Taxonomy
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
taxonomy
the branch of science that identifies, describes, names, and classifies organisms
taxonomist
someone who studies taxonomy
classification
method used to group and organize organisms
Carolus Linnaeus
came up with binomial nomenclature
binomial nomenclature
2-word naming system; first word is the genus and is capitalized, second word is the species and is lowercase
taxon
each level of classification
three domains
archaea, bacteria, and eukarya
Kingdom Archaebacteria
prokaryotic, unicellular, autotrophic and heterotrophic, have cells walls without peptidoglycan, and live in harsh environments
Kingdom Eubacteria
prokaryotic, unicellular, autotrophic and heterotrophic, and have cells walls with peptidoglycan
Kingdom Animalia
eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, and no cell walls
Kingdom Plantae
eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic, and have cell walls made of cellulose
Kingdom Fungi
eukaryotic, mostly multicellular though some are unicellular, heterotrophic, and have cell walls made of chitin
Kingdom Protista
eukaryotic, mostly unicellular though some are multicellular, autotrophic and heterotrophic, and have cell walls made of cellulose
dichotomous key
used to identify organisms
Classification levels from broadest to narrowest
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
clade
a group of organisms in a phylogenetic tree that includes a single common ancestor and all of its descendants, living or extinct
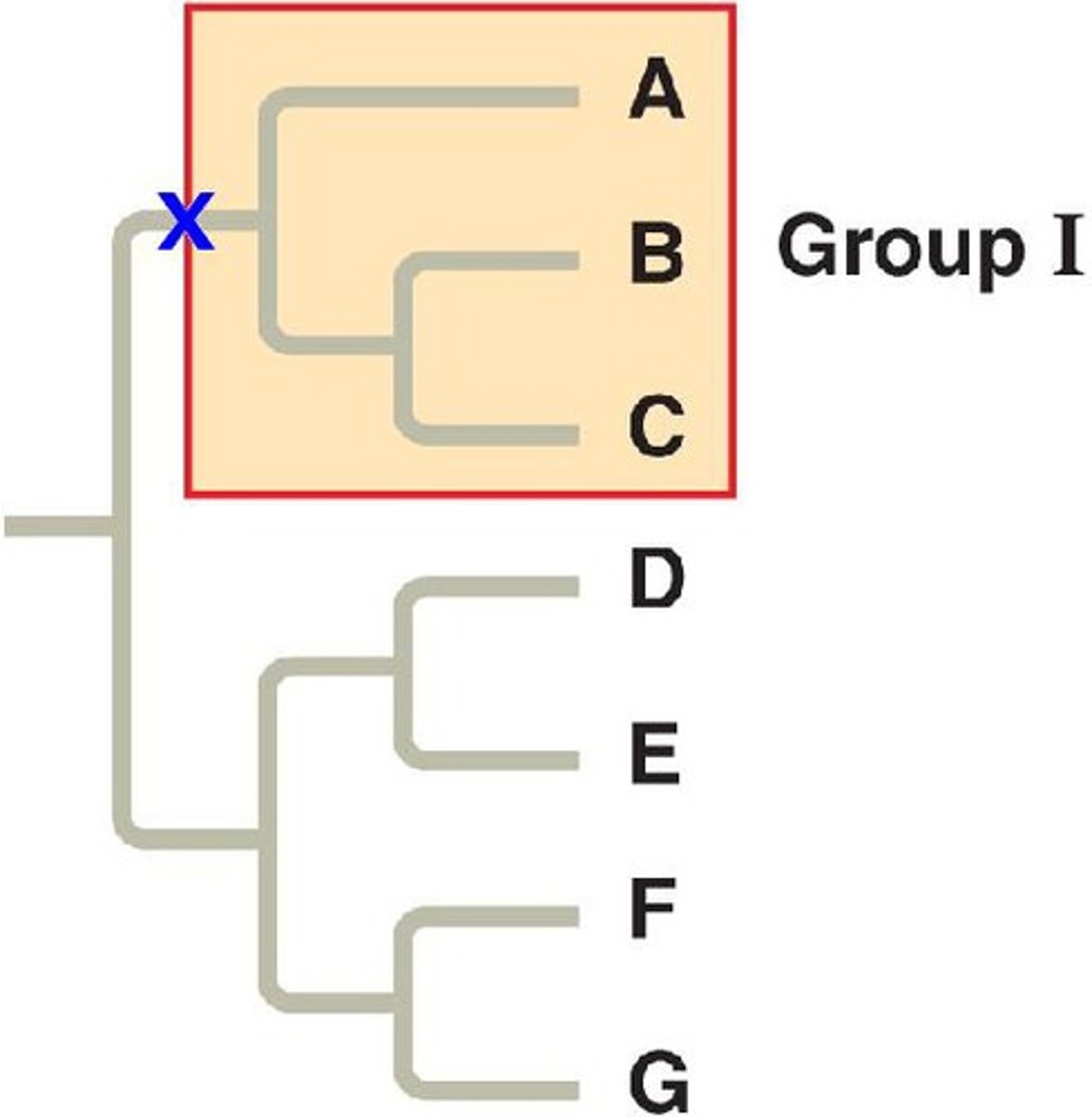
node
represents a common ancestor in a phylogenetic tree