Maths March Assessment: important things to remember
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
formula for probability of an event when all the outcomes are equally likely
number of ways the event can happen
total number of possible outcomes
Mutually exclusive events
events that can’t happen at the same time e.g. rolling a 1 and rolling a 3 on one dice roll.
Independent events
events that have no effect on the probability of each other
P(event A and event B) for independent events
P(A) x P(B)
P(event A or event B) for mutually exclusive events
P(A) + P(B)
P(event A or event B) for non mutually exclusive events
P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
Dependent / conditional events
events that depend / are influenced by other events
opposite of independent events
function for and in probability generally speaking
multiply
function for or in probability generally speaking
add
Arithmetic sequences (aka linear sequences)
terms increase or decrease by the same value each time
Geometric sequence (aka geometric progressions)
consecutive terms are found by multiplying/dividing by the same value (called the common ratio)
nth term of an arithmetic/linear sequence
bn + a
where a = the difference between the terms
and b = the term with n = 0 (the one before the first one)
nth term of a geometric sequence
a x rn-1 where a is the first term of the sequence and r is the common ratio
nth term of a quadratic sequence
Work out the difference between each pair of terms
Work out the second difference - the difference between the differences.
Divide the second difference by 2 to get the coefficient of the n² term. Write this down.
For each term in the sequence, work out the coefficient of the n² term you just worked out, subbing 1, 2, 3 etc into n for each term.
Now subtract those numbers you just worked out from each term in the original sequence (term - coefficient) to give a new sequence
Work out the nth term of this new sequence, and simply add it onto the end of the coefficient you worked out in step 3.
form of linear graphs
y = mx + c where m is the gradient and c is the y-intercept
form of quadratic graphs
ax² + bx + c where c is the y-intercept
what do quadratic graphs look like
parabola: u-shape
1 turning point
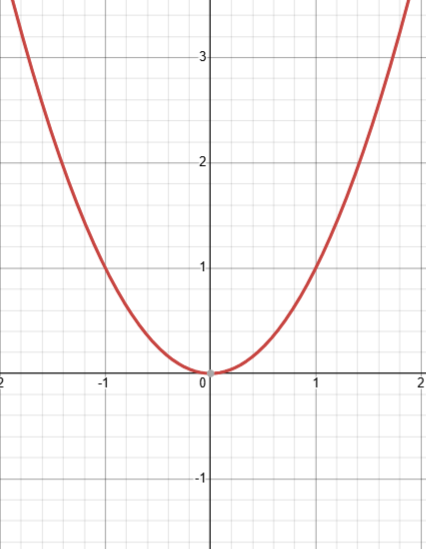
how to find the roots of a quadratic or cubic equation from its graph
they are the points at which the graph crosses the x-axis
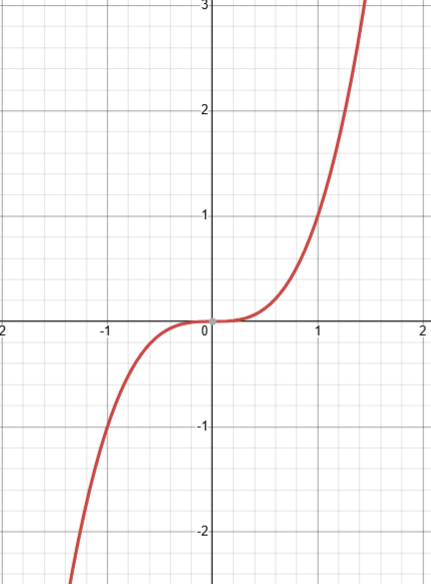
form of cubic graphs
ax³ + bx² +cx + d
what do cubic graphs look like
curve with a wiggle in the middle
2 turning points
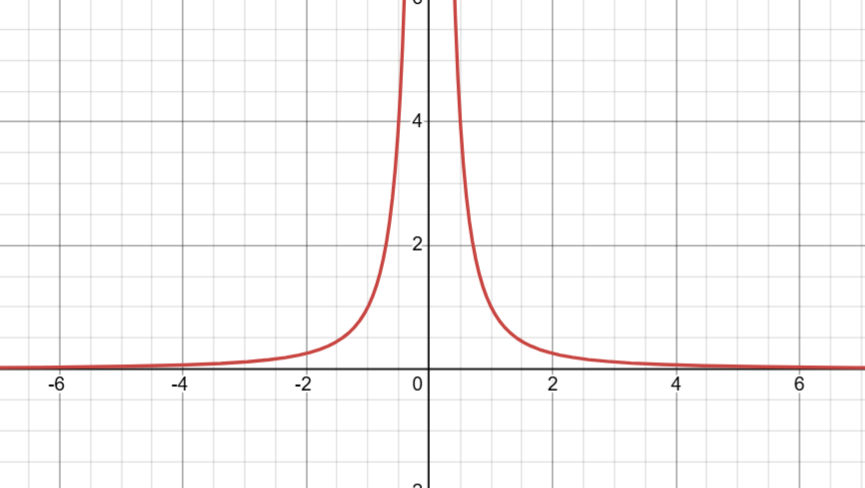
form of reciprocal graphs
a
f(x)
f(x) means that y is some function of x, such as x+1
you can recognise them by their fraction
asymptotes of reciprocal graphs
denominators of reciprocals can never equal 0, if it does the function is undefined
asymptotes are lines that the graph gets very close to but never touches.
what happens if a reciprocal term is squared
it will only have positive values so the graph will look like this
form of exponential graphs
y = ax (where a > 0)
when a is bigger than 1 the graph increases really quickly
when a is smaller than 1 the graph decreases really quickly
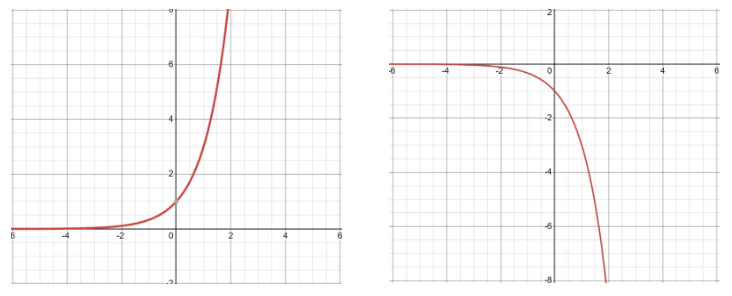
what coordinate do all exponential graphs go through
(0, 1)
form of circle graphs
(x - a)2 + (y - b)2 = r2
r is the radius
the centre is (a, b) but with the opposite signs than the numbers in the equation
give this a look bestie :)

1 tonne in kg
1000kg
ml - cm³
1ml = 1cm³