ITC PART 2: DENTAL INSTRUMENTS
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
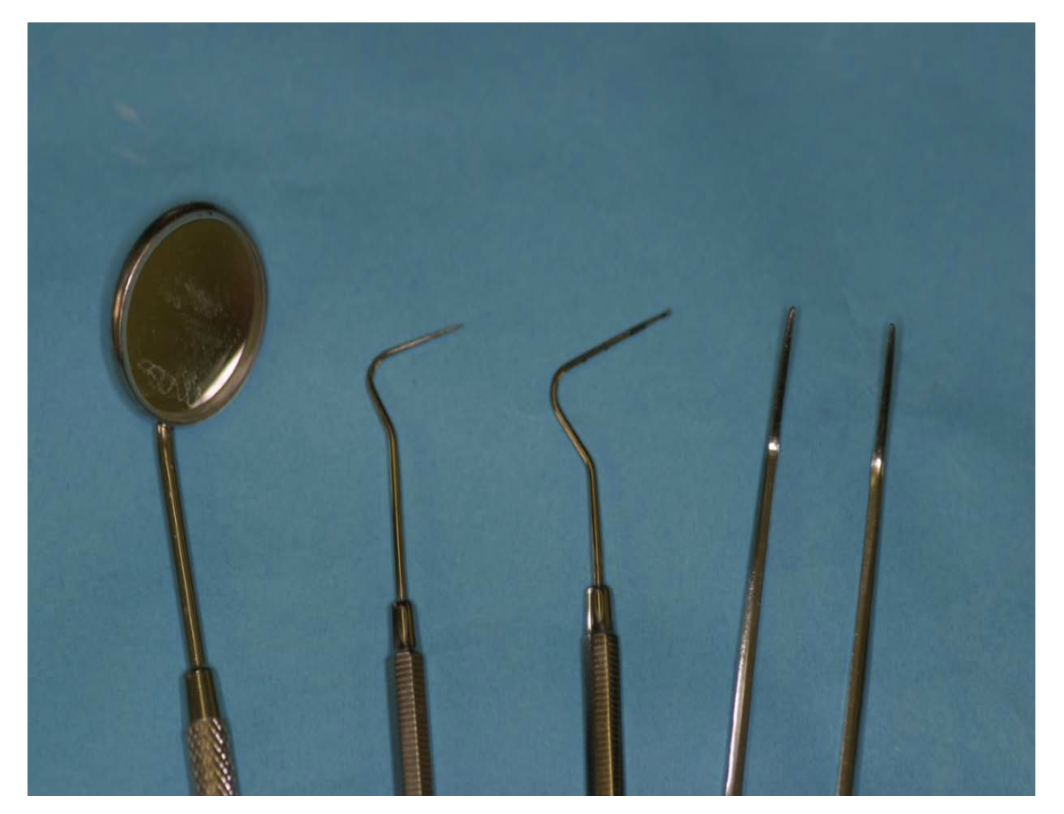
what instruments are in a basic examination kit and what are their functions
dental mirror - allows indirect vision and retraction of soft tissues
dental probes
sharp: checking restoration margins and assessing roughness of tooth and restoration surfaces
blunt: WHO/ Williams/ UNC15 are used for periodontal examination, straight
college tweezers - to place cotton wool rolls and remove large pieces of intraoral debris
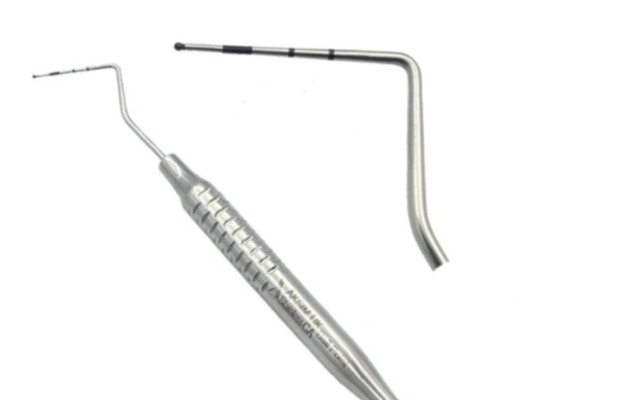
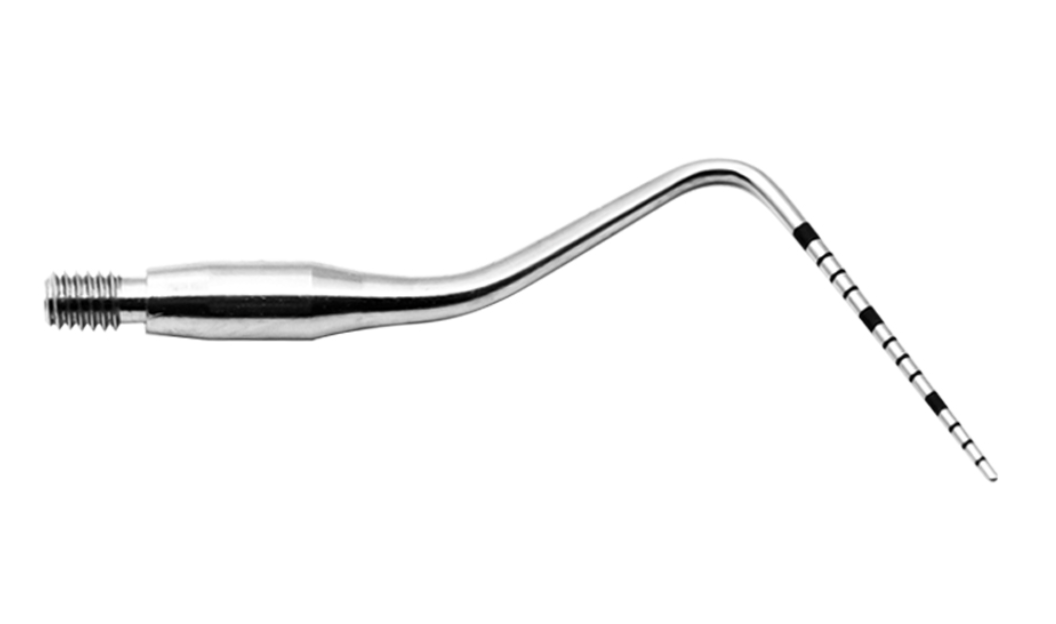
WHO probe/ BPE probe
has a 0.5mm ball at the end
markings at 3.5, 5.5, 8.5 and 11.5mm
used in BPE
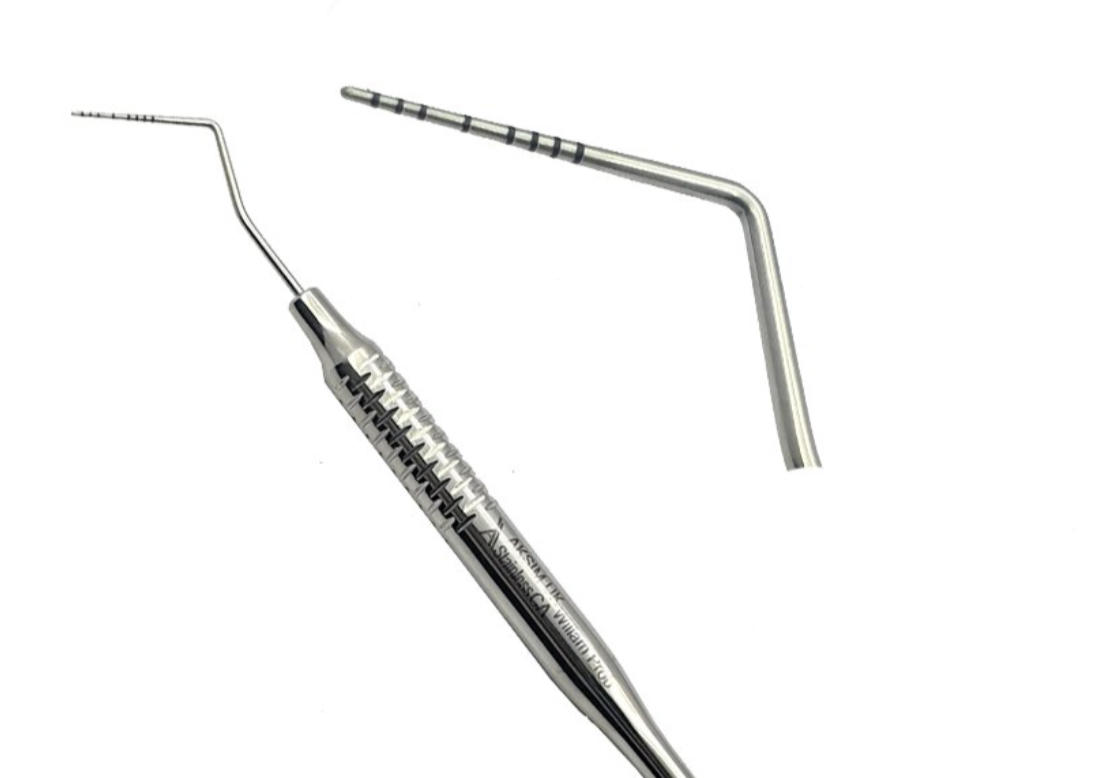
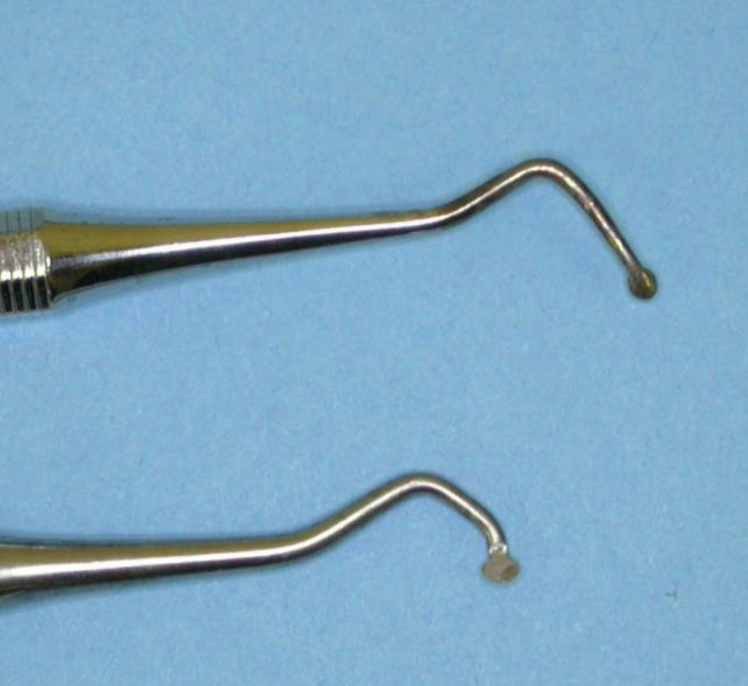
Williams probe
grooves/ markings at 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10mm (4 and 6mm markings are missing to avoid confusion when reading)
commonly used to measure periodontal pocket depths

UNC15 probe
slightly thicker than Williams probe
assesses periodontal pocket depth
15mm probe with 1mm markings from 1-15mm
4-5mm, 9-10mm, 14-15mm markings are shaded

what instrument is this and what is its function
excavators
sharpened cutting edge on a discoid/ ovoid blade
removes caries and temporary restorations
can also be used to carve amalgam restorations
available in different sizes
usually double ended

chisels, hatchets and hoes function
chisels, hatchets and hoes
used to remove unsupported enamel at the cavity margins (cavity preparation)
seldom used now
chisels VS hatchets
chisel: the cutting edge is perpendicular to the instrument handle
hatchet: the cutting edge is parallel (or close to parallel) to the instrument handle
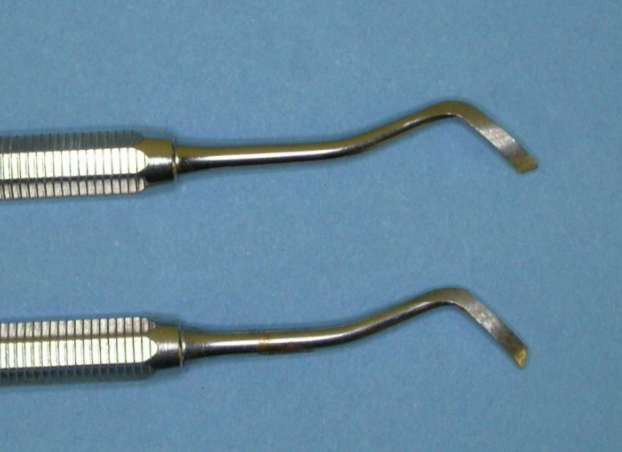
what instrument is this and what is its function
gingival marginal trimmer
used to remove unsupported enamel margins (cavity preparation)
comes as a set of two instruments with curved blades
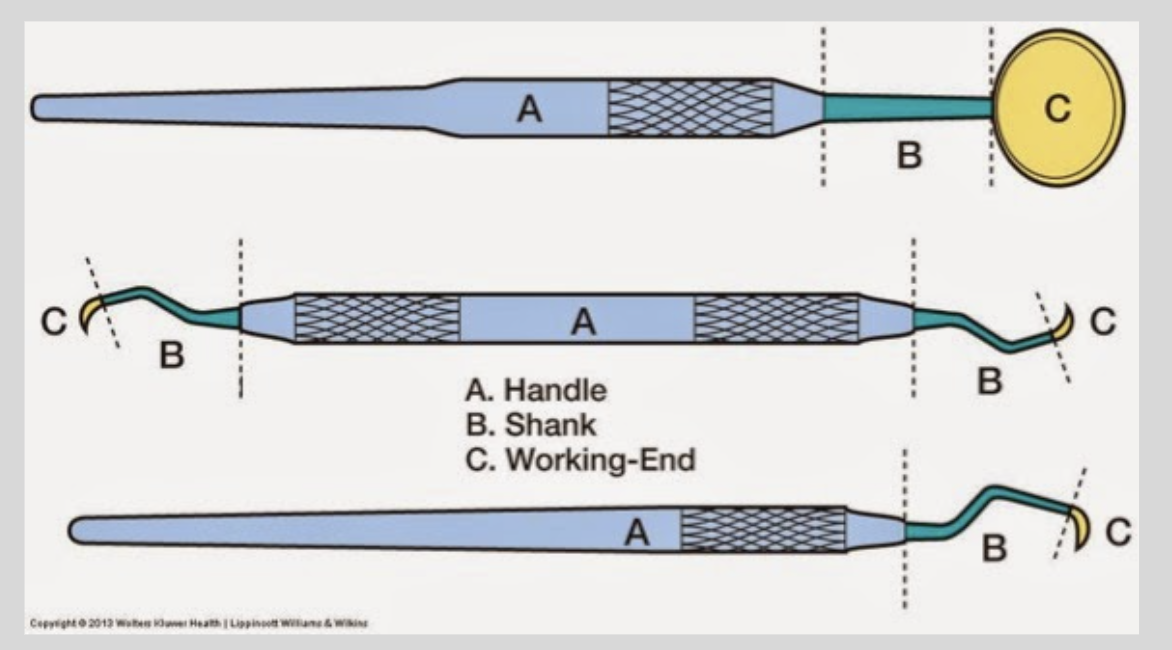
what is the design of hand instruments
most are stainless steel or carbon steel
may have tungsten carbide tips on cutting edge to retain sharpness for longer
3 parts: blade, shank, handle
primary cutting edge is at the end of the blade
instruments have a number of bends in the shank to allow access to different areas of mouth
handle may be serrated to enhance grip
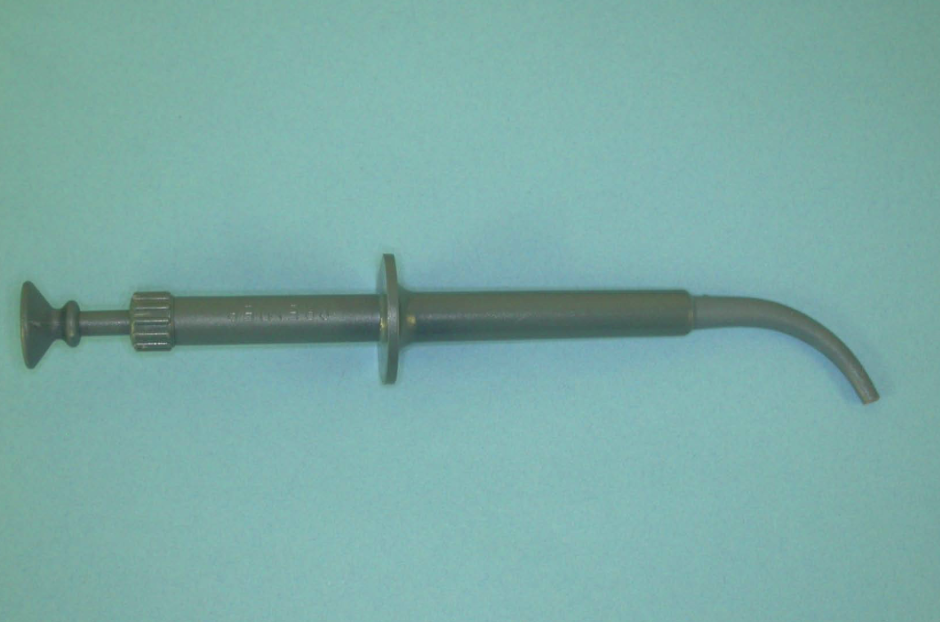

what instrument is this and what is its function
amalgam carrier
convey mixed amalgam alloy to express into prepared cavity
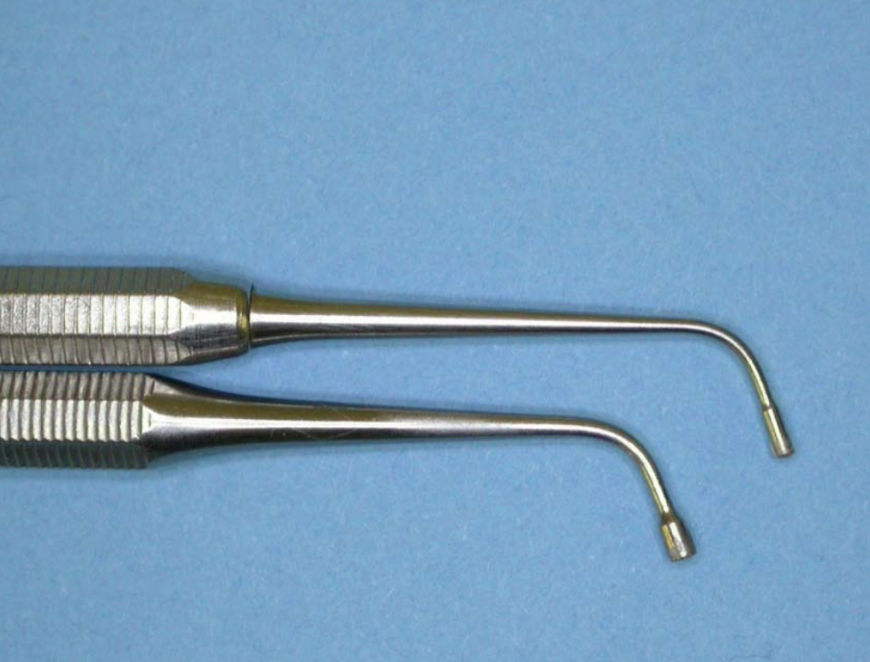
what instrument is this and what is its function
amalgam condensers
also known as pluggers/ packers
instrument for packing plastic restorative materials into cavities under pressure and eliminating voids
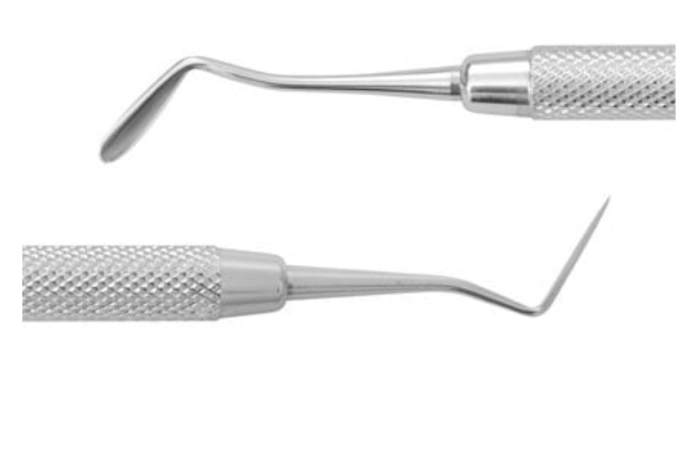
what instrument is this and what is its function
carvers
semi-sharp blades
carve the shape of a restoration by a scraping action
different patterns e.g. Wards, Frahm, Hollenback
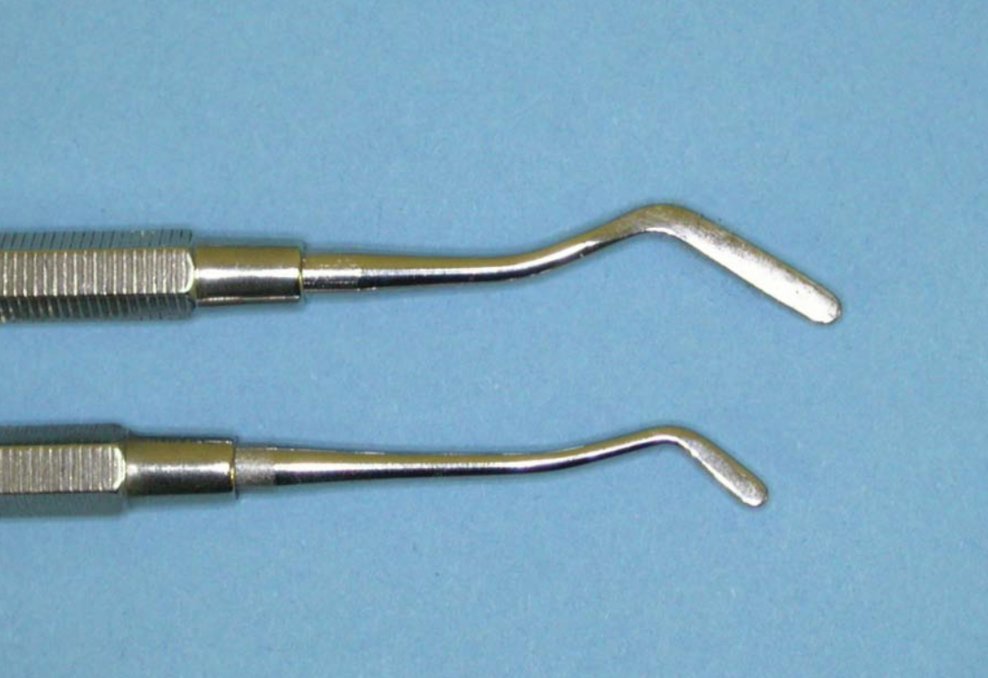
what instrument is this and what is its function
flat plastic
used for conveying, placing and shaping plastic materials not requiring heavy pressure
usually made of stainless steel, may be Teflon-coated for composite placement
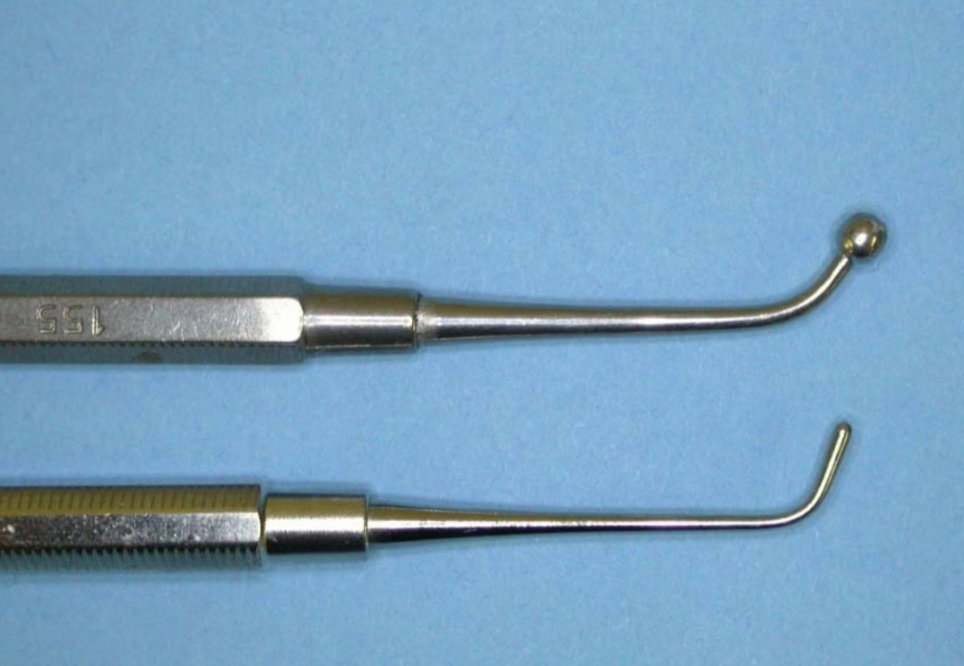

what instrument is this and what is its function
burnishers
round ended smooth surfaces for using straight after a filling to bring mercury rich amalgam to the surface
also used to place and shape composite restorations so they are functional and aesthetically pleasing
state types of rotary instruments
burs
files
stones
discs
ALL ROTATED IN HANDPIECES
how can rotary instruments be powered
compressed air
electric motor
what are the types of handpieces
high speed: air rotor
low speed: contra-angle or straight
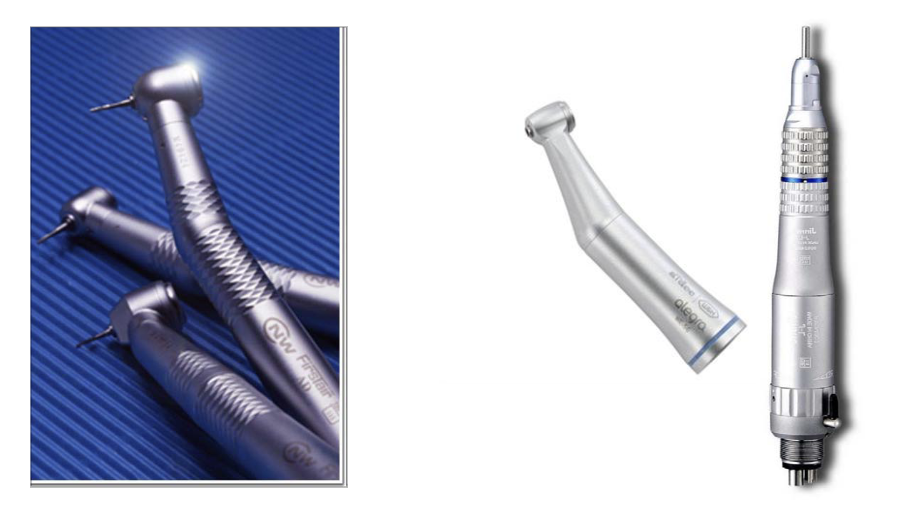

what instruments are these and what is its function
dental burs
used with high and slow speed hand pieces
cut, shape and polish hard tissues - prep. for restorative work
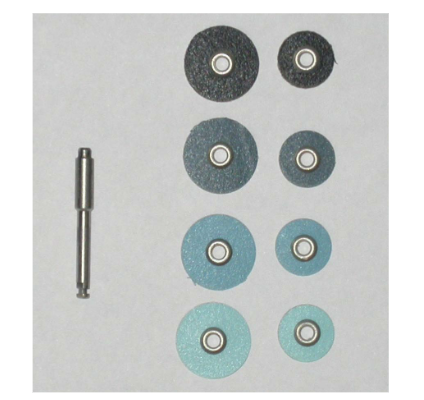
what instruments are these and what is its function
dental discs
used with slow speed hand pieces
removing hard tissues during procedures like crown preparation
finishing and polishing restorations
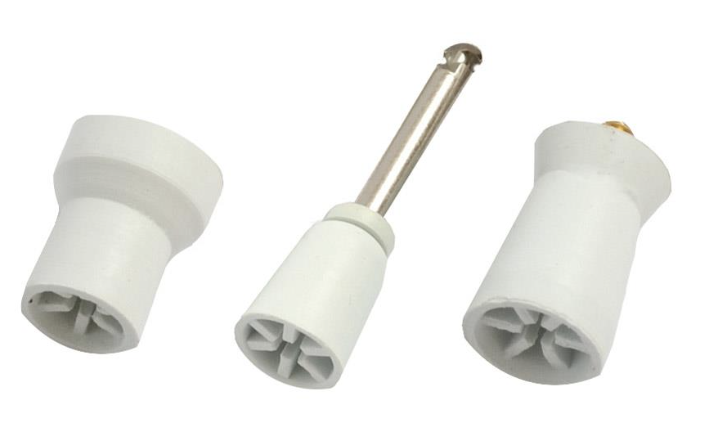

what instrument is this and what is its function
dental polishing cup
used with low speed hand piece
remove surface stains, plaque and smooth tooth surfaces

what instruments are these and what is their function
dental (polishing) stones
used with slow and high speed hand pieces
used to shape, contour and polish dental restorations
different colours are used for different material restorations
what instruments are used in oral surgery
oral surgery: extractions
elevators or luxators are often used first to loosen the tooth in its socket
elevators pry teeth out of their sockets
luxators separate teeth from surrounding soft tissues
extraction forceps come in various shapes and sizes depending on the tooth being extracted
sign on disposable instruments

give examples of disposable instruments
matrix bands
files
reamers - shape root canals
aspirators
3-in-1 plastic syringe tips
impression trays
mouthwash cups
absorbent patient bibs
rubber prophylaxis cup
what is the procedure if a dental instrument breaks
check oral cavity
try to retrieve the broken instrument with tweezers or suction
senior nurse and supervising tutor must be informed
if you suspect the patient may have aspirated or swallowed it a chest X-ray is required
inform the patient of the situation and document it in their records
fill in a Datix form
fractured endodontic instruments during a root canal treatment
if a file fractures you must always inform the patient and document it in their notes
it is recommended that an X-ray of the tooth be taken to verify the location of the file within the root canal
depending on where the file is it may be better to monitor the tooth
other times it may be necessary to remove the file or refer the patient to a specialist endodontist
needle breakage during administration of local anaesthesia
it is possible for an anaesthetic needle to break particularly if it has been bent
inform the patient of what has occurred
document it in the patient’s notes
unless the needle is sticking out of the tissue an oral and maxillofacial surgeon must be contacted to have the patient seen immediately for its removal