Micro MCQ Exam 1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
It was mentioned in an earlier lecture that science should be "predictive". What does this mean?
A. If you repeat the same experiment, you will get the same results.
B. You know in advance which experiments will work and which will not.
C. If you change a variable in an experiment, you know how the results will change.
D. You can try a completely new experiment and know in advance what the results will be.
E. You can deduce how a biological system will evolve in the future.
If you change a variable in an experiment, you know how the results will change
In Pasteur's famous experiment that finally disproved spontaneous generation, bacteria grew____.
A. Only in the flasks with a swan neck.
B. Only in media that came into contact with air.
C. Only in media that came into contact with other bacteria.
D. Only once the media had been boiled.
E. In all flasks, regardless of how they were treated experimentally.
Only in media that came into contact with other bacteria
There is must interest in using bacteriophages to kill the bacteria that cause infectious diseases in humans. Which of the following is a valid concern about such therapy?
A. The bacterial viruses might also infect humans.
B. The bacterial viruses might carry bacterial DNA into human cells.
C. Bacterial viruses might mutate into uncontrollable "superbugs".
D. The virus preparation might be contaminated with a few live bacterial cells.
E. The viruses might evolve into new bacterial cells.
The virus preparation might be contaminated with a few live bacterial cells
What are prions?
A. Infectious proteins with no nucleic acid.
B. Very tiny virus-like particles.
C. Infectious RNA with no protein.
D. Peptidoglycan particles that affect the immune system.
E. Small cells that lack a cell membrane.
Infectious proteins with no nucleic acid
What happens when water hydrates itself?
A. Molecules stick together and become cohesive.
B. It expands and freezes.
C. It cannot be transported through aquaporins anymore.
D. H3O+ and OH- ions form.
E. Water cannot hydrate itself.
H3O+ and OH- ions form
6. Rank the following lipids in order from MOST SOLID to LEAST solid at room temperature.
(1) Saturated lipids (2) Cis-unsaturated (3) Trans-unsaturated
A. MOST SOLID (1) > (2) > (3) LEAST SOLID
B. MOST SOLID (3) > (2) > (1) LEAST SOLID
C. MOST SOLID (1) > (3) > (2) LEAST SOLID
D. MOST SOLID (3) > (1) > (2) LEAST SOLID
E. MOST SOLID (2) > (1) > (3) LEAST SOLID
MOST SOLID (1) > (3) > (2) LEAST SOLID
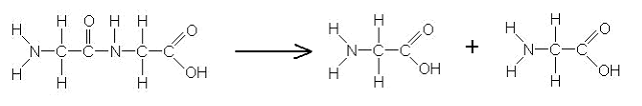
This reaction is an example of ___________.
A. Hydrolysis
B. Oxidation
C. Reduction
D. Condensation
E. Transpeptidation
Hydrolysis
The pH inside bacterial cells is 7. The pH outside is 5. What is the size of the H+ gradient?
A. You need more information to answer this question.
B. There are two more protons inside the cell than outside.
C. There are twenty times as many protons outside the cell than inside.
D. There are one hundred times as many protons inside the cell than outside.
E. There are one hundred times as many protons outside the cell than inside.
There are one hundred times as many protons outside the cell than inside
Humans cannot digest cellulose, though, bacteria can because ______________________.
A. Humans cannot deal with the many branches in the polymer.
B. Cellulose is too highly crosslinked by H-bonds for our digestive system.
C. Humans cannot make cellulose storage polymerase, but bacteria can.
D. Humans cannot digest β-glycosidic bonds, but bacteria can.
E. Cellulose is polymer of sugars and amino acids much like peptidoglycan
Humans cannot digest β-glycosidic bonds, but bacteria can
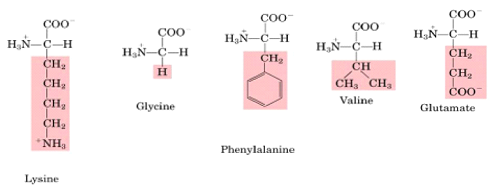
Which of the following amino acids does NOT have D- and L- stereoisomers?
A. Phenylalanine
B. Glycine
C. Glutamate
D. Valine
E. Lysine
Glycine
What type of microscope views a specimen with light refracted from the specimen rather than light that passed through the specimen?
A. Bright field
B. Phase contrast
C. Atomic force
D. Differential interference contrast (Nomarski)
E. Dark field
Dark field
Which of the following CANNOT participate in hydrogen bond formation?
A. The O in C=O
B. The H in N-H
C. The N in N-H
D. The H in C-H
E. The O in O-H
The H in C-H
What type of microscope measures electric current passing through a probe rather than using part of the electromagnetic spectrum?
A. Bright field
B. Phase contrast
C. Atomic force
D. Differential interference contrast (Nomarski)
E. Dark field
Atomic force
In an environment that was isotonic to a bacterial cell's cytoplasm, what effect would penicillin have on logarithmic phase Gram-positive round-shaped cells?
A. There would be no effect.
B. The cells would lose their shape.
C. The cells would die but remain intact.
D. The cells would lyse.
E. The cells would become Gram-negative.
The cells would lose their shape
15. What type of microscope uses special prisms to make a thin specimen appear pseudo-3-dimensional?
A. Bright field
B. Phase contrast
C. Atomic force
D. Differential interference contrast (Nomarski)
E. Dark field
Differential interference contrast (Nomarski)
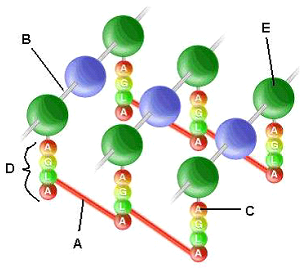
Refer to the diagram of peptidoglycan on the right. What is different between Gram-negative and Gram-positive peptidoglycan?
A. The structure marked "A" is only found in Gram-positive cells.
B. The bond marked "B" is an α-1,4 bond in Gram-positive cells and a β-1,4 in Gram-negative cells.
C. The amino acid marked "C" is an L-amino acid in Gram-positive cells and a D-amino acid in Gram-negative cells.
D. The structure marked "D" does not exist inGram-negative cells.
E. The molecule marked "E" is a sugar in Gram-positive cells and an amino acid in Gram-negative cells.
The structure marked "A" is only found in Gram-positive cells
What is the main advantage of using an electron beam rather than light to illuminate a specimen?
A. The electron beam is brighter.
B. The beam penetrates thick specimens better.
C. Electrons have a shorter wavelength than light.
D. It is easier to focus an electron beam.
E. An electron beam can be used to view live, unstained cells.
Electrons have a shorter wavelength than light
What is one unique feature of the Mycobacterial cell wall?
A. It contains a thick layer of very dense lipids.
B. Its peptidoglycan is crosslinked directly rather than a pentaglycine spacer.
C. It is made of protein rather than lipids and peptidoglycan.
D. It stains better with a negative stain that with a positive stain.
E. It has no cell wall. It only has a cell membrane.
It contains a thick layer of very dense lipids
Which of the following is NOT true of the PTS (phosphotransferase) transport system?
A. It involves the direct transfer of a phosphate from ATP to glucose.
B. It uses energy from a high energy phosphate, though not from ATP.
C. It is found only in Bacteria, not Archaea or Eukaryotes.
D. It involves multiple phosphate transfers in a "relay".
E. It is used mostly for transport of carbohydrates.
It involves the direct transfer of a phosphate from ATP to glucose
What is the "Sec translocon"?
A. A transporter that imports fully folded proteins.
B. A transporter that moves molecules through the outer membrane.
C. A transporter that inserts proteins with a signal sequence through the cytoplasmic membrane.
D. A chaperone that keeps proteins unfolded for insertion through the cytoplasmic membrane.
E. A transporter that makes a single channel through both bacterial membranes.
A transporter that inserts proteins with a signal sequence through the cytoplasmic membrane
An organism that does not have a respiratory electron chain, but produces some catalase or superoxide dismutase, would be classified as _____________________.
A. obligate aerobe
B. obligate anaerobe
C. microaerophile
D. facultative anaerobe
E. aerotolerant anaerobe
aerotolerant anaerobe
A bacterium is growing in a medium with a [K+] of 1mM. The bacterium uses uniport to accumulate K+ to a 10mM concentration inside the cell. What is the energy for this transport?
A. The membrane potential.
B. The K+ gradient.
C. The pH gradient.
D. ATP hydrolysis.
E. No energy is required for this transport.
The membrane potential
Which of the following is NOT a function of capsules or slime layers?
A. Surface adhesion
B. Preventing phagocytosis
C. Motility
D. Enhancing biofilm formation
E. Biofouling of filters
Motility
Why are scientists interested in Type III secretion systems?
A. The allow secretion of fully folded proteins.
B. They are often associated with insertion of toxins directly into eukaryotic cells.
C. They can secrete proteins constantly without an external secretion signal.
D. They produce a periplasmic intermediate whose folding in the periplasm is unique.
E. They are involved in bacterial cell motility just like flagella.
They are often associated with insertion of toxins directly into eukaryotic cells
Which of the following statements about enzyme inhibitors is correct?
A. An allosteric inhibitor functions at a much lower concentration than the substrate.
B. A competitive inhibitor induces an irreversible shape change in the active site.
C. An allosteric inhibitor binds to an enzyme’s active site.
D. Competitive inhibitors are usually for anabolic pathways.
E. A noncompetitive inhibitor must resemble the substrate at least partially.
An allosteric inhibitor functions at a much lower concentration than the substrate
The bacterium E. coli exhibits flagellar motility and chemotaxis toward the amino acid alanine. If E. coli is placed in a 100mM solution of alanine, which of the following would best describe its behavior?
A. There would be no motion. Cells would not be motile in this solution.
B. There would be random, undirected motion.
C. There would be directed motion with occasional, random reorientations.
D. There would be motion in continuous counterclockwise circles.
E. There would be motion in a straight line.
There would be random, undirected motion
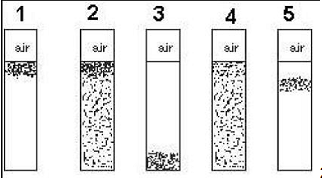
Tubes 1-5 represent growth in shake tubes with thioglycolate media. Which of the following is true of the organisms growing in Tube 5?
A. They are facultatively anaerobic.
B. They list mostly by fermentation.
C. They produce lots of catalase.
D. They are very heavy cells.
E. They use O2 as a terminal electron acceptor.
They use O2 as a terminal electron acceptor
How are pili involved in bacterial motility?
A. A H+ gradient causes them to rotate like propellers.
B. They move back and forth like oars.
C. They are extended and retracted like grappling hooks.
D. They vibrate rapidly and jiggle the bacterium across a surface.
E. They hook two bacteria together making other motion more efficient.
They are extended and retracted like grappling hooks
An enrichment culture for a psychrophile would involve which of the following steps?
A. Grow a mixed culture in at a low pH.
B. Grow a mixed culture in a complex medium which would grow other cells too.
C. Grow a pure culture at 15ºC.
D. Grow a mixed culture at 4ºC.
E. Grow a pure culture in a defined medium in which only nutritionally fastidious organisms cangrow.
Grow a mixed culture at 4ºC
One adaptation made my alkaliphiles to live in their environment is ______________.
A. The ability to maintain an acidic cytoplasm.
B. Synthesis of osmoprotectants.
C. Ability to use sodium motive force rather than a proton motive force.
D. Modification of soluble proteins to have numerous surface charges.
E. Proteins with increased stability at high temperatures.
Ability to use sodium motive force rather than a proton motive force
Which of the following equations would be used to solve this problem? (You do not need a calculator for this.)
How many bacteria would you need to start with to have as many cells as the Earth's population(7.9 billion) within 12 hours? The bacterium divides in 30 minutes.
A. (7.9 x 10^9) = X e^(1.39)(12)
B. (7.9 x 10^9) = X e^(0.5)(12)
C. (7.9 x 10^9) = X e^12 x
D. X = (7.9 x 10^9) e^(2)(12)
E. X = (7.9 x 10^9) e^(1.39)(12)
(7.9 x 10^9) = X e^(1.39)(12)
One major difference between batch culture and continuous cultures is that ____________.
A. Batch culture never reaches stationary phase.
B. Batch culture is best used to produce primary metabolites, such as ethanol.
C. Continuous culture involves fewer nutrients.
D. Continuous culture is set up in a series of flasks, not just one.
E. Continuous culture allows the researcher to change the bacterial growth rate.
Continuous culture allows the researcher to change the bacterial growth rate
The main purpose of fermentation in a typical bacterial cell is __________________.
A. To generate a little bit more energy than is produced in glycolysis.
B. To prepare pyruvate to enter the TCA cycle.
C. To oxidize NADH to NAD+.
D. To carry out the first step in anabolic reactions that make new cell material.
E. To make a PMF in the absence of an electron transport chain.
To oxidize NADH to NAD+
A bacterial growth medium is prepared with Na3PO4, K2SO4, NH4Cl, C6H12O6 and yeast extract. What is the purpose of the yeast extract?
A. It allows the growth of nutritionally fastidious organisms.
B. It makes the medium selective.
C. It makes the medium differential.
D. It increases the length of the lag phase in the growth curve.
E. Without it, organotrophic bacteria will not be able to grow in the medium.
It allows the growth of nutritionally fastidious organisms
You are using a fluorescence microscope and an antibody-based stain to examine a mixed culture from a patient's blood for the titer of Treponema pallidum, the bacterium that causes syphilis. What would be the best method to make this titer determination?
A. Petroff-Hauser chamber
B. Weighing a cell pellet
C. Membrane filtration and plating
D. Coulter counter
E. Spread plating on agar petri dishes
Petroff-Hauser chamber
In the United States, swimming beaches are periodically tested for bacterially counts. In Indiana, a beach is closed if the bacterial titer exceeds 125 bacteria per 100mL. Which of the following would be the best way to determine this titer?
A. Petroff-Hauser chamber
B. Weighing a cell pellet
C. Membrane filtration and plating
D. Coulter counter
E. Spread plating on agar petri dishes
Membrane filtration and plating
From which central metabolic pathway(s) is DNA synthesized by the cell?
A. From TCA cycle intermediates
B. From the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
C. From glycolytic intermediates
D. From the pentose phosphate pathway
E. From glycolytic intermediates condensed with a product of acetyl CoA
From the pentose phosphate pathway