Coordination and Response
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
How do organisms respond to changes in their environment?
* land animals survive by responding to changes in their surroundings
* there are many different stimuli, such as temperature which they respond to
* this is contolled by the nervous system
* there are many different stimuli, such as temperature which they respond to
* this is contolled by the nervous system
2
New cards
homeostasis
the maintenace of a constant internal environment e.g body water content + body temperature
3
New cards
coordinated response requires
* stimuli
* receptor
* effector
* receptor
* effector
4
New cards
stimuli
change in the environment
5
New cards
receptor
* cells that detect change and send nerve impulses to the spinal chord
* found in sense organs
* found in sense organs
6
New cards
effector
* cells that coordinate a response to the stimuli
* found in muscles and glands
* found in muscles and glands
7
New cards
plants respond to many different stimuli
* direction of light - more photosynthesis
* gravity
* climbing plants have a sense of touch so they can find things to climb
* gravity
* climbing plants have a sense of touch so they can find things to climb
8
New cards
stems experience
* positive phototropism
* negative geotropism
* negative geotropism
9
New cards
roots experience
* negative phototropism
* positive geotropism
* positive geotropism
10
New cards
positive phototropism
grow in the direction of sunlight
11
New cards
negative phototropism
grow away from sunlight
12
New cards
positive geotropism
grow in the direction of gravity
13
New cards
negative geotropism
grow in the opposite direction of gravity
14
New cards
auxin definition
a plant hormone produced in the tips of stems and roots which controls the direction of growth
15
New cards
role of of auxin in the phototropic response of stems
* auxin produced at the tip will be distributed by light receptors to the shaded side of the stem
* cells on the shaded side will grow larger and elongate, whilst cells on the side exposed to light will grow at a slower rate
* as a result the plant will grow towards the light
* cells on the shaded side will grow larger and elongate, whilst cells on the side exposed to light will grow at a slower rate
* as a result the plant will grow towards the light
16
New cards
characteristics of the nervous system
electrical impulses
short lived and quick responses
localised responses
temporary
17
New cards
endocrine system
* chemicals
* longer lasting and takes much longer to travel
* widespread response
* permanent
* longer lasting and takes much longer to travel
* widespread response
* permanent
18
New cards
central nervous system
* brain
* spinal chord
* spinal chord
19
New cards
how is the CNS linked to the sense organs?
CNS is liked to the sense organs by nerves made up of neurones (nerve cells)
20
New cards
three types of neurones
* sensory neurones
* relay neurones
* motor neurones
* relay neurones
* motor neurones
21
New cards
has no involvement with the conscious part of the CNS
the reflex arc, this is why it is so fast and effective
22
New cards
reflex arc
* when a receptor detects a stimuli, electrical impulses are sent to the CNS along sensory neurones
* they then pass the impulse to the relay neurone, which pass it to a motor neurone
* they then pass it to the effector (muscle)
* the effector reacts and responds to the change
* they then pass the impulse to the relay neurone, which pass it to a motor neurone
* they then pass it to the effector (muscle)
* the effector reacts and responds to the change
23
New cards
synapse
junction between two neurones
24
New cards
role of neurotransmitters at synapses
* when electrical impulses are at the end of a neurone, neuro transmitters are released
* they diffuse across the synapse and bind with the receptor moleucles of the second neurone
* this stimulates the electrical impulse to continue along the neurone
* they diffuse across the synapse and bind with the receptor moleucles of the second neurone
* this stimulates the electrical impulse to continue along the neurone
25
New cards
structure of a simple reflex arc - withdrawal of a finger from a hot object example
1. temperature receptors in the skin detect the hot object
2. electrical impulses are passed along to the CNS along the sensory neurones
3. electrical impulses are passed through the relay neurones and then through the motor neurones
4. the impulses will then travel from the motor neurone to an effector (muscle)
5. the muscle contracts and the hand moves away from the hot object
26
New cards
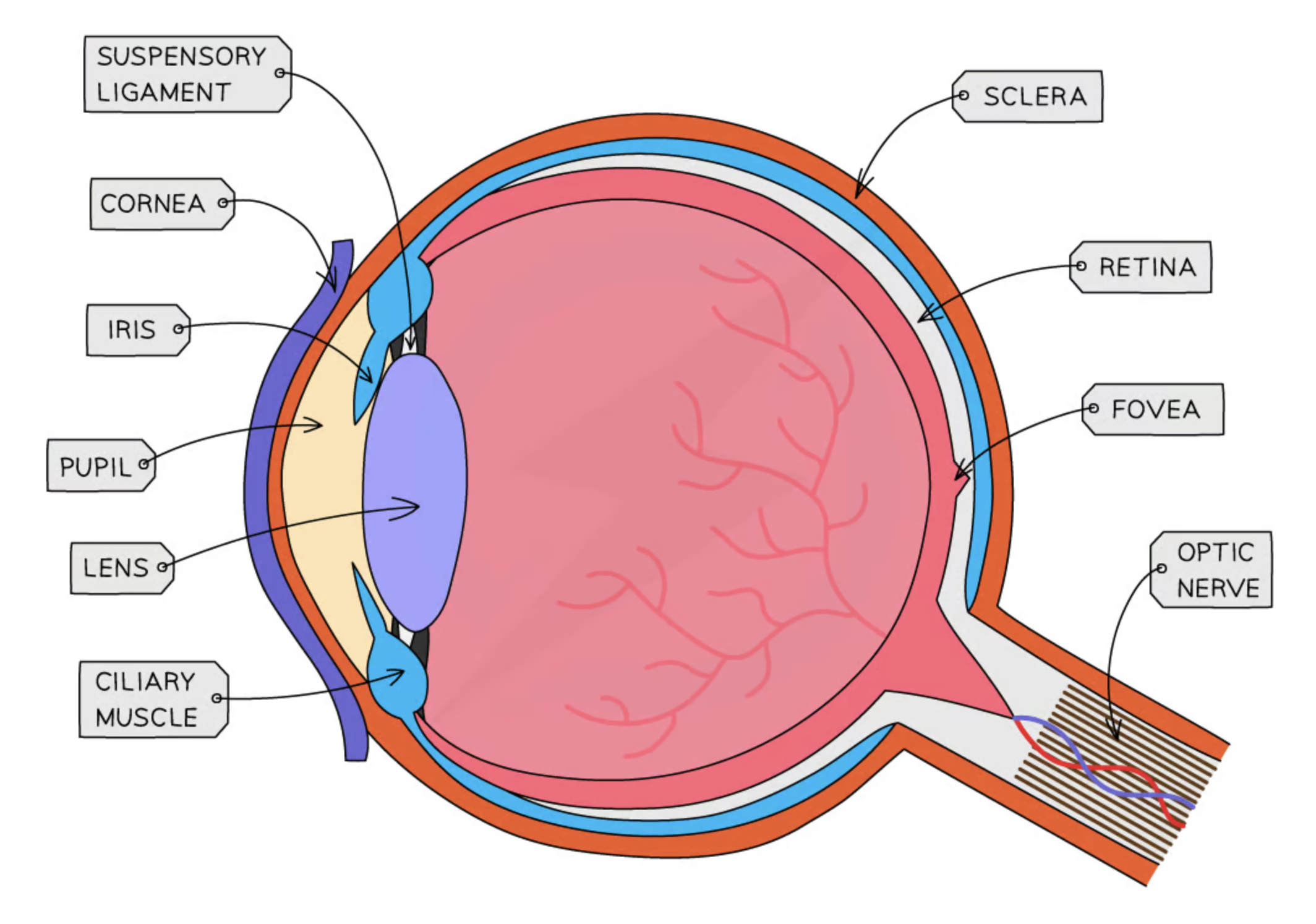
diagram of an eye
memorise
27
New cards
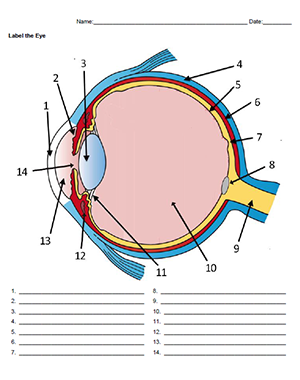
label this
28
New cards
functions of the iris
made of circular and radial muscles to control the amount of light entering
29
New cards
function of the lens
refracts light to create image on retina
30
New cards
function of the pupil
hole in the middle of the iris to let light through
31
New cards
function of the cornea
first lens, part of the sclera
32
New cards
conjunctiva
membrane covering the cornea, lines the eyelid
33
New cards
ciliary muscles
changes shape of the lens
34
New cards
chloroid
dark layer containing pigment cells, stops reflection
35
New cards
sclera
tough outer layer that protects the eye
36
New cards
retina
covered in light receptors called cones and rods, changes light into electric energy
37
New cards
fovea
dip in retina, concentration of cone cells
38
New cards
blind spot
area with no rod, cone cells, where the optic nerve leaves the retina
39
New cards
optic nerve
carries impulses from the receptors to the brain
40
New cards
eye focusing on far objects
* suspensory ligaments pulled tight
* lens pulled flat
* ciliary muscles relax
* less light refraction
* lens pulled flat
* ciliary muscles relax
* less light refraction
41
New cards
eye focusing on near objects
* suspensory ligaments slacken
* lens is more rounded
* ciliray muscles contract
* more light refraction
* lens is more rounded
* ciliray muscles contract
* more light refraction
42
New cards
eye focusing on bright light
* radial muscles relax
* circular muscles contract
* pupil is constricted (smaller)
* circular muscles contract
* pupil is constricted (smaller)
43
New cards
eye focusing on dim light
* radial muscles contract
* circular muscles relax
* pupil is dilated (bigger)
* circular muscles relax
* pupil is dilated (bigger)
44
New cards
vasoconstriction - when the body is cold
* blood vessels constrict
* blood flows through deeper vessels
* less heat is radiated
* blood flows through deeper vessels
* less heat is radiated
45
New cards
shivering
* hair erector muscles contract to trap insulating layer of air
* shivering increases rate of respiration which transfers more energy to warm the body
* shivering increases rate of respiration which transfers more energy to warm the body
46
New cards
vasodilation
* blood vessels dilate
* blood flows through surface vessels
* more heat is radiated
* blood flows through surface vessels
* more heat is radiated
47
New cards
sweating
* vasodilation occurs
* sweat glands produce sweat
* skin uses body heat to evporate
* hair erector muscles relax so hair lies flat
* sweat glands produce sweat
* skin uses body heat to evporate
* hair erector muscles relax so hair lies flat
48
New cards
adrenaline (source, role, effects)
* source - adrenal glands
* role - readies body for ‘fight’ or ‘flight’ response
* effects - increase in heart rate and blood flow to the muscles
* role - readies body for ‘fight’ or ‘flight’ response
* effects - increase in heart rate and blood flow to the muscles
49
New cards
insulin (source, role, effects)
* source - pancreas
* role - controls blood sugar levels
* effects - stimulates the liver to turn glucose into glycogen
* role - controls blood sugar levels
* effects - stimulates the liver to turn glucose into glycogen
50
New cards
four hormones that control the menstrual cycle
oestrogen
progesterone
FSH
LH
51
New cards
oestrogen and progesterone role and source
maintaining the uterus lining
oestrogen produced by the ovaries
progesterone produced by the corpus luteum
52
New cards
FSH role and source
maturation of an egg in the ovary
stimulates the ovaries to start releasing oestrogen
pituitary gland
53
New cards
LH role and source
stimulates the release of the egg
stimulates the release of progesterone from the ovary
pituitary gland
54
New cards
testosterone source and role
produced in the male testes
responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics in males