Week 2
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
Catechol
A type of organic compound that contains a catechol ring
Two OH’s on a benzene ring next to each other
Catecholamine
A group of hormones and neurotransmitters in the body
Autoreceptor
Own neuron that released it
Sympathomimetics
Drug that mimics sympathetic nervous system
Sympatholytic
Drug that decreases activity of sympathetic nervous system
Baroreceptor reflex
A natural bodily mechanism that helps regulate blood pressure
Monoamine oxidase (MAO)
An enzyme in the body that breaks down certain important neurotransmitters called mono amines, including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine
Bound to outer membrane of mitochondria
Two iOS forms: MAO-A and MAO-B
Oxidizes amine to carbonyl
Catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT)
An enzyme in the body that plays a role in the breakdown and inactivation of certain neurotransmitters and catecholamines, such as dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine
Predominantly cytotoxic
Significant expression in hepatic tissue
Methylates the meta hydroxy group
Cheese reaction
A potential interaction when eating cheese and medications with monoamine oxidase
Norepinephrine transporter (NET)
Takes norepinephrine from the synaps back to the neuron
Renin
Substance produced by kidney (blood pressure)
Adrenergic Neurotransmitters
Adregengic neurons utilize the amino acid tyrosine to synthesize catecholamine neurotransmitters
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine
Dopamine
Catecholamine Metabolism
Catecholamine neurotransmitter may be recycled or metabolized
About 90% of NE taken back up by NET
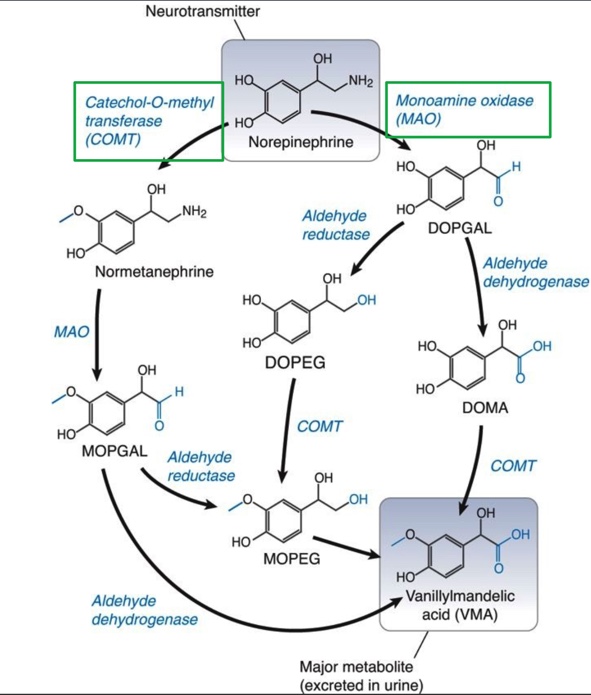
Focus on the green boxes
Minimum requirements for binding ARs
Aromatic ring
Basic nitrogen
Carbon bridge (two C’s between 1 and 2)
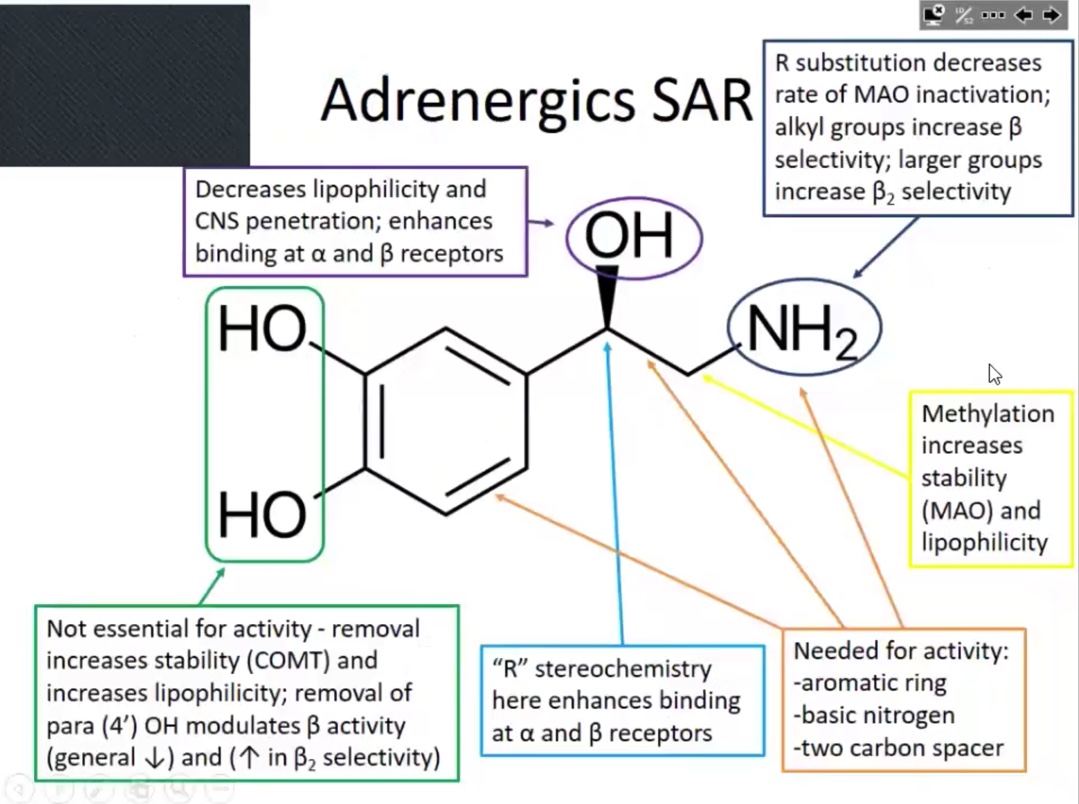
OH
Decreases lipophilicity
Enhances binding alpha and beta receptors
R stereochemistry
Enhances binding alpha and beta receptors
Methlation
Increases stability (MAO) and lipophilicity
Increases potency
1 to 3 carbons (on nitrogen)
Beta selective
4 or more carbons (on nitrogen)
Beta 2 selective
For non essential
Removal of the OH’s will increased stability and increases lipophilicity
Alkyl substituents to on nitrogen increases…
Beta selectivity
(Picture) Para-hydroxyl (4‘) more important for…
Beta activity
Also affects beta 1 & beta 2 selectivity
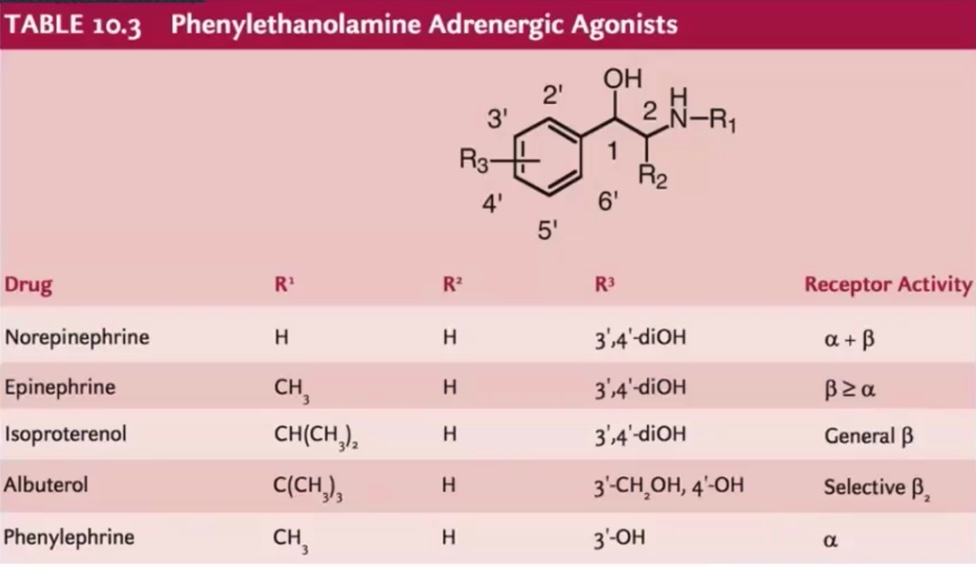
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine
Isoproterenol
Albuterol
Phenylephrine
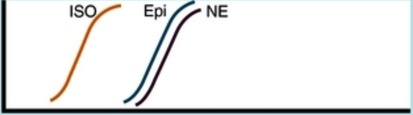
Contraction of arterial strips (alpha 1 receptor)
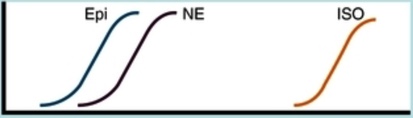
Relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle (beta 2 receptor)

Augmented contraction of heart (beta 1 receptor)
Ruler of the circulatory system
Mean arterial pressure
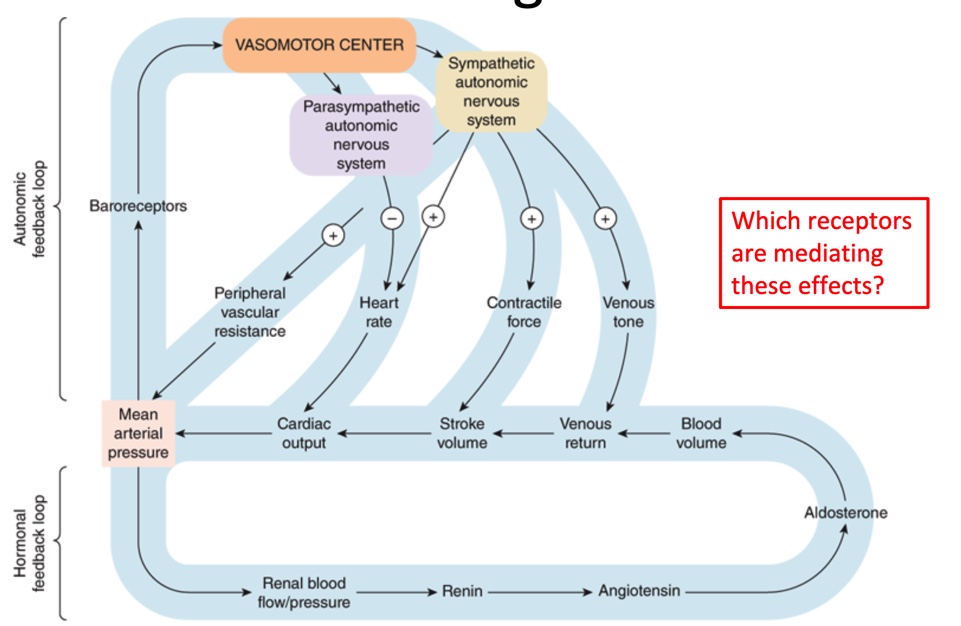
Know this
Adrenergic receptors activity maintains homeostasis; key cardiovascular effects of agonists include:
alpha 1
Alpha 2
Beta 1
Beta 2
Vasoconstriction, venous tone
Decreases central sympathetic outflow
Increases heart rate and contractility, contractile force
Airway and vascular dilation
Catecholamine (dopamine, NE, Epi)
Synthesized from amino acids (tyrosine)
Reuptake: important mode of signal termination
Degraded MAO and COMT
Structure-activity relationships: key considerations for affinity and selectivity at Adrenergic receptors
stereochemistry
Groups on nitrogen
Groups on aromatic ring
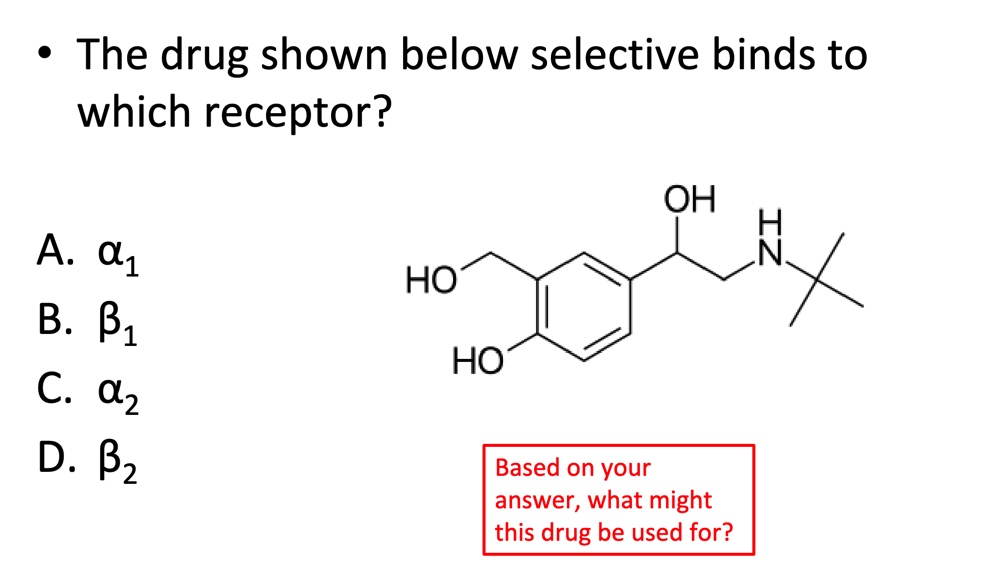
D. Beta 2
Pressor
Anything that increases blood pressure
Endotracheal administration
Delivering medication to the windpipe (trachea) through the mouth or nose
Intracavernous administration
Injection of medication or substances directly into a specific cavity or chamber
Imidazoline
a chemical compound that is often found in various medications and substances
Usually beta receptors
Xerostomia
Dry mouth
Hypokalemia / Hyperkalemia
Low/high potassium
AV node
A node located in the middle of your heart
SABA and LABA
Short / long acting beta agonist
Hypertensive crisis
A severe and potentially life-threatening increase in blood pressure
Hemolytic anemia
A medical condition where the red blood cells in the bloodstream break down or are destroyed more rapidly than the body can replace them
Pheochromocytoma
a rare, usually non-cancerous tumor that develops in the adrenal glands, which are located on top of the kidneys
Studying for adregenerics
What happens when stimulated or inhibited
Focus on MOA
Chemistry: a little knowledge about structure will go long way
Use concept maps, charts, mnemonics
Sympathosmimetic
A substance that enhances activity of the sympathetic nervous system
Direct acting
A1 and B agonists, a2 antagonists
Indirect acting
Releasing agents
Reuptake inhibitors
Mixed acting
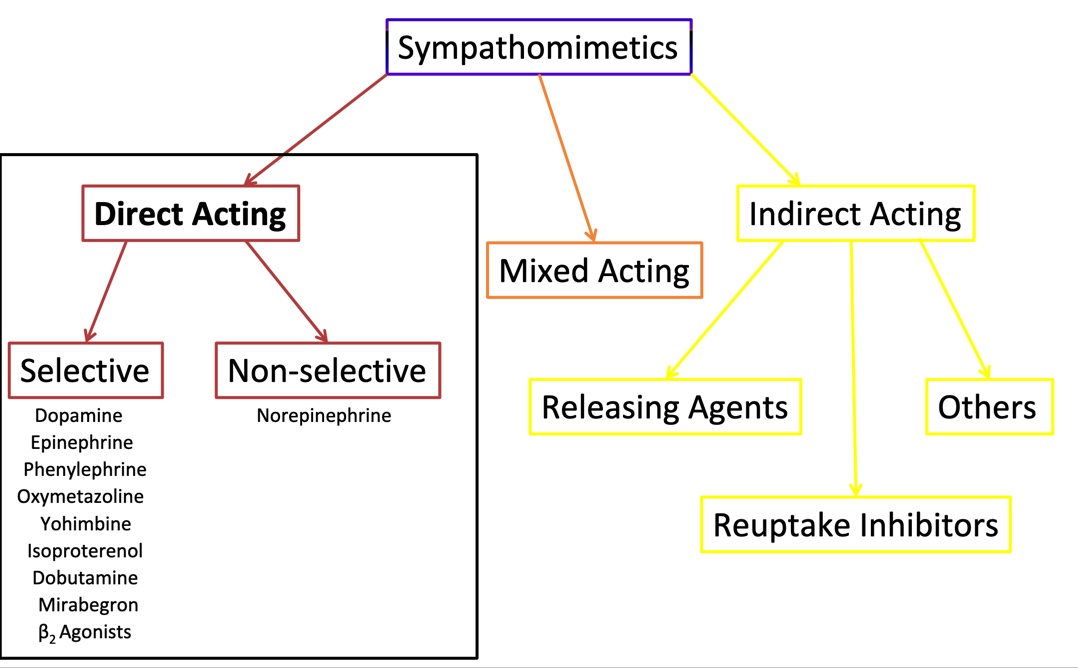
Endogenous Catecholamines
Considerations:
Effects are often dose dependent
Therapeutic uses: will generally be used in emergency / critical care settings
Hemodynamic support
Inotropic support
Pharmacokinetics: no oral availability, doesn’t cross BBB; COMP and MAO substrates
Common ADRs:
CV (hemodynamics, palpitations, arrhythmias)
CNS (headache, anxiety)
Other (N/V, hyperglycemia (epi), polyuria (dopamine))
Drug interactions and therapeutic considerations:
Other Adrenergic / hemodynamic agents
Pregnancy category C
IV administration
Direct acting: B agonists
Increase cardiac output
Increase smooth muscle relaxation
Lungs, uterus, smooth muscle
Therapeutic uses:
Inotropic support, bradycardia, arrhythmias, AV noda block
Class considerations
Usually inhalation or IV administration
Selectivity
4’ hydroxy and size of R group on amine
Hemodynamics (may increased and or lower BP)
Increase glucose
Common ADRs: CNS (headache. Anxiety, insomnia), tremor, hemodynamic instability, hypokalemia, vision disturbances
Direct acting: B2 agonists
Mediate bronchodilation
Chemistry considerations
B2 selectivity enhanced by modification of catechol group and large R group on amine
Resorcinol or hydroxymethyl group
These chagnes also increase stability by decreasing susceptibility to COMT and MAO
Long acting B2 agonists (LABAs) utilize very large, lipophilic R groups
Used for respiratory conditions
Typically administered by inhalation
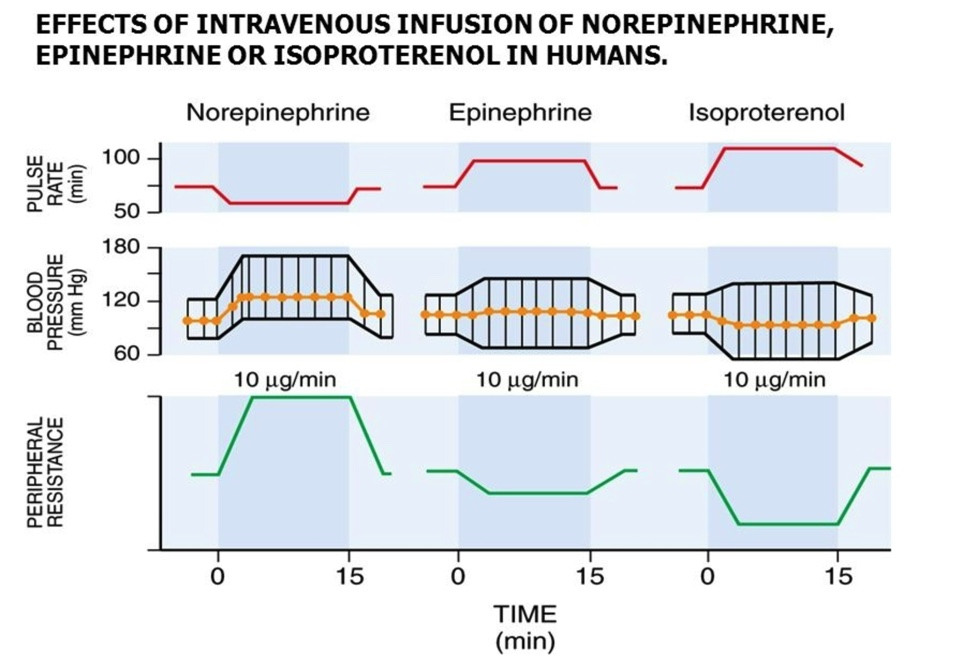
What is the direct effect?
What is the reflex response?
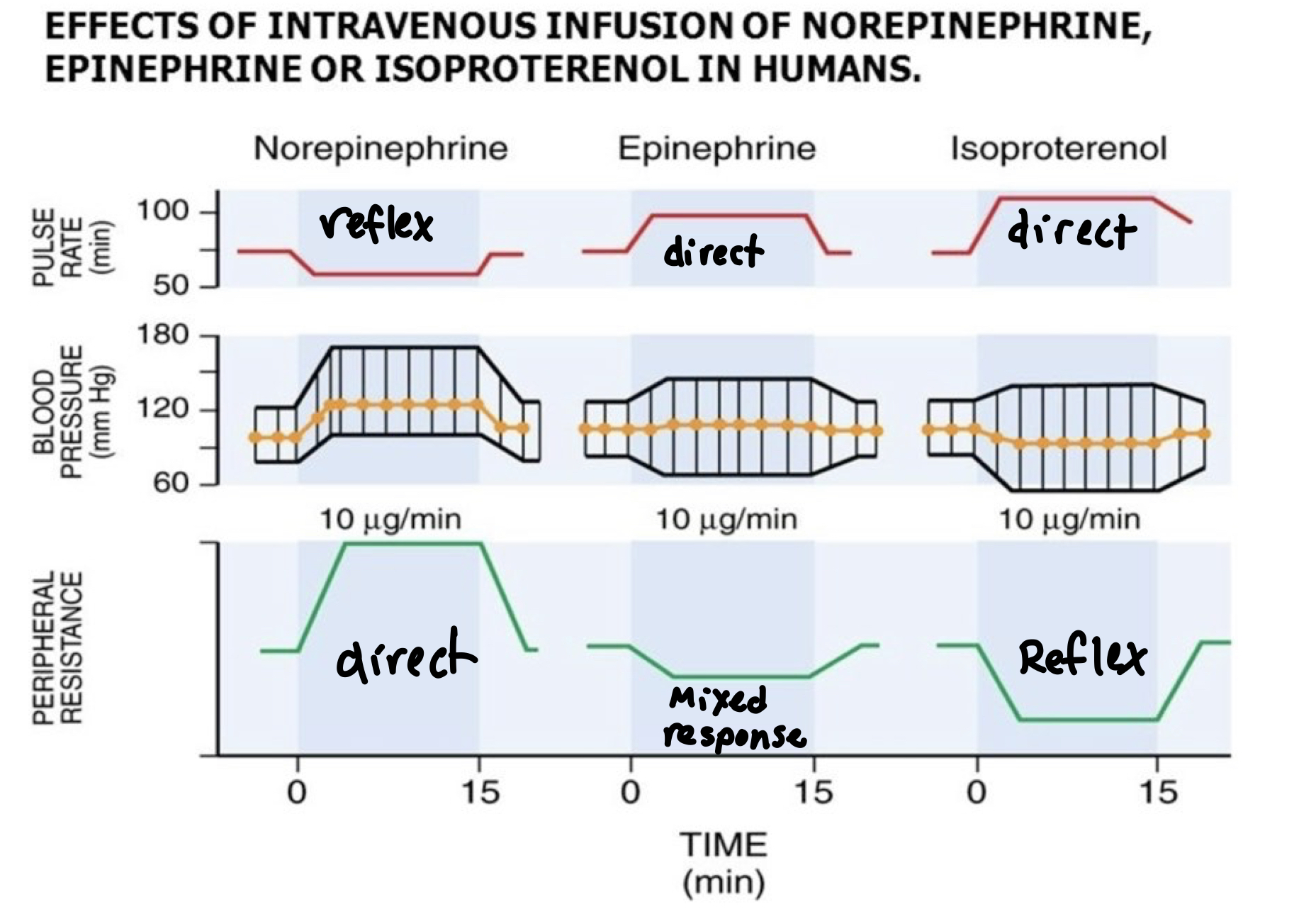
Albuterol (Ventolin)
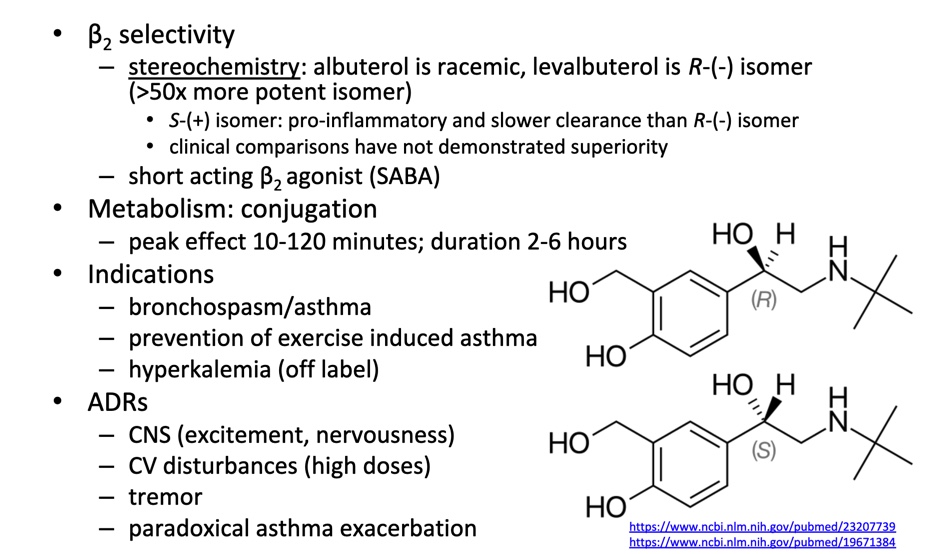
Extended Duration B2 agonists
Mixed Acting: Ephedrine (Akovaz) and Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)
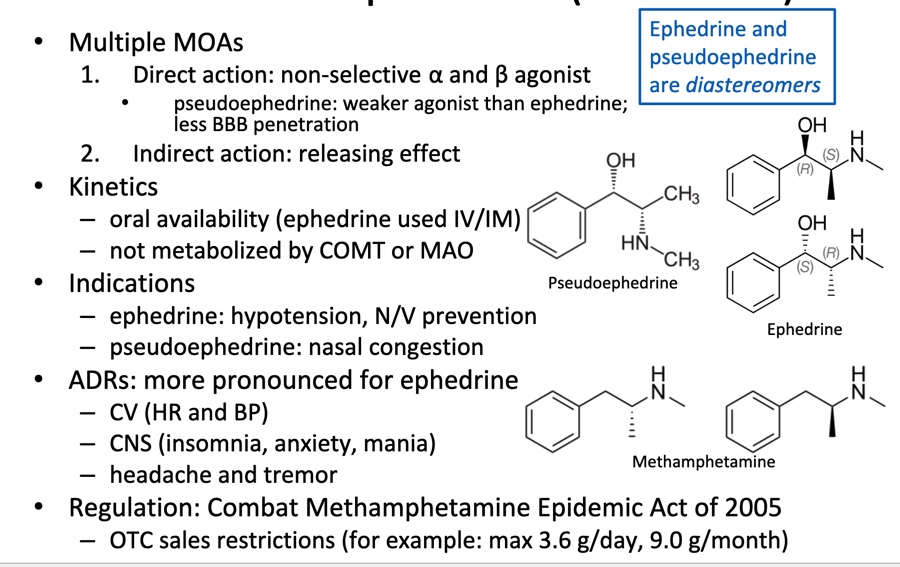
Sympatholytics
A substance that inhibits activity of the sympathetic nervous system
Indirect acting: principal activity at presynaptic adrenergic receptors (ARs) or do not bind AR
A2 agonists (centrally acting)
Direct (peripherally) acting: bind the ARs
A selective antagonists
B selective antagonists (1st generation)
b1 selective antagonist (2nd generation)
non-selective a and b antagonists (3rd generation)
Direct acting: a antagonists
Selectivity:
Non selective a1 and a2
Selective: activity at a1
Consideration: how would you expect the effects of selective vs non selective agents to differ
Significant chemical diversity
Therapeutic uses: non selective
Pheochromocytoma
Hypertension
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
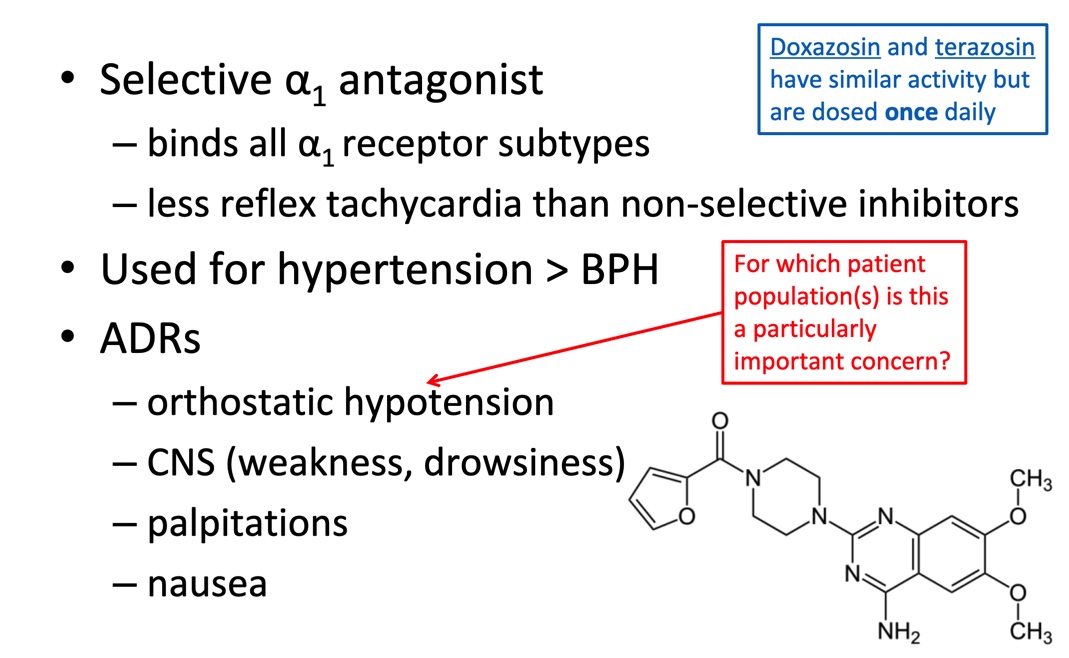
Direct acing: a1 antagonists
Pharmacology: mechanism considerations
Inhibits a1 receptors (reduces vasoconstriction)
Relatively more NE to bind a2 receptors
Pharmacological distinctions: two groups
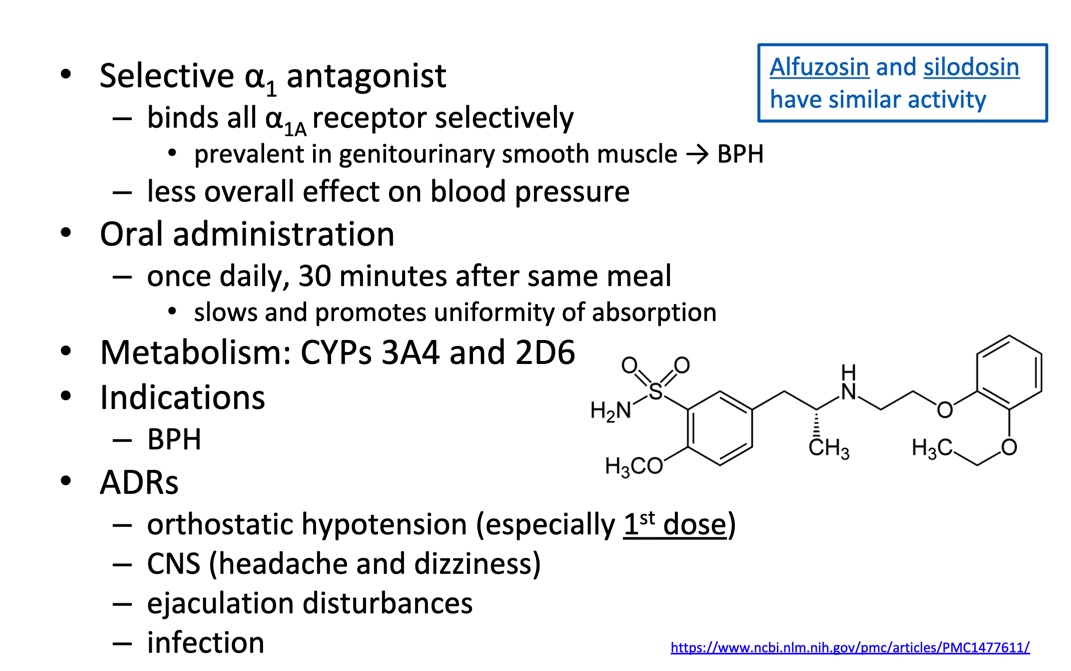
Low a1 subtype selectivity: (a1a, A1b, a1d)
A1 subtype selective: a1a
Chemistry distinctions: two groups
Piperazynl quinoa olives
Benzenesulfonamides/ analogs
Therapeutic uses
Hypertensin
Benign prostatic hyperplasia BPH
Prazosin
Tamsulosin
Direct acting: b antagonists
Selectivity
Non selective (1st gen): activity at b1 and b2
Selective (2nd gen): activity at b1
Mixed (3rd gen): activity at a and b
Therapeutic uses
Arrhythmias
Ischemia heart disease
Cardiovascular Disorders
Additional conditions
B antagonists: Common ADRs
Cardiovascular
CNS
Endocrine
Other
Boxed warning
Additional considerations: b antagonists
Hydrophilic vs. Lipophilic
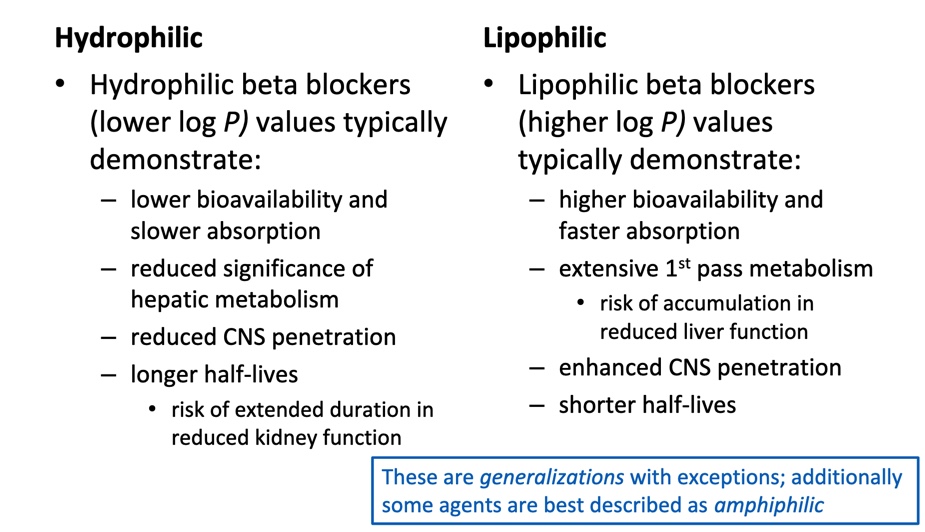
B antagonists: Chemisty considerations
Required: aryloxypropanolamine
For b1 selectivity:
Para- (4’) group with H-bond acceptor (heteroatom with lone pair of electrons)
For mixed a and b activity:
Larger, aromatic-containing group attached to amine
Review structures of a1 antagonists
ISA
Partial agonist
Non-selective b antagonists
Non selective b1 and b2 antagonists
Decrease CO (HR and conractility)
Effect dependent on sympathetic tone
Reduce renin release (b1); decreased BP over time
Caution in patients with respiratory or metabolic diseases
D
Goals of Metabolism
Contribute to elimination
Reduce toxicity
Convert to active moieties
Understanding xenobiotic metabolism
Drug → liver → cytochrome p450 → metabolism
Most xenobiotics are hydrophobic chemicals that are normally accumulated
Metabolism convert hydrophobic chemicals into more hydrophilic derivatives that are easily eliminated through the urine or bile
Accomplished via cytochrome p450 enzymes
Give me ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
Which of the following is accomplished with xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes?
A. Increased hydrophilicity of the xenobiotic
B. Decreased hydrophilicity of the xenobiotic
C. Increased lipophilicity of the xenobiotic
D. Decreased lipophilicity of the xenobiotic
A & D
Why is Metabolism necessary?
Termination or alteration of a drug
The alternate method of termination is renal excretion
Metabolic products can be:
Less phacodynamically active than the parent drug and may be inactive
Biotransfermation products with enhanced activity or greater toxic properties
Inactive prodrugs that are converted to active molecules via drug-metabolizing enzymes
Metabolism and Clearance
Renal excretion is most effective when xenobiotics possess polar characteristics; FG that are fully ionized at physiological level
Most active drugs tend to be lipophilic and remain unionized or partially ionized-
Hence: metabolism assists the chemical conversion so that excretion of the drug is more efficient
General Pathway of Drug Metabolism
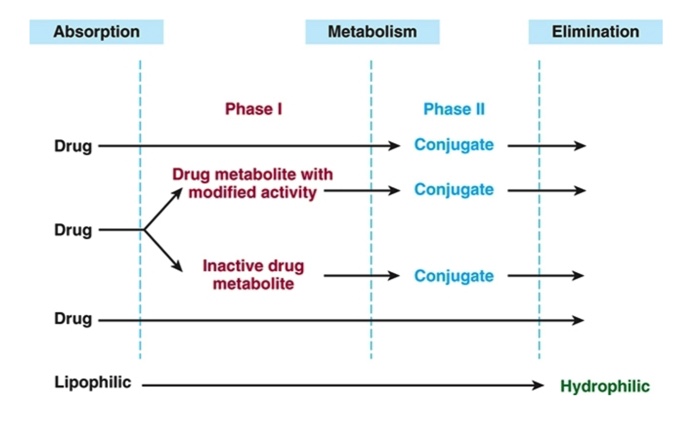
Main goal of first pass effect
Metabolism
(Metabolism → biotransformation)
Phase I vs. Phase II

Prodrugs
Patient takes an inactive form of a drug
Inactive form is converted by CYP enzymes to either active or inactive metabolites
Active metabolites prolong the bioavailability of the drug
Inactive metabolites are not bioavailable
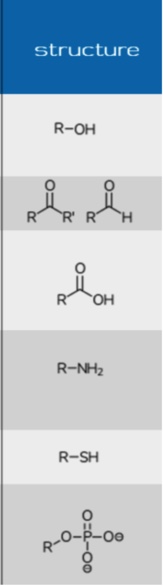
Also know which make drugs hydrophilic and hydrophobic
Which structure will increased clearance, half-life, therapeutic window, bioavailability, distribution
Phase I: Redox and Drugs
Oxidation and reduction refers to the overall oxidation state of the drug
Phase I: Oxidation
Increase of oxidation state of a substance by:
Removal of electrons
Change in polarity
Increased polarity of covalent bond to create increase partial charge
With regards to drugs:
Replace hydrogen or carbon on a drug molecule with oxygen
May form active or inactive metabolites
Requirements:
Oxidizing agent
Enzyme
Phase I: CYP450 Catalytic Cycle Hydroxylation
Embedded in the lipid bilateral of the ER and mitochondria in hepatocytes
P450 oxidizes or reduces drugs using a reactive heme ring
Iron is the electron acceptor or donor
NADPH is a co-factor
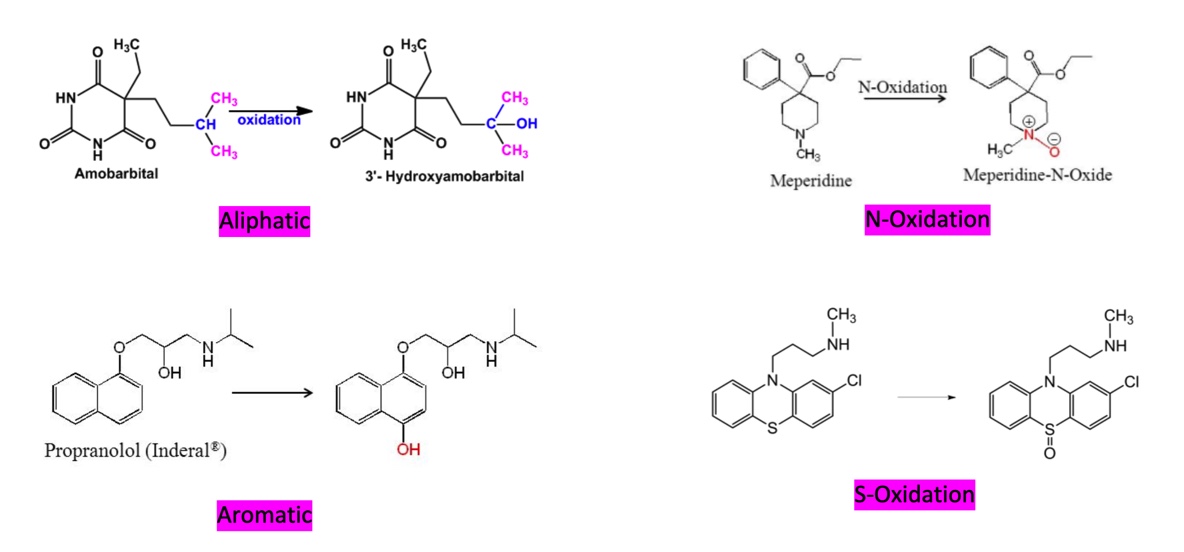
Phase I: Common hydroxylations
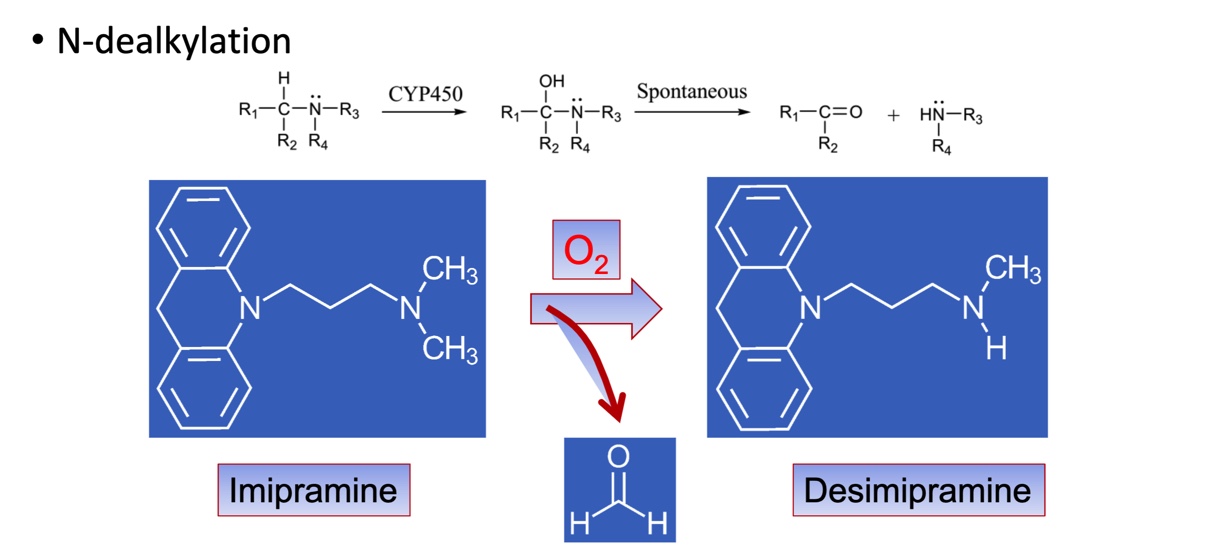
Phase I: Dealkylations
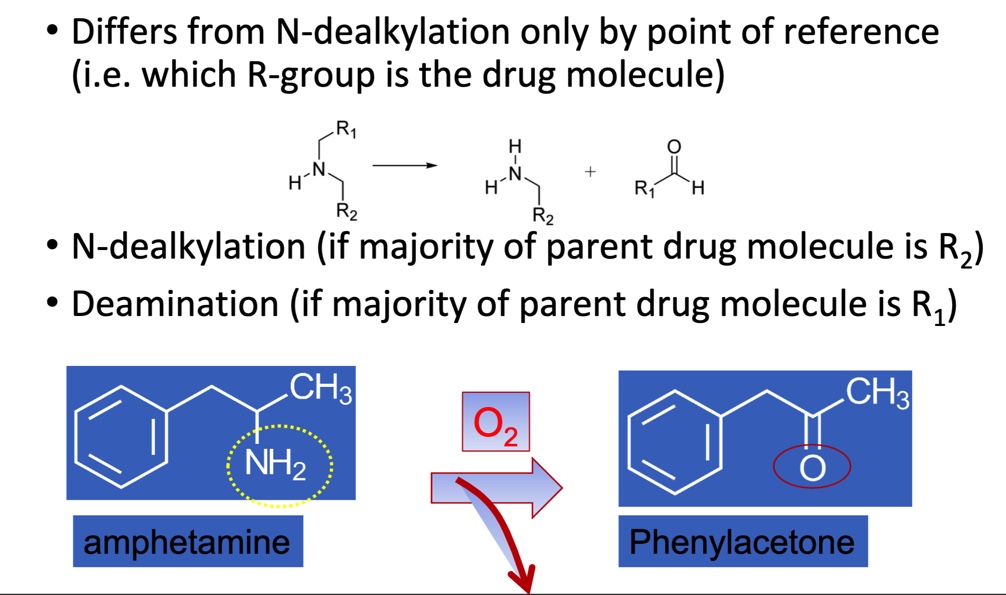
Phase I: Deamination
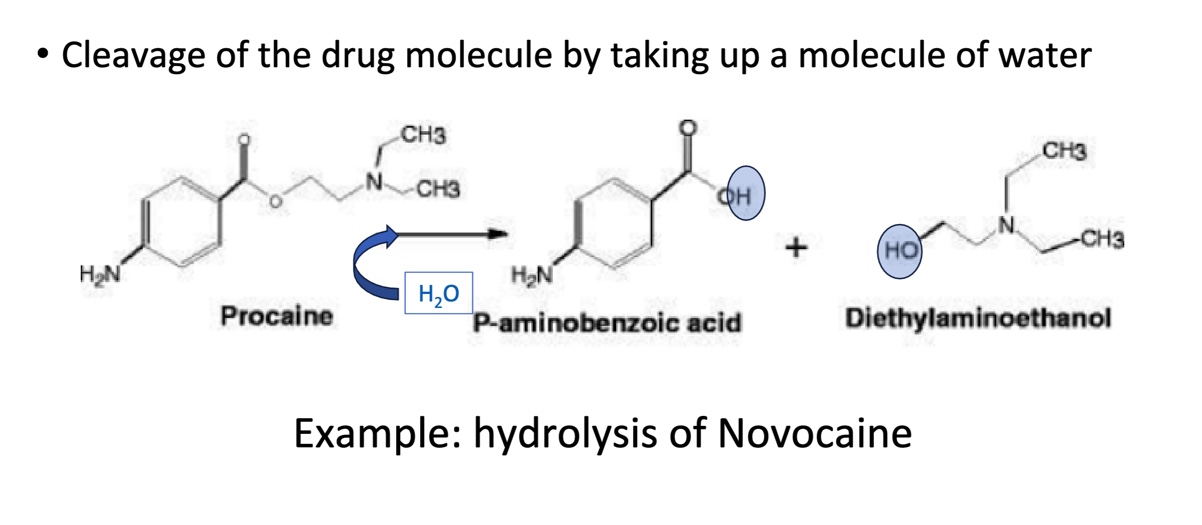
Phase I: Hydrolysis
Phase II
Conjugation of the phase I metabolite (or drug) with an endogenous substrate (increases polarity)
Phase II: Glucuronidation
Most common pharmacological phase II pathway
Typically coupled with many phase I oxidation products
Phase II requires
IRON
OTC
Over-the-counter
Herbal
Plants used for medicinal purposes
Boxed warning
A serious and prominent warning placed on the packaging, label, or informational materials for certain prescription drugs
Polyvalent cations
Ions that have multiple positive charges
Ca2+ Fe2+ Fe3+ ✅
H+ Na+ K + ❌
Enol
OH attached to a double bond
Insoluble complex
Type of chemical that doesn’t dissolve or mix well in water or other solvents
Enols create insoluble complex
Booster
Prodrug
A medication that is inactive or less active when you take it but becomes active when processed in your body.
Improve absorption, stability, and reduce side effects
Inhibitor
Interferes with or limits the function of enzymes, reactions, or other process
Inducer
Triggers or encourages a specific process or activity
Substrate
A substance that undergoes a chemical reaction or is acted upon by an enzyme