A&P2 LAB EXAM 1 PHYSIOEX AND PROCEDURE
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/63
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
Hematocrit
Refers to the percentage of red blood cells in a sample of whole blood
2
New cards
Buffy coat
A ________ ______ layer of white blood cells appears as a thin, white layer between heavier RBC layer and yellow plasma
3
New cards
Measuring the height of the RBC layer and dividing that by the height of the total blood sample.
How is hematocrit determined
4
New cards
42-52%
The avg hematocrit for males is:
5
New cards
37%-47%
The avgt hematocrit for females is:
6
New cards
Anemia
A lower than normal hematocrit indicates:
7
New cards
Polycythemia
A higher-than0normal hematocrit indicates:
8
New cards
Hemoglobin
Oxygen carrying pigment in the RBC
9
New cards
1) inadequate numbers of RBC
2) decreased amount of hemoglobin
3) abnormally shaped hemoglobin
2) decreased amount of hemoglobin
3) abnormally shaped hemoglobin
3 possible causes for anemia
10
New cards
Iron-deficiency anemia
When there is inadequate amounts of iron in hemoglobin
11
New cards
Aplastic anemia
The failure of the bone marrow to produce adequate RBC numbers
12
New cards
Sickle cell anemia
_____ ____ ______ is an inherited condition in which the protein portion of hemoglobin molecules folds incorrectly when oxygen levels are low.
13
New cards
1) living at high altitudes
2) strenuous athletic training
3) tumors in the bone marrow
2) strenuous athletic training
3) tumors in the bone marrow
3 causes of polycythemia
14
New cards
Antigens
All of the cells in the human body are surrounded by a plasma membrane that contains genetically determined glycoproteins called __________
15
New cards
Agglutinogens
Antigens on red blood cell membranes are called ________
16
New cards
Agglutinins
Antibodies in red blood cells are called _______
17
New cards
Type O
Blood type with no antigens
18
New cards
Type B
Blood type with both a and b antigens
19
New cards
Type a
Blood type with a antigens
20
New cards
Type b
Blood type with b antigens
21
New cards
type ab
Blood type with no antibodies
22
New cards
Type o
Blood type with both antibodies
23
New cards
Hemothermic
When the human body maintains an internal body temperature within the 35.8-38.2 C range even though the external temperature is changing.
24
New cards
Hyperthermia
Elevated body temperature
25
New cards
Hypothermia
Low body temperature
26
New cards
Poikilothermic
of animals except birds and mammals; having body temperature that varies with the environment
27
New cards
Ringers solution
Consists of essential electrolytes in a physiological solution and is required to keep the isolated, intact heart viable.
28
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
The _____ ______ ______ is activated in times of fight or flight
29
New cards
Norepinephrine and epinephrine
These two hormones increase the frequency of action potentials by binding to B1 adrenergic receptors embedded in the plasma membrane of sinoatrial node cells
30
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system
The _______ ______ ___ , our resting and digesting branch.
31
New cards
Acetylcholine
Parasympathetic nerve fibers release this neurotransmitter that decreases teh frequency of action potentials by binding to their muscarinic cholinergic receptors embedded in the plasma memrbane of the SA node
32
New cards
Cholinergic
releasing or activated by acetylcholine or a related compound
33
New cards
Adrenergic
Chemical modifiers that inhibit, mimic, or enhance the action of epinephrine in the body are _________
34
New cards
Agonist
If the modifier works in the same fashion as the neurotransmitter, it is an _______
35
New cards
Antagonist
If the modifier works in opposition to the neurotransmitter, it is an __________
36
New cards
Pilocarpine
cholinergic agonist used in eyedrops to treat glaucoma
37
New cards
Atropine
A competitive antagonist against parasympathetic nervous system (adrenergic)
38
New cards
Digitalis
Cholinergic agonist
39
New cards
Neutrophil
What is thsi
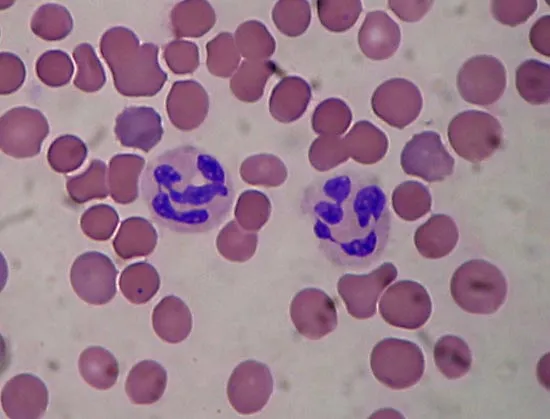
40
New cards
Lymphocyte
What is this
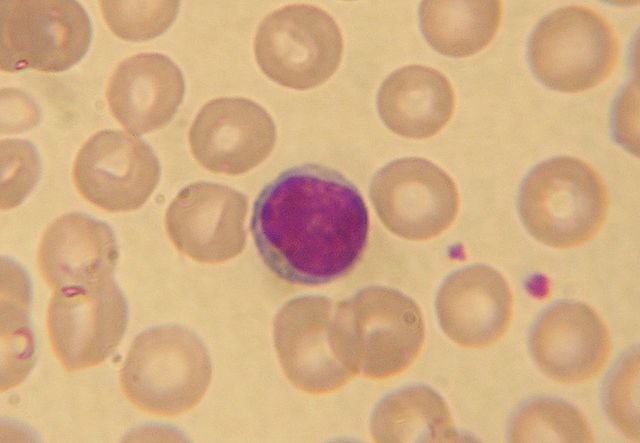
41
New cards
Erythrocyte
What it’s hsi
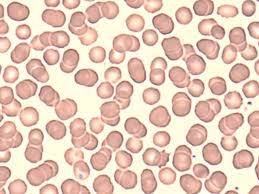
42
New cards
Platelets
What is this
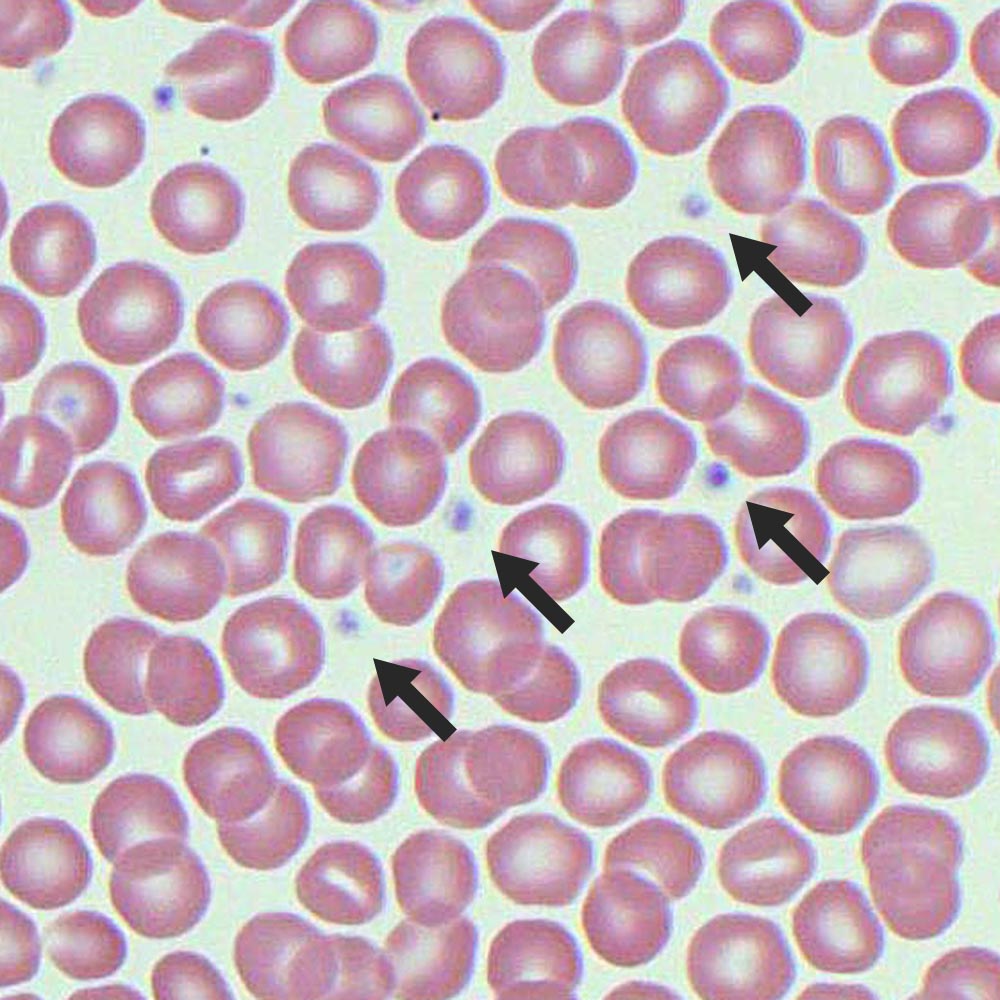
43
New cards
Umbilical vein
The _______ ____ transports blood rich in oxygen from the mother to the fetus
44
New cards
Umbilical arteries
The ________ _____ returns deoxygenated fetal blood to the placenta
45
New cards
Placenta
The _______ is the site of oxygen, nutrient, and waste exchange between fetal and maternal blood
46
New cards
Ductus arteriosus
The _______ _________ is the vessel which connects the pulmonary artery with the aorta, bypassing the fetal lungs; it also atrophies after birth
47
New cards
Ductus venosus
The _______ ________ is the vessel which permits most blood to bypass the liver, and atrophies after birth
48
New cards
Foramen ovale
The _____ _____ allows blood flow to bypass the lungs
49
New cards
Pulse
The alternating surges of pressure in an artery that occur with each contraction and relaxation of the left ventricle
50
New cards
Dorsalis pedis
What pulse is on the dorsal of the foot
51
New cards
Superficial temporal
Which pulse is on the temple region
52
New cards
Facial artery
Which pulse is on the jaw
53
New cards
Radial artery
Which pulse is on the wrist
54
New cards
Ventricular depolarization
QRS represents
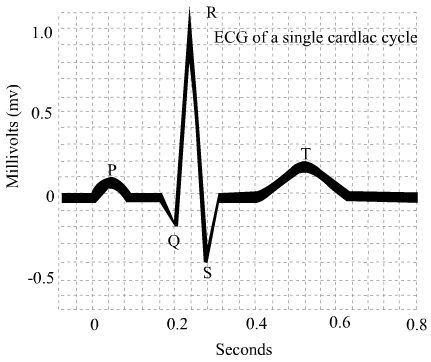
55
New cards
Ventricular repolarization
T wave represents
56
New cards
Atrial repolarization
P wave represents
57
New cards
atrial fibrillation
fibrillation of the muscles of the atria of the heart
58
New cards
Sinus bradycardia
Slower than normal heartbeat
59
New cards
Sinus tachycardia
Faster than normal heartbeat
60
New cards
Ventricular fibrillation
fibrillation of heart muscles resulting in interference with rhythmic contractions of the ventricles and possibly leading to cardiac arrest
61
New cards
Closure of the atrioventricular valves
What does the first heart sound associated with
62
New cards
Closure of the semilunar valves
What is associated with the second heart sound
63
New cards
Hypertension
What can a widened pulse pressure indicate?
64
New cards
BPM
How is pulse rate expressed