Tudor and Stuart Explorers and Their Impact
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Christopher Columbus
Sailed for Spain in 1492, seeking new trade routes.
John Cabot
Explored Canada for England in 1496, found no riches.
John Hawkins
Financed slave-trading voyages, knighted in 1588.
Privateers
Authorized pirates attacking foreign ships for profit.
Roanoke
Failed British colony attempt in the Americas.
Cash crops
Profitable crops like sugar, cotton, and tobacco.
Indentured servants
Workers contracted for a set period to pay for voyage.
Royal Navy
Established anti-piracy measures to protect trade.
Plantations
Large farms growing cash crops for export.
Puritans
Sought religious freedom, emigrated to the Americas.
Economic motives
Desire for profit drove British emigration to the Americas.
Religious conflict
Groups fled Britain to escape persecution.
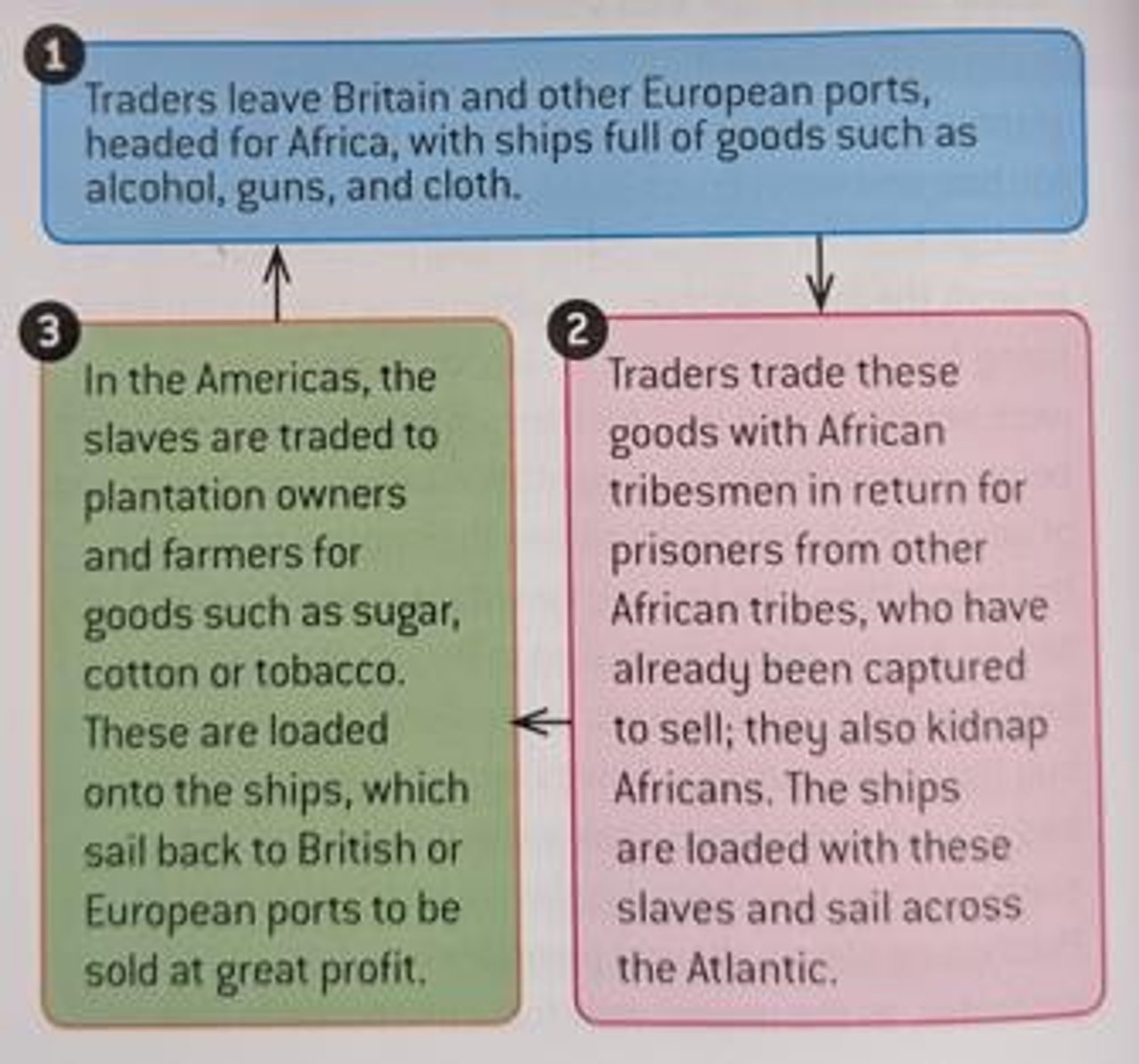
Slave trade
Profitable business capturing and selling West Africans.
Monarchs
Granted privateers permission to attack foreign vessels.
West Indies
Region where Columbus landed, part of the Americas.
Plantation owners
Used slaves instead of indentured servants for labor.
Profitability
Plantations became more profitable than piracy.
Disease
New diseases affected labor force on plantations.
Crop failure
Led to food shortages, decreasing plantation labor.
Economic growth
Trade in Americas funded British empire expansion.
1607
Year the first successful British colony was established.
Anti-piracy measures
Royal Navy actions to eliminate piracy in Americas.
Nassau
A safe haven for escaped slaves in the Bahamas.
Plantation Profitability
Purchasing slaves increased plantation profitability significantly.
Queen Elizabeth I
Sponsored businesses involved in the slave trade.
Economic Impact
Slave trade generated £60 million for Britain (1761-1808).
Coastal Town Growth
Towns like Bristol and Liverpool grew wealthy.
Abolition of Slavery
Slavery abolished in Britain by 1807; empire by 1833.
Protests Against Slavery
By 1700s, public began protesting against slavery.
Virginia Colony
Established in 1607, faced starvation and local attacks.
Tobacco Profits
Tobacco cultivation led to significant economic success.
Puritan Migration
80,000 Puritans migrated to America (1630-1641).
Mayflower
Ship that brought settlers to Massachusetts in 1620.
Democratic Principles
Settlers established society based on democratic ideals.
Sugar Plantations
Became lucrative, contributing to economic growth.
Native American Decline
Population dropped from 560,000 to 280,000 by 1700.
Disease Impact
Settlers introduced diseases like Smallpox to natives.
Navigation Acts
Colonists restricted to trade only with British ships.
Stamp Act
1765 tax imposed on paper products in colonies.
Boston Tea Party
1773 protest against tea tax; £11,000 worth dumped.
Colonial Taxation
High taxes imposed on goods like coffee and sugar.
American Revolution
Colonial desire for independence led to revolution.
Religious Persecution
Catholics and Puritans fled to America for freedom.
Tea Dumping
£11,000 worth of tea discarded in harbour.
First Congress
1774 meeting of 56 representatives against Britain.
Washington's Appointment
July 1775, Washington became leader of colonists' army.
Declaration of Independence
July 1776, Congress declared independence from Britain.
Battle of Yorktown
1781, Americans and French defeated British forces.
Treaty of Paris
Signed September 3, 1783, recognized American independence.
Canada's Self-Government
Gained self-government from Britain in 1867.
Britain's War Cost
Cost Britain £80 million and 30,000 soldiers.
USA's War Losses
Lost 25,000 men, impacting industry and economy.
USA's Development
Gained freedom to develop independently after war.
French Revolution
Began in 1789, influenced by American Revolution.
Australia's Penal Colony
Britain sent criminals to Australia as punishment.
Huguenots
French Protestants persecuted by Catholics, skilled craftsmen.
Bartholomew's Day Massacre
1572, 70,000 Huguenots killed in France.
Edict of Nantes
1598, granted Huguenots freedom to practice religion.
Huguenot Migration Impact
Established paper industry, supplied 70% of Britain's paper.
Louis XIV's Persecution
1685, Edict revoked, Huguenots faced renewed attacks.
Ulster Plantations
1600s, settlers encouraged to farm in Ulster.
Highland Clearances
1746, Highlanders evicted for sheep farming.
Jacobite Rebellions
Highlanders supported uprisings against British monarchy.
Emigration from Highlands
Many Highlanders emigrated due to evictions.
Cultural Suppression
Bagpipes banned during Highland Clearances.
Population Growth in Canada
Settlers sought better life, rapidly increased population.