PD special populations
1/411
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
412 Terms
What is a tip to making the pediatric assessment less intimidating?
try the least aversive portion of the exam first
auscultate the heart and lungs then move to more potentially disturbing portions
What are the 4 principles of pediatric development?
child development proceeds in a predictable pathway
range of normal development is wid
various physical, social and environmental factors as well as diseases can affect child development and health
the childs developmental level affects how you conduct the hx and physical exam
What is considered age appropriate guidance you can offer to children and their parents?
childs development
expected maturation changes
childhood immunizations
What are the stages of development?
newborn- birth
infancy- 0-12 months
early childhood- 1 to 4
middle childhood- 5-10
adolescence 11-20
What are the key components of pediatric health promotion?
age appropriate developmental achievements
health supervision visits
integration of physical exam findings with health lifestyles
immunizations
healthy habits
oral health
preventive methods
school, family relationships
What is the first exam of the newborn exam?
immediately after birth
determine general condition
developmental status
abnormalities in gestational development
congenital abnormalities
gestational age and weight
apgar score
What is the apgar score?
a 5 components scoring system that classifies the newborns neurological recovery from birth and immediate adaptation to extra uterine life
What is the scoring of the apgar score?
rates
appearance- color
pulse- HR
grimace - reflex irritability
activity- muscle tone
respiration
scale 0,1,2

What is a normal score for 1 minute apgar score?
8-10
What is a score of 5-7 on apgar 1 minute test indicative of?
some nervous system depression
What is a score of 0-4 on 1 minute apgar score indicative of?
severe depression, requiring immediate resuscitation
What is the normal score for an apgar 5 minute test?
8-10
What is a 5 minute apgar score of 0-7 indicative of?
high risk of subsequent CNS and other organ system dysfunction
What should you do if the apgar score is low?
repeat exam at 5 minute intervals until score is >7
What does the classification of newborns based on weight and age help predict?
medical problems and morbidity
How is gestational age determined?
ballard scoring system
estimates gestational age to within 2 weeks and is based on specific neuromuscular signs and physical characteristics that change with gestational maturity
What is considered preterm?
<34 weeks
What is considered late preterm?
34-36 weeks
What is considered term?
37-42 weeks
What is considered postterm?
>42 weeks
What is considered extremely low birth weight?
<1000 g - 2.2 lbs
What is considered very low birth weight?
<1500 g - 3.3lbs
What is considered low birth weight?
<2500 g - 5.5 lbs
What is considered normal birth weight?
> or = 2500 g
What percentile is considered small for gestational age?
SGA
<10th
What is considered appropriate for gestational age?
AGA
10-90th
What is considered large for gestational age?
LGA
>90th
What is the second exam of the newborn exams?
performed within first 24 hours of life
have parents present
start with child swaddles
undress as exam process
examine head to toe
reswaddle
What is the growth rate in the first year of life?
fastest in 1st year of life
height increase by 50%
weight triples
What is the neurological development in the first year of life?
progresses centrally to peripherally
learn head control before trunk control
arm/leg control before hands/feet control
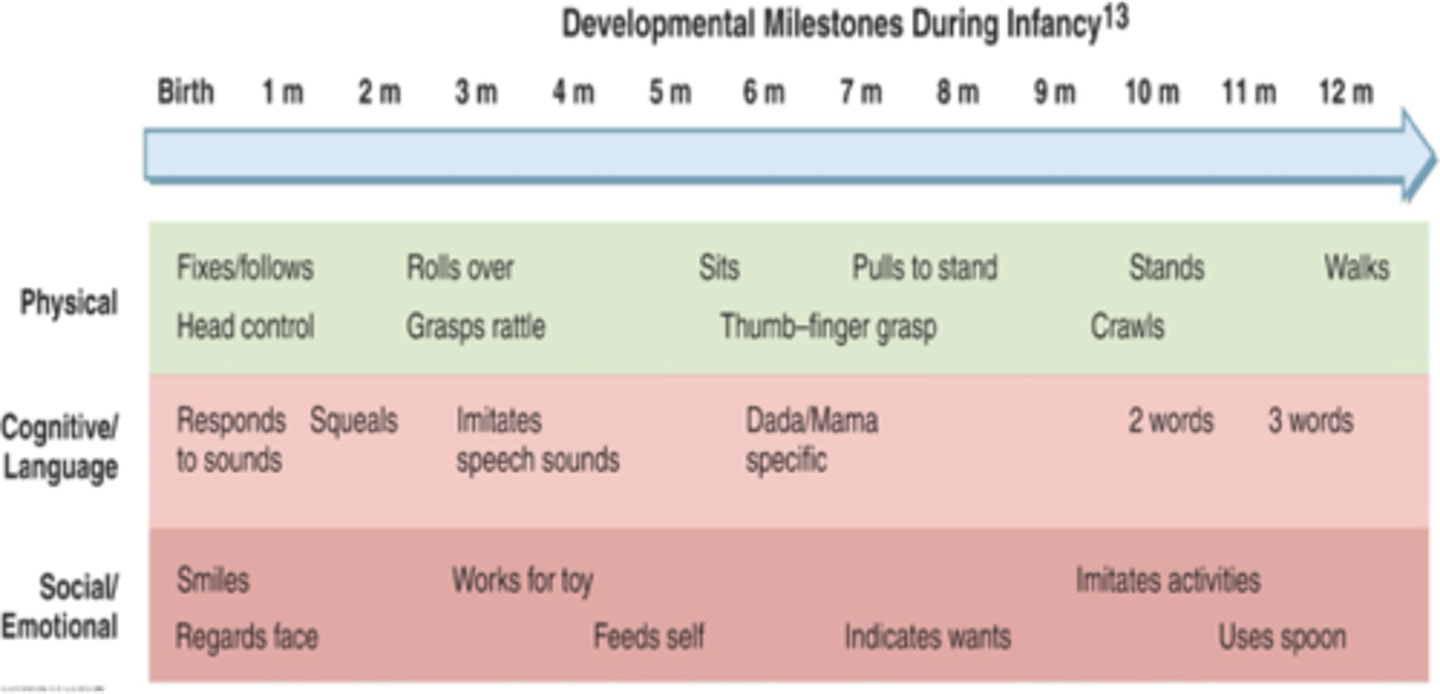
What is the language cognition level in the first year of life?
speak 1 to 3 words by 1 year
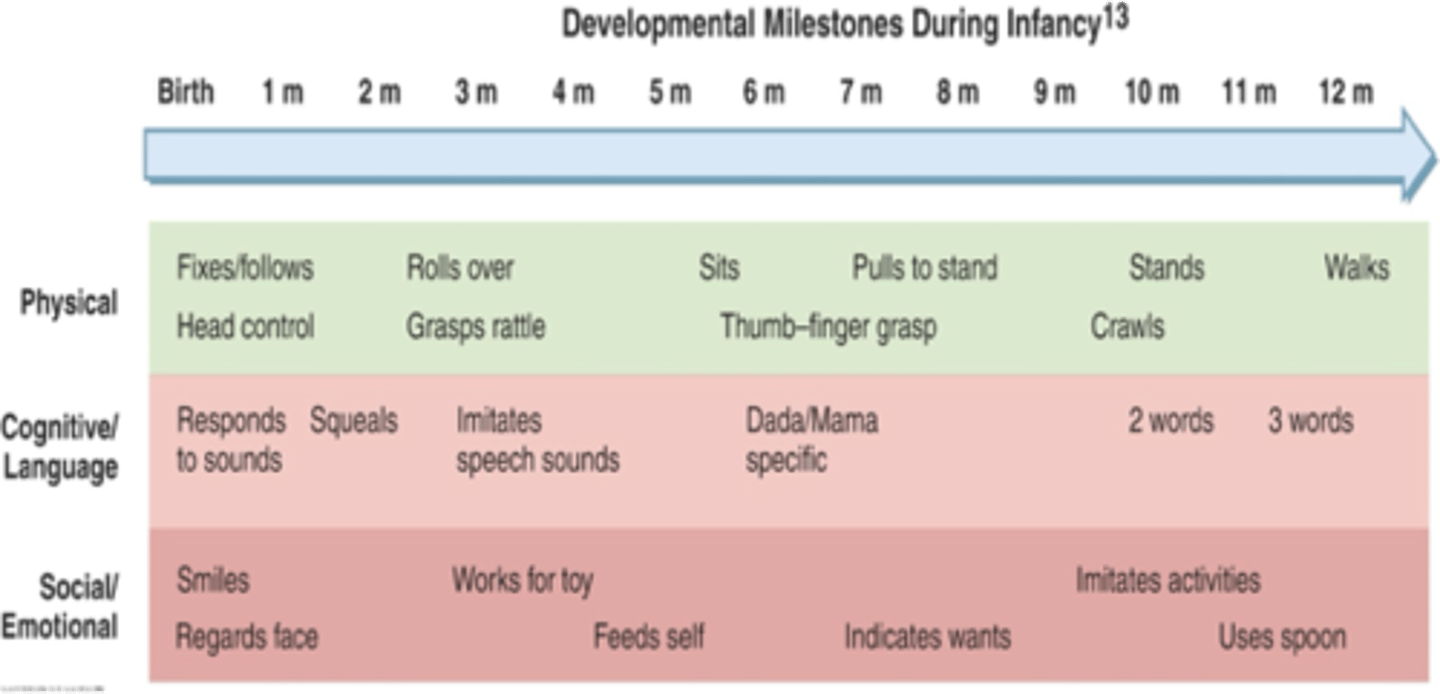
What is the social/environmental development in the first year of life?
birth to one month- smiles and regards faces
seven months- indicates wants
one year- imitates activities, uses spoon
What does the american academy of peds recommend for childhood screening for developmental delays and and disabilities?
9 months
18 months
30 months
What is the main goal for developmental monitoring?
to help children who are low functioning but to also focus on anticipatory guidance to help promote normal development
What is the denver developmental screening test II?
125 items divided into four parts
social/personal
fine motor function
language
gross motor function
What ages are covered by the denver developmental screening test II?
2 months to 6 years
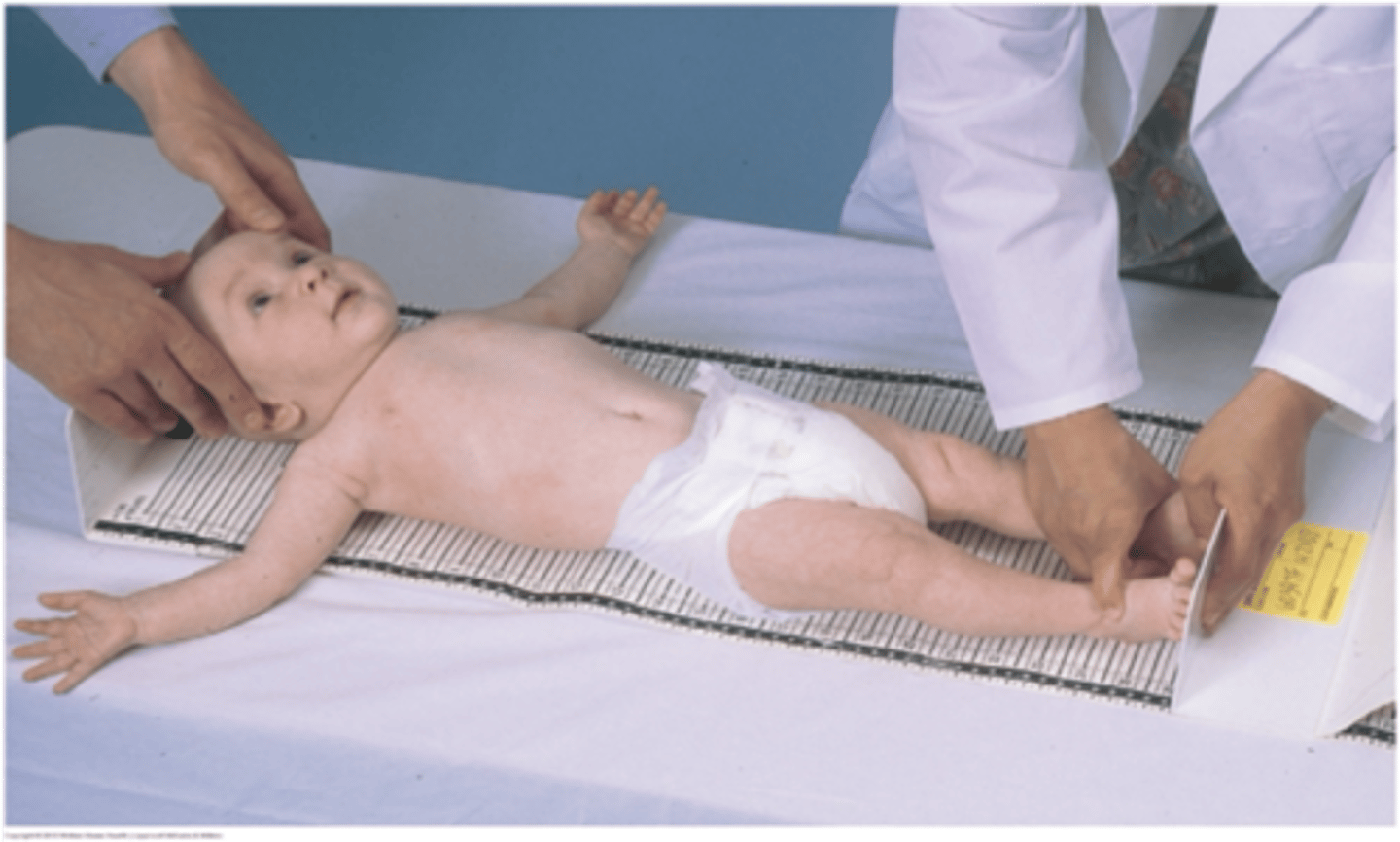
What vitals signs are taken at the infant exams?
height- every visit ( supine on measuring board for <2
weight- every visit ( naked or with diaper) + BMI or BSA
Head circumference- every visit btw birth and 2 yo
Blood pressure - after age 3
Pulse- higher in infancy
Respiratory rate-higher in infancy
Temp
What is the avg pulse in the first year of life?
115 and 140
What is the avg RR in a newborn?
30-60/min in a newborn
tachypnea>60/min- birth to 2 months
>50 min from 2 m-12 m
How do you measure temperature in an infant?
<2 months - rectal temp- 99F
>= 2 months- tympanic membrane - ( fluctuates up to 3 deg)
What is included in the inspection of pediatric skin exam?
benign birth marks vs more insidious findings
salmon patch
cafe-au-lait
mongolian spots
eyelid patch
How do you check for jaundice in a infant exam?
apply pressure to skin to press out normal color
yellow blanching = jaundice
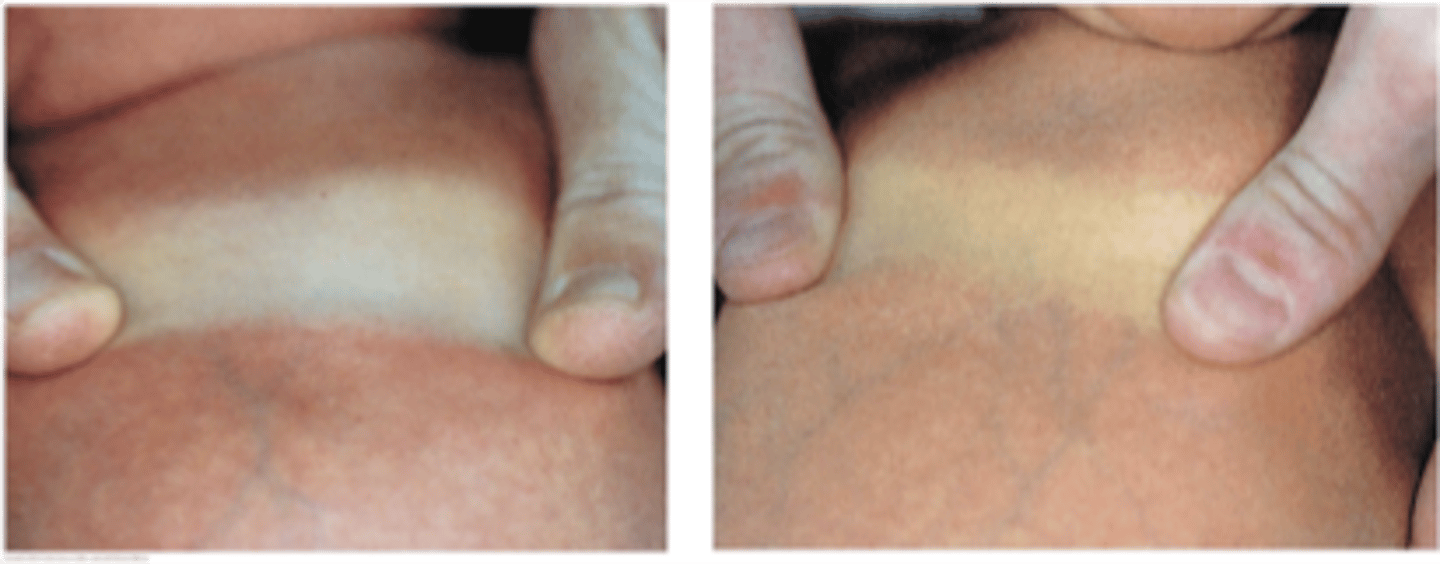
What is breast feeding jaundice?
common source of jaundice in the first couple of weeks of life
resolves around 10-14 days
What is normal physiologic jaundice in infants?
occurs in up to 1/2 of all newborns and appears on the 2nd and third day and peaks around the 5th day- usually disappears within 1 week
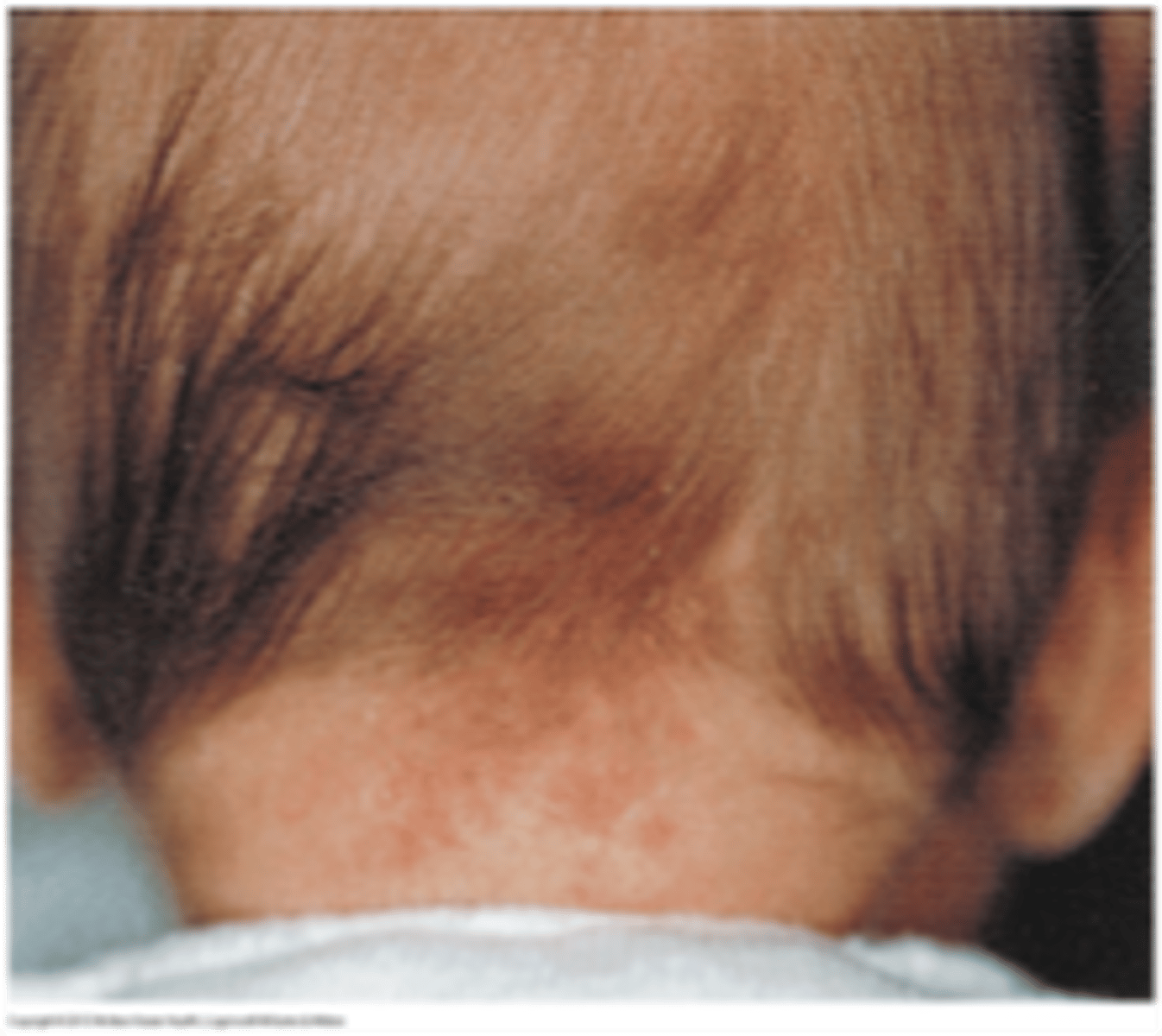
What is a salmon patch?
stork bite or angel kiss
common vascular marking most common ar the nape of the neck
fades with age
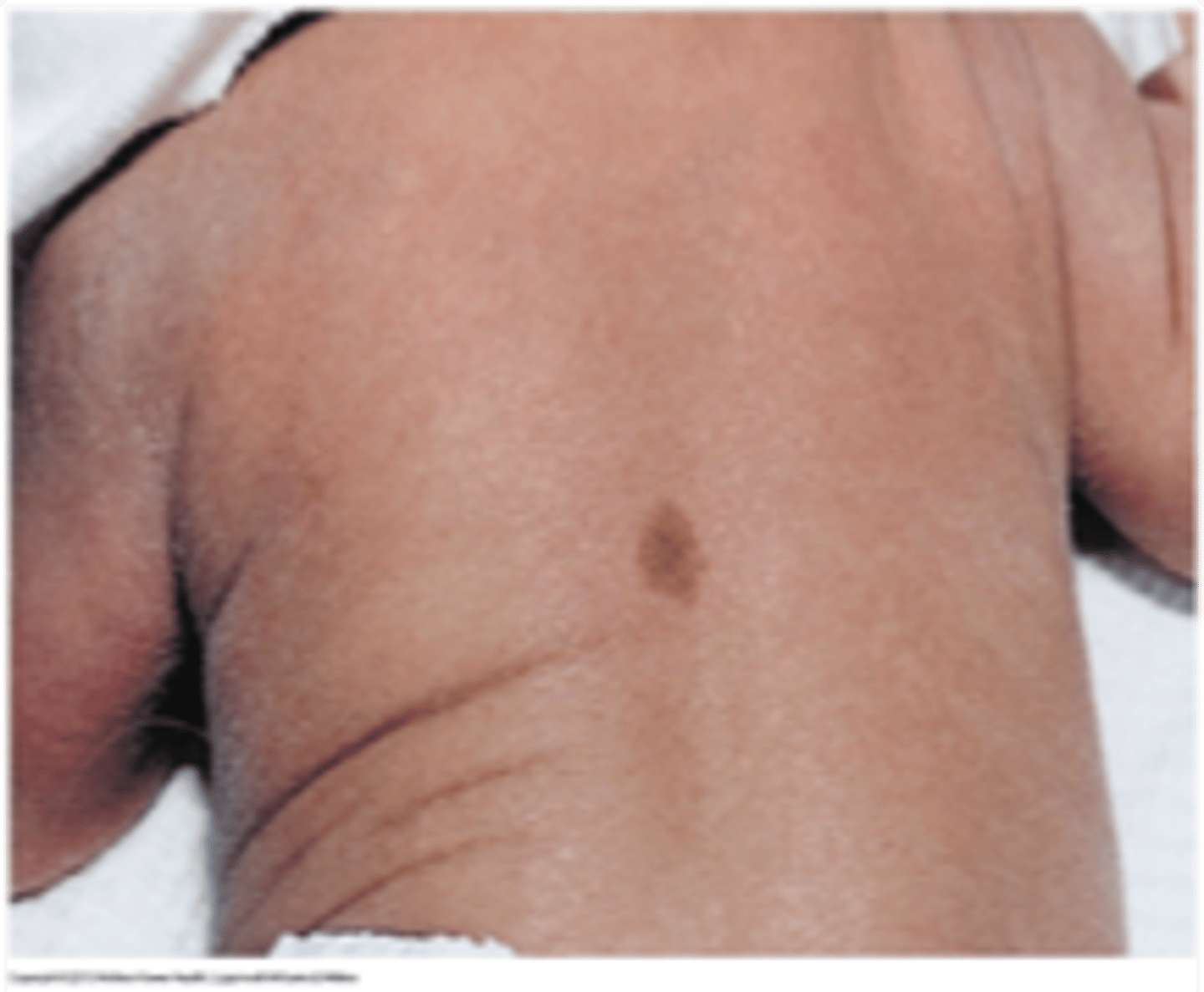
What is a cafe au- lait spot?
light brown pigmented lesions
if more than 5 consider pathognomonic for neurological disease
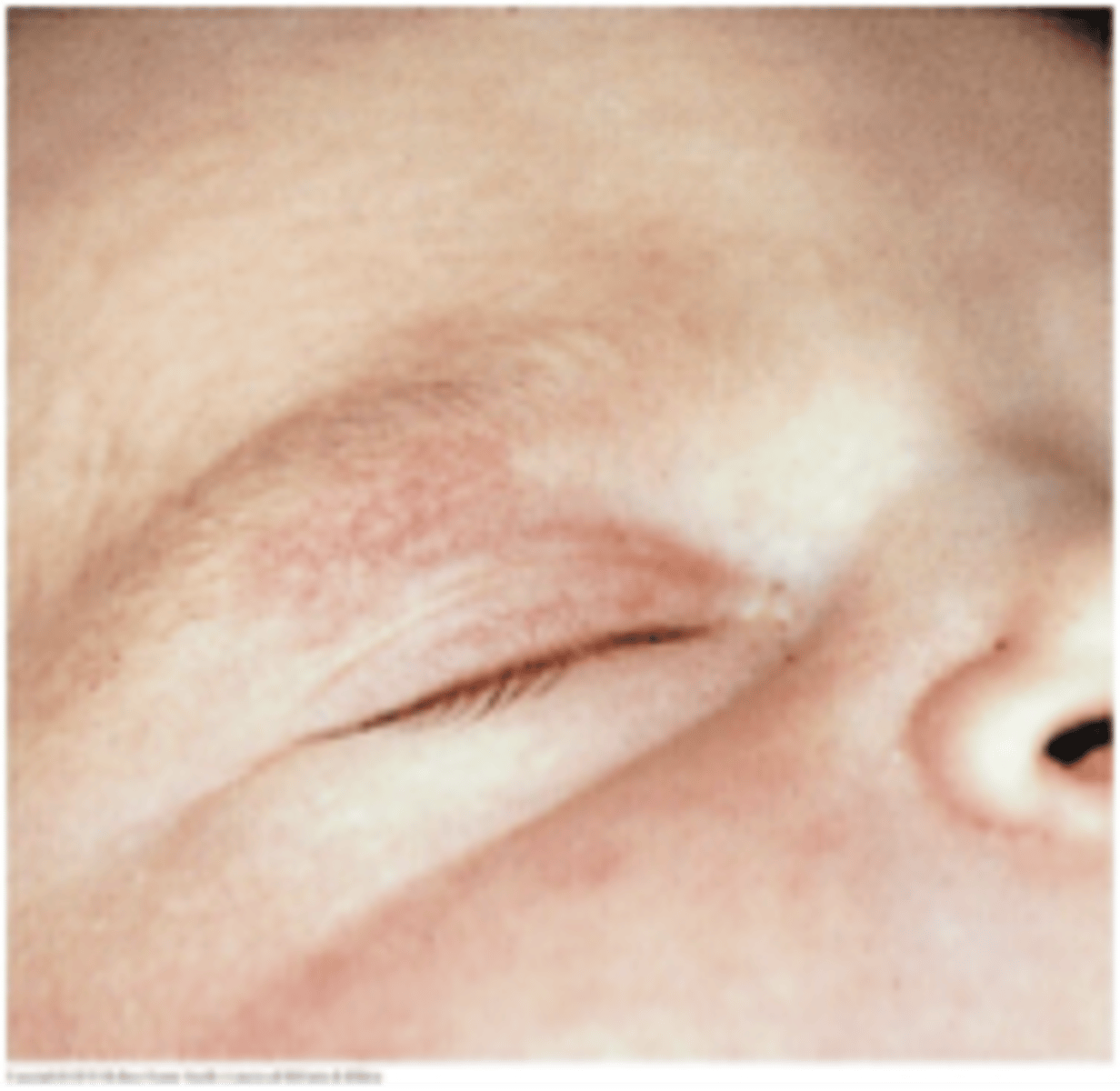
What is an eyelid patch?
birthmark
fased within first year of life
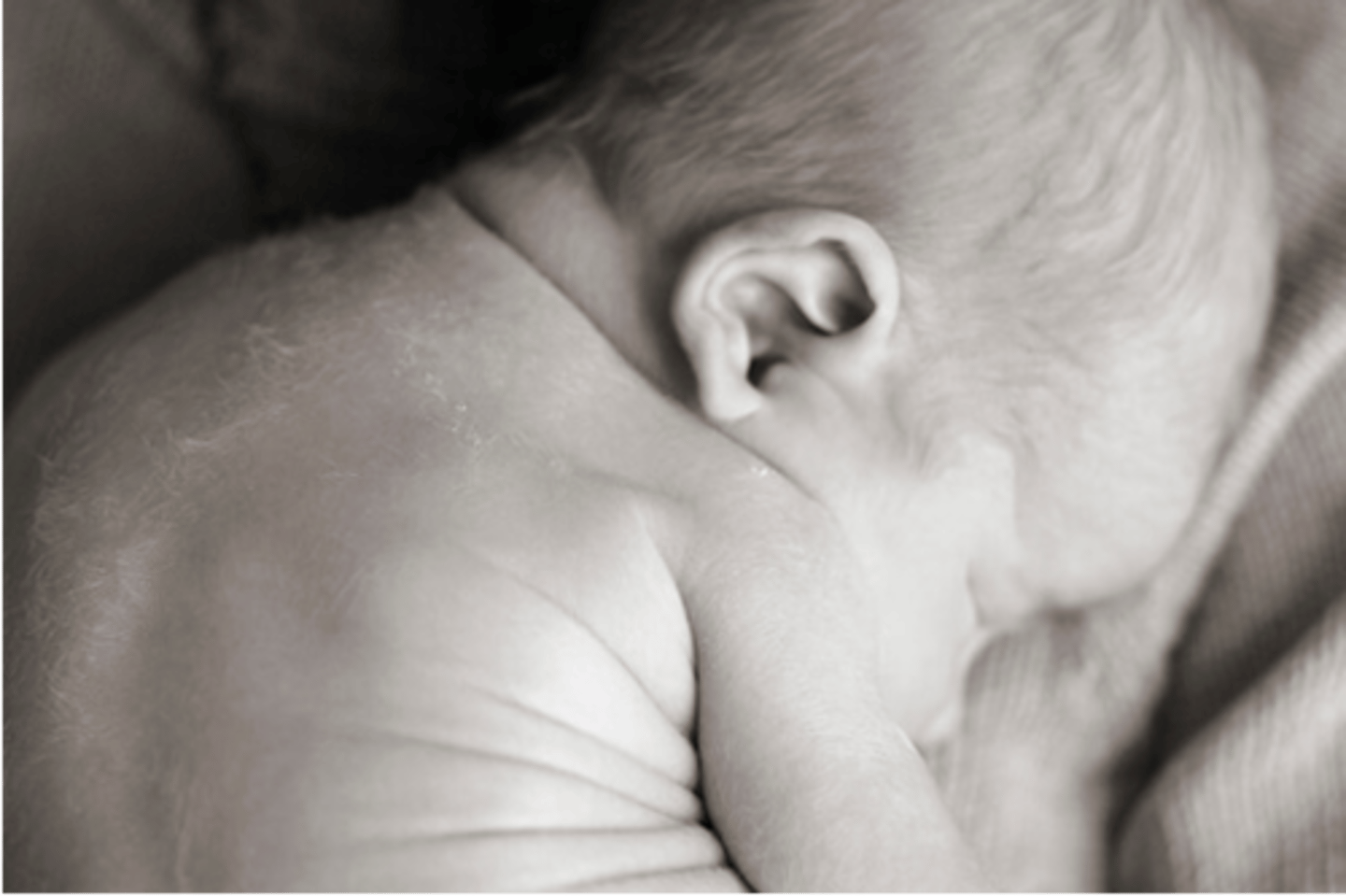
What is a mongolian spot (slate blue patch)?
common in newborns of African, asian and mediterranean descent
results from pigmented cells in the deep layers of the skin
document these areas to avoid later concern about bruising
What is a lanugo?
fine downy growth of hair over the entire body, especially shoulders and back
prominent in premature infants- this hair is generally shed in the first few weeks

What is neonatal acne?
red pustules and papules prominent over the cheeks and nose
due to maternal or infant androgens usually clears within 4 months
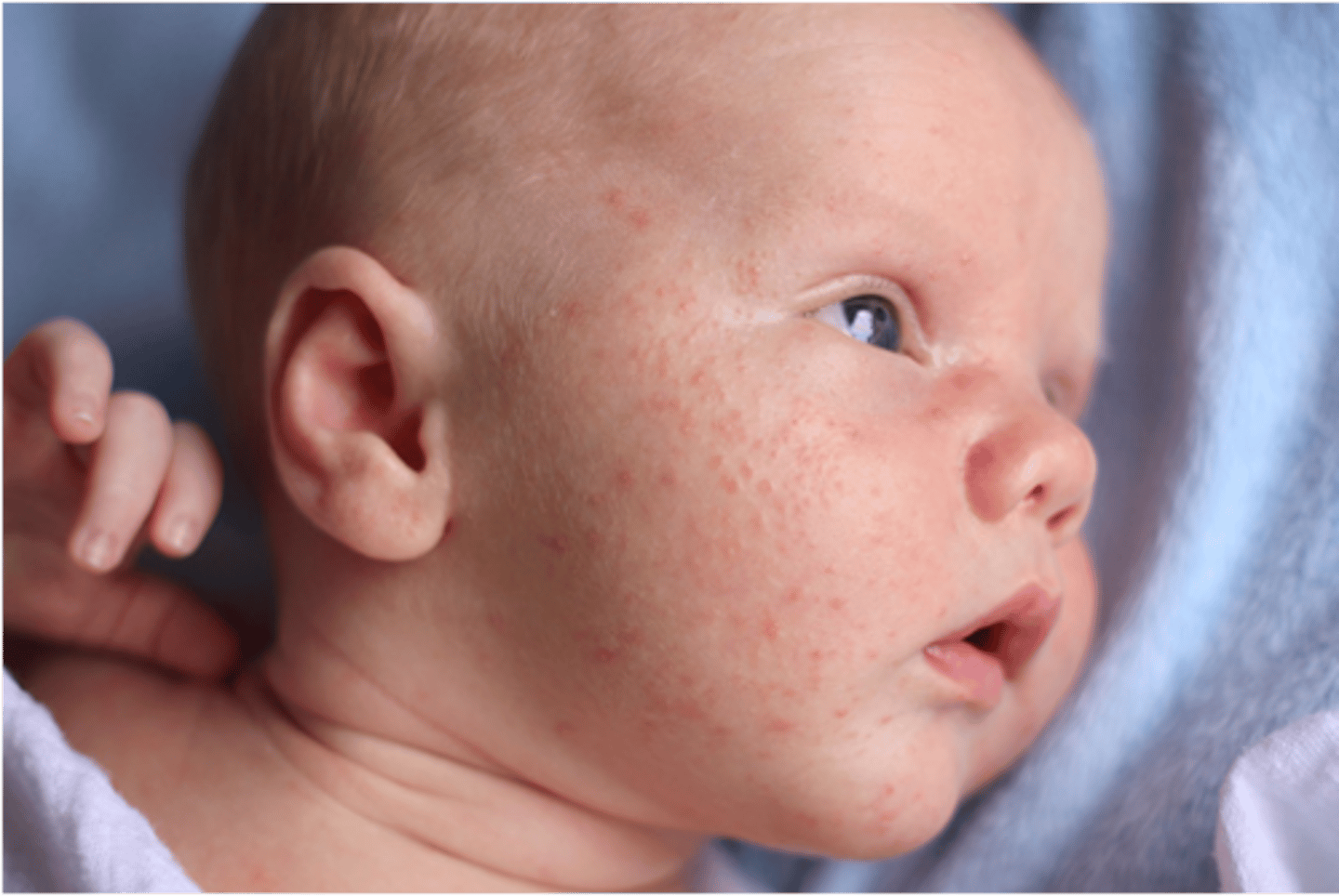
What is miliaria rubra?
scattered vesicles on an erythematous base
results from obstructed sweat glands
disappears spontaneously within weeks
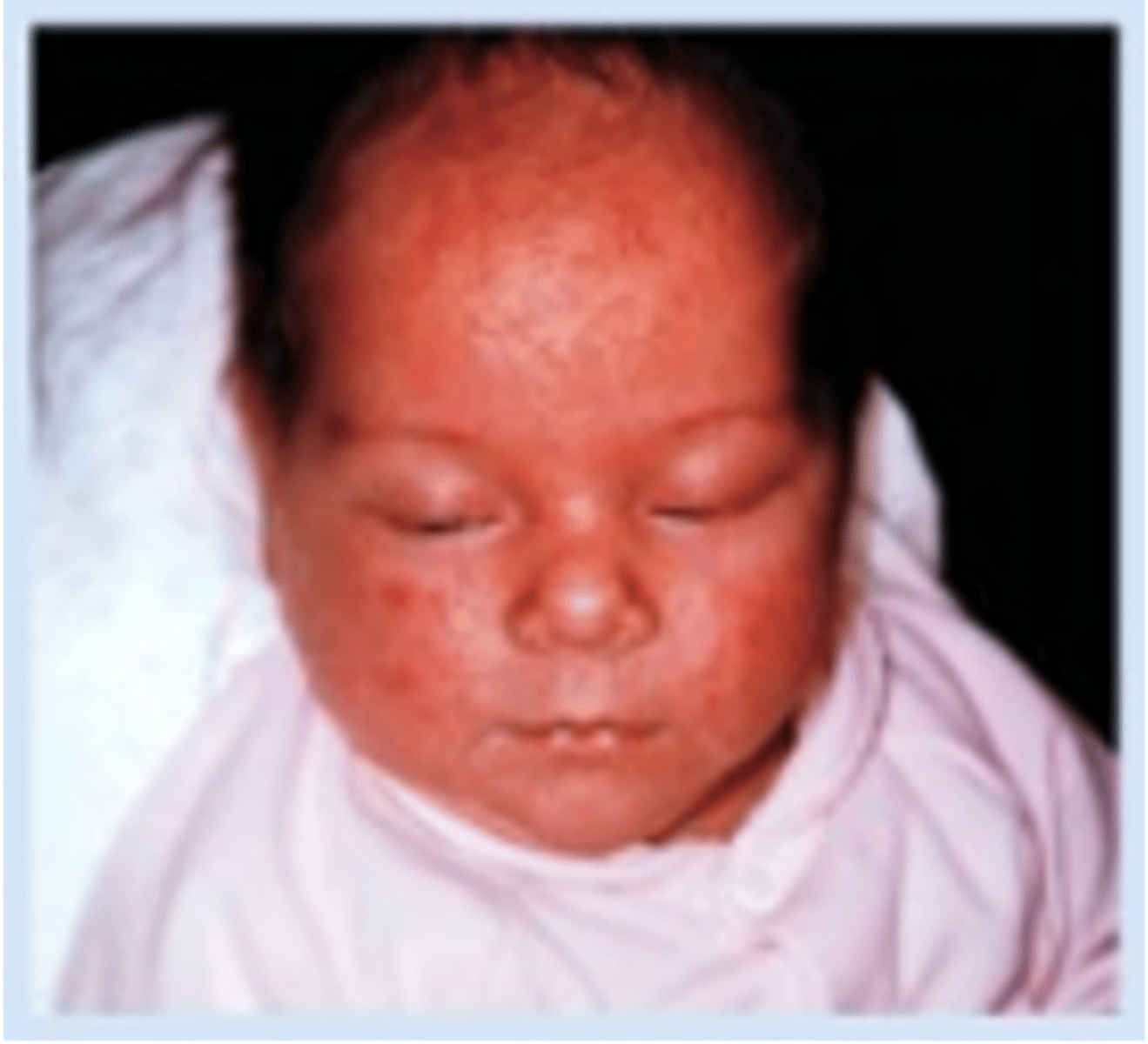
What is erythema toxicum?
usually appears on days 2-3 of life
erythematous macules with central pinpoint vesicles scattered diffusely over entire body
appears similar to flea bites
cause unknown
disappear within 1st week
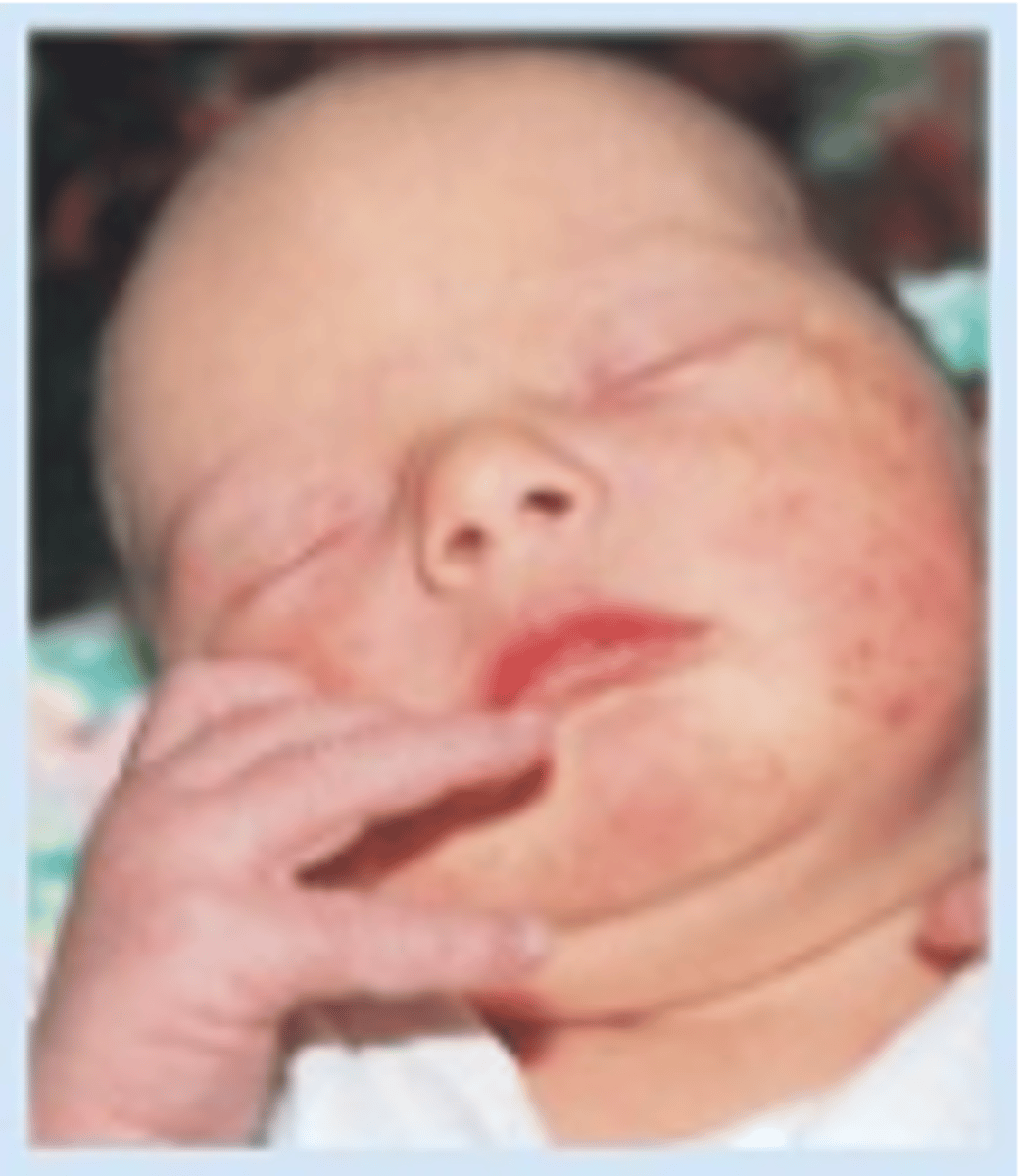
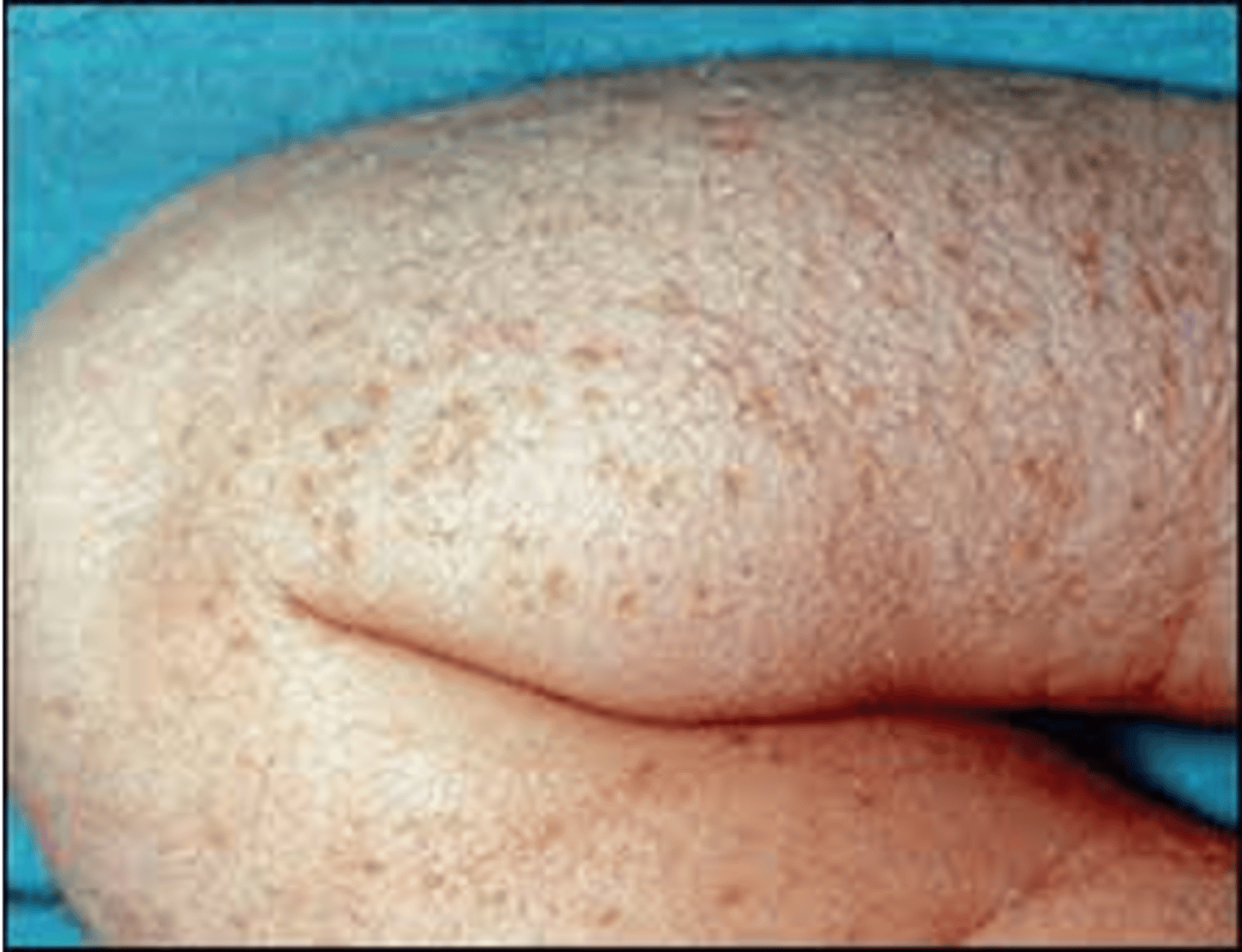
What is pustular melanosis?
occurs in 5% black newborns and <1% of white newborns
presents at birth as small vesiculopustular lesions with a brown macular base
all areas of the body may be affected
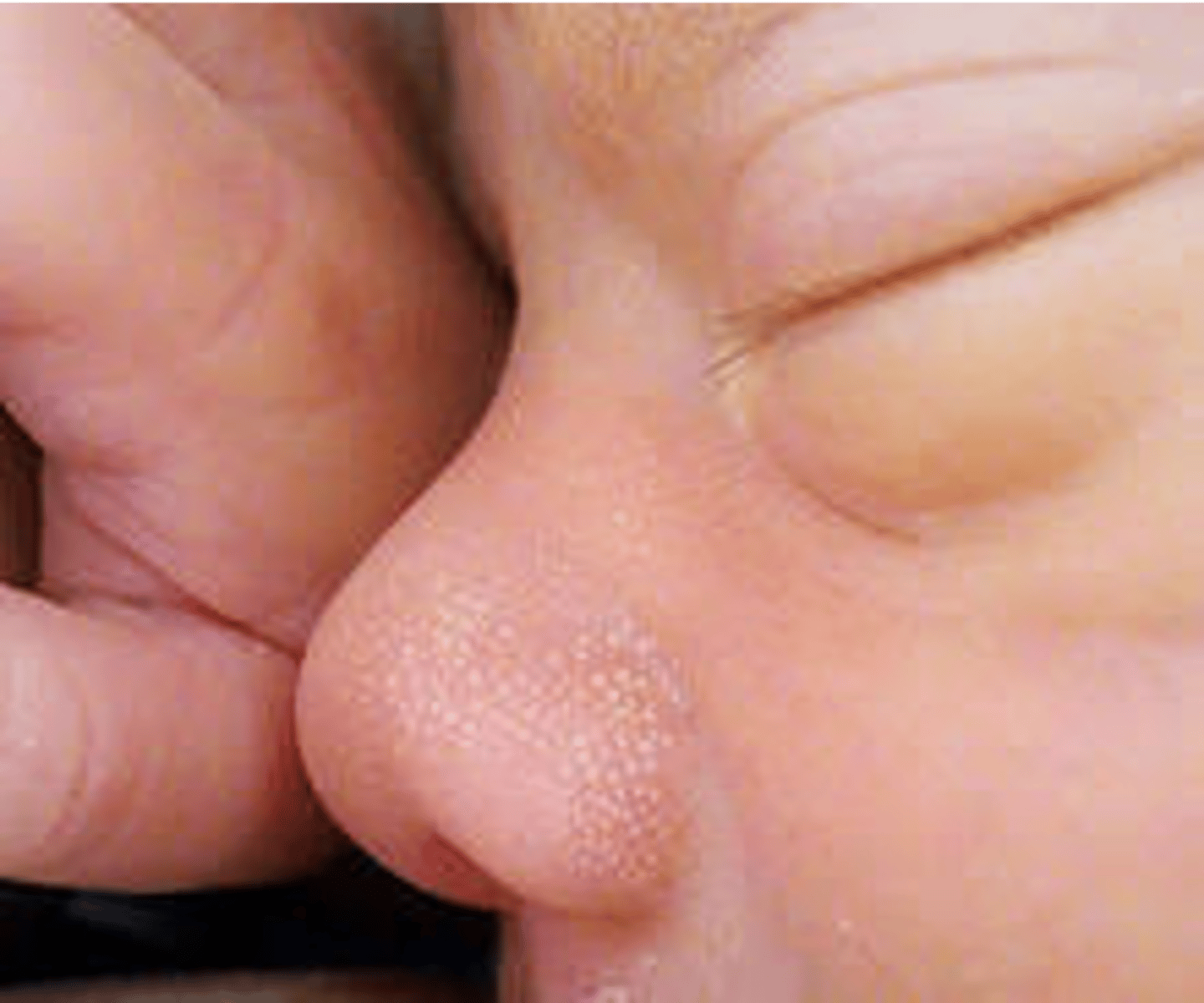
What are milia?
pinhead sized smooth white raised areas without surrounding erythema on nose,chin, foreheat
usually appear within first few weeks and dissapear over several weeks
What do you assess during skin palpation in the infant exam?
turgor
roll skin of abdominal wall to determine hydration
usually due to insufficient intake or excess loss (ask about # of wet diapers)
What is important to note when inspecting the infant head?
symmetry
overall shape
look from all sides to see any abnormalities, flattening
examine shape of head from behind
inspect scal veins for dilation
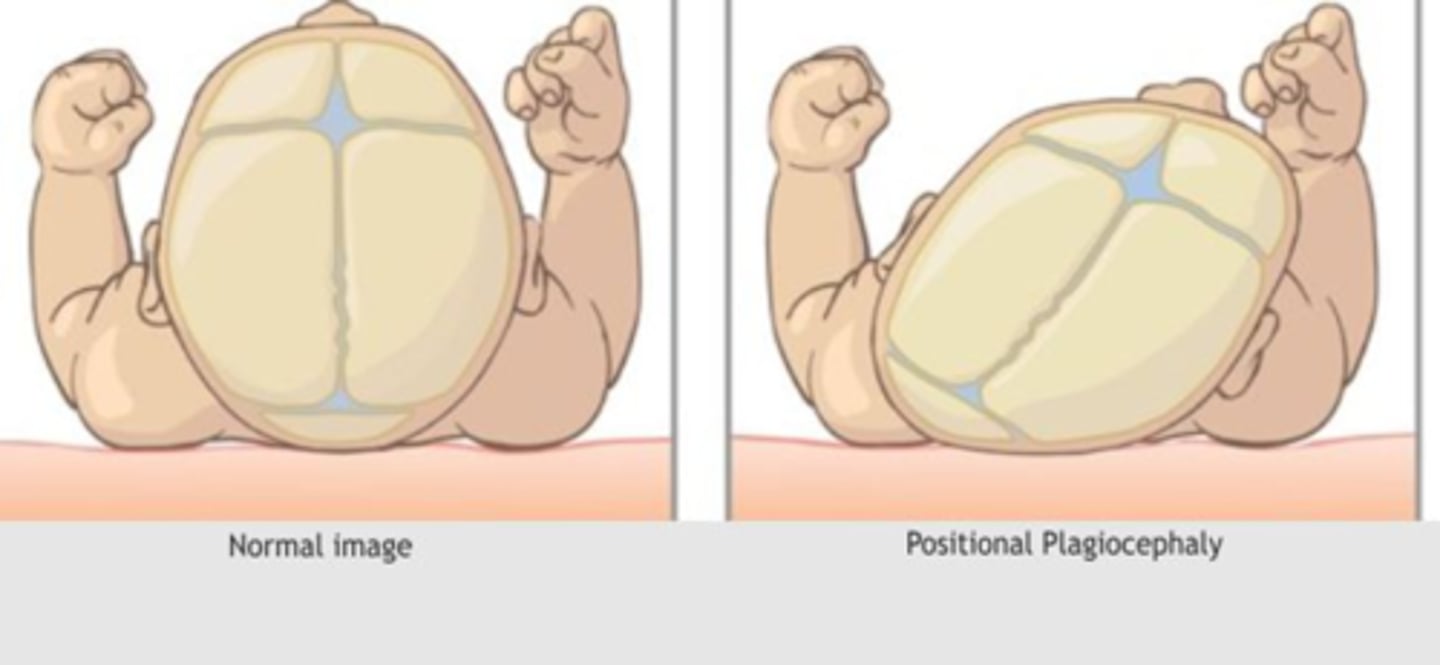
What is positional plagiocephaly?
occurs when infant lies on one side more than the other
disappears as baby becomes more active
What are the characteristics of the infant head?
1/4 of body length and 1/3 of body weight
What is the size of the anterior fontanelle at birth and when does it close?
4-6 cm in diameter
closes btw 2-26 months
what is the size of the posterior fontanelle at birth and when does it close?
1-2 cm
closes within 2 months
What is included when palpating the infant scull?
assess fontanelles for fullness - reflects intracranial pressure
ant fontanelle is soft and flat
palpate while child is sitting or held upright
be gentle as the bones are soft and pliable
measure circumference
What is bulging fontanelle concening for?
increased ICP
What does a depressed fontanelle suggest?
dehydration
What is included in facial exam for infants?
compare child's face to head of parent
if abnormal does the feature fit any recognizable syndrome
What is included when examining an infant's eyes?
try dimming light so they open them
presence of red reflex
inspect clear, pupils, EOM
ophthalmic exam is difficult
can asses VA- use reflexes to assess vision
What reflexes can you use when assessing the eyes instead of visual acuity?
direct and consensual light
blink response to bright light or object moving quickly towards eyes
What is included in the inspection of infant ears?
determine position, shape and features of the ear to detect abnormalities
imaginary line drawn across the inner and outer canthus of the eyes should cross the pinna or the auricle
How do you do an otoscope exam on an infant?
ear canals directed down
pull auricle down not up
What is included in the hearing exam with an infant?
acoustic blink reflex
blinking infants eyes in response to sharp sudden noise
What are the signs that an infant can hear?

What are the steps to inspecting the nose and the paranasal sinuses?
nasal patency
only maxillary and ethmoid sinuses are present at birth
inspect for nasal positioning and septum
What is important to inspect in the mouth/pharynx of an infant?
inspect tongue with blade and flashlight
insect mucosa tongue, gums, palate, tonsils, posterior pharynx
inspect frenulum for tightness that may produce angyloglossie or tongue tie
palpate gums and teeth
pharynx best seen when baby cries
listen for quality of the cry
How many teeth should babies have?
6-26 months of age= 1 tooth per month - up to max of 20 primary teeth
central and lat erupt first, molars last
What should be inspected and palpated in the infant neck exam?
masses
palpate: while infant is supine, check position of thyroid and trachea
palpate clavicle for fracture
assess mobility of neck
What is included in the thorax infant exam?
the thorax is more rounded in infants than in older children and adults
assess RR, breathing pattern and color of child
assess component of breathing- flaring nares
listen for audible breath sounds and work of breathing
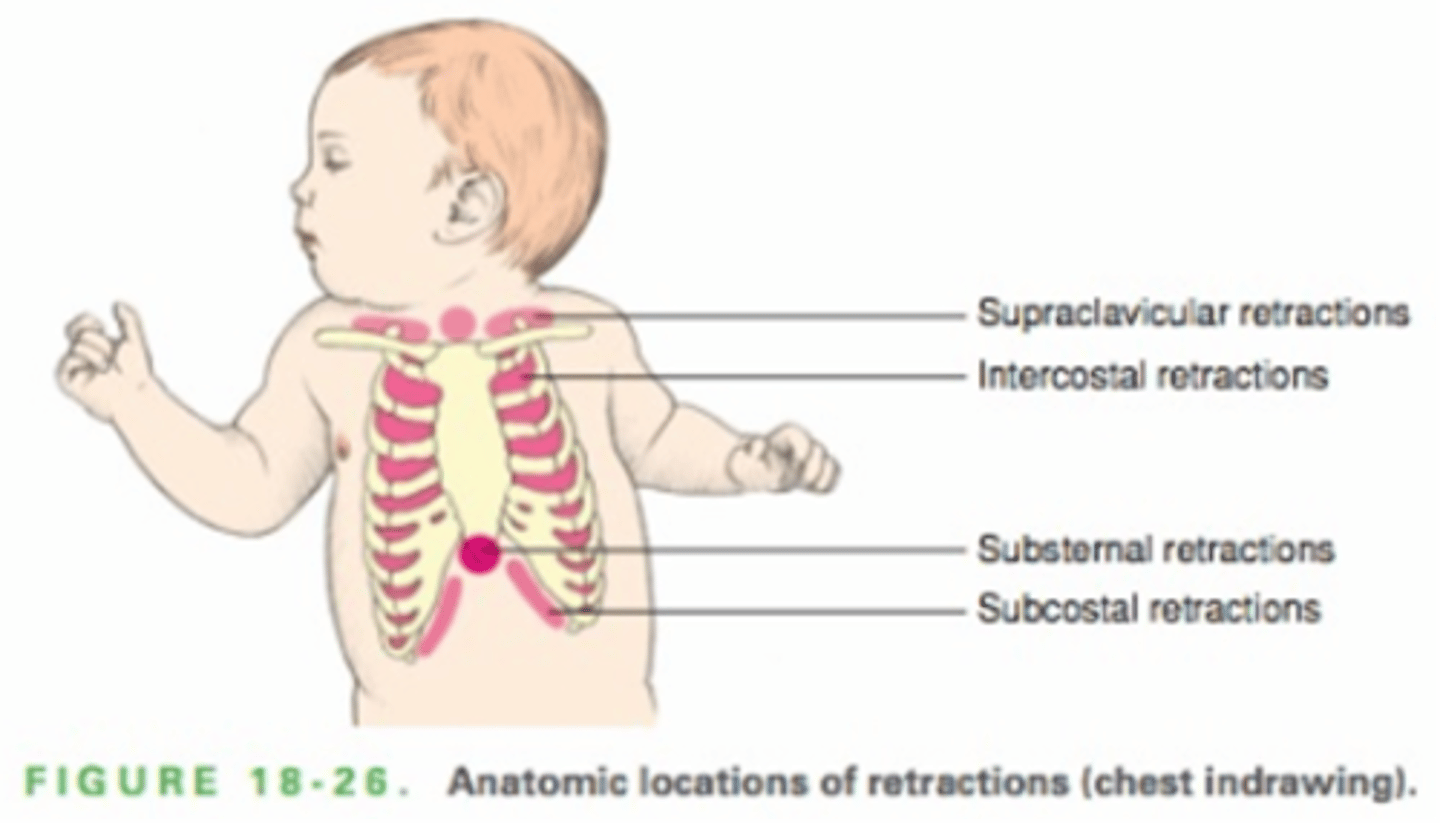
How do you palpate the infant thorax>
tactile fremitus if infant is crying or making noise
look for symmetry
percussion nor helpful- hyperresonance
What is heard during the infant auscultation of the infant thorax?
generally sounds are louder and harsher than adults
wheezes and rhonchi are common
distinguish btw upper and lower airway sounds
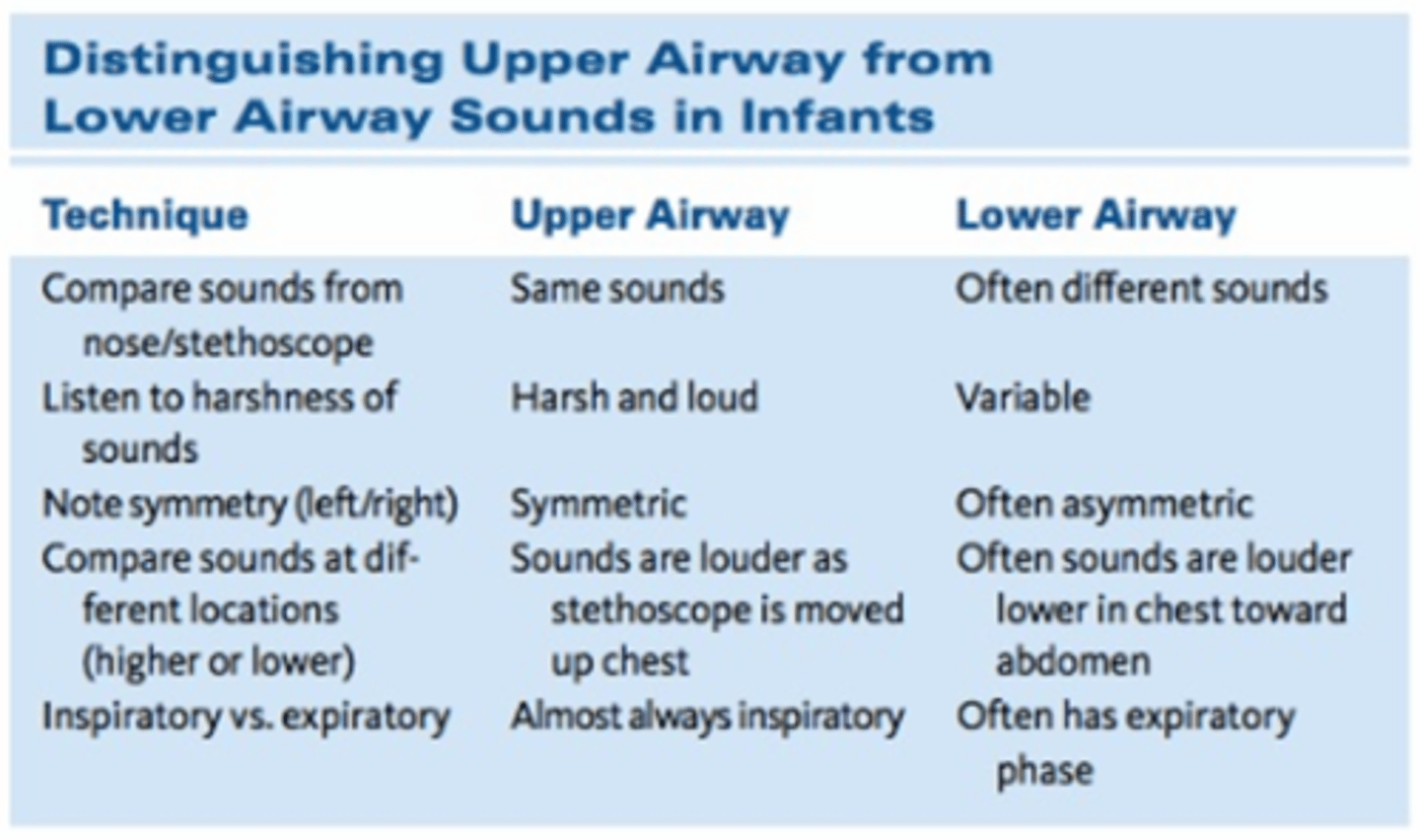
What should be inspected in the infant heart exam?
general signs of health- nutritional status, responsiveness, irritability, fatigue,
RR and pattern
cyanosis
mouth, tongue, conjunctivae
What should you palpate during the infant heart exam?
peripheral pulses esp brachial
PMI not always palpable
What should you auscultate for in the infant heart exam?
easier to assess heart rhythm in peripheral pulses
S1 and Se
S3 heard frequently and normal
S4 not usually heard
murmurs
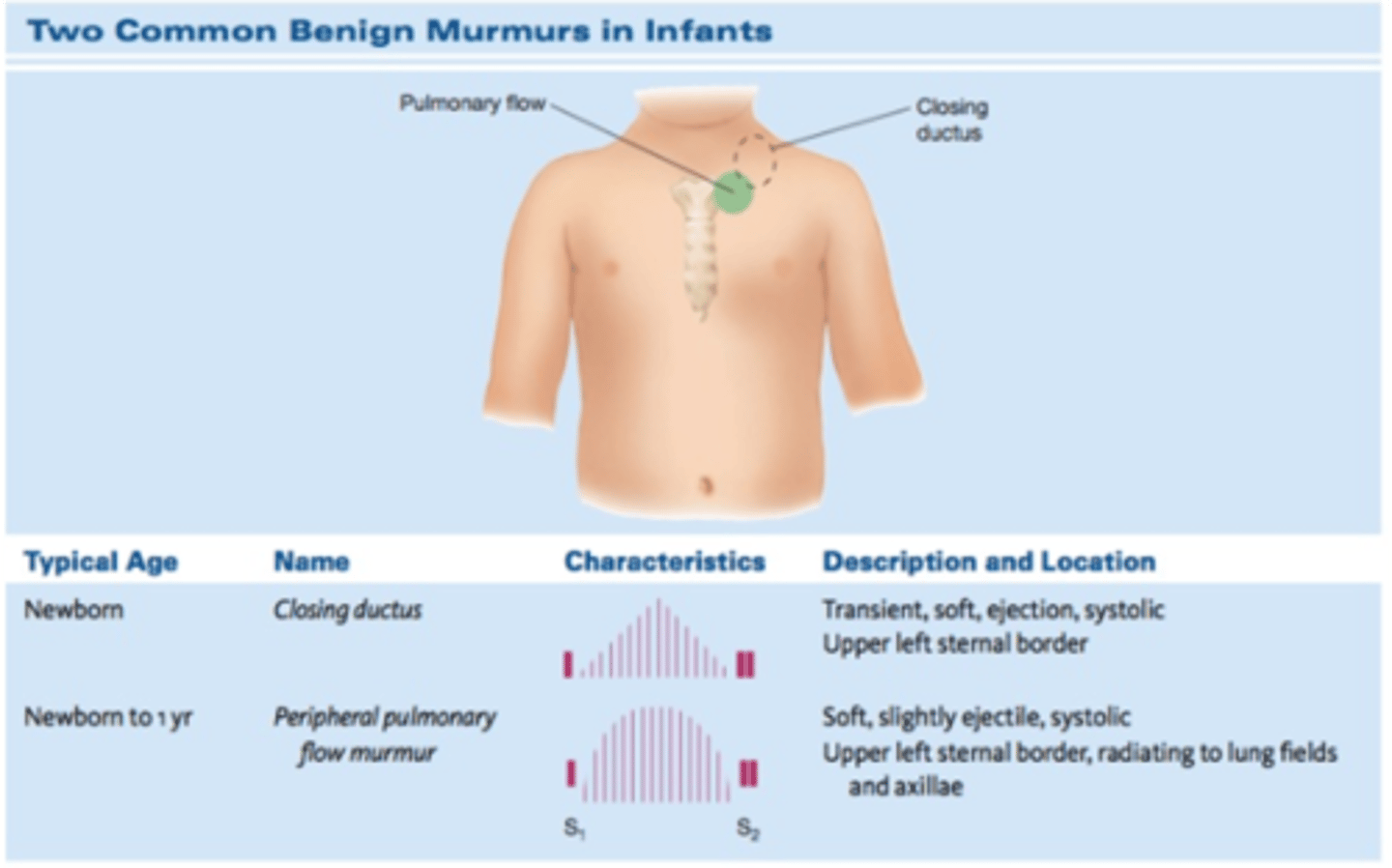
What are the benign infant murmurs and where can you hear them?
What are common non cardiac findings with cardiac disease?
poor feeding
failure to thrive
irritability
tachypnea
hepatomegaly
clubbing
poor overall appearance
weakness
what does central cyanosis indicate?
abnormality
congenital cardiac abnormalities
respiratory disease
acrocyanosis - may be normal in early infancy
What is normal skim color and what is abnormal skin color in infants?
strawberry pink- normal
raspberry red - abnormal- desaturation
What do you insect for in the infant breast exam?
enlarged in newborns secondary to maternal estrogen, can last several months
may be engorged with white liquid- 1-2 weeks
palpate for masses
Hoand what do you inspect the infant abdomen for?
infant lying supine and hopefully asleep
abdomen is protuberant due to poorly developed abdominal muscles
umbilical cord dries and falls off within 2 weeks
may see diasrasis recti
What do you inspect the umbilical cord for?
2 thick walled arteries and 1 larger but thin walled vein
inspect for redness or swelling
umbilical hernias are detectable by a few weeks- most disappear within 1 year of buy age 5
how do you percuss the infant abdomen?
may percuss as a normal adult but it may be more tympanic
palpating abdomen may be easier if you hold legs flexed at the hips and knees and palpate
pulsations are common from aorta
kidneys may be palpable
descending colon is sausage like mass in LLQ
What is included in the palpation of the infant abdomen exam?
palpable spleen tip is normally 1-2cm below costal margin
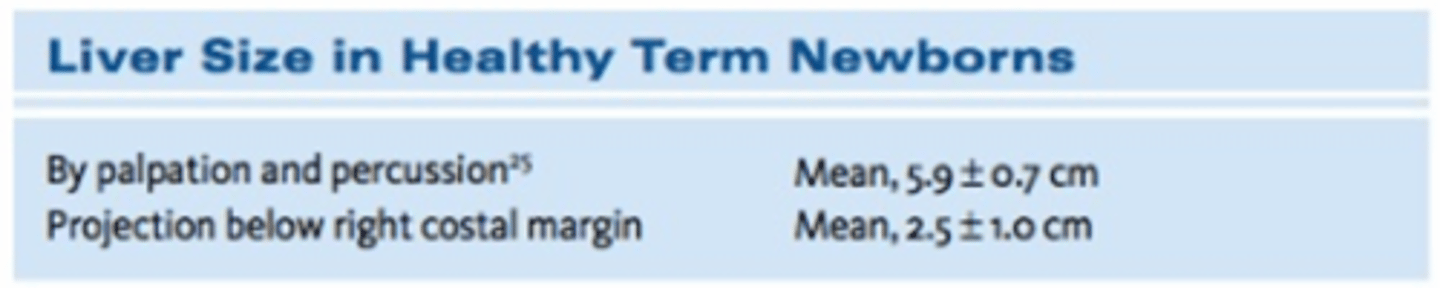
liver edge is generally 1-3 cm below costal margin - make sure to start lower in abdomen to avoid missing enlarged liver
may use scratch test to evaluate for enlarged liver
When would you do an infant rectal exam?
typically not done unless there is concern for patency of anus or abdominal mass
What do you inspect for in the infant male genitalia?
note appearance of penis, testes and scrotum
foreskin covers glans and is not retractable at birth but it loosesn over months to years
What is included in the palpation of infant male genitalia?
descent of testes into scrotal sac
evaluate for masses - apply gentle pressure to reduce or try to transilluminate
What do you inspect in the infant female genitalia?
genitalia is prominent in newborns due to moms estrogen levels
assess all structures - note opening
What is included in the inspection fo infant MSK?
focus on detecting congenital abnormalities particularly in the hands, spine, hips, legs and feet
extend fingers to examine them
inspect spine for pigmented spots, hairy patches, deep pits
What should you suspect if there are any pigmented spots, hair patches or deep pits noted within 1 cm of the midline?
external openings of sinus tracts into spinal canal- DO NOT probe risk introducing infection
What do you palpate during the infant MSK exam?
clavicle- lumps, tenderness, and crepitus
hips, legs, feet
T/F bowlegged growth to age 18 months is normal
True
How do you check for hip dysplasia in infants?
look for dislocation or subluxation using barlow or ortolani
soft click should prompt careful exam for dislocated hip
test best done before 3 m
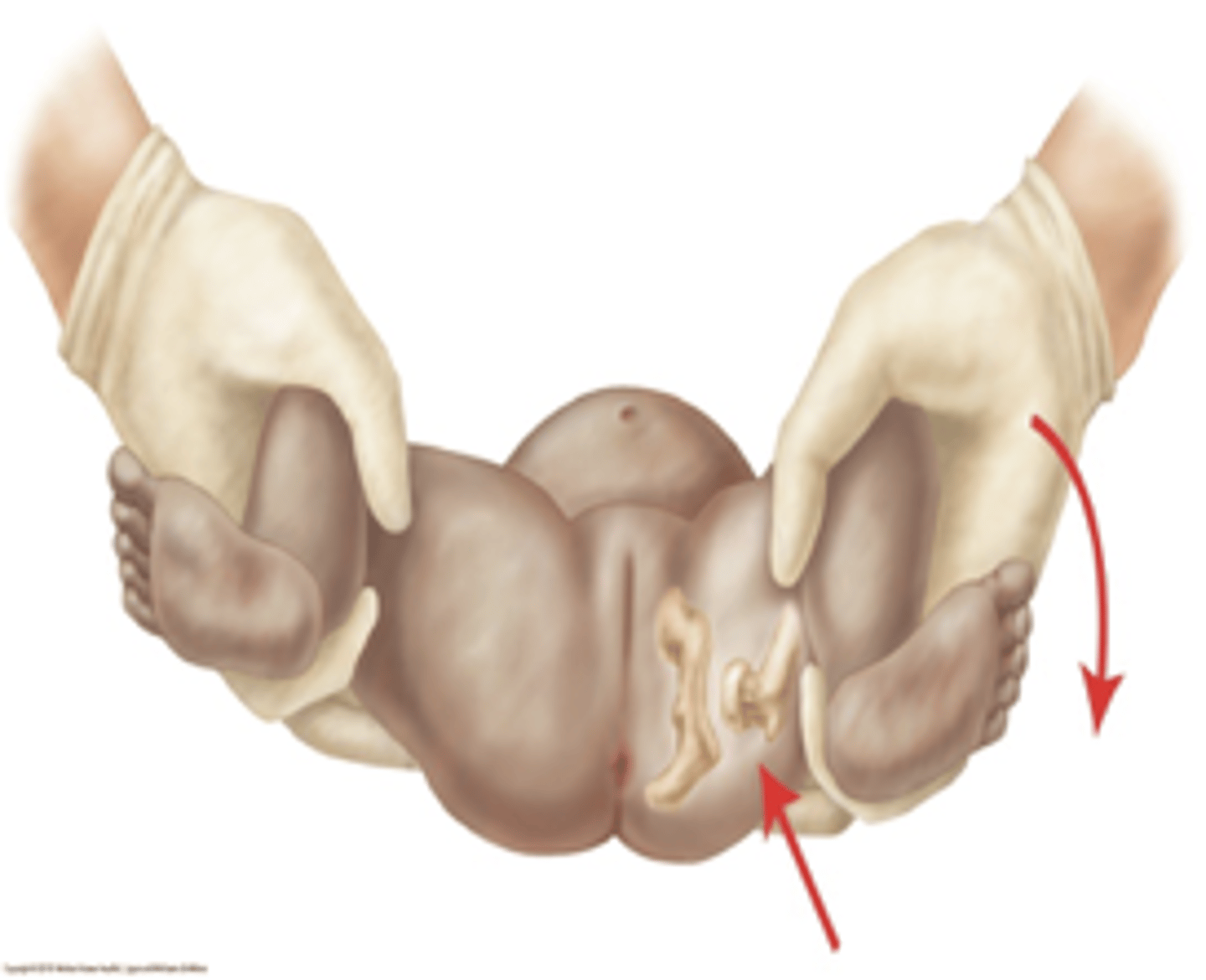
What are the steps to the barlow test?
•Place your index/middle fingers over greater trochanter and your thumbs over the lesser trochanter
•Adduct the legs at a 90 degree angle with gentle posterior force applied to hips
•Assess the ability to sublux or dislocate an intact but unstable hip
•No movement is NORMAL
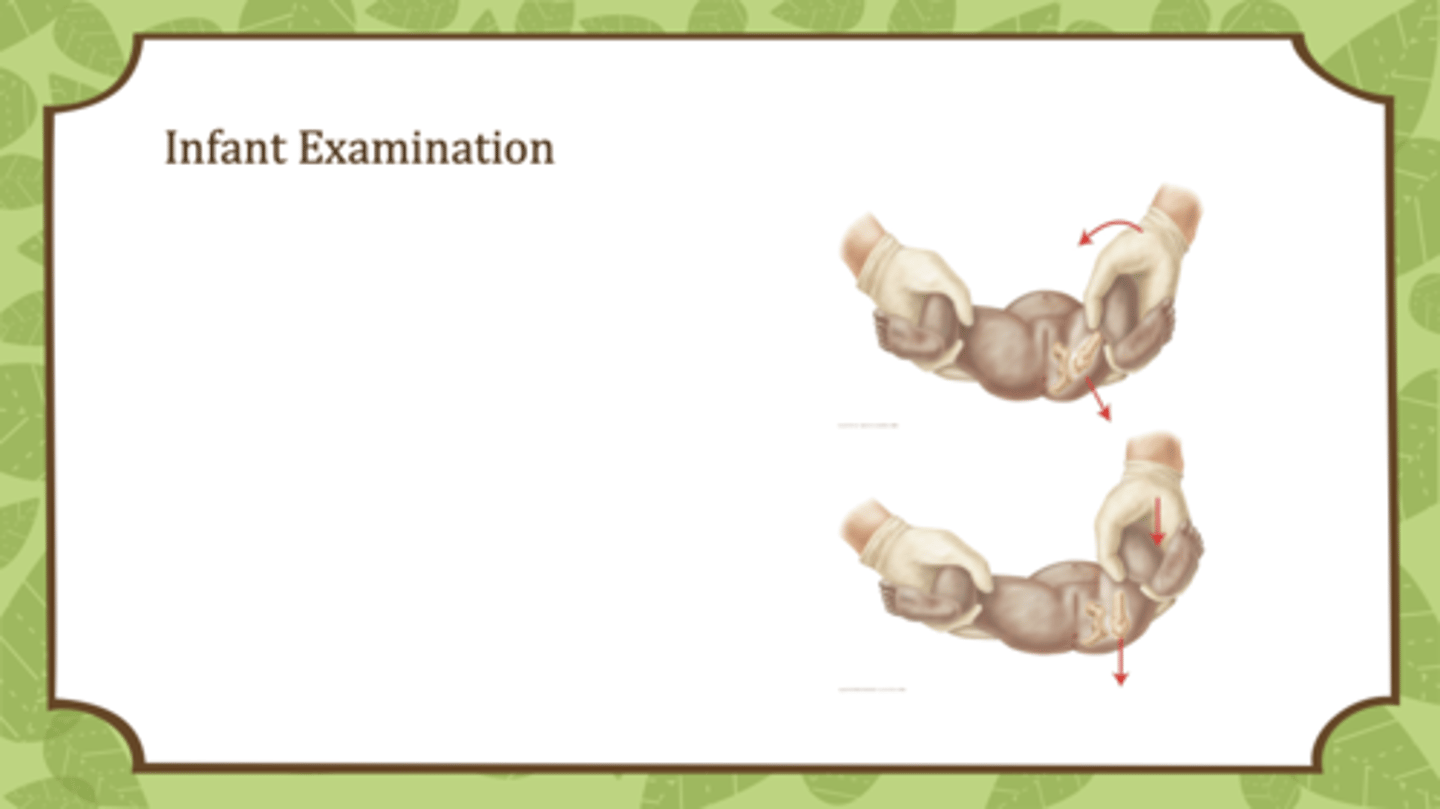
What are the steps of the ortolani test?
•Flex legs to form right angle at hips and knees
•Place index finger over great trochanter
•Abduct legs until reach table, applying forward pressure to the greater trochanters
•Testing for the presence of a posteriorly dislocated hip - an audible "clunk" is considered positive