6-7: Protective Tissues and Vascular Tissues
5.0(2)Studied by 22 people
Card Sorting
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:13 PM on 10/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
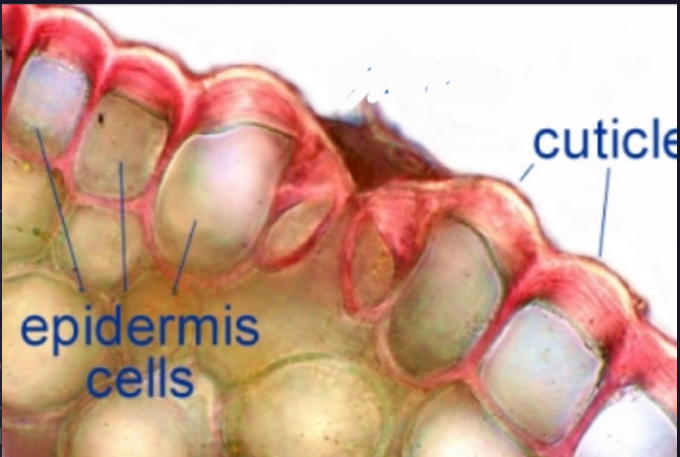
epidermis
- Outermost layer of cells of the primary plant body
- Usu. one layer
- With cuticle (cutin and waxes)
- Usu. one layer
- With cuticle (cutin and waxes)
2
New cards
primary plant body
body during primary growth; increase in height
3
New cards
• Reduce water loss
• Mechanical protection
• Gaseous exchange (stomata)
• Mechanical protection
• Gaseous exchange (stomata)
function of epidermis
4
New cards
• Epidermal cells (ordinary epidermal cells)
• Stoma/ta • Trichomes
• Stoma/ta • Trichomes
cell types in the epidermis
5
New cards
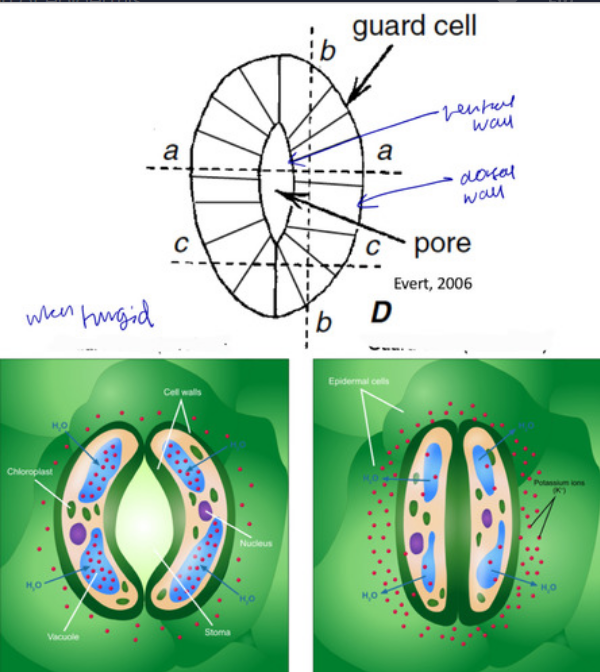
stomata
• Openings bounded by guard cells
• Most abundant on leaves
• Rare in roots
• Most abundant on leaves
• Rare in roots
6
New cards
Guard cells
- regulate the exchange of water vapor and CO2
- with neighboring cells or subsidiary cells
- Unevenly thickened walls with radially arranged cellulose microfibrils
- with neighboring cells or subsidiary cells
- Unevenly thickened walls with radially arranged cellulose microfibrils
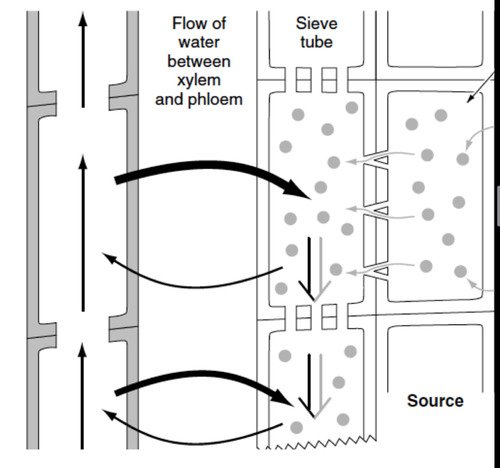
7
New cards
Amphistomatic leaf
stomata occur on both surfaces
8
New cards
epistomatic leaf
stomata only on upper surface; common in aquatic plants that float
9
New cards
Hypostomatic leaf
stomata only on lower surface; common in most
10
New cards
trichomes
• Epidermal appendages
• Reduces transpiration rate
• Defense against insects
• Reduces transpiration rate
• Defense against insects
11
New cards
root hairs
extension of absorbing surface
12
New cards
trichomes
what are cotton fibers
13
New cards
periderm
replaces the epidermis in roots and stems when it cant cope w increase in diameter
14
New cards
• Phellem/cork cells
• Phellogen/cork cambium
• Phelloderm
• Phellogen/cork cambium
• Phelloderm
periderm consists of
15
New cards
phellogen
• Mostly arises in the subepidermal or epidermal layer (stem); sometimes in vascular tissues (phloem)
• Arises in the pericycle (roots)
• meristematic cell layer responsible for the development of the periderm
• Arises in the pericycle (roots)
• meristematic cell layer responsible for the development of the periderm
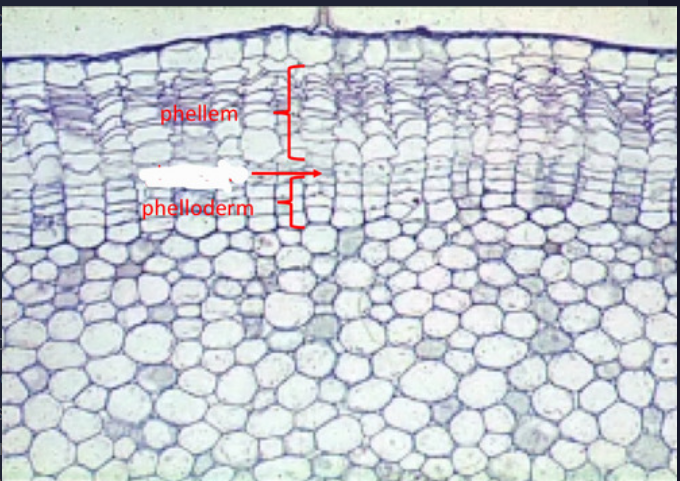
16
New cards
cork (phellem)
- tissue formed on the outer side of phellogen or cork cambium
- dead, suberized
- dead, suberized

17
New cards
phelloderm
- parenchymatous
- bellow the phellogen
- 2ndary cortex
- bellow the phellogen
- 2ndary cortex
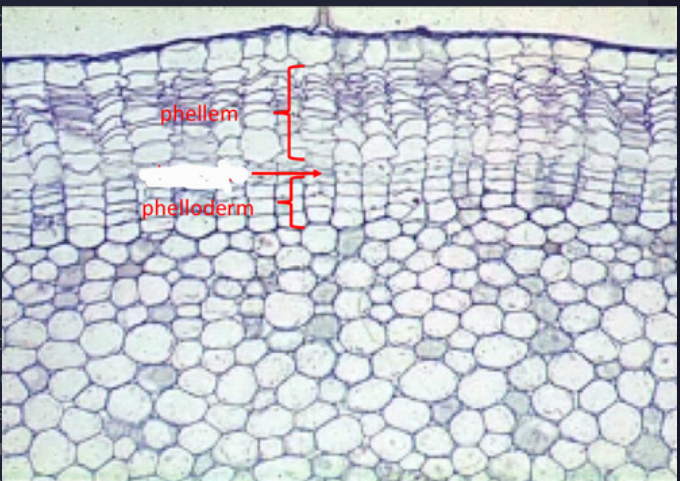
18
New cards
bark
• All tissues outside vascular cambium
• Component varies between primary and secondary state
• Component varies between primary and secondary state
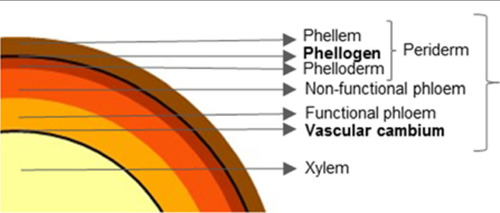
19
New cards
rhytidome
outer bark
20
New cards
outer nonfunctional
inner living
inner living
outer vs inner bark
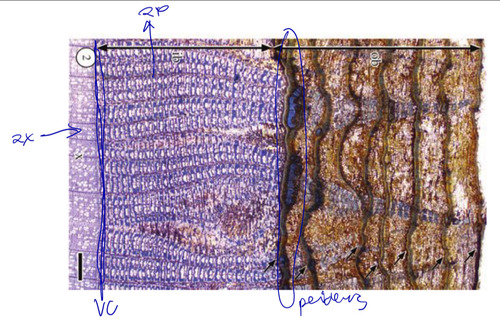
21
New cards
lenticels
- permitting entry of air
- has a loose arrangement of cells compared to the rest of the periderm.
- has more phellogen and is more active than the phellogen of the peri derm.
- numerous intercellular spaces
- has a loose arrangement of cells compared to the rest of the periderm.
- has more phellogen and is more active than the phellogen of the peri derm.
- numerous intercellular spaces

22
New cards
- tracheary elements (tracheids, vessel elements)
- xylary fibers
- xylem parenchyma
- xylary fibers
- xylem parenchyma
xylem axial system
23
New cards
xylem parenchyma
xylem radial system
24
New cards
primary xylem has no rays
why does xylem systema only apply to 2X
25
New cards
tracheary elements
Water-conducting cells in plants that, when mature, are always dead and empty of cytosol
26
New cards
sclerenchyma
what are tracheids and vessel elements made of
27
New cards
lumen
space inside trach elements
28
New cards
Spindle (long and tapered at both ends)
tracheids shape
29
New cards
Drum or barrel shaped
vessel elements shape
30
New cards
imperforate
tracheids perforation
31
New cards
yes, devoid at both end walls
vessel elements perforation
32
New cards
overlapping
tracheids arrangement
33
New cards
end on end
vessel elements arrangement
34
New cards
less efficient
tracheids water conduction
35
New cards
more efficient
vessel elements water conduction
36
New cards
water leaves + enters tracheids thru bordered pits
water moves w no resistance in vessel elements
water moves w no resistance in vessel elements
why do vessel elements conduct water more efficiently than tracheids
37
New cards
mx and 2x
where are simple and bordered pits located in Tracheids and Vessels
38
New cards
annular, helical/spiral, scaliforme, reticulate
2ndary walls ng primary xylem
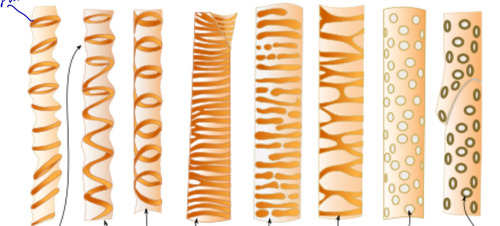
39
New cards
cavitation
• Creation of embolism
• Blocks the movement of water
• Freezing and drought
• Blocks the movement of water
• Freezing and drought
40
New cards
embolism
air space that prevents water from passing thru vessel element
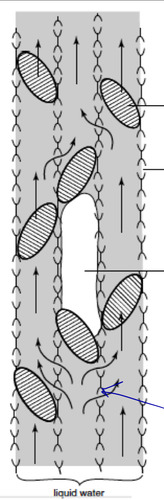
41
New cards
thru bordered pit pairs
how does water take a detour pag may embolism
42
New cards
water column breaks when water vapor/gas is trapped within; alternation betw freezing and thawing
how does cavitation happen
43
New cards
xylem sap
the water and dissolved minerals in the xylem
44
New cards
conifers in cold climate
where is cavitation common
45
New cards
xylary fibers
• Long cells, tapered both ends
• With lignified secondary walls
• Wall thicker than tracheids
• strengthening and storage
• With lignified secondary walls
• Wall thicker than tracheids
• strengthening and storage
46
New cards
fiber tracheids
xylary fibers w bordered pits and slit-like inner aperture

47
New cards
libriform fibers
xylary fibers w thicker walls and longer; slit like aperture (simple pit)
48
New cards
xylem parenchyma
• With lignified secondary walls but living (2x)
• Storage of starch or fat
• Found in axial and ray parenchyma
• Storage of starch or fat
• Found in axial and ray parenchyma
49
New cards
procambium
origin of primary xylem
50
New cards
protoxylem
early-formed xylem when organs r still elongating
51
New cards
lacuna
since the protoxylem cells are mature when the stem is elongating, they are stretched and destroyed, forming a space called what?
52
New cards
metaxylem
- late-formed xylem after organs stop elongation
- most of the functional xylem in the primary xylem is this
- pag may 2ndary growth, loses its function na
- most of the functional xylem in the primary xylem is this
- pag may 2ndary growth, loses its function na
53
New cards
- sieve elements (sieve cells, sieve-tube elements)
- sclerenchyma (fibers, sclereids)
- parenchyma
- sclerenchyma (fibers, sclereids)
- parenchyma
axial phloem
54
New cards
sieve elements
• Breakdown of nucleus and tonoplast (not entire protoplast)
• Sieve areas (with pores)
• Sieve areas (with pores)
55
New cards
sieve cells
sieve elements ng gymnosperms
56
New cards
sieve tube elements
sieve elements ng angiosperms
57
New cards
sieve plate containing sieve pores
specialised end wall of sieve tube, with holes allowing connections between one cell and the next
58
New cards
sieve tube elements/members
• Contain phloem protein (p-protein/slime)
• Lack ribosomes
• With companion cells
• Lack ribosomes
• With companion cells
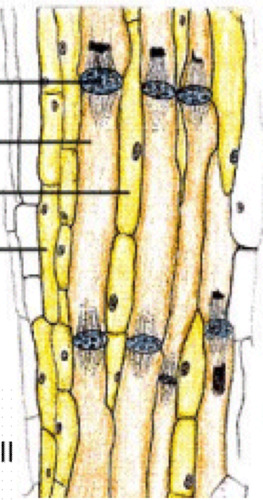
59
New cards
companion cells
• Related to sieve-tube element in function and development (ontogeny)
• With prominent nucleus
• Intimately connected with associate sieve-tube element
• Provides information molecules, proteins, and ATP to sieve-tube element
• With prominent nucleus
• Intimately connected with associate sieve-tube element
• Provides information molecules, proteins, and ATP to sieve-tube element