Chapter 10 - Stockholders' Equity
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
retained earning’s calculation
beg. retained earning
+net income
-dividend
=ending retained earning
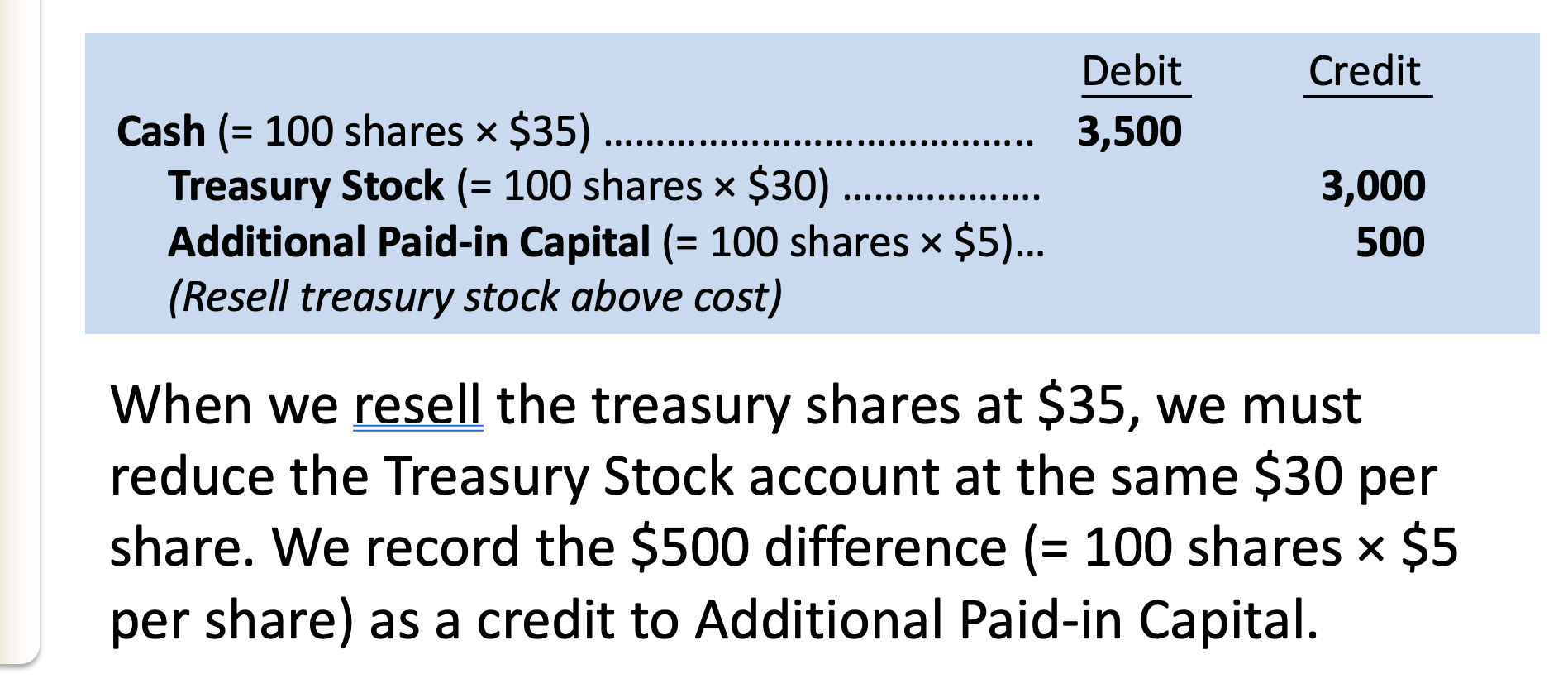
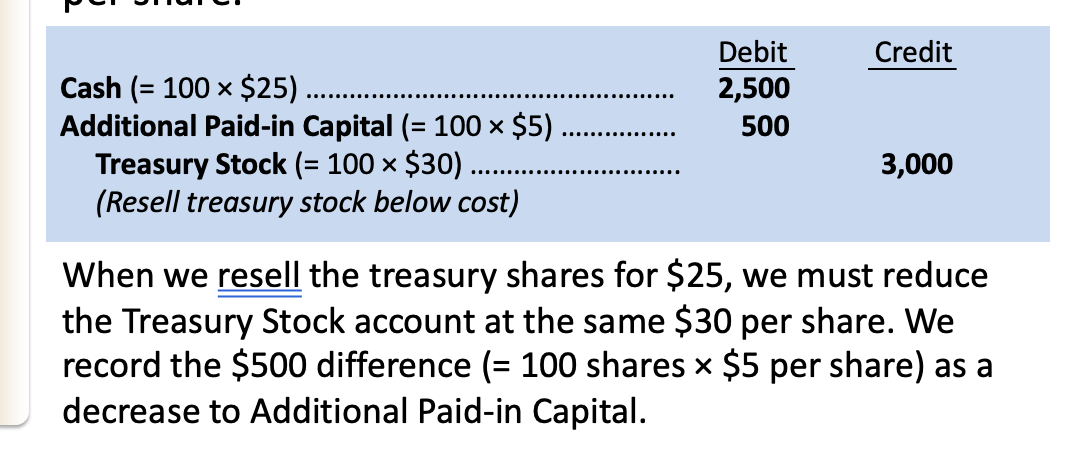
treasury stock
contra equity account - BS & SE
advantages of corporation
limited liability
ability to raise capital and transfer ownership
disadvantages of corporation
additional taxes
more paperwork
only pay dividends to _____
outstanding stocks
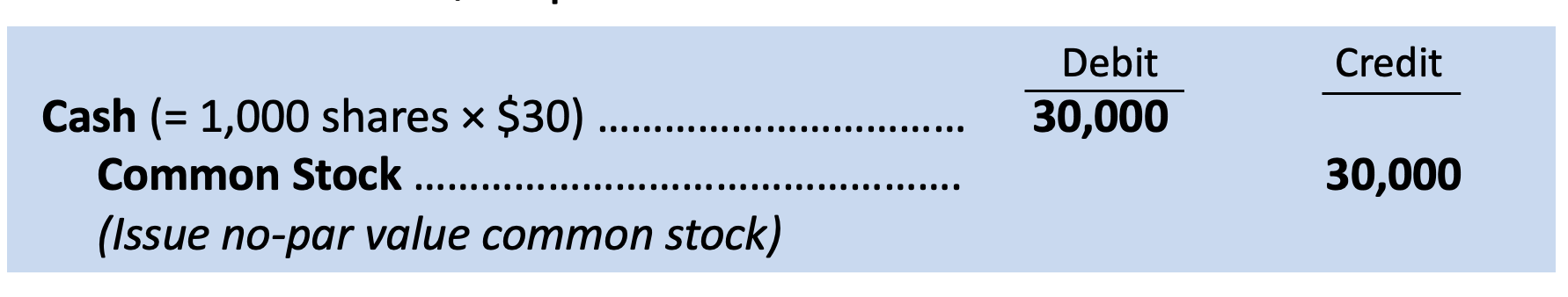
legal capital per share of stock that’s assigned when the corporation is first established
par value

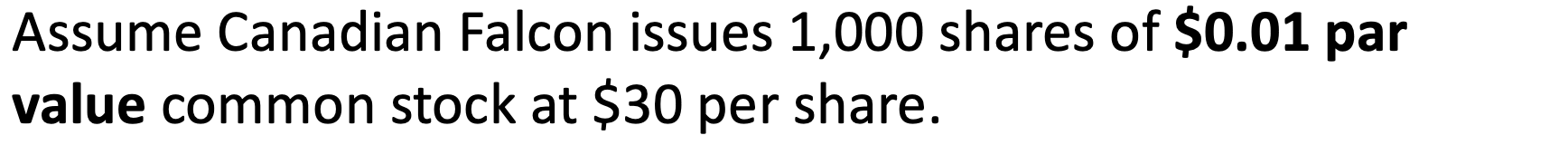
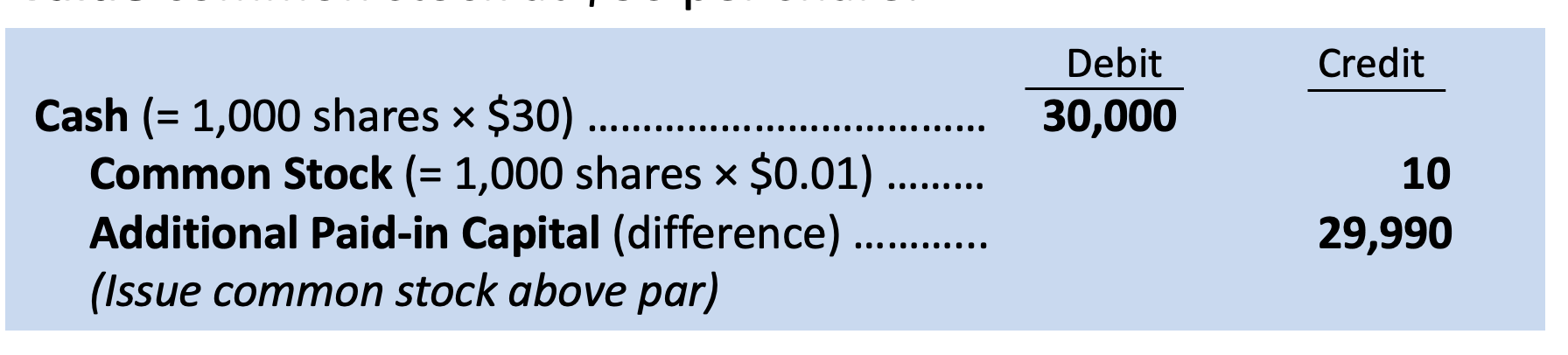
right to vote
right to receive dividends
right to share in the distribution of assets
stockholder rights
_____ stock do not have a right to vote
preferred
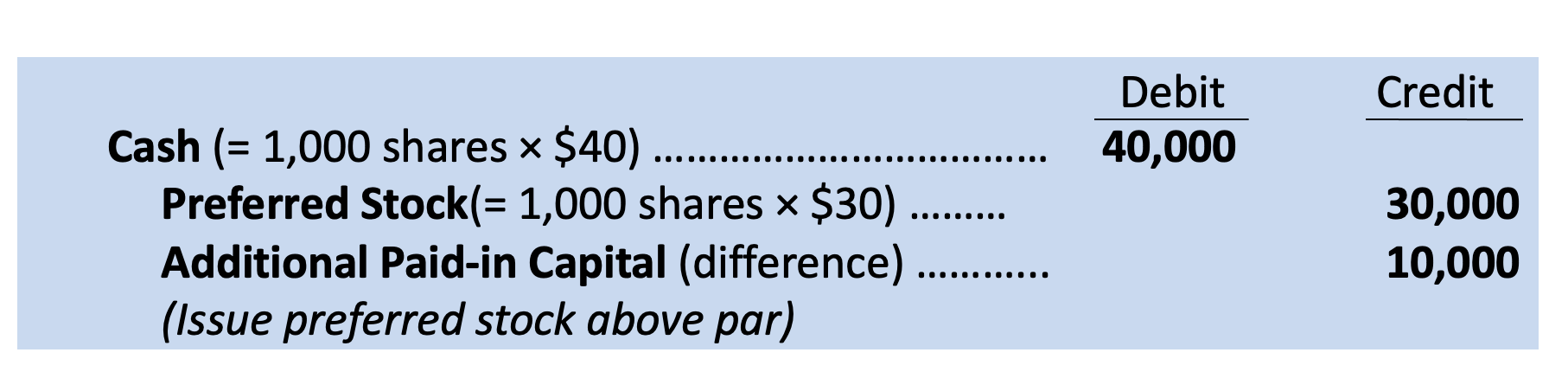
Preferred stockholders usually have first rights to a specified amount of dividends.
Preferred stockholders receive preference over common stockholders in the distribution of assets in the event the corporation is dissolved.
Preferred stock is “preferred” over common stock in these two ways.

Features of Preferred Stock: Shares can be exchanged for common stock.
convertible
Features of Preferred Stock: Shares can be returned to the corporation at a fixed price.
redeemable
Features of Preferred Stock: Shares receive priority for future dividends if dividends are not paid in a given year.
cumulative
To boost underpriced stock
To distribute surplus cash without paying dividends
To boost earnings per share
To satisfy employee stock ownership plans
reasons why companies buy back their own stock
Treasury stock is the purchase of a corporation’s own stock, and we record it as a _____ in stockholders’ equity. It is not an asset; a company cannot invest in itself.
reduction

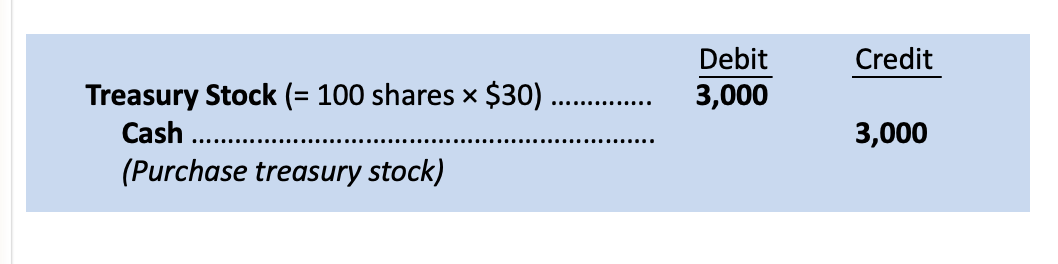


Earnings retained in the corporation and not paid out as dividends
Equals all net income less all dividends, since the company began operations
Has a normal credit balance
retained earnings
_____ represent all net income, less all dividends, since the company began operations.
retained earnings
Distributions by a corporation to its stockholders
A change in a quarterly or annual cash dividend paid by a company can provide useful information about future prospects
Not all companies pay dividends; for example, growth companies prefer to reinvest earnings rather than distribute them
cash dividends
Dividend Dates: Date on which board of directors announces the next dividend to be paid.
declaration date
Dividend Dates: The date on which the company looks at its records to determine who the stockholders of the company are.
record date
Dividend Dates: The date of the actual distribution of dividends.
payment date
Dividends are based on the number of _____ shares since dividends are not paid on treasury stock.
outstanding




has no journal entries
record date
How does the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet differ from the statement of stockholders' equity?
The stockholders' equity section shows the balances at a point in time and the statement of stockholders' equity shows activity over time.
Measures the ability of company management to generate earnings from the resources that owners provide.
return on equity
return on equity formula
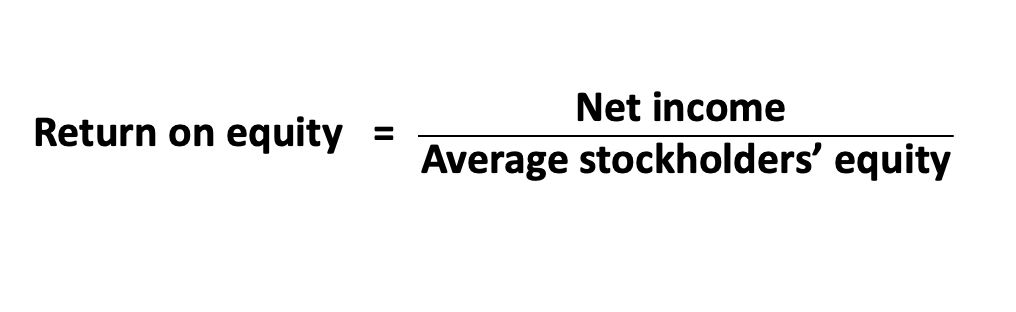
Measures how much a company pays out in dividends relative to its share price.
dividend yield
dividend yield formula

Measures net income earned per share of common stock.
earnings per share
earnings per share formula

Indicates how the stock is trading relative to current earnings.
Price-Earnings Ratio (PE Ratio)
PE ratio formula
