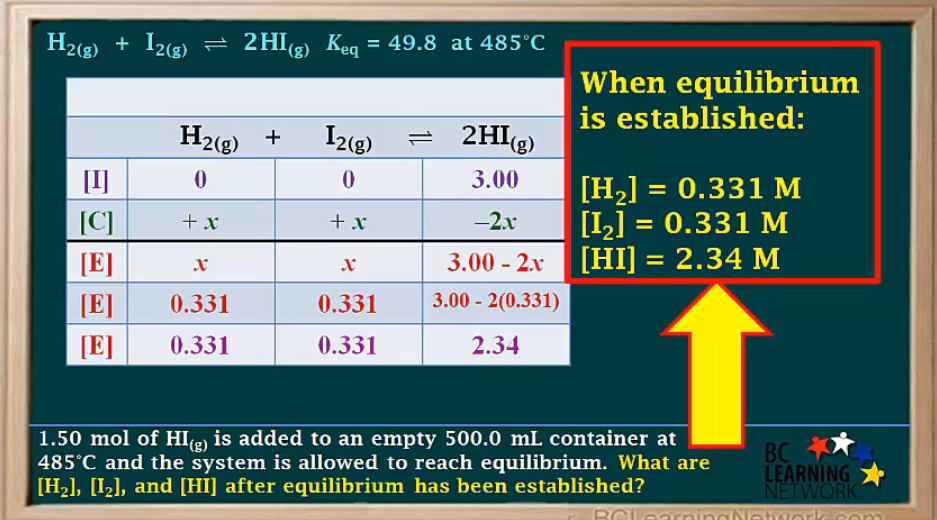
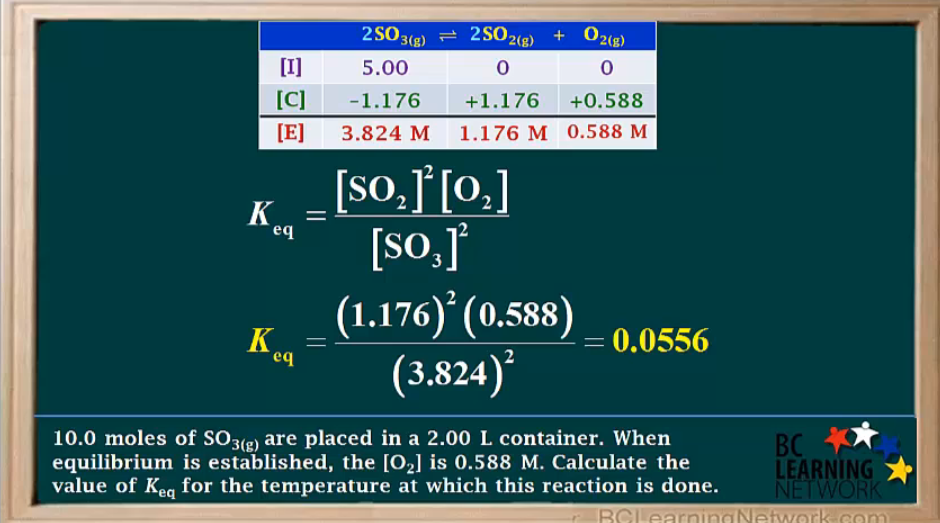
Keq = 2.67×10³
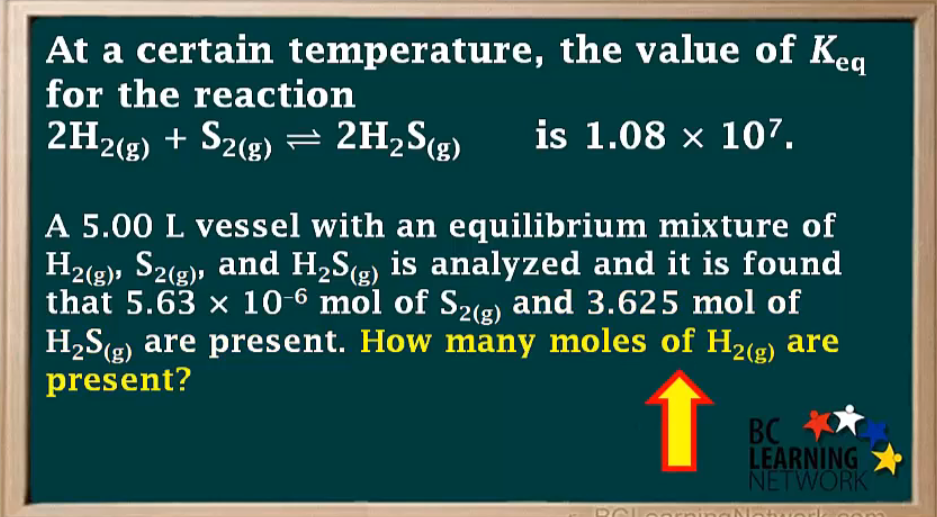
1.04 mol H2


a)


b)

c)