Exercise Physiology: Cardiovascular physiology
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What are the functions of the cardiovascular system?
deliver O2 and substrates
remove CO2 and other waste products
transport hormones
regulate temperature and fluid balance
maintain acid-base balance
regulate immune function
What are the components of the cardiovascular system?
heart - pump
blood vessels - system of channels or tubes
fluid - blood
What is the primary goal of the cardiovascular system?
the primary goal of the cardiovascular system is to ensure adequate blood flow to meet metabolic demands
What circulatory route are the right and left sides of the heart?
Right (pulmonary)
Left (systemic)
What is the route of blood flow through the heart?
right atrium
Right ventricle
lungs
left atrium
left ventricle
body
Does the right side of the heart (pulmonary circulation) pump oxygenate or de-oxygenated blood? Where does it pump blood to?
pumps de-oxygenated blood from body to lungs
What is the flow of blood in pulmonary circulation (right heart)?
superior and inferior vena cava
right atrium
tricuspid valve
right ventricle
pulmonary valve
pulmonary arteries
lungs
Is the pulmonary circulation (right heart) a low- or high-pressure system compared to systemic (left heart)?
low pressure system
Does systemic circulation (left heart) receive oxygenated or de-oxygenated blood? Where does it pump the blood to?
receives oxygenated blood and pumps to the systemic circulation
what is the flow of blood in systemic circulation (left heart)?
lungs
pulmonary veins
left atrium
mitral (bicuspid) valve
left ventricle
aortic valve
aorta
Is the left heart (systemic) a high- or low-pressure system compared to pulmonary (right heart)
high pressure
What is myocardium?
cardiac muscle
What does thickness of the myocardium depend on?
dependent on force generation
Which ventricle is the thickest? Why is it the thickest?
left ventricle has greatest thickness
must overcome the force of gravity (pooling of blood in legs)
particularly thick in athletes or individuals with disease
How many fibers types does cardiac muscle?
one fiber type
Type one has a high capillary and mitochondrial density
striated in appearance
How does the heart contract?
calcium-induced calcium release
How does Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release work?
action potential on sarcolemma and through t-tubules inside the cell
Ca2+ from out the cell goes into t-tubule, enters the cell, and binds to the sarcoplasmic reticulum
results in Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
What are the parts of a cardiac action potential?
pacemaker potential
depolarization
repolarization
What happens during pacemaker potential?
slow depolarization due both opening Na+ channels and closing K+
membrane potential never a flat line
What happens during depolarization?
the action potential begins when the pacemaker potential reaches threshold
depolarization due to Ca2+ influx though Ca2+ channels
What happens during repolarization?
due to Ca2+ channels inactivating and K+ channels opening
allows K+ efflux, which brings the membrane potential back to most negative value
What is entering the cell during depolarization?
Na+
Ca2+
what element leaves during repolarization?
K+
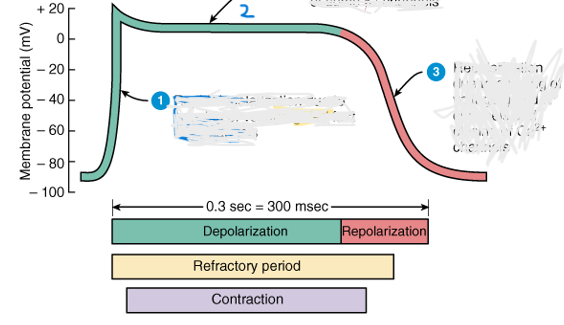
Describe what’s happening at each part of the action potential
rapid depolarization due to opening of voltage-gated fast Na+ channels
Plateau (maintained depolarization) due to opening of voltage gated slow Ca2+ channels and closing of some K+ channels
repolarization due to opening of voltage gated K+ channels and closing Ca2+ channels
Which nervous system input is active below or above 100 bpm?
Below 100 BPM - parasympathetic
above 100 BPM - sympathetic
What arteries provide nutrient delivery and waste removal for the heart?
coronary arteries
left anterior descending artery called the widow maker (when heart not getting enough blood)
what is teh intrinsic heart rate?
100 BPM
What specialized cells in the heart initiate electrical signals?
Sinoatrial (SA) node
Atrioventricular (AV) node
AV bundle (bundle of his)
Purkinje fibers
What has extrinsic control of heart activity?
parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
endocrine system
How does the parasympathetic nervous system control the heart?
release acetylcholine
Vagus nerve hyperpolarizes cell (decrease heart rate and force of contraction)
What is normal resting heart rate?
60-100 bpm (depending on vagal control)
35 bpm for elite endurance athletes
How does the sympathetic nervous system control the heart?
facilitates depolarization of heart cells
increase heart rate and force of contraction
determine heart rate during stress
max of 250 bpm
release norepinephrine
How do you determine heart rate max?
220 - age = Heart rate max
Which system has a greater oxygen demand?
sympathetic
Does the sympathetic system kick in immediately?
no
parasympathetic input must decrease fist
How does the endocrine system control the heart?
catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine)
increases heart rate and force of contraction
What are the parts of an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
P wave - atrial depolarization
QRS complex - ventricular depolarization. Atrial repolarization underneath QRS complex
ST segment - ventricular repolarization
T wave - ventricular repolarization
PR interval - AV delay
QT interval - ventricular depolarization/repolarization
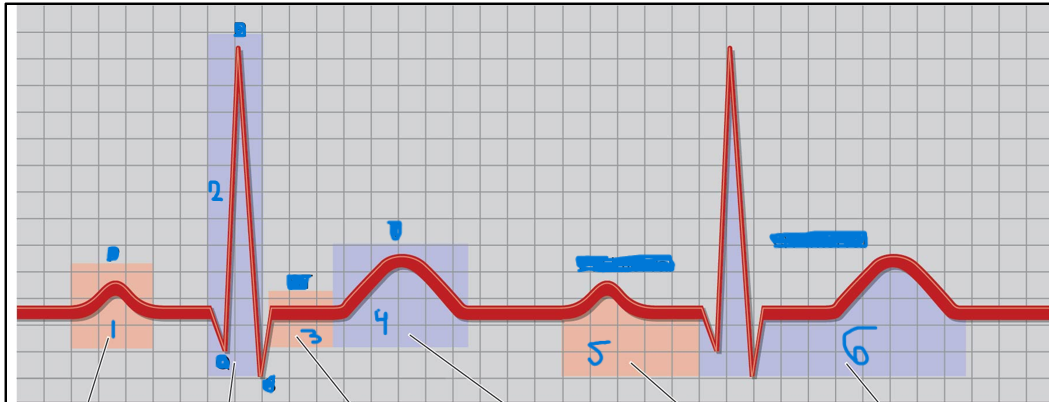
Label the parts of the ECG
P wave
QRS complex
ST segment
T wave
PR interval
QT interval
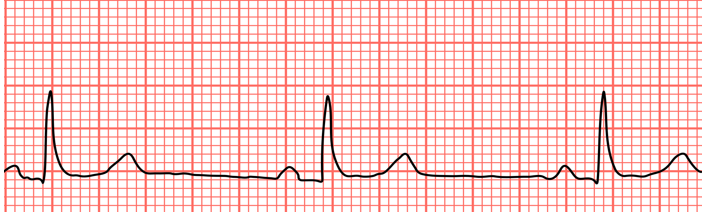
What does this show?
Sinus Bradycardia
<60 bpm
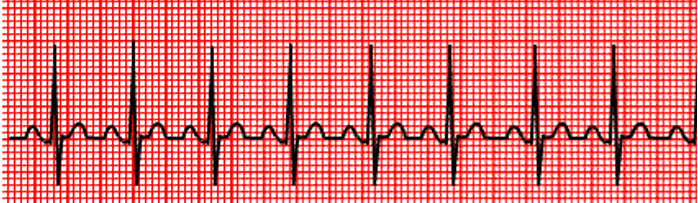
What does this show?
Sinus Tachycardia
>100bpm
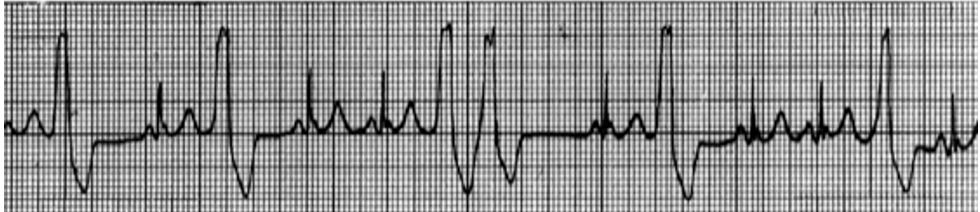
What does this show?
Premature ventricular contractions (PVC)
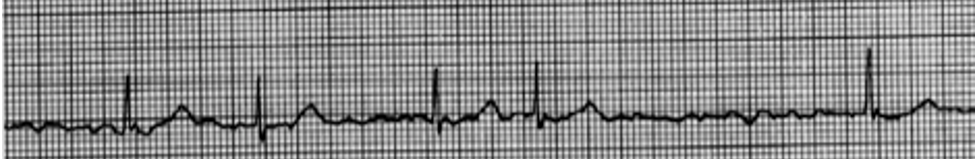
What does this show?
Atrial fibrillation
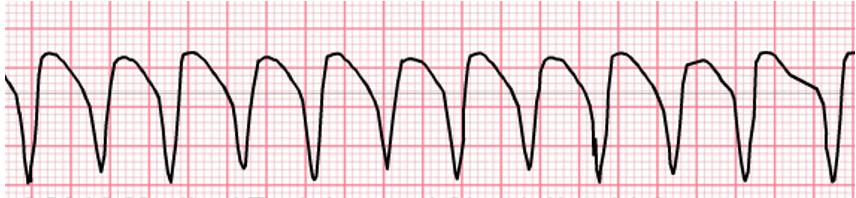
What does this show?
Ventricular tachycardia
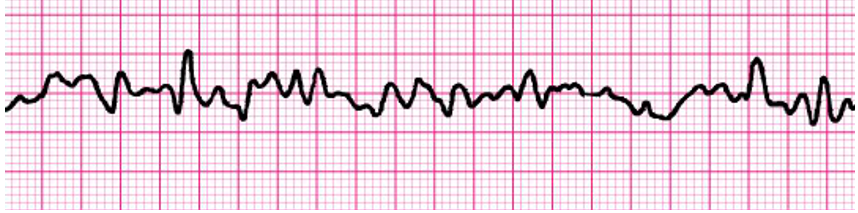
What does this show?
ventricular fibrillation
What is diastole and systole?
Diastole: relaxation phase (heart chambers filling)
Systole: contraction phase (ventricles emptying)
What is stroke volume?
volume of blood in mL pumper per beat
How do you calculate stroke volume?
EDV-ESV
Normal stroke volume: 110mL-40mL=70mL
What is most adaptable with endurance training?
stoke volume
What is ejection fraction?
fraction of blood pumped out of the left ventricle
EF=SV/EDV
70mL/110mL=64%
What is cardiac output (Q)?
total volume of blood pumped per minute (L/min)
Q=HR x SV
70 bpm x 70mL= 4900 mL/min (4.9L/min)
What makes up the vascular system?
arteries
arterioles
capillaries
venules
veins
What are arteries and arterioles?
Arteries
carry blood away from heart
large, muscular, elastic
Aorta is largest artery
Arterioles
have greatest control of blood flow within the system
resistance vessels
controlled by the sympathetic nervous system
What are capillaries and venules?
Capillaries
exchange zone vessels
narrowest and simplest vessels
site of exchange between circulation and tissues (gasses, nutrients, hormones, etc)
Venules
collect blood from capillaries
What are veins?
carry blood from venules back to heart
vena cave (superior and inferior) are the largest veins
largest storage site for blood
70% of blood in veins at rest
Where is most of blood volume at rest?
most of the blood volume is housed in the venous side of circulation at rest
What is blood pressure?
pressure exerted against the wall of the vessel
typically it’s arterial blood pressure that is of interest
pressure is a function of blood volume and vascular size/diameter
What is diastolic blood pressure?
pressure in the artery during cardiac filling
normally 80mmHg at rest
What is systolic blood pressure?
pressure in the artery during ventricular ejection
normally 120 mmHg at rest
What is mean arterial pressure (MAP)?
average pressure exerted by the blood in the arteries
MAP = (0.67 x DBP) + (0.33 x SBP)
What is normal mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) at rest?
93 mmHg
What is hemodynamics?
blood flows from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure
What three conditions can result in increased blood flow?
exercise
lack of oxygen
sitting to standing
anything not coming from rest
What tissues receive most blood?
metabolically active tissue
What receives most blood at rest?
GI tract
skin
What receives most blood during exercise?
skeletal muscle
What are the three types of intrinsic control of blood flow?
metabolic regulation
endothelium mediated vasodilation
myogenic response
What happens during metabolic regulation?
increased O2 demand is the primary and strongest stimulus
other chemical changes: CO2, K+, H+, lactic acid
What happens during endothelium mediated vasodilation?
substances produced in the inner lining of arteriole
What are the myogenic responses?
pressure changes cause dilation/constriction
increase pressure causes smooth muscle to constrict
decrease pressure causes smooth muscle to dilate
What is extrinsic control of blood flow mediated by?
sympathetic nervous system
system or organ level control
In tissue, does SNS stimulation causes smooth muscle contraction or vasoconstriction
both contraction and vasodilation
What is vasomotor tone?
presence of the SNS influence at rest in order to maintain adequate blood pressure
What does an increase and decrease of SNS activity cause?
increase: vasoconstriction
decrease: vasodilation
What are baroreceptors?
sense changes in arterial pressure
detect changes in blood pressure and adjust accordingly
What are chemoreceptors?
blood and muscle receptors
monitor chemical environment for O2, CO2, and pH
What are mechanoreceptors?
ensure muscle is receiving adequate blood flow relative to mechanical activation
What is venous return?
blood flow back to heat
What aids venous return in overcoming the force of gravity?
Venous valves
allow blood flow in only one direction
Muscle pump
skeletal muscle contraction pumps blood back toward heart
Respiratory pump
inspiration raises abdominal pressure and lowers thoracic pressure
What is the function of blood?
transport gases, substrates, metabolic byproducts
regulate temperature
acid-base balance
What is hematocrit (Hct)?
blood cell volume/total blood volume
What percentage of blood is plasma and formed elements?
55% plasma
45% formed elements
How many times is thicker is blood than water?
two times
Does viscosity increase as hematocrit increase?
yes
What must increase as red blood cells increase?
plasma volume